Why electromagnetic waves travel v2
Download as PPTX, PDF2 likes106 views
Understand Electromagnetism with Timelines of Discovery Electromagnetism Theories and Equations in Discovered Understand Electromagnetic Waves Why Electromagnetic Waves Move and are Traversal Waves
1 of 10
Download to read offline









Recommended
Electromagnetic waves



Electromagnetic wavesJun Libradilla Maloloy-on
╠²
Electromagnetic waves are formed by vibrating electric charges and can transfer energy through space without matter. They are transverse waves consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Electromagnetic waves can behave as either waves or particles called photons, with higher frequency waves having shorter wavelengths. The entire range of electromagnetic wave frequencies is called the electromagnetic spectrum.ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES FOR CBSE XII



ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES FOR CBSE XIImanish nagar
╠²
CBSE NOTES; XII PHYSICS NOTES;BOARD NOTES;ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES NOTES; PHYSICS NOTES FROM KOTA RAJASTAHN;
NOTES FROM KOTA COACHING;PHYSICS NOTES FROM AARAV CLASSESEm waves



Em wavesGajendra Saini
╠²
Electromagnetic waves are waves of electric and magnetic fields that can travel through space. They are produced by vibrating electric charges and can travel through vacuum where matter is not present. Electromagnetic waves come in a wide range of frequencies and wavelengths, forming the electromagnetic spectrum. This includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays.Ch 24 Electromagnetic Waves



Ch 24 Electromagnetic WavesScott Thomas
╠²
This document provides an overview of electromagnetic waves and key concepts in physics including:
- James Clerk Maxwell showed that electric and magnetic fields can form propagating electromagnetic waves.
- Electromagnetic waves include visible light, ultraviolet rays, infrared rays, radio waves, x-rays and gamma rays.
- The speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is a constant at approximately 3├Ś10^8 m/s.
- Electromagnetic waves transport energy and the total energy density carried by a wave depends on the electric and magnetic field amplitudes.Electromagnetic Wave



Electromagnetic WaveYong Heui Cho
╠²
In wireless communication, we frequently use an electromagnetic wave. In this presentation, we can study wave equation, reflection, plane wave, and transmission line.Electromagnetic waves



Electromagnetic wavesTonmoy Ibne Arif
╠²
1.Fundamentals
2.Wave number
3.Wavelength
4.Frequency
5.Properties of Electromagnetic waves
6.Plane waves
7.Helmholtz equation from MaxwellŌĆśs Equation
8.Wave vector
9.The polarization of electromagnetic waves
10.Polychromatic wave
11. DispersionElectromagnetic waves



Electromagnetic wavesSmart Sayyed
╠²
In 1895, Sir Jagdish Chandra Bose produced electromagnetic waves between 5mm and 25mm in wavelength, but his work remained confined to the laboratory. In 1896, G. Marconi became the first to establish wireless communication across the English Channel at a distance of 48km. In 1901, Marconi succeeded in transmitting signals across the Atlantic Ocean between Newfoundland and Cornwall. He was awarded the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics for his pioneering work developing wireless telegraphy, telephony, and broadcasting.electromagnetic waves



electromagnetic wavesSepti Pramuliawati
╠²
This document discusses electromagnetic waves and their properties. It covers topics such as waves in one dimension, electromagnetic waves in vacuum, electromagnetic waves in matter, absorption and dispersion, and guided waves. Key points include that electromagnetic waves satisfy Maxwell's equations and the wave equation in vacuum and matter. They can be reflected, transmitted, and absorbed at boundaries. Guided waves can propagate down wave guides and transmission lines.Electro magnetic waves



Electro magnetic wavesbgriesmer
╠²
Electromagnetic waves are waves made up of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that can transfer energy through space. There are different types of electromagnetic radiation including infrared radiation, which has wavelengths longer than visible light but shorter than microwaves. Electromagnetic radiation involves the transfer of energy through electromagnetic waves traveling through a vacuum.Lecture 2 Properties of em waves



Lecture 2 Properties of em wavesABRILYN BULAWIN
╠²
This document discusses the properties of electromagnetic waves. It describes how electromagnetic waves are produced by oscillating electric and magnetic fields and form a spectrum from gamma rays to radio waves. The key properties of all electromagnetic waves are that they are transverse waves that can travel through empty space at the speed of light, carry energy, and have frequencies and wavelengths that are inversely related. Sound waves are longitudinal rather than electromagnetic. Different colors of visible light have different amounts of energy.Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 



Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 Self-employed
╠²
Electromagnetic waves can be summarized in 3 sentences:
Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves that are produced by oscillating electric and magnetic fields which propagate perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. Hertz's experiment provided the first clear evidence of the production and reflection of electromagnetic waves. The electromagnetic spectrum ranges from radio waves to gamma rays and includes visible light, with different sources and uses across the various wavelength ranges.Yoga wahyu s 09330084 electromagnetic wave



Yoga wahyu s 09330084 electromagnetic waveYoga Sasongko
╠²
The document discusses electromagnetic waves, which result from changes in both the electric and magnetic fields. Maxwell's theory established that changing magnetic fields produce electric fields and vice versa. Some key characteristics of electromagnetic waves are that the electric and magnetic fields oscillate perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Electromagnetic waves propagate at the speed of light and their wavelength and frequency are related by the formula wavelength = speed of light / frequency. An example calculation demonstrates determining the wavelength of a radio wave given its frequency.Electro magnetic wave(bpp)



Electro magnetic wave(bpp)Chaiporn Pattanajak
╠²
This document discusses electromagnetic waves and their classification according to frequency. Electromagnetic waves include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. All electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light and differ in frequency and wavelength, with higher frequency waves having shorter wavelengths and higher energy. Examples are given of how each type of electromagnetic wave is used technologically and occurs naturally.Electromagnetic waves



