Wildlife conservation
ŌĆóDownload as PPTX, PDFŌĆó
39 likesŌĆó21,653 views
principles and roles of Wildlife conservation : conservation of ecosystem and conservation threatened species and conservation wildlife resources.
1 of 25
Downloaded 284 times
























Recommended
A BRIEF OVERVIEW ON WILDLIFE MANAGEMENT



A BRIEF OVERVIEW ON WILDLIFE MANAGEMENTPintu Kabiraj
╠²
Wildlife management aims to maintain desirable wildlife populations and involves understanding population trends, influencing factors, species interactions, and landscape impacts. It addresses the balance between wildlife and human activities. Approaches include modifying animal behavior, human behavior, and interactions through barriers, zoning, and reserves. Depletion results from habitat loss, pollution, and absence of shelter. Conservation approaches encompass protection by law, sanctuaries, research, education, and international agreements like CITES that regulate trade. The goal is sustainable wildlife populations and balancing human and wildlife coexistence.Protected areas



Protected areasDebiprasad1997
╠²
Protected areas are those in which human occupation or at least the exploitation of resources is limited.
The definition that has been widely accepted across regional and global frameworks has been provided by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) in its categorization guidelines for protected areas.
There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the enabling laws of each country or the regulations of the international organizations involved.
The term "protected area" also includes
Marine Protected Areas, the boundaries of which will include some area of ocean, and
Trans boundary Protected Areas that overlap multiple countries which remove the borders inside the area for conservation and economic purposes.
wildlife conservation



wildlife conservationAbhishek Giri
╠²
This document provides an overview of wildlife conservation in India. It defines wildlife and the meaning of conservation. It outlines the benefits of wildlife conservation and threats such as habitat loss and pollution. It describes conservation efforts including national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, biosphere reserves, and legal protections. International conservation groups like IUCN are working to document endangered species and guide conservation programs to protect threatened biodiversity. The overall message is that wildlife is an essential part of ecosystems that needs to be preserved through active conservation measures.home range and territoriality.pptx



home range and territoriality.pptxPunjabiKuriPunjabiKu1
╠²
Home ranges are areas where individual animals carry out normal activities like finding food, water, and shelter. They are not defended from other animals and home ranges of different individuals may overlap. Within a home range is a core area where most activities are concentrated, like around a nest site. The size of home ranges varies depending on factors like body size, sex, diet, habitat, and resources. Territories are smaller defended areas that provide necessary resources and do not overlap with each other. Animals use behaviors like scent marking and aggression to defend territories.Wildlife conservation



Wildlife conservationVivek Kumar
╠²
Wildlife conservation is important to protect endangered species and habitats. Over 1,000 animal and 750 plant species worldwide are endangered or threatened. In India, many species are threatened due to habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. The government has established many protected areas and enacted wildlife laws to promote conservation. Continued conservation efforts are needed to protect India's rich biodiversity for future generations.Benefits Of Wildlife



Benefits Of WildlifeSahil Bhatiani
╠²
There are four main benefits that wildlife provides to humans: economic, medical/scientific, aesthetic/recreational, and ecological. Economically, wildlife benefits humans through industries like hunting, fishing, and wildlife watching, which together amount to over $18 billion annually in the US. Medicinally, plants have provided medicine for 80% of the world's population and make up about 40% of all medicines. Aesthetically, wildlife viewing motivates recreational activities and ecotourism. Ecologically, all living things interact within ecosystems, so impacts to one species can affect many others.Wildlife rules in world. Wildlife rules in pakistan. 



