What is BPM and why should I use it
- 1. WHAT IS BPM AND WHY SHOULD I USE IT
- 2. HELLO! I am Ruben J Garcia Twitter: @imrubenjgarcia Blog: rubenjgarcia.es
- 4. “Business process management (BPM) is a field in operations management that focuses on improving corporate performance by managing and optimising a company's business processes
- 5. “ BUSINESS PROCESS A sequence of activities performed by one or more business participants in order to deliver value to business
- 6. WHY MODEL PROCESSES â–¸Understand your processes â–¸Improve your processes â–¸Design new processes â–¸Automate processes
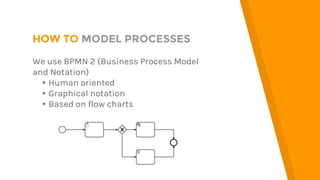
- 7. HOW TO MODEL PROCESSES We use BPMN 2 (Business Process Model and Notation) â–¸Human oriented â–¸Graphical notation â–¸Based on flow charts
- 8. HOW TO MODEL PROCESSES
- 10. EVENTS Something that happens to the business process BPMN ELEMENTS ACTIVITIES A work performed in the process GATEWAYS Control the process flow
- 11. BASIC EVENTS Start event Intermediate event Intermediate boundary event End event
- 12. EVENT TYPES Timer event - At / After / Every Message event - 1 to 1. Sender and receiver have references Signal event - 1 to many. Sender and receiver are not specified Conditional event - Boolean value or expression
- 13. BASIC ACTIVITIES User task - A work that a human must do Service task - Invoke a service Script task - Automated activity that executes an arbitrary code Business rule task - Automated activity that is executed by a Business Rule Engine
- 14. BASIC ACTIVITIES Send task - Send a message Receive task - Receive a message Manual task - A task that someone does externally to the process
- 15. GATEWAYS Exclusive gateway - Single output based on condition Parallel gateway - Multiple outputs Inclusive gateway - Fork / join Event based gateway - Single output based on events
- 16. 3. EXAMPLES
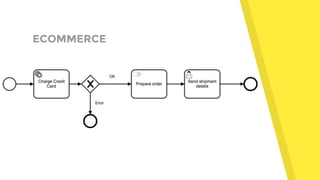
- 17. ECOMMERCE
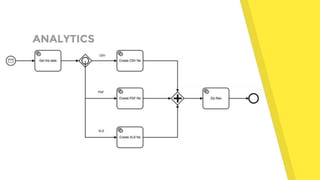
- 18. ANALYTICS
- 19. RESTAURANT
- 23. Web server BPM Engine 1 2 Tas k 1 Tas k 2 Tas k 3 3 4 5
- 24. Web server BPM Engine 1 2 Tas k 1 3 5 6 4
- 25. THANKS! Any questions? You can find me at @imrubenjgarcia & rubenjgarcia.es