WealthManagement_PPT
- 2. Meaning of Wealth Management ï A professional service to optimize, protect and manage wealth ï An investment advice on loans, investment and insurance ï Also advice on tax, estate planning, business planning and charity foundation. ï It is an ongoing process with define steps that involve planning, execution, review and management.
- 3. Wealth management ï Wealth management services are provided by ï Corporate entities ï Independent financial advisor ï Portfolio managers ï Banks ï Brokerage houses
- 4. Need for WM ï Planning ï Asset Management ï Risk Management ï Lending ï Advisory Services
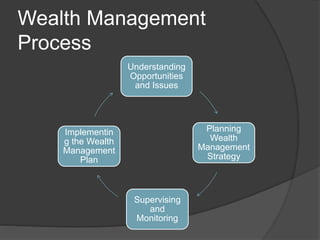
- 5. Wealth Management Process Understanding Opportunities and Issues Planning Wealth Management Strategy Supervising and Monitoring Implementin g the Wealth Management Plan
- 6. Wealth Management Process ï Understanding Opportunities and Issues ï Investors know thyself ï Understanding values, goals and needs ï Developing rational investment expectation ï Planning wealth management strategy ï Impact of Taxes ï Developing an investment policy ï Importance of asset allocation ï Integrated wealth planning
- 7. Wealth Management Process ï Implementing the wealth management plan ï Supervising and monitoring process
- 8. Goals of WM ï Asset Management ï Asset allocation aims to optimize return by minimizing risk. ï Achieve the goal through diversification and customized investment strategies. ï Planning ï Advance thinking and necessary services to formulate, manage and complete financial requirement
- 9. Goals of WM ï Equity Risk Management ï Preserve capital against decrease in value of stock ï Generate liquidity ï Diversify the exposure
- 10. Stages in Human Life Cycle ï Childhood Stage ï Young Unmarried Stage ï Young Married Stage ï Both Partners Working ï Single Partner Working ï Young Married with Children Stage ï Married with Older Children Stage ï Post Family and Pre Retirement Stage ï Retirement Stage
- 11. Financial Needs ï Survival Money ï Household need for food, clothing and shelter ï Liquid instruments ï Need for emergency situation ï Safety Money ï To meet lifeâs unexpected turns ï To protect the assets ï To protect the person who generates the assets
- 12. Financial Needs ï Freedom Money ï Funds to support non - basic needs ï Investment in short term instruments â savings, treasury bills, money market fund ï Gift Money ï Charitable institution or foundation ï Education and estate for their children ï Investment in long term instruments â bonds, mutual funds, equities
- 13. Financial Needs ï Dream Money ï Funds required to have all the things that a person dream of being, having or doing ï Funds that will need beyond peak income years ï Funding for medical expenses after retirement ï Invest in long term instruments â bonds, notes, mutual funds.
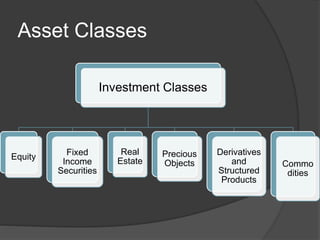
- 14. Asset Classes Investment Classes Equity Fixed Income Securities Real Estate Precious Objects Derivatives and Structured Products Commo dities
- 15. Asset Classes ï Equity ï Rewards associated with equities â Dividend â Capital Gains â Right to subscribe to new shares â Right to vote â Right to information ï Risk Associated with equity â Residual capital â Capital Loss â Liquidity risk
- 16. Asset Classes ï Real Estate ï Residential House ï Commercial Property ï Agricultural Property ï Suburban Land ï Real Estate Investment Trust ï Precious objects ï Gold ï Silver
- 17. Asset Classes ï Fixed Income Securities ï Issued by govt., govt. agencies, state govt., corporation, municipalities, banks. ï Cash flow promised to buyer represent contractual obligations on issuer. ï Stream of payments by way of interest and repayment of principal at maturity. ï Mutual Funds
- 18. Asset Classes ï Commodities ï Includes all kinds of goods ï Types of commodities â Energy ï Primary â crude oil, coal, natural gas, nuclear fuel ï Secondary â electricity, refined oil products, diesel, petrol, LPG ï Half-products â petrochemicals, ethylene â Mineral ore â iron, steel, copper, zinc, gold, silver, platinum, aluminum â Agricultural food products â wheat, corn, rice, tea, coffee, apple, grapes, cotton, jute, fish
- 19. Asset Classes ï Derivatives and Structured Products ï Derivatives â derives its value from some underlying asset like securities, currency, commodities or stock. ï Types of derivatives â Exchange traded derivatives ï Future contract â OTC derivatives ï Forward contract
- 20. Products in WM ï Direct Equity ï Mutual Funds ï Insurance ï Structured Products ï Private Equity ï Real Estate ï Estate Planning ï Commodities