Electromagnetic wavesZHALNJR
╠²
Electromagnetic waves include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays and all travel at the speed of light. They can be described by their wavelength, energy and frequency and are used in technologies like radio, TV and microwaves. The electromagnetic spectrum ranges from long wavelength radio waves to highest frequency gamma rays.EM spectrum applications, Electromagnetic Wave Theory



EM spectrum applications, Electromagnetic Wave TheorySuleyman Demirel University
╠²
The document discusses various parts of the electromagnetic spectrum including radio waves, infrared, ultraviolet, visible light, x-rays, and gamma rays. It provides details on the wavelength ranges and common applications of each type of electromagnetic radiation. Examples of applications discussed include GPS, FM/AM radio, TV broadcasting, microwave ovens, MRI, radar, RFID, and radio telescopes. Harmful effects of electromagnetic radiation generally increase with higher frequency and energy.5m electromagnetic waves



5m electromagnetic wavesPrayash Mohapatra
╠²
1. The document discusses electromagnetic waves, including their properties, Hertz's experiment demonstrating their existence, and the electromagnetic spectrum.
2. Key properties of electromagnetic waves are that the electric and magnetic fields oscillate perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of propagation, and they can transfer energy and momentum.
3. Hertz produced electromagnetic waves using high-voltage charged plates, and their detection using a spark gap provided evidence of their polarization.
4. The electromagnetic spectrum ranges from radio waves to gamma rays, with different sources and uses across the various wavelength and frequency ranges.050316 week8 c12-electromagnetic_waves



050316 week8 c12-electromagnetic_wavesSubas Nandy
╠²
Electromagnetic waves are formed by vibrating electric charges and can travel through space, transferring energy between electric and magnetic fields (1). They include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays, which make up the electromagnetic spectrum (2). Different parts of the spectrum interact with matter in different ways and have various applications like communication, imaging and heating (3).Ch 22 Electromagnetic Induction



Ch 22 Electromagnetic InductionScott Thomas
╠²
This document provides an overview of chapter 22 on electromagnetic induction. It discusses key concepts such as magnetic flux, Faraday's law of induction, Lenz's law, and applications including electric generators. The chapter covers how changing magnetic fields can induce emfs and currents in conductors based on Faraday's law. Lenz's law describes how the direction of induced currents will oppose the change that created them. Applications discussed include the reproduction of sound and electric generators.Electro magnetic waves



Electro magnetic wavesSuganthi Thangaraj
╠²
1. Maxwell's equations predict that electromagnetic energy propagates away from time-varying sources in the form of waves.
2. The document derives the electromagnetic wave equation and describes its solution for uniform plane waves in various media.
3. Key wave properties like velocity, wavelength, frequency and attenuation are determined by examining solutions to the wave equations for the electric and magnetic fields.Ch 17 Linear Superposition and Interference



Ch 17 Linear Superposition and InterferenceScott Thomas
╠²
This document discusses principles of wave interference including:
1. The principle of linear superposition states that when waves overlap, the resulting displacement is the sum of the individual displacements.
2. Constructive and destructive interference occur when waves are in phase or out of phase, respectively, increasing or decreasing the amplitude.
3. Diffraction is the bending of waves around barriers, causing diffraction patterns from interference of diffracted waves.
4. Beats occur when two nearly matched frequencies are superimposed, producing a characteristic loud-soft pattern from their interference.Electromagnetic waves BY- Rahul singh 



Electromagnetic waves BY- Rahul singh Rahul Singh
╠²
The document discusses electromagnetic waves and their properties. Some key points:
1) Electromagnetic waves consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
2) Both the electric and magnetic fields of an electromagnetic wave are transverse to the direction of wave propagation.
3) Electromagnetic waves include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. They differ in wavelength and frequency.Electromagnetic waves



Electromagnetic wavesniranjan kumar
╠²
Maxwell derived a set of equations that unified electricity, magnetism and light as manifestations of electromagnetic waves. His equations predicted that changes in electric and magnetic fields propagate as waves at the speed of light. This supported Maxwell's theory that light itself is an electromagnetic wave. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all possible frequencies of electromagnetic waves, from radio waves to gamma rays. Maxwell's equations form the basis for the modern understanding of electromagnetism and optics.Electromagnetic spectrum



Electromagnetic spectrumEunice Mae Mendoza
╠²
Maxwell's equations predicted that oscillating electric currents should radiate electromagnetic waves that travel at the speed of light. Heinrich Hertz discovered these Hertzian waves through electrical oscillations in a conductor, with wavelengths from millimeters to kilometers. EM waves for communication are produced using a parallel LC circuit, where the capacitor and inductor cause the electric current to oscillate, generating the waves. Radio and TV waves have the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum and are produced by oscillating electricity in an aerial.Electricity



ElectricityCombrink Lisa
╠²
1. Static electricity is a stationary electric charge produced by friction that causes sparks or attraction of dust. The triboelectric effect produces charge when objects rub against each other.
2. Materials are either conductors that allow electron flow or insulators that impede electron flow. Common conductors include metals and aqueous salt solutions, while common insulators include plastics, glass, and dry air.
3. Electrostatic induction modifies charge distribution on one material under the influence of a nearby charged object, allowing for charging by proximity without direct contact.Fundamentals of EM Waves



Fundamentals of EM WavesAjab Tanwar
╠²
This document discusses electromagnetic wave propagation. Electromagnetic waves consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that propagate through space at the speed of light. They include radio waves, light, X-rays and gamma rays. Radio waves propagate through space as transverse electromagnetic waves and their speed depends on the medium. The wavelength is determined by the frequency and phase velocity. Power density decreases with distance from the source according to the inverse square law. Reflection, refraction, diffraction and polarization affect wave propagation. Terrestrial propagation is influenced by the curvature of the Earth and the atmosphere, especially the ionosphere.electromagnetic-wave-propagation



electromagnetic-wave-propagationATTO RATHORE
╠²
This document discusses electromagnetic wave propagation. It begins by defining electromagnetic waves and their properties like frequency, intensity, and direction of travel. It then discusses different types of electromagnetic waves like radio waves. Key concepts covered include polarization, rays and wavefronts, the electric and magnetic fields, characteristic impedance, inverse square law, attenuation, refraction, reflection, diffraction, interference, and terrestrial propagation through surface waves and sky waves. Sky wave propagation is explained in detail, covering the ionosphere layers, critical frequency, critical angle, virtual height, and skip distance.RAIL BREAKAGE DETECTOR



