What Does Urban Mean - DP
- 1. World Cities ÔÇô an introduction Key question: What does urban mean?
- 2. Odd one out ÔÇô image set 1 A B C D
- 3. Odd one out ÔÇô image set 2 C A B D
- 4. ÔÇó What do we mean by urban? ÔÇó How might rural and urban areas differ from one another?
- 5. Activity ÔÇÿMight be likeÔÇÖ? A rural settlement An urban settlement Size Functions Employment Density Administration Character
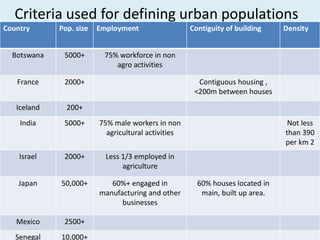
- 6. Criteria used for defining urban populations Country Pop. size Employment Contiguity of building Density Botswana 5000+ 75% workforce in non agro activities France 2000+ Contiguous housing , <200m between houses Iceland 200+ India 5000+ 75% male workers in non agricultural activities Not less than 390 per km 2 Israel 2000+ Less 1/3 employed in agriculture Japan 50,000+ 60%+ engaged in manufacturing and other businesses 60% houses located in main, built up area. Mexico 2500+ Senegal 10,000+
- 7. Defining towns and cities ÔÇó No internationally agreed definition. ÔÇó UK census uses its own definition: - built up - services for residents and others in the surrounding area - focal point for transport networks - free standing Unofficial figure used? UK difference between a town and a city?
- 8. Delimiting towns and cities e.g. Manchester Well defined historic ÔÇÿcity of ManchesterÔÇÖ? Conurbation of Greater Manchester? The city region and its hinterland? This is why population figure vary so much between sources