Web content management
- 1. WEB CONTENT MANAGEMENT Smita Chandra Librarian Indian Institute of Geomagnetism smitac@iigs.iigm.res.in
- 2. UNDERSTANDING CONTENT ïĒ What is âContentâ ïĒ How is âContentâ different from âDataâ and âInformationâ ? ïĒ How is content managed ? ïĒ What is Content Management ïĒ What is Web Content Management
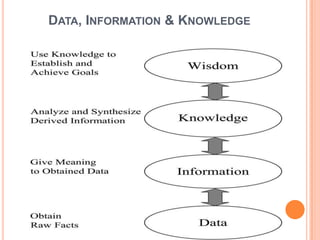
- 3. WHAT IS DATA ? ïĒ ââĶfacts or information used in deciding or discussingâĶâ. Source : The Oxford Dictionary ïĒ ââĶany form of information whether in paper or electronic form. In electronic form, data refers to files and databases, text documents, images and digitally encoded voice and videoâ. Source : Computer Glossary ïĒ âis a representation of facts in a formalized manner suitable for some sort of technology system, which is called a databaseâ. Source : Encyclopedia of Library & Information Science
- 4. DATA ïĒ Term appeared in 16th century ïĒ Two types â ï Structured Data : eg. address of a supplier, customerâs list, library catalogue, employee list, etc ï Unstructured Data : eg. Letters, proposal, etc Data are raw and unprocessed unlike information.
- 5. WHAT IS INFORMATION ? ïĒ ââĶthat portion of the data which impacts our actions, or if missing, or not available will impact our actionsâ Eliyahu M Goldratt ïĒ âIt is evidence that exists in many forms including traditional sources like data, books or documents, and non-traditional sources like events and objects.â Tomyia J Tidline ïĒ Information ï Abstract & ï Is independent of its form
- 6. DATA, INFORMATION & KNOWLEDGE
- 7. WHAT IS CONTENT ? ïĒ Etymology : âcontentumâ â to contain âcontinereâ â to hold together or enclosed ïĒ Content is data or information embodied ïĒ âthings contained inâ â Random House Dictionary & the Oxford Dictionary ïĒ âa list of âpreliminariesâ and chapter headings of a book in their correct order, or of articles in a periodical, with its pages on which they beginâ â Harrodâs Glossary & ALA Glossary
- 8. âĶ CONTINUED ïĒ Literature from 1990âs takes a broader perspective, ï inclusive of all type of materials (external or internal) ï all types of format (multimedia) ï all data (structured and unstructured) ïĒ âInformation made available by an electronic medium or productâ â Microsoft Encarta ïĒ âSubject matter embodied in some definable format e.g., email messages, spreadsheets, word processing documents, videos, reports, etc. It is a process which generates objects like brochures, price lists, pictures, metadata, etc.â â Todayâs Context
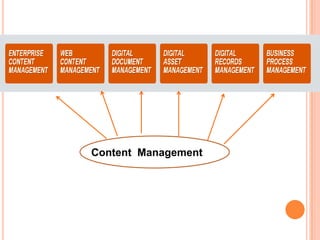
- 9. CONTENT MANAGEMENT ïĒ Content management stands for the management of any content ranging from data residing offline on a paper, or in simple Word document to a complex high-volume dynamic web publishing, whether as e-catalogues or portals. ïĒ âThe management of the content by combining rules, process and/or workflows in such a way that centralized (technical) and de-centralized (non-technical) staff can create, edit, manage and publish a variety of content in accordance with a given framework or requirements.â
- 10. ---CONTINUED ïĒ CM process creates, manages and develops content while maintaining the content separate from its presentation ïĒ CM integrates traditional Document Management and Web CM ïĒ CM helps to scale websites and save on the cost of content change ïĒ CM helps to fill the gap between building the site and keeping the siteâs content current ïĒ CM helps to provide dynamic, relevant and timely information ïĒ CM provides access to escalating unstructured data
- 11. ---CONTINUED ïĒ CM is empowering non-technical content contributors ïĒ CM is removing the burden from the traditional webmasters ïĒ CM manages content in ways such that the incremental cost of each update cycle and output production shrinks dramatically overtime ïĒ CM is Business Management
- 12. ïĒ CM as a concept helps ï Non-technical authors to contribute content ï Organizations to streamline the workflow ï Faster updating and managing of unstructured, dynamic content embodied in varied formats ï Structured and synthesized delivery of content in the format of usersâ choice ï Management of both online and offline content
- 13. CONTENT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (CMS) ïĒ A CM âsystemâ is a technical environment (hardware tools, software expertise) that supports the systematic processing of digital content from authorship to publication. ïĒ CMS is a tool or combination of tools to facilitate the efficient and effective production of the desired web pages using the managed content ïĒ Analogy : difference between CM and CMS is the same as the difference between Library Management and Library Management System (LMS)
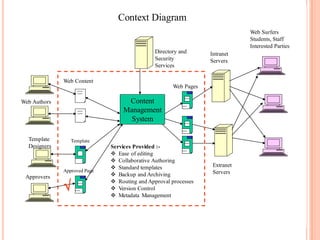
- 14. Context Diagram Web Surfers Students, Staff Interested Parties Directory and Intranet Security Servers Services Web Content Web Pages Web Authors Content Management System Template Template Designers Services Provided :- ïķ Ease of editing ïķ Collaborative Authoring ïķ Standard templates Extranet Approved Page Servers Approvers ïķ Backup and Archiving ï ïķ Routing and Approval processes ïķ Version Control ïķ Metadata Management
- 15. BENEFITS OF CMS
- 16. WHAT IS NOT CONTENT MANAGEMENT ïĒ It is NOT a library, archive or museum management or cataloguing system ïĒ It is NOT word processing or other kinds of files, text or presentation ïĒ It is NOT multimedia application ïĒ It is NOT authoring tools
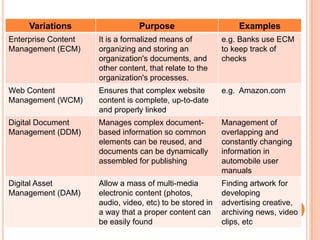
- 18. Variations Purpose Examples Enterprise Content It is a formalized means of e.g. Banks use ECM Management (ECM) organizing and storing an to keep track of organization's documents, and checks other content, that relate to the organization's processes. Web Content Ensures that complex website e.g. Amazon.com Management (WCM) content is complete, up-to-date and properly linked Digital Document Manages complex document- Management of Management (DDM) based information so common overlapping and elements can be reused, and constantly changing documents can be dynamically information in assembled for publishing automobile user manuals Digital Asset Allow a mass of multi-media Finding artwork for Management (DAM) electronic content (photos, developing audio, video, etc) to be stored in advertising creative, a way that a proper content can archiving news, video be easily found clips, etc
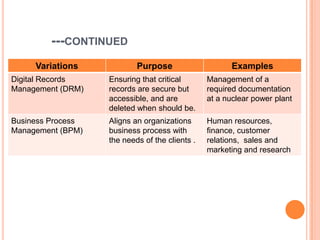
- 19. ---CONTINUED Variations Purpose Examples Digital Records Ensuring that critical Management of a Management (DRM) records are secure but required documentation accessible, and are at a nuclear power plant deleted when should be. Business Process Aligns an organizations Human resources, Management (BPM) business process with finance, customer the needs of the clients . relations, sales and marketing and research
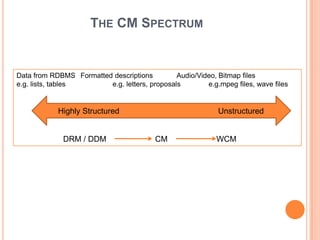
- 20. THE CM SPECTRUM Data from RDBMS Formatted descriptions Audio/Video, Bitmap files e.g. lists, tables e.g. letters, proposals e.g.mpeg files, wave files Highly Structured Unstructured DRM / DDM CM WCM
- 21. WEB CONTENT MANAGEMENT ïĒ âA set of tasks and processes for managing content explicitly targeted for publication on the web throughout its life from creation to archive.â âOvum Ltd. ïĒ âManaging content that drives an externally facing website and facilitating multichannel publishing of content in digital form. --Gartner
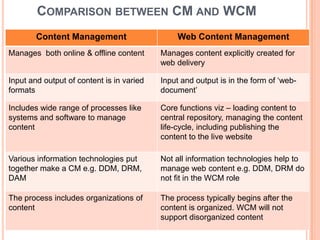
- 22. COMPARISON BETWEEN CM AND WCM Content Management Web Content Management Manages both online & offline content Manages content explicitly created for web delivery Input and output of content is in varied Input and output is in the form of âweb- formats documentâ Includes wide range of processes like Core functions viz â loading content to systems and software to manage central repository, managing the content content life-cycle, including publishing the content to the live website Various information technologies put Not all information technologies help to together make a CM e.g. DDM, DRM, manage web content e.g. DDM, DRM do DAM not fit in the WCM role The process includes organizations of The process typically begins after the content content is organized. WCM will not support disorganized content
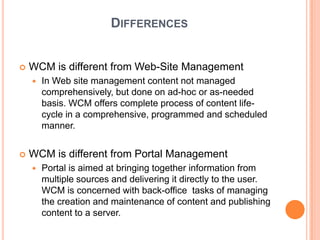
- 23. DIFFERENCES ïĒ WCM is different from Web-Site Management ï In Web site management content not managed comprehensively, but done on ad-hoc or as-needed basis. WCM offers complete process of content life- cycle in a comprehensive, programmed and scheduled manner. ïĒ WCM is different from Portal Management ï Portal is aimed at bringing together information from multiple sources and delivering it directly to the user. WCM is concerned with back-office tasks of managing the creation and maintenance of content and publishing content to a server.