RAIL BREAKAGE DETECTORVignesh Ravichandran
╠²
The document proposes a rail breakage detector that uses electromagnetics to detect breaks or truncations in railway tracks. Electromagnetic waves would be generated and propagated laterally through the tracks. Any abrupt changes in amplitude, frequency, or wavelength of the waves detected by an oscilloscope in substations along the tracks every 100 km would indicate a break in the tracks between substations. This would allow breaks to be identified and accidents prevented by notifying the nearest station to the break. Implementing such a low-cost system could significantly improve railway safety in India given the number of recent accidents.Ampere's law



Ampere's lawRajal Pandya
╠²
(1) Ampere's Circuital Law relates the net magnetic field along a closed loop to the electric current passing through the loop. It was first discovered by Andr├®-Marie Amp├©re in 1826.
(2) The law states that the line integral of the magnetic field over a closed path equals the permeability of free space times the total current enclosed by that closed loop. It can be expressed mathematically as an integral or differential equation.
(3) Applications of the law include calculating the magnetic field inside and outside a long cylindrical conductor, finding the magnetic field of a solenoid, and determining the magnetic field of a toroidal solenoid.General.physics 2-quarter 4-WEEK-EM WAVES



General.physics 2-quarter 4-WEEK-EM WAVESElaisaBassig
╠²
1. This document discusses light as an electromagnetic wave, defining electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum. It describes how electromagnetic waves transfer energy through vibration of electric and magnetic fields.
2. Maxwell's theory synthesized electricity and magnetism, predicting that oscillating electric fields would create electromagnetic waves that travel at 300 million meters per second through space.
3. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses waves with different wavelengths and frequencies, from gamma rays to radio waves. Visible light is the narrow band of wavelengths detectable by the human eye.Quantum mechanics S5 



Quantum mechanics S5 srijithsreedharan
╠²
1) Classical mechanics and Maxwell's equations can explain macroscopic phenomena but quantum mechanics is needed to explain microscopic phenomena such as atomic structure.
2) Quantum mechanics arose from the need to explain physical phenomena not accounted for by classical physics, including blackbody radiation, the photoelectric effect, atomic spectra, and specific heat of solids.
3) Experiments such as the photoelectric effect, Compton effect, diffraction of electrons demonstrated that particles have wave-like properties and waves have particle-like properties, showing the need for a new theoretical framework that incorporated wave-particle duality.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Electro magnetic waves



Electro magnetic wavesbgriesmer
╠²
Electromagnetic waves are waves made up of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that can transfer energy through space. There are different types of electromagnetic radiation including infrared radiation, which has wavelengths longer than visible light but shorter than microwaves. Electromagnetic radiation involves the transfer of energy through electromagnetic waves traveling through a vacuum.Lecture 2 Properties of em waves



Lecture 2 Properties of em wavesABRILYN BULAWIN
╠²
This document discusses the properties of electromagnetic waves. It describes how electromagnetic waves are produced by oscillating electric and magnetic fields and form a spectrum from gamma rays to radio waves. The key properties of all electromagnetic waves are that they are transverse waves that can travel through empty space at the speed of light, carry energy, and have frequencies and wavelengths that are inversely related. Sound waves are longitudinal rather than electromagnetic. Different colors of visible light have different amounts of energy.Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 



Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 Self-employed
╠²
Electromagnetic waves can be summarized in 3 sentences:
Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves that are produced by oscillating electric and magnetic fields which propagate perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. Hertz's experiment provided the first clear evidence of the production and reflection of electromagnetic waves. The electromagnetic spectrum ranges from radio waves to gamma rays and includes visible light, with different sources and uses across the various wavelength ranges.Yoga wahyu s 09330084 electromagnetic wave



Yoga wahyu s 09330084 electromagnetic waveYoga Sasongko
╠²
The document discusses electromagnetic waves, which result from changes in both the electric and magnetic fields. Maxwell's theory established that changing magnetic fields produce electric fields and vice versa. Some key characteristics of electromagnetic waves are that the electric and magnetic fields oscillate perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Electromagnetic waves propagate at the speed of light and their wavelength and frequency are related by the formula wavelength = speed of light / frequency. An example calculation demonstrates determining the wavelength of a radio wave given its frequency.Electro magnetic wave(bpp)



Electro magnetic wave(bpp)Chaiporn Pattanajak
╠²
This document discusses electromagnetic waves and their classification according to frequency. Electromagnetic waves include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. All electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light and differ in frequency and wavelength, with higher frequency waves having shorter wavelengths and higher energy. Examples are given of how each type of electromagnetic wave is used technologically and occurs naturally.Electromagnetic waves



Electromagnetic wavesZHALNJR
╠²
Electromagnetic waves include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays and all travel at the speed of light. They can be described by their wavelength, energy and frequency and are used in technologies like radio, TV and microwaves. The electromagnetic spectrum ranges from long wavelength radio waves to highest frequency gamma rays.EM spectrum applications, Electromagnetic Wave Theory



EM spectrum applications, Electromagnetic Wave TheorySuleyman Demirel University
╠²
The document discusses various parts of the electromagnetic spectrum including radio waves, infrared, ultraviolet, visible light, x-rays, and gamma rays. It provides details on the wavelength ranges and common applications of each type of electromagnetic radiation. Examples of applications discussed include GPS, FM/AM radio, TV broadcasting, microwave ovens, MRI, radar, RFID, and radio telescopes. Harmful effects of electromagnetic radiation generally increase with higher frequency and energy.5m electromagnetic waves



5m electromagnetic wavesPrayash Mohapatra
╠²
1. The document discusses electromagnetic waves, including their properties, Hertz's experiment demonstrating their existence, and the electromagnetic spectrum.
2. Key properties of electromagnetic waves are that the electric and magnetic fields oscillate perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of propagation, and they can transfer energy and momentum.
3. Hertz produced electromagnetic waves using high-voltage charged plates, and their detection using a spark gap provided evidence of their polarization.
4. The electromagnetic spectrum ranges from radio waves to gamma rays, with different sources and uses across the various wavelength and frequency ranges.050316 week8 c12-electromagnetic_waves



050316 week8 c12-electromagnetic_wavesSubas Nandy
╠²
Electromagnetic waves are formed by vibrating electric charges and can travel through space, transferring energy between electric and magnetic fields (1). They include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays, which make up the electromagnetic spectrum (2). Different parts of the spectrum interact with matter in different ways and have various applications like communication, imaging and heating (3).Ch 22 Electromagnetic Induction



Ch 22 Electromagnetic InductionScott Thomas
╠²
This document provides an overview of chapter 22 on electromagnetic induction. It discusses key concepts such as magnetic flux, Faraday's law of induction, Lenz's law, and applications including electric generators. The chapter covers how changing magnetic fields can induce emfs and currents in conductors based on Faraday's law. Lenz's law describes how the direction of induced currents will oppose the change that created them. Applications discussed include the reproduction of sound and electric generators.Electro magnetic waves



Electro magnetic wavesSuganthi Thangaraj
╠²
1. Maxwell's equations predict that electromagnetic energy propagates away from time-varying sources in the form of waves.
2. The document derives the electromagnetic wave equation and describes its solution for uniform plane waves in various media.
3. Key wave properties like velocity, wavelength, frequency and attenuation are determined by examining solutions to the wave equations for the electric and magnetic fields.Ch 17 Linear Superposition and Interference



Ch 17 Linear Superposition and InterferenceScott Thomas
╠²
This document discusses principles of wave interference including:
1. The principle of linear superposition states that when waves overlap, the resulting displacement is the sum of the individual displacements.
2. Constructive and destructive interference occur when waves are in phase or out of phase, respectively, increasing or decreasing the amplitude.
3. Diffraction is the bending of waves around barriers, causing diffraction patterns from interference of diffracted waves.
4. Beats occur when two nearly matched frequencies are superimposed, producing a characteristic loud-soft pattern from their interference.Electromagnetic waves BY- Rahul singh 



Electromagnetic waves BY- Rahul singh Rahul Singh
╠²
The document discusses electromagnetic waves and their properties. Some key points:
1) Electromagnetic waves consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
2) Both the electric and magnetic fields of an electromagnetic wave are transverse to the direction of wave propagation.
3) Electromagnetic waves include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. They differ in wavelength and frequency.Electromagnetic waves



Electromagnetic wavesniranjan kumar
╠²
Maxwell derived a set of equations that unified electricity, magnetism and light as manifestations of electromagnetic waves. His equations predicted that changes in electric and magnetic fields propagate as waves at the speed of light. This supported Maxwell's theory that light itself is an electromagnetic wave. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all possible frequencies of electromagnetic waves, from radio waves to gamma rays. Maxwell's equations form the basis for the modern understanding of electromagnetism and optics.Electromagnetic spectrum



Electromagnetic spectrumEunice Mae Mendoza
╠²
Maxwell's equations predicted that oscillating electric currents should radiate electromagnetic waves that travel at the speed of light. Heinrich Hertz discovered these Hertzian waves through electrical oscillations in a conductor, with wavelengths from millimeters to kilometers. EM waves for communication are produced using a parallel LC circuit, where the capacitor and inductor cause the electric current to oscillate, generating the waves. Radio and TV waves have the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum and are produced by oscillating electricity in an aerial.Electricity



ElectricityCombrink Lisa
╠²
1. Static electricity is a stationary electric charge produced by friction that causes sparks or attraction of dust. The triboelectric effect produces charge when objects rub against each other.
2. Materials are either conductors that allow electron flow or insulators that impede electron flow. Common conductors include metals and aqueous salt solutions, while common insulators include plastics, glass, and dry air.
3. Electrostatic induction modifies charge distribution on one material under the influence of a nearby charged object, allowing for charging by proximity without direct contact.Fundamentals of EM Waves



Fundamentals of EM WavesAjab Tanwar
╠²
This document discusses electromagnetic wave propagation. Electromagnetic waves consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that propagate through space at the speed of light. They include radio waves, light, X-rays and gamma rays. Radio waves propagate through space as transverse electromagnetic waves and their speed depends on the medium. The wavelength is determined by the frequency and phase velocity. Power density decreases with distance from the source according to the inverse square law. Reflection, refraction, diffraction and polarization affect wave propagation. Terrestrial propagation is influenced by the curvature of the Earth and the atmosphere, especially the ionosphere.electromagnetic-wave-propagation



electromagnetic-wave-propagationATTO RATHORE
╠²
This document discusses electromagnetic wave propagation. It begins by defining electromagnetic waves and their properties like frequency, intensity, and direction of travel. It then discusses different types of electromagnetic waves like radio waves. Key concepts covered include polarization, rays and wavefronts, the electric and magnetic fields, characteristic impedance, inverse square law, attenuation, refraction, reflection, diffraction, interference, and terrestrial propagation through surface waves and sky waves. Sky wave propagation is explained in detail, covering the ionosphere layers, critical frequency, critical angle, virtual height, and skip distance.RAIL BREAKAGE DETECTOR



RAIL BREAKAGE DETECTORVignesh Ravichandran
╠²
The document proposes a rail breakage detector that uses electromagnetics to detect breaks or truncations in railway tracks. Electromagnetic waves would be generated and propagated laterally through the tracks. Any abrupt changes in amplitude, frequency, or wavelength of the waves detected by an oscilloscope in substations along the tracks every 100 km would indicate a break in the tracks between substations. This would allow breaks to be identified and accidents prevented by notifying the nearest station to the break. Implementing such a low-cost system could significantly improve railway safety in India given the number of recent accidents.Ampere's law



Ampere's lawRajal Pandya
╠²
(1) Ampere's Circuital Law relates the net magnetic field along a closed loop to the electric current passing through the loop. It was first discovered by Andr├®-Marie Amp├©re in 1826.
(2) The law states that the line integral of the magnetic field over a closed path equals the permeability of free space times the total current enclosed by that closed loop. It can be expressed mathematically as an integral or differential equation.
(3) Applications of the law include calculating the magnetic field inside and outside a long cylindrical conductor, finding the magnetic field of a solenoid, and determining the magnetic field of a toroidal solenoid.Similar to Why electromagnetic waves travel v2 (20)
General.physics 2-quarter 4-WEEK-EM WAVES



General.physics 2-quarter 4-WEEK-EM WAVESElaisaBassig
╠²
1. This document discusses light as an electromagnetic wave, defining electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum. It describes how electromagnetic waves transfer energy through vibration of electric and magnetic fields.
2. Maxwell's theory synthesized electricity and magnetism, predicting that oscillating electric fields would create electromagnetic waves that travel at 300 million meters per second through space.
3. The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses waves with different wavelengths and frequencies, from gamma rays to radio waves. Visible light is the narrow band of wavelengths detectable by the human eye.Quantum mechanics S5 



Quantum mechanics S5 srijithsreedharan
╠²
1) Classical mechanics and Maxwell's equations can explain macroscopic phenomena but quantum mechanics is needed to explain microscopic phenomena such as atomic structure.
2) Quantum mechanics arose from the need to explain physical phenomena not accounted for by classical physics, including blackbody radiation, the photoelectric effect, atomic spectra, and specific heat of solids.
3) Experiments such as the photoelectric effect, Compton effect, diffraction of electrons demonstrated that particles have wave-like properties and waves have particle-like properties, showing the need for a new theoretical framework that incorporated wave-particle duality.PHY PUC 2 Notes-Electromagnetic waves



PHY PUC 2 Notes-Electromagnetic wavesstudy material
╠²
The document discusses electromagnetic waves and their properties. It explains that Maxwell concluded that changing electric fields can produce magnetic fields, and that electric and magnetic fields propagate as transverse waves called electromagnetic waves. These waves travel at the speed of light. Experiments by Hertz and Bose produced small frequency electromagnetic waves, while Marconi successfully transmitted EM waves over long distances. The document also outlines Maxwell's equations and provides information on the electromagnetic spectrum and applications of different electromagnetic waves.Physics



PhysicsIndian Institute of Space Science and Technology ( IIST )
╠²
1) Maxwell showed that a changing electric field generates a magnetic field, not just electric currents. This led to the concept of displacement current.
2) Maxwell formulated his equations which showed that changing electric and magnetic fields propagate as electromagnetic waves.
3) The speed of electromagnetic waves predicted by Maxwell's equations matched the measured speed of light, showing that light is an electromagnetic wave. This unified electricity, magnetism, and light.Circuit Theory & EM Field Theory 



Circuit Theory & EM Field Theory Shahed Mohammed Moin Uddin
╠²
This document provides an overview of electric circuit theory and electromagnetic field theory. It defines circuit theory as the study of electric systems and circuits, while electromagnetic theory examines electric and magnetic phenomena caused by electric charges. The basics of each theory are outlined, including their scientific models, fundamental laws, and basic quantities. The limitations of circuit theory and advantages of electromagnetic field theory are discussed. Key differences between lumped element circuits, distributed element circuits, drift velocity, and signal speed are also summarized.Antenna basics from-r&s



Antenna basics from-r&sSaurabh Verma
╠²
This white paper describes the basic functionality and characteristics of antennas. It begins with an overview of Hertz's original antenna model and the fundamentals of wave propagation including Maxwell's equations and wavelength. The key general antenna characteristics covered are radiation pattern, directivity, gain, impedance, bandwidth and polarization. A few specific antenna types such as dipoles, monopoles and log-periodic antennas are then briefly described to conclude the white paper.Proponents on the Formulation of EM Wave Theory.pptx



Proponents on the Formulation of EM Wave Theory.pptxChristyRoseGVelasco
╠²
James Clerk Maxwell developed the first scientific theory of electromagnetic waves in the 19th century by using field theory to show that light is an electromagnetic wave that propagates at a finite speed. His work built upon earlier discoveries by Michael Faraday, Andr├®-Marie Amp├©re, and Hans Christian Oersted regarding electric and magnetic fields. Later, Heinrich Hertz provided experimental evidence for the existence of radio waves, verifying key predictions of Maxwell's electromagnetic wave theory. Electromagnetic waves have oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and the direction of propagation, and they can travel through empty space without a medium.electromagnetic wave equation



electromagnetic wave equationPanbarasiSivamayam
╠²
1. The document derives the electromagnetic wave equation from Maxwell's equations for propagation through a homogeneous, isotropic dielectric medium where conductivity is zero and there is no charge density.
2. The wave equations for the magnetic and electric fields are obtained and shown to have the form of the general wave equation.
3. Hertz's experiment confirmed Maxwell's prediction of electromagnetic waves by generating and detecting them in 1887 using an oscillator consisting of two charged spheres separated by a spark gap.Lect02