Wildlife rules in world. Wildlife rules in pakistan. Tahir Ali,Punjab University Lahore
╠²
This document lists 26 wildlife acts and laws in Pakistan that regulate the protection and management of wildlife. It also describes 4 schedules that are part of the laws: Schedule I details wild animals that can be hunted with an ordinary permit, Schedule II lists animals that require certificates for possession, transfer or export, Schedule III protects wild birds and animals year-round, and Schedule IV lists unprotected wild birds and animals. The main focus of the laws is to protect and conserve Pakistan's wildlife populations through restrictions on hunting and regulating the trade and transport of protected species.Wildlife of pakistan threat and consservation



Wildlife of pakistan threat and consservationGovernment College of Education, Jutial Gilgit
╠²
The document discusses wildlife and conservation efforts in Pakistan. It provides information on the types of wildlife found in Pakistan, including 188 mammal species and 666 bird species. It then outlines several major threats facing Pakistani wildlife, such as habitat loss due to deforestation, agriculture, and urban growth. The document also describes Pakistan's national parks system and the 21 national parks established to protect the country's biodiversity and wildlife. It emphasizes that conservation is important to preserve Pakistan's biological heritage for future generations.Wild life of pakistan



Wild life of pakistanQamar iqbal
╠²
The document provides information on the wildlife of Pakistan. It discusses the country's geographical features and climate. It notes that Pakistan has a moderately rich diversity of animal and plant species despite human impacts like urbanization, hunting, and habitat loss that have led to population declines. Tables show the number of species in major taxonomic groups and the conservation status of different animal species found in Pakistan. The document also describes the different vegetation zones and their characteristic wildlife.Iucn



Iucnvagh sarman
╠²
The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) is an international organization working in nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. It is involved in data gathering, research, field projects, lobbying and education. It is best known for compiling and publishing the Red List which assesses the conservation status of species worldwide. IUCN's mission is to influence societies to conserve nature and ensure sustainable use of natural resources.Biosphere Reserves



Biosphere ReservesManideep Raj
╠²
A description of the logistics of declaring biosphere reserves in India along with the role of different zones and their functionsWildlife in india



Wildlife in indiaprasadvagal
╠²
This document discusses wildlife conservation in India. It notes that India is home to significant biodiversity and many threatened species. National parks and wildlife sanctuaries aim to preserve this wildlife, while the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 and Project Tiger provide legal protections. However, habitat loss and fragmentation from human activities like deforestation, grazing, and infrastructure development threaten Indian wildlife. Increased awareness and community involvement are important for effective long-term conservation.Wild life



Wild lifeBahuddin Zakariya University, Multan
╠²
The document discusses the history and importance of wildlife conservation in Pakistan. It begins with the founding of the Society for the Promotion of Nature Reserves in 1912 in London, which aimed to identify and protect areas for wildlife. It then describes the various ecosystems and species of plants and animals found across Pakistan, from mammals like the snow leopard and markhor, to insects and birds. The document emphasizes the economic, nutritional, recreational, scientific, and ecological benefits of wildlife for humans. However, threats from population growth, agriculture, hunting, and habitat loss have endangered many species and ecosystems in Pakistan. Strong laws and protected areas are needed to promote biodiversity and conserve Pakistan's valuable wildlife.Wildlife management techniques and methods of wildlife conservation



Wildlife management techniques and methods of wildlife conservationAnish Gawande
╠²
Wildlife Conservation is the practice of protecting wild plant and animal species and their habitat. Wildlife plays an important role in balancing the environment and provides stability to different natural processes of nature. The goal of wildlife conservation is to ensure that nature will be around for future generations to enjoy and also to recognize the importance of wildlife and wilderness for humans and other species alike. Many nations have government agencies and NGO's dedicated to wildlife conservation, which help to implement policies designed to protect wildlife. Numerous independent non-profit organizations also promote various wildlife conservation causes.
Wildlife conservation has become an increasingly important practice due to the negative effects of human activity on wildlife. An endangered species is defined as a population of a living species that is in the danger of becoming extinct because the species has a very low or falling population, or because they are threatened by the varying environmental or prepositional parameters.Elephant project sites



Elephant project sitesRuchika Kulshrestha
╠²
The document discusses elephant reserves in India. It notes that elephants require large areas and optimal forest conditions to survive. It outlines the goals of Project Elephant, launched in 1992, which are to protect elephants, their habitats, and corridors. Project Elephant aims to ensure the long-term survival of wild elephant populations through various conservation activities like habitat restoration, addressing human-elephant conflict, research, and awareness programs. It also lists the 28 elephant reserves across India where Project Elephant is being implemented.Iucn red list