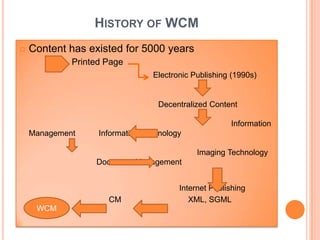
- 24. HISTORY OF WCM ïĒ Content has existed for 5000 years Printed Page Electronic Publishing (1990s) Decentralized Content Information Management Information Technology Imaging Technology Document Management Internet Publishing CM XML, SGML WCM
- 25. WEB CONTENT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (WCMS) A web content management system (WCMS) is a software system that provides website authoring, collaboration, and administration tools designed to allow users with little knowledge of web programming languages or markup languages to create and manage website content with relative ease. A robust WCMS provides the foundation for collaboration, offering users the ability to manage documents and output for multiple author editing and participation.
- 26. CHARACTERISTICS OF WCMS ïĒ It manages small units of information (web pages) - each unit of information is interconnected via a navigation structure or path. ïĒ Each unit (web page) is defined by its location on the site ïĒ There is extensive cross-linking between pages ïĒ It is focused primarily on page creation and editing ïĒ It provides a publishing engine that allows created or amended content to be made available to a website visitor ïĒ It often provides an approval process or workflow that ensures that content is validated before it is released or published to a website.
- 27. CAPABILITIES OF WCMS ïĒ A WCMS typically has the following features: ïĒ Automated templates ïĒ Access control ïĒ Scalable expansion ïĒ Easily editable content ïĒ Scalable feature sets ïĒ Web standards upgrades ïĒ Workflow management ïĒ Collaboration ïĒ Delegation ïĒ Document management ïĒ Content virtualization ïĒ Content syndication ïĒ Multilingual ïĒ Versioning
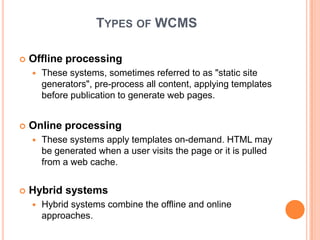
- 28. TYPES OF WCMS ïĒ Offline processing ï These systems, sometimes referred to as "static site generators", pre-process all content, applying templates before publication to generate web pages. ïĒ Online processing ï These systems apply templates on-demand. HTML may be generated when a user visits the page or it is pulled from a web cache. ïĒ Hybrid systems ï Hybrid systems combine the offline and online approaches.
- 29. ADVANTAGES OF WCMS ïĒ Low cost ïĒ Easy customization ïĒ Easy to use ïĒ Workflow management
- 30. DISADVANTAGES OF WCMS ïĒ Cost of implementation ïĒ Cost of maintenance ïĒ Latency issues ïĒ Tool mixing
- 31. NOTABLE WCMS ïĒ WordPress is the most popular content management system. It originated as a blogging CMS, but later evolved into a full-fledged CMS. ïĒ Joomla! is a popular content management system that can be used to easily create and edit webpages, but it is more complex than Wordpress. ïĒ Drupal is the third top used CMS and originated before WordPress and Joomla. It is more difficult to learn and understand than the above two CMSs, but is the most secure. It powers the White House site.
- 33. OSS IN WCM
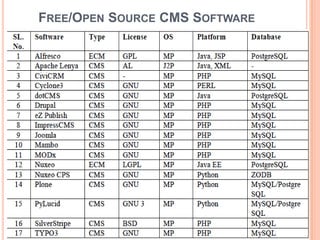
- 34. FREE/OPEN SOURCE CMS SOFTWARE
- 35. WCMS IN LIBRARIES ïĒ Many libraries have started to use content management systems as a tool to build and manage their web presence. ïĒ The advantages of using a CMS to build a library website include: ï Separation of content, logic, and data ï Ability for multiple content providers (many staff members can edit the website, rather than just one expert) ï Easier or automatic integration with Web 2.0 tools (built in RSS for instance) ï Many cool add-ons that provide added functionality to the website (an Events Calendar for instance)
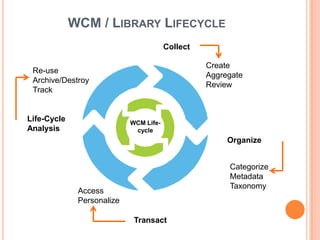
- 36. WCM / LIBRARY LIFECYCLE Collect Create Re-use Aggregate Archive/Destroy Review Track Life-Cycle WCM Life- Analysis cycle Organize Categorize Metadata Taxonomy Access Personalize Transact
- 37. WCMS IN LIBRARIES ïĒ What libraries are using ï Drupal : http://drupal.org ï Joomla : http://www.joomla.org ï Plone : http://plone.org/ ï Expression Engine : http://ellislab.com/expressionengine ï Wordpress : http://wordpress.org/ ï Silverstripe : http://www.silverstripe.com/
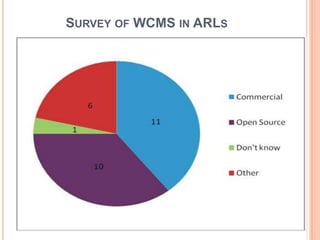
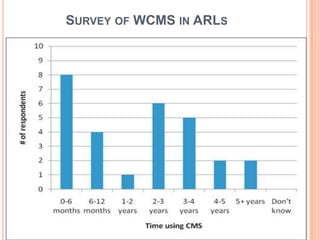
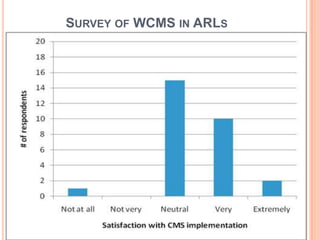
- 39. SURVEY OF WCMS IN ARLS
- 40. SURVEY OF WCMS IN ARLS
- 41. SURVEY OF WCMS IN ARLS
- 42. SURVEY OF WCMS IN ARLS Reasons for / against considering a new CMS Considering a new CMS because: Not considering a new CMS because: â[We currently have a very] flexible â[There are lots] of options available.â system âĶ [it] can adapt to complex needs.â âCascade Server does not suit dynamic âIt is controlled by others at the webpages that often are used in library university.â applications.â âWe are now in the process of moving towards Drupal so that we can benefit from âCampus decision.â the Drupal tools that others create.â âMaintaining a homegrown CMS is a challenge. Weâd prefer an open source âWe are happy with the features and system. However, weâve yet to find one that capabilities of Drupal. We have briefly looked meets all our needs and havenât had the at other systems, but they seem far less staffing to add on the functionality we flexible and suitable to our needs.â needed.â
- 43. WHAT TO LOOK OUT FOR WHEN CHOOSING A WCMS ïĒ ensure that you will be provided with good development and technical support ïĒ find a CMS that will integrate with (at least) some of your main applications, such as Outlook ïĒ it should support a degree of document management ïĒ ensure your CMS is user friendly
- 44. WCMS TODAY
- 45. "Don'tannoy, or worse alienate, prospective customers because your cousin's friend's aunt's next-door neighbor's brother volunteers to design your website on the cheap"























![SURVEY OF WCMS IN ARLS
Reasons for / against considering a new CMS
Considering a new CMS because: Not considering a new CMS because:
â[We currently have a very] flexible
â[There are lots] of options available.â system âĶ [it] can adapt to complex
needs.â
âCascade Server does not suit dynamic âIt is controlled by others at the
webpages that often are used in library university.â
applications.â
âWe are now in the process of moving
towards Drupal so that we can benefit from âCampus decision.â
the Drupal tools that others create.â
âMaintaining a homegrown CMS is a
challenge. Weâd prefer an open source âWe are happy with the features and
system. However, weâve yet to find one that capabilities of Drupal. We have briefly looked
meets all our needs and havenât had the at other systems, but they seem far less
staffing to add on the functionality we flexible and suitable to our needs.â
needed.â](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webcontentmanagement-130319021628-phpapp02/85/Web-content-management-42-320.jpg)