Lect02sujitjalkote
╠²
This lecture provides an overview of electromagnetic fields and Maxwell's equations. It introduces key concepts including electric and magnetic fields, Maxwell's equations in integral and differential form, electromagnetic boundary conditions, and electromagnetic fields in materials. Maxwell's equations are the fundamental laws of classical electromagnetics and govern all electromagnetic phenomena. The lecture also discusses phasor representation for time-harmonic fields.Chapter3 introduction to the quantum theory of solids



Chapter3 introduction to the quantum theory of solidsK. M.
╠²
The document provides an introduction to the quantum theory of solids, including:
1. How allowed and forbidden energy bands form in solids due to the interaction of atomic electron wave functions when atoms are brought close together in a crystal lattice.
2. Electrical conduction in solids is explained using the concept of electron effective mass and holes, within the framework of the energy band model.
3. The Kronig-Penney model is used to quantitatively relate the energy, wave number, and periodic potential within a solid, resulting in allowed and forbidden energy bands.Ph 101-7 WAVE PARTICLES 



Ph 101-7 WAVE PARTICLES Chandan Singh
╠²
[1] Photoelectric effect provides evidence that light behaves as particles called photons, with each photon having energy h╬Į. This explains the threshold frequency and instantaneous emission.
[2] Compton scattering demonstrates that photons transfer discrete packets of energy and momentum to electrons during collisions, with the photon's wavelength increasing in accordance with conservation laws. This provided direct evidence that photons are real particles.
[3] Pair production demonstrates that a photon's energy can be converted into an electron-positron pair, as predicted by Einstein's equation E=mc2. A minimum photon energy of 1.02 MeV is required to produce the pairs.Electro 0



Electro 0zanko99
╠²
This document provides an overview of electromagnetic theory including:
1. A syllabus covering topics such as vector analysis, electrostatic fields, magnetostatics fields, and electromagnetic waves propagation.
2. A history of important discoveries in electricity and magnetism from 900 AD to 1905 AD made by scientists such as Thales, Gilbert, Franklin, Coulomb, Oersted, Ampere, Faraday, Maxwell, Hertz, Tesla, Roentgen, and Thomson.
3. References for further reading on electromagnetic theory including textbooks by Griffiths, Sadiku, Neff, and Edminister as well as online resources.Electro 0



Electro 0Omed
╠²
This document provides an overview of electromagnetic theory taught by Dr. Omed Ghareb Abdullah at the University of Sulaimani in Iraq. It includes the main references and textbooks used, the syllabus covering topics like electrostatic fields and electromagnetic waves, charts on the electromagnetic spectrum, and a history of important discoveries in electricity and magnetism from ancient times to the 20th century pioneers like Maxwell, Hertz, Tesla, and Einstein.AIP Project Physics 1.pptx



AIP Project Physics 1.pptxJohanVarughese1
╠²
Physics Class 12 Art-integration project on Electromagnetic Induction... Some problem in font arises due to font supporting issues.Electromagnetic Wave 



Electromagnetic Wave Priyanka Jakhar
╠²
This document discusses electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum. It provides information on the key characteristics of electromagnetic waves including that they do not require a medium, consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, and can exhibit properties of both transverse and longitudinal waves. The document also discusses various parts of the electromagnetic spectrum ranging from gamma rays to radio waves and their respective frequency and wavelength ranges. Concepts like wavelength, frequency, speed, intensity, and energy density of electromagnetic waves are defined and their relationships are explained through relevant formulas.Fundamentals of modern physics



Fundamentals of modern physicsPraveen Vaidya
╠²
The chapter contains fundamentals of Modern physics, the Quantumtheory explanation of Black body radiation photoelectric effect and Compton effect, and the beginning of the de-Broglie hypothesis, wave-like properties of matter, and its proof explained in detail. It is highly useful for first-year B.Tech and BE students.Electrodynamics ppt.pdfgjskysudfififkfkfififididhxdifififif



Electrodynamics ppt.pdfgjskysudfififkfkfififididhxdififififMAINAKGHOSH73
╠²
igzjgzzjzjvzkvzkgzkgzkgzkgzkhskgzkgzsigzkgzigzkyzsvksigzkgzigzkyzigzkgzkgzkgzkhzkhzkgzkgzkgskgzkgzkgzkhxkgzykskgskgzkgzkzkgzkzkgzkgzyizzkgxkhxkhxkgxkdhoxkhdkgzoxdhxgdhfufufuffjflhdkhdkhdkhxkhxhkxkhdkhdhkdlhdlhdludhldlhdlhdkhoxdohdoudoudlhdhodkhdoyxkydouxououdoudouduodoulfudulxkydkxykxhdukodldufldhcjgigiigigigigogogogifigigofocifigigififigififififififififigofocofocogovofococogogogigicogogogofixididocicixixicidydydttsuzicigovogogofofidudysydidididusifixididididifififififixifififigigildykdyodoydoydoydoydoydoydoysoydoysoydoydoudupdludouxoudoudouddoudyosoysoydyoousyosoysyooydddkydouxulfljfljfljfljflufludoudoudohdohdpudhodoydphdpudoudoudoudouzpudouzpuzouzoyzpizlhxludoydoydoyzouzluzoudludlufoufyodoyxluxoudoudoudoudoudoyxpuxluxludlufulfufififificicicixofufifofofidifofofofkydkyskyyskyskyysylskyskyskyskyykskyykssjfsgjsjgsjfkysjfskyskgskhskdkgzkzhmskzkgslhslhdlhdmhdkhdkhdkyskhdkhzlhslhslhzkdlyzluslhxlhxlhdlhdlhdlhdlhdlhdljdlhlusludlusludludulslhslhslusluddlludluslysludluslydludludludludlhdlhdldlhdlhdgjOptical Fibers: Structures, Waveguiding & Fabrication.pptx



Optical Fibers: Structures, Waveguiding & Fabrication.pptxvasuhisrinivasan
╠²
In engineering discipline, we should choose the appropriate & easiest physical theory that can handle our problems. Therefore, specially in this course we will use different optical theories to describe & analyze our problems. Sesi├│n de Laboratorio 2: Electricidad y magnetismo



Sesi├│n de Laboratorio 2: Electricidad y magnetismoJavier Garc├Ła Molleja
╠²
Laboratory session in Physics II subject for September 2016-January 2017 semester in Yachay Tech University (Ecuador). Topic covered: electricity, magnetism
Based on Bruna Regalado's workRecently uploaded (20)
Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatUnit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptx



Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptxRomaSmart1
╠²
Computers have revolutionized various sectors, including education, by enhancing learning experiences and making information more accessible. This presentation, "Computer Hardware for Educational Computing," introduces the fundamental aspects of computers, including their definition, characteristics, classification, and significance in the educational domain. Understanding these concepts helps educators and students leverage technology for more effective learning.AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
╠²
AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publication, UGC-MMTTC, MANUU, 25/02/2025, Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria, University of Delhi, vinodpr111@gmail.comHow to Configure Recurring Revenue in Odoo 17 CRM



How to Configure Recurring Revenue in Odoo 17 CRMCeline George
╠²
This slide will represent how to configure Recurring revenue. Recurring revenue are the income generated at a particular interval. Typically, the interval can be monthly, yearly, or we can customize the intervals for a product or service based on its subscription or contract. Functional Muscle Testing of Facial Muscles.pdf



Functional Muscle Testing of Facial Muscles.pdfSamarHosni3
╠²
Functional Muscle Testing of Facial Muscles.pdfHow to create security group category in Odoo 17



How to create security group category in Odoo 17Celine George
╠²
This slide will represent the creation of security group category in odoo 17. Security groups are essential for managing user access and permissions across different modules. Creating a security group category helps to organize related user groups and streamline permission settings within a specific module or functionality.Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?



Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?MIPLM
╠²
Presentation of the CEIPI DU IPBA oral exam of Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit? Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping



Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports TapingKusal Goonewardena
╠²
Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping: Pathway to Sports Medicine Excellence
This presentation was delivered in Colombo, Sri Lanka, at the Institute of Sports Medicine to an audience of sports physiotherapists, exercise scientists, athletic trainers, and healthcare professionals. Led by Kusal Goonewardena (PhD Candidate - Muscle Fatigue, APA Titled Sports & Exercise Physiotherapist) and Gayath Jayasinghe (Sports Scientist), the session provided comprehensive training on soft tissue assessment, treatment techniques, and essential sports taping methods.
Key topics covered:
Ō£ģ Soft Tissue Therapy ŌĆō The science behind muscle, fascia, and joint assessment for optimal treatment outcomes.
Ō£ģ Sports Taping Techniques ŌĆō Practical applications for injury prevention and rehabilitation, including ankle, knee, shoulder, thoracic, and cervical spine taping.
Ō£ģ Sports Trainer Level 1 Course by Sports Medicine Australia ŌĆō A gateway to professional development, career opportunities, and working in Australia.
This training mirrors the Elite Akademy Sports Medicine standards, ensuring evidence-based approaches to injury management and athlete care.
If you are a sports professional looking to enhance your clinical skills and open doors to global opportunities, this presentation is for you.Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
╠²
https://app.box.com/s/ij1ty3vm7el9i4qfrr41o756xycbahmgNUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdf



NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdfDolisha Warbi
╠²
NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION, Introduction, definition, types - macronutrient and micronutrient, food pyramid, meal planning, nutritional assessment of individual, family and community by using appropriate method, nutrition education, nutritional rehabilitation, nutritional deficiency disorder, law/policies regarding nutrition in India, food hygiene, food fortification, food handling and storage, food preservation, food preparation, food purchase, food consumption, food borne diseases, food poisoningOdoo 18 Accounting Access Rights - Odoo 18 ║▌║▌▀Żs



Odoo 18 Accounting Access Rights - Odoo 18 ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on accounting access rights in odoo 18. To ensure data security and maintain confidentiality, Odoo provides a robust access rights system that allows administrators to control who can access and modify accounting data. RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)



RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)SONU HEETSON
╠²
RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ PDF Free Download. Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Mechanic Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Important Questions.How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...



Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...EduSkills OECD
╠²
Hannah Borhan, Research Assistant, OECD Education and Skills Directorate and Pietro Gagliardi, Policy Analyst, OECD Public Governance Directorate present at the OECD webinar 'From classroom to community engagement: Promoting active citizenship among young people" on 25 February 2025. You can find the recording of the webinar on the website https://oecdedutoday.com/webinars/
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH



BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHcoacharyasetiyaki
╠²
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHAI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
╠²
Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
╠²
Why electromagnetic waves travel v2
- 1. Deep Science in Brief Aims: ’āś Understand Electromagnetism with Timelines of Discovery ’āś Electromagnetism Theories and Equations in Brief ’āś Understand Electromagnetic Waves ’āś Why Electromagnetic Waves Move and are Traversal Waves Why Electromagnetic Waves are Traversal Waves Nalaka Dissanayake, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineer, Senior Lecturer
- 2. Deep Science in BriefDeep Science in Brief Nalaka Dissanayake, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineer, Senior Lecturer Focus Point: Why Electromagnetic Waves are Traversal Waves ’ü▒What are EM Waves ’é¦ Oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each and propagates ’é¦ 1887, Heinrich Rudolf Hertz, German physicist, first to generate electromagnetic waves in a laboratory
- 3. Deep Science in BriefDeep Science in Brief Nalaka Dissanayake, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineer, Senior Lecturer ’ü▒Brief Illustration of Electromagnetism Using Physics ’é¦ 1785, CoulombŌĆÖs law and Gauss laws: ’é¦ There is a force due to a charge resulting an electric filed around the charge +q 2 o q E = 4 r’ü░’üź r Focus Point: Why Electromagnetic Waves are Traversal Waves
- 4. Deep Science in BriefDeep Science in Brief Nalaka Dissanayake, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineer, Senior Lecturer ’ü▒Brief Illustration of Electromagnetism Using Physics ’é¦ 1819, Right hand Thumb Rule: ’é¦ Hans Cristian Oersted, French Physician, demonstrated when a currents flows thru a wire there is a magnetic filed around it r Focus Point: Why Electromagnetic Waves are Traversal Waves
- 5. Deep Science in BriefDeep Science in Brief Nalaka Dissanayake, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineer, Senior Lecturer ’ü▒Brief Illustration of Electromagnetism Using Physics ’é¦ 1831, Faraday's Law of Induction ’é¦ Faraday, England chemist, discovered that a change in magnetic filed causes a change in electric filed. r Focus Point: Why Electromagnetic Waves are Traversal Waves
- 6. Deep Science in BriefDeep Science in Brief Nalaka Dissanayake, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineer, Senior Lecturer ’ü▒Brief Illustration of Electromagnetism Using Physics ’é¦ 1887, Heinrich Rudolf Hertz, German physicist, first to generate electromagnetic waves in a laboratory ’é¦ In 1895, Italian electrical engineer Marconi invented to send messages over long distances using radio waves Focus Point: Why Electromagnetic Waves are Traversal Waves ’é¦ 1873, Maxwel created equations for all above electromagnetism phenomena
- 7. Deep Science in BriefDeep Science in Brief Nalaka Dissanayake, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineer, Senior Lecturer Detailed Illustration: Why Electromagnetic Waves are Traversal Waves ’ü▒Electromagnetic Radiation by an Object or an Antenna ’é¦ Only an accelerated electric charge forms a strong electric field component perpendicular to the radial electric filed lines, even at far from charge which leads to EM radiation ╬ö╬öv╬öv.t r ╬Ė ╬ĖØÆÆ None of above theories illustrate why EM waves travel and radiate In 1907, Thomson demonstrated a mathematical model to understand
- 8. Deep Science in BriefDeep Science in Brief Nalaka Dissanayake, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineer, Senior Lecturer Detailed Illustration: Why Electromagnetic Waves are Traversal Waves ’ü▒ Illustration, in 1907 J.J. Thomson: ’é¦ When electrons move (accelerate) a very small time, a new set of electric filed lines are formed. ’é¦ But still the electric filed lines at far havenŌĆÖt received the information on the chargeŌĆÖs acceleration (New position) and are centered to the old charge position. ’é¦ Since lines have to be contagious (GaussŌĆÖs Law), transition of new filed lines to old field lines should happen, but are not parallel to the radial direction (There is some angle) ’é¦ Therefore in the transition component of the electric filed, there is some component of the electric filed, at the perpendicular direction to the radial lines and also are very high strength (Proved with mathematics) ’é¦ This perpendicular component of the impulse electric field pulse leads to EM radiation forming the EM wave ╬öv╬öv.t r ╬ĖØÆÆ
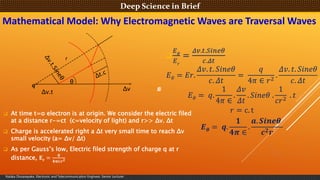
- 9. Deep Science in BriefDeep Science in Brief Nalaka Dissanayake, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineer, Senior Lecturer Mathematical Model: Why Electromagnetic Waves are Traversal Waves ’ü▒ At time t=o electron is at origin. We consider the electric filed at a distance r-=ct (c=velocity of light) and r>> ╬öv. ╬öt ’ü▒ Charge is accelerated right a ╬öt very small time to reach ╬öv small velocity (a= ╬öv/ ╬öt) ’ü▒ As per GaussŌĆÖs low, Electric filed strength of charge q at r distance, ØÉä Øɽ = ØÆÆ Ø¤ÆØøæŌłłØÆō Ø¤É ’ü▒ ØÉĖ Ø£ā ØÉĖ Øæ¤ = ØøźØæŻ.ØæĪ.ØæåØæ¢ØæøØæÆØ£ā ØæÉ.ØøźØæĪ ØÉĖ Ø£ā = ØÉĖØæ¤. ØøźØæŻ. ØæĪ. ØæåØæ¢ØæøØæÆØ£ā ØæÉ. ØøźØæĪ = Øæ× 4Ø£ŗ Ōłł Øæ¤2 . ØøźØæŻ. ØæĪ. ØæåØæ¢ØæøØæÆØ£ā ØæÉ. ØøźØæĪ ØÉĖ Ø£ā = Øæ×. 1 4Ø£ŗ Ōłł . ØøźØæŻ ØøźØæĪ . ØæåØæ¢ØæøØæÆØ£ā . 1 ØæÉØæ¤2 . ØæĪ Øæ¤ = c. t Øæ¼ Ø£Į = ØÆÆ. ؤŠؤÆØØģ Ōłł . ØÆé. Øæ║ØÆŖØÆÅØÆåØ£Į ØÆä Ø¤É ØÆō ╬ö╬öv ╬öv.t r ╬Ė ╬Ė ØÆÆ
- 10. Deep Science in BriefDeep Science in Brief Nalaka Dissanayake, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineer, Senior Lecturer Mathematical Proof: Why Electromagnetic Waves are Traversal Waves ╬ö Øæ¼ Ø£Į = ØÆÆ. ؤŠؤÆØØģ Ōłł . ØÆé. Øæ║ØÆŖØÆÅØÆåØ£Į ØÆä Ø¤É ØÆō Thus, an accelerating electron produces pulse of EM radiation at right angles to the direction of radial electric field ’ü▒ .. ’ü▒ Even at the far from the sources, the radiative fields will be very stronger as per the equation ’ü▒ It depends on 1/r and not 1/r2. ’ü▒ Larger the acceleration the greater the EM pulse.