Iucn red listHarshraj Shinde
╠²
The IUCN Red List is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of species. It uses a set of criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and publishes its assessments. Major goals are to convey the urgency of conservation and provide information to guide actions to conserve biological diversity. Key findings from assessments over the years have shown increasing numbers of threatened species, including many moving into critically endangered categories. Major taxonomic groups like corals, amphibians, and mammals are particularly at risk.Protected area network :Biosphere reserves 



Protected area network :Biosphere reserves Almas Tamake
╠²
Protected areas are a cornerstone of in situ conservation and include national parks, bioreserves, and sanctuaries. They are managed areas dedicated to protecting biodiversity. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has established seven categories of protected areas and guidelines for their management. India has over 600 protected areas covering a variety of ecosystems and hosting many endangered species. These areas help maintain biodiversity through conserving habitats and genetic diversity. Biosphere reserves specifically aim to balance conservation and sustainable development through zoning of areas for strict protection and various levels of human involvement. India has established 18 biosphere reserves recognized for their unique biodiversity and ecosystems.Territoriality



TerritorialityHaider Ali Malik
╠²
Territorial behaviour are the methods by which an animal, or group of animals, protects its territory from incursions by others of its species.
Protected Areas of Pakistan. 



Protected Areas of Pakistan. Mishkat Noor
╠²
This document provides information on protected areas in Pakistan. It defines protected areas and notes that Pakistan has four types: national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, game reserves, and community-controlled hunting areas. It lists the number of each type of protected area by province. National parks are described as set aside for scenic and wildlife protection. Several major national parks are highlighted, including the largest - Central Karakoram National Park. Wildlife sanctuaries are areas where public access is restricted to protect flora and fauna. Game reserves allow controlled hunting.Wildlife sanctuaries and National Park in India



Wildlife sanctuaries and National Park in IndiaJamia Millia Islamia
╠²
This document provides information on various wildlife sanctuaries and national parks in India through a presentation by Aditya Ranjan. It discusses that wildlife sanctuaries are protected areas where animals can live naturally, and India has over 442 such sanctuaries home to thousands of species. National parks are areas protected for conservation that allow recreation and education, and India's first was Jim Corbett National Park. The presentation then gives multi-paragraph descriptions of several prominent national parks in India, including their locations, features, and the wildlife found there.Wildlife management - threats to wildlife



Wildlife management - threats to wildlifeAnish Gawande
╠²
There are few places left on the planet where the impact of people has not been felt. We have explored and left our footprint on nearly every corner of the globe. As our population and needs grow, we are leaving less and less room for wildlife.
Wildlife are under threat from many different kinds of human activities, from directly destroying habitat to spreading invasive species and disease. Most ecosystems are facing multiple threats. Each new threat puts additional stress on already weakened ecosystems and their wildlife.
project tiger,project lion,crocodile breeding



project tiger,project lion,crocodile breedingPriyanka Jaipal
╠²
Project Tiger and Project Gir Lion are wildlife conservation programs in India that focus on single species and their habitats. Project Tiger, started in 1973, aims to protect tigers and increase their population in tiger reserves. It helped increase tigers from 1,200 to 3,500 but the population later dropped to 1,411. Project Gir Lion, started in 1965, focuses on the last wild population of Asiatic lions in Gir Forest. It has increased lions from 285 to over 500. Both projects use technologies like mapping and GIS modeling to monitor populations and habitats.Red list categories



Red list categoriesShekhar Tidke
╠²
Species are organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classifies species into different categories based on extinction risk. The IUCN Red List evaluates thousands of species and subspecies to convey the urgency of conservation and help reduce extinction. Species are classified into groups including Extinct, Critically Endangered, Endangered, Vulnerable, Near Threatened, Least Concern, Data Deficient, and Not Evaluated based on population decline, size, distribution and other risk factors.Wildlife Corridors



Wildlife CorridorsSimu Dulai
╠²
Wildlife corridors are areas of habitat that connect separate areas of similar habitat and allow animal movement and gene flow between populations. They are important for maintaining biodiversity as they help counteract the effects of habitat loss and fragmentation. Effective corridors should be wide and maintain natural vegetation and habitat. They enable species migration and support genetic diversity. Management aims to enhance habitat quality and protect ecological processes within corridors. The Siju-Rewak Corridor in India links two protected areas and preserves an important elephant crossing point along the Simsang River.wildlife conservation



wildlife conservationapoorvkumar9277
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation on wildlife conservation in India. It discusses India's biodiversity, defining wildlife conservation and importance. It outlines causes of wildlife destruction like habitat loss, poaching, and fragmentation. Specific endangered species are highlighted. The document also reviews India's past wildlife, current status, government role in conservation like the Wildlife Protection Act and Project Tiger, and provides recommendations.Optimal Foraging Theory (OFT)



Optimal Foraging Theory (OFT)Tikeshkumar7
╠²
Presentation on Optimal Foraging Theory (a behavioral ecology model that helps predict how an animal behaves when searching for food).National and international agencies involved in wildlife conservation and ma...



National and international agencies involved in wildlife conservation and ma...Noor Zada
╠²
The document discusses several national agencies involved in wildlife conservation and management in Pakistan. It describes 5 key organizations: 1) Society for Conservation and Protection of Environment (SCOPE) which focuses on water/sanitation and social mobilization projects. 2) Bioresource Research Center (BRC) which works to curb bear baiting. 3) Zoological Survey Department which conducts wildlife surveys and has a natural history museum. 4) Pakistan Animal Welfare Society (PAWS) which coordinates animal rescues and adoptions. 5) Pakistan Museum of Natural History which exhibits the natural history of Pakistan across various galleries.Wildlife management - habit, habitat, territory & niche of animals



Wildlife management - habit, habitat, territory & niche of animalsAnish Gawande
╠²
The document discusses various concepts related to animal behavior including habit, habitat, territory, niche, herbivores, carnivores, solitary animals, packs, and herds.
It defines habit as aspects of animal behavior or structure. Habitat is described as the physical area where a species lives, defined by factors like temperature and rainfall. Territory refers to the area an animal defends against others of its species. Niche is the role a species plays in its ecosystem, such as how it obtains energy.
Herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores are discussed in detail. Examples of solitary animal behaviors and specific pack behaviors in species like wolves are provided. Herds are describedBiodiversity and wildlife



Biodiversity and wildlifeStudy
╠²
The document discusses biodiversity and wildlife conservation. It defines biodiversity as the variety of life forms on Earth, including species, ecosystems, and genes. There are three main types of biodiversity: species diversity, ecosystem diversity, and genetic diversity. Biodiversity provides both consumptive value through resources like food and medicine, and non-consumptive value through benefits like recreation and research. Wildlife faces threats from habitat loss, overexploitation, invasive species, pollution, climate change, and more. India is home to significant biodiversity and many endangered species. The government plays an important role in wildlife conservation through laws and programs like Project Tiger to protect threatened species and their habitats.Wildlifeconservationsuryanshsinghppt 140714000450-phpapp02



Wildlifeconservationsuryanshsinghppt 140714000450-phpapp02Prateek Gupta
╠²
This presentation discusses wildlife conservation in India. It covers the key laws and organizations related to wildlife protection, including the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, the Forest Conservation Act of 1980, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature. The document outlines the main threats to wildlife such as habitat loss and pollution, and emphasizes the importance of conservation efforts like protected areas and breeding programs.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Wild life of pakistan



Wild life of pakistanQamar iqbal
╠²
The document provides information on the wildlife of Pakistan. It discusses the country's geographical features and climate. It notes that Pakistan has a moderately rich diversity of animal and plant species despite human impacts like urbanization, hunting, and habