Wikispaces
- 2. вҖ«Ш§Щ„вҖ¬вҖ«ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ШіШЁЩҠШівҖ¬ Wikispaces вҖ«Щ…ЩҒвҖ¬вҖ«ЩҮвҖ¬вҖ«ЩҲЩ…вҖ¬ Wikis paces вҖ«Щ…Щ…ЩҠШІШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„вҖ¬вҖ«ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ШіШЁЩҠШівҖ¬ Wikispaces вҖ«Ш№ЩҠЩҲШЁвҖ¬ Wikispaces вҖ«ШҘЩ…ЩғШ§ЩҶЩҠШ§ШӘвҖ¬ Wikispaces вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ…Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш®Ш·ЩҲШ§ШӘвҖ¬ Wikis paces вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҒЩҲШ§ШҰШҜвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠШ©вҖ¬ Wikis paces
- 3. пӮӣвҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ШӘЩҠвҖ¬ ШҢвҖ«Ш§ШҘЩ„ЩҶШӘШұЩҶШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ШҙШЁЩғШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ШіШ§ШӯШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№ШЁШ§ШұШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҮЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ШұЩҲШ§ШЁШ·вҖ¬ ШҢвҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ШөЩҲШұвҖ¬ ШҢвҖ«ЩҲШ§ШЈЩ„ЩҒЩғШ§ШұвҖ¬ ШҢвҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш№Щ…Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ШҙШ§ШұЩғШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩ…ЩғЩҶЩғвҖ¬ШҢ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠвҖ¬ ШҢвҖ«ЩҲШ§ШҘЩ„Ш№Ш§Щ„ЩҶШ§ШӘвҖ¬ ШҢвҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„Щ…ЩҲШ§ШҜвҖ¬ ШҢвҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ЩҒЩҠШҜЩҠЩҲвҖ¬ШҢвҖ«Щ…Ш§ШӘвҖ¬ ШҢвҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ЩӮЩҲШ§ЩҶЩҠЩҶвҖ¬ ШҢвҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ШӘЩҲШ¬ЩҠЩҮШ§ШӘвҖ¬.вҖ«ШӘЩӮШҜЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШЁШұЩ…Ш¬ЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҮШ°ЩҮвҖ¬ вҖ«ШҘЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈЩҶЩҲШ§Ш№вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш¬Щ…ЩҠШ№вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШЁШ§ШҜЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШ¬Ш№Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШЈЩ„ШҜЩҲШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…Ш¬Щ…ЩҲШ№Ш©вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„Щ…Ш№Щ„Щ…ЩҠЩҮЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„Щ„Ш·Ш§Щ„ШЁвҖ¬ ЩӢвҖ«ШЎвҖ¬вҖ«ШіЩҲШ§вҖ¬ ЩӢвҖ«Ш¬ШҜШ§вҖ¬ ЩӢвҖ«ШіЩҮШ§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Щ„ЩҒШ§ШӘвҖ¬. вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ§Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШіШ§ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ§ШҰЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш©вҖ¬
- 7. пӮӣвҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬вҖ«Ш®Ш§ШөЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„ЩҮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШ№Ш§ЩҲЩҶЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҲЩӮШ№вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҮЩҲвҖ¬В«вҖ«Щ…ЩҒШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШӯШұЩҠШұвҖ¬вҖ«ЩҲШӯвҖ¬В» вҖ«ШЈЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮШЁЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш№Щ„ЩҲЩ…Ш§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШӯШұЩҠШұвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠЩ…ЩғЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈЩҶЩҮвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁЩ…Ш№ЩҶЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ШіШӘШ®ШҜЩ…вҖ¬. пӮӣвҖ«ШЈвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Щ…ЩғЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҒЩ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШөЩҒШӯШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№ШҜЩҠЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„Щ„Ш№Ш§Щ…Ш©вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠШӘЩҠШӯвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬вҖ«ЩҠШӘЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩ„ЩҒвҖ¬вҖ«ЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШөЩҒШӯШ§ШӘвҖ¬вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩ…ЩғЩҶЩҮвҖ¬вҖ«ЩҶЩҮШ§ШҰЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁШҙЩғЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӯШ°ЩҒЩҮШ§вҖ¬. пӮӣвҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш¶Щ„Щ„Ш©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш№Щ„ЩҲЩ…Ш§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҶШҙШұвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁШіЩҮЩҲЩ„Ш©вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠЩ…ЩғЩҶвҖ¬вҖ«ШіШЁЩҠШівҖ¬ пӮӣвҖ«ЩҠШ№ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…Ш§вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӯШ°ЩҒвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӢШ§вҖ¬вҖ«ШЁвҖ¬вҖ«Щ…ЩҶШ§ШівҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…Ш§ЩҠШұШ§ЩҮвҖ¬ вҖ«ШҘШ¶Ш§ЩҒШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҒЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӯШұЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„ЩҮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ШӘШ№Щ„Щ…вҖ¬вҖ«ШЈЩҶЩҮвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮШҜвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш¬вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш®Щ„ЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«ШҘЩ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠШӨШҜЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮШҜвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…Щ…Ш§вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶШ§ШіШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ШәЩҠШұвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁШ§Щ„Щ…ЩҲШ¶ЩҲШ№вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ШұШӘШЁШ·вҖ¬ вҖ«ШәЩҠШұвҖ¬вҖ«ЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ШӘШ№ШөШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш№ШҜШ§ШҰЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҶЩҲШ№вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӯШӘЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШҘЩ„ШӯШЁШ§Ш·вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШұШ¶Ш§вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№ШҜЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШҙШ®ШөЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„ШўЩ„ШұШ§ШЎвҖ¬. вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ§Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШіШ§ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ§ШҰЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш©вҖ¬
- 8. пӮӣвҖ«ШҘЩ…ЩғШ§ЩҶЩҠШ©вҖ¬вҖ«ШұШ§ШЁШ·вҖ¬ вҖ«ШҘШҜШұШ§Ш¬вҖ¬LinkвҖ«Щ„Щ…ЩҲЩӮШ№вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШұШ§ШЁШ·вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҮШ°Ш§вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠЩғЩҲЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲЩӮШҜвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӯШӘЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ШҜШ§Ш®Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈШ®ШұЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„ШөЩҒШӯШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш®Ш§ШұШ¬вҖ¬ вҖ«ШўШ®ШұвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬. пӮӣвҖ«ШҘЩ…ЩғШ§ЩҶЩҠШ©вҖ¬вҖ«Ш¬ШҜЩҲЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШҘШҜШұШ§Ш¬вҖ¬TableвҖ«Ш№ШҜШҜвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШӯШҜЩҠШҜвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲЩҠЩ…ЩғЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш¬ШҜЩҲЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҒЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§ШЈЩ„Ш№Щ…ШҜШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШөЩҒЩҲЩҒвҖ¬вҖ«ШӘЩҶШіЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ШҘЩ…ЩғШ§ЩҶЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…Ш№вҖ¬вҖ«ЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш¬ШҜЩҲЩ„вҖ¬. пӮӣвҖ«ШҘЩ…ЩғШ§ЩҶЩҠШ©вҖ¬вҖ«ШөЩҲШұШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…Щ„ЩҒвҖ¬ вҖ«ШҘШҜШұШ§Ш¬вҖ¬FileвҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Щ„ЩҒвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Ш®ШӘЩҠШ§ШұвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠШӘЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӯШ§ШіШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҒЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩҲШ¬ЩҲШҜШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Щ„ЩҒШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ШҘШҜШұШ§Ш¬ЩҮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ШұШ§ШҜвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ШҘЩ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШӯЩ…ЩҠЩ„ЩҮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш«Щ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШўЩ„Щ„ЩҠвҖ¬. вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ§Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШіШ§ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ§ШҰЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш©вҖ¬
- 9. пӮӣвҖ«Ш§ШҘЩ„Щ„ЩғШӘШұЩҲЩҶЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШЁШұЩҠШҜвҖ¬ вҖ«ШұШіШ§ШҰЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШЁШ§ШҜЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠШӘЩҠШӯвҖ¬вҖ«ШЁЩҠЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш©вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШҘЩ„Щ„ЩғШӘШұЩҲЩҶЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШЁШұЩҠШҜвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„Щ…Ш№ШұЩҒШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӯШ§Ш¬ШӘЩҮЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ШҜЩҲЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШЈЩ„Ш№Ш¶Ш§ШЎвҖ¬вҖ«ЩғЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ШіШӘШ®ШҜЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШіЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШіШӘШ®ШҜШ§Щ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш·ШұЩҠЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШҘЩҶЩ…Ш§вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Ш¶ЩҲвҖ¬. пӮӣвҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ШөШәШұШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ·ШЁЩҠЩӮШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШ¶Щ…ЩҠЩҶвҖ¬WidgetвҖ«ЩҲШӘШЁШұШІвҖ¬вҖ«ЩҮШ°ЩҮвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҒЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ШӘЩҠвҖ¬ ШҢвҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШіШӘШ®ШҜШ§Щ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲЩ…ШұЩҲЩҶШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ШіЩҮЩҲЩ„Ш©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш®Ш§ШөЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…Ш®ШӘЩ„ЩҒШ©Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҲШ§ЩӮШ№вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШ·ШЁЩҠЩӮШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШ¶Щ…ЩҠЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШӘЩҠШӯвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШҘЩ„ЩҶШӘШұЩҶШӘвҖ¬. вҖ«Щ…Ш«Щ„вҖ¬: (TeacherTube,GoogleVide,YahooVideo) вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ§Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШіШ§ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ§ШҰЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш©вҖ¬
- 10. пӮӣвҖ«Ш§Ш№ШӘШЁШ§вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШ№ШӘЩ…ШҜвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҒЩ„ШіЩҒШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠЩӮЩҲЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬вҖ«ШЈЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ШұвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„Щ…ЩҶШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҮШҜЩҒвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҮЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш·Ш§Щ„ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁЩҮШ§вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠЩ…ШұвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш№Щ…Щ„ЩҠШ©вҖ¬ШҢвҖ«Ш¬вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш¬Щ…Ш§Ш№ЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„Ш№Щ…Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Ш§ЩҲЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ…Щ„ЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁЩ…Ш№ЩҶЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШЁШ§ШҜЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҮШ§ШұШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШӘЩҶЩ…ЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш·Ш§Щ„ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁЩҠЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ШӘЩҒШ§Ш№Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҮШҜЩҒвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҮЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШЈЩ„ШҜЩҲШ§ШұвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШӘЩҲШІЩҠШ№вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„Щ…Ш№ШұЩҒЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҒЩғШұЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШіШӘШ®ШҜШ§Щ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШұШ§ШЎвҖ¬. пӮӣвҖ«Ш·ШұЩҠЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш·Ш§Щ„ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„ШҜЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ШіШӨЩҲЩ„ЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӯШівҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩҶЩ…ЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҲЩӮШ№вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁЩ…ЩҶШҙЩҲШұвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Ш§Щ„Ш№ШӘЩҶШ§ШЎвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ШіШӨЩҲЩ„ЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩҲЩ„ЩҠШӘЩҮЩ…вҖ¬вҖ«ЩҮвҖ¬ вҖ«ШІЩ…Ш§Щ„ШҰЩҮЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш№Щ„Щ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠЩӮШӘШөШұвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш¬Щ…ЩҮЩҲШұвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁШ§Щ„ШөЩҒвҖ¬. вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ§Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШіШ§ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ§ШҰЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш©вҖ¬
- 11. пӮӣвҖ«ШӘЩҶЩ…ЩҠШ©вҖ¬вҖ«Щ„Щ„Щ…ШӘШ№Щ„Щ…ЩҠЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҶЩӮШҜЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘЩҒЩғЩҠШұвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ШіШӘЩҲЩүвҖ¬вҖ«Ш®Ш§Щ„Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩҲШ¬ЩҲШҜШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш№Щ„ЩҲЩ…Ш§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ШҜЩӮШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӯШұШөЩҮЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠШ·вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…Ш§вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҶЩӮШҜвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲЩғШ°Щ„ЩғвҖ¬ ШҢвҖ«ШЁЩҮЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш®Ш§ШөШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ШөЩҒШӯШ§ШӘвҖ¬вҖ«ШұШӯЩҮвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ШІЩ…Ш§Щ„ШӨЩҮЩ…вҖ¬вҖ«Щ…Ш№Щ„ЩҲЩ…Ш§ШӘвҖ¬. пӮӣвҖ«Щ„Щ„Щ…Ш№Щ„ЩҲЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ЩҒЩҮЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ЩғШӘШ§ШЁШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩӮШұШ§ШЎШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҮШ§ШұШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШ·ЩҲЩҠШұвҖ¬вҖ«Ш§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШӯЩӮЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЈШ¬Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш·Ш§Щ„ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩҠЩҮШ§вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠШӯШөЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩғШӘШҙЩҒШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§ШЈЩ„Ш®Ш·Ш§ШЎвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШӘШөШӯЩҠШӯвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁШҜЩӮШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩӮШ§ШҰШ№вҖ¬вҖ«ШЁЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШІЩ…Ш§Щ„ШҰЩҮЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ§Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШіШ§ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ§ШҰЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш©вҖ¬
- 12. пӮӣвҖ«Ш·ШұЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш°ЩҮЩҶЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҮШ§ШұШ§ШӘЩҮЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩҶЩ…ЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш·Ш§Щ„ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠШіШ§Ш№ШҜвҖ¬вҖ«ЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШҙШұШӯвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШӘШұЩғЩҠШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁШӘШӯЩ„ЩҠЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„ЩҠЩӮЩҲЩ…ЩҲШ§вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Ш§ЩҲЩҶЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш№Щ…Щ„вҖ¬вҖ«ШӯЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ…Щ„ЩҮЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш®Ш§Щ„Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШ№ШӘШұШ¶ЩҮЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ШҙШ§ЩғЩ„вҖ¬. пӮӣвҖ«Ш§ШўЩ„Ш®ШұЩҠЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…Ш№вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ШӘЩҲШ§ШөЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№ШЁЩҠШұвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш·ШұЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШӘШ·ЩҲЩҠШұвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩҶЩ…ЩҠШ©вҖ¬вҖ«Ш№ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ШөЩҲШӘЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ШұШҰЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„Щ…ЩӮШ§Ш·Ш№вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ШөЩҲШұШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҶШөвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш·ШұЩҠЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШәЩҠШұЩҮвҖ¬. пӮӣвҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш¬Щ…Ш§Ш№ЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш№Щ…Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШҘЩ„ЩҶШ¬Ш§ШӯвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш§Щ„ШІЩ…Ш©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩҮШ§ШұШ§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩҶЩ…ЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘШЁШ§ШҜЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш·ШұЩҠЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Ш¬Щ…ЩҠШ№вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҠШіШ№ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӯЩҠШ«вҖ¬ ШҢвҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ№Ш§ЩҲЩҶЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҲШӯШҜвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҮШҜЩҒвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„ШӘШӯЩӮЩҠЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…Ш®ШӘЩ„ЩҒШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁШЈШҜЩҲШ§ШұвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШ§Щ„ЩӮЩҠШ§Щ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш№ШұЩҒШ©вҖ¬ пӮӣвҖ«ЩҲЩ…ЩҲШ«вҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ШөШҜШ§ЩӮЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩӮЩҠЩҠЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩӮШҜШұШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҲШӘШ·ЩҲЩҠШұвҖ¬ вҖ«ШӘЩҶЩ…ЩҠШ©вҖ¬вҖ«ЩҲЩӮЩҠШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш®ШӘЩ„ЩҒШ©вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ…Ш№Щ„ЩҲЩ…Ш§ШӘвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ШөШ§ШҜШұвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ§Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШіШ§ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ§ШҰЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш©вҖ¬
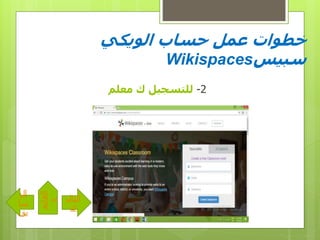
- 13. вҖ«Ш§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӯШіШ§ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ…Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш®Ш·ЩҲШ§ШӘвҖ¬вҖ«ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ШіШЁЩҠШівҖ¬Wikispaces 1-вҖ«Ш§Щ„Щ„ЩҠЩҶЩғвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ„ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«ЩҶШҜШ®Щ„вҖ¬ www.wikispaces.com 2-вҖ«Ш§Ш®ШӘШ§ШұвҖ¬вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩҲЩҠЩғЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…ЩҶвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШәШұШ¶вҖ¬(вҖ«ШӘШ№Щ„ЩҠЩ…ЩүвҖ¬вҖ“вҖ«Ш§Ш®ШұвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ…Ш¬Ш§Щ„вҖ¬.) вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШіШ§вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ§ШҰЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш©вҖ¬
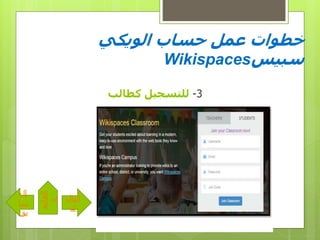
- 14. вҖ«Ш§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӯШіШ§ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ…Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш®Ш·ЩҲШ§ШӘвҖ¬вҖ«ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ШіШЁЩҠШівҖ¬Wikispaces 2-вҖ«Щ„Щ„ШӘШіШ¬ЩҠЩ„вҖ¬вҖ«Щ…Ш№Щ„Щ…вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩғвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШіШ§вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ§ШҰЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш©вҖ¬
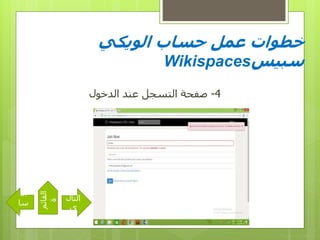
- 15. вҖ«Ш§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӯШіШ§ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ…Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш®Ш·ЩҲШ§ШӘвҖ¬вҖ«ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ШіШЁЩҠШівҖ¬Wikispaces 3-вҖ«ЩғШ·Ш§Щ„ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«Щ„Щ„ШӘШіШ¬ЩҠЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШіШ§вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ§ШҰЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш©вҖ¬
- 16. вҖ«Ш§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШӯШіШ§ШЁвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№Щ…Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш®Ш·ЩҲШ§ШӘвҖ¬вҖ«ЩҲЩҠЩғЩҠвҖ¬ вҖ«ШіШЁЩҠШівҖ¬Wikispaces 4-вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШіШ¬Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШөЩҒШӯШ©вҖ¬вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШҜШ®ЩҲЩ„вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш№ЩҶШҜвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ШӘШ§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ЩүвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„вҖ¬ вҖ«ШіШ§вҖ¬ вҖ«ШЁЩӮвҖ¬ вҖ«Ш§Щ„ЩӮШ§ШҰЩ…вҖ¬ вҖ«Ш©вҖ¬