Waves
- 1. Properties of WavesProperties of Waves May 4, 2014May 4, 2014
- 2. ObjectivesObjectives 1.1. Recognize the different types of wavesRecognize the different types of waves 2.2. Sketch and identify the different parts ofSketch and identify the different parts of a transverse wavea transverse wave 3.3. Define and calculate the properties ofDefine and calculate the properties of waveswaves
- 3. WavesWaves ’āś Not just the ones you surf on!!!!Not just the ones you surf on!!!! ’āś A vibration that moves through space andA vibration that moves through space and timetime ’ü¼ Light and soundLight and sound
- 4. Types of WavesTypes of Waves 1.1. Transverse wavesTransverse waves 2.2. Longitudinal or Compressional waves -Longitudinal or Compressional waves - soundsound 3.3. Electromagnetic waves ŌĆō lightElectromagnetic waves ŌĆō light
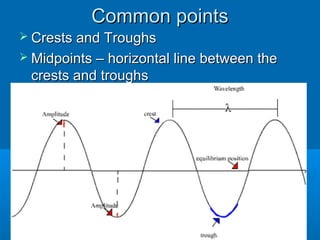
- 5. Common pointsCommon points ’āś Crests and TroughsCrests and Troughs ’āś Midpoints ŌĆō horizontal line between theMidpoints ŌĆō horizontal line between the crests and troughscrests and troughs
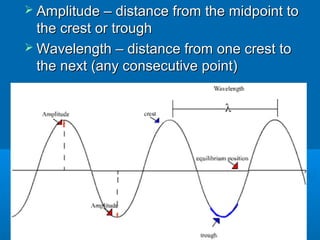
- 6. ’āś Amplitude ŌĆō distance from the midpoint toAmplitude ŌĆō distance from the midpoint to the crest or troughthe crest or trough ’āś Wavelength ŌĆō distance from one crest toWavelength ŌĆō distance from one crest to the next (any consecutive point)the next (any consecutive point)
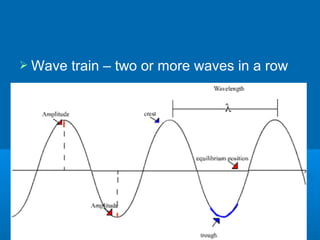
- 7. ’āś Wave train ŌĆō two or more waves in a row
- 8. 0 x
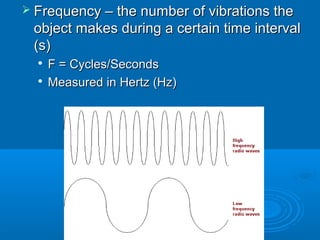
- 9. ’āś Frequency ŌĆō the number of vibrations theFrequency ŌĆō the number of vibrations the object makes during a certain time intervalobject makes during a certain time interval (s)(s) ’ü¼ F = Cycles/SecondsF = Cycles/Seconds ’ü¼ Measured in Hertz (Hz)Measured in Hertz (Hz)
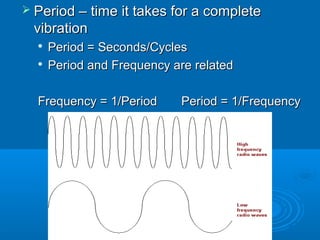
- 10. ’āś Period ŌĆō time it takes for a completePeriod ŌĆō time it takes for a complete vibrationvibration ’ü¼ Period = Seconds/CyclesPeriod = Seconds/Cycles ’ü¼ Period and Frequency are relatedPeriod and Frequency are related Frequency = 1/Period Period = 1/FrequencyFrequency = 1/Period Period = 1/Frequency
- 11. ExamplesExamples 1.1. An electric toothbrush completes 90An electric toothbrush completes 90 cycles every second. What is itŌĆÖscycles every second. What is itŌĆÖs frequency? What is its period?frequency? What is its period? 2.2. Gusts of wind cause the Sears buildingGusts of wind cause the Sears building in Chicago to sway back and forth,in Chicago to sway back and forth, completing a cycle every ten seconds.completing a cycle every ten seconds. What is its frequency? What is itsWhat is its frequency? What is its period?period?
- 12. Problem ’āś A weight suspended from a spring bobs up and down over a distance of 20 cm twice each second. What is its frequency? Its period? Its amplitude?
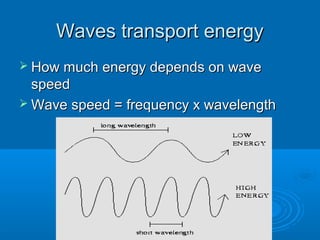
- 13. Waves transport energyWaves transport energy ’āś How much energy depends on waveHow much energy depends on wave speedspeed ’āś Wave speed = frequency x wavelengthWave speed = frequency x wavelength
- 14. ExamplesExamples 1.1. If a train of freight cars, each 10m long,If a train of freight cars, each 10m long, rolls by you at the rate of three cars eachrolls by you at the rate of three cars each second, what is the speed of the train?second, what is the speed of the train? 2.2. If a water wave vibrates up and downIf a water wave vibrates up and down three times each second and thethree times each second and the distance between the wave crests is 2m,distance between the wave crests is 2m, what is the waveŌĆÖs frequency? Itswhat is the waveŌĆÖs frequency? Its wavelength? Its wave speed?wavelength? Its wave speed?
- 15. Problem ’āś A skipper of a boat notices wave crests passing his anchor chain every 5s. He estimates the distance between wave crests to be 15 m. He also correctly estimates the speed of the waves. What is this speed?
- 16. Frequency and Wave Speed May 13, 2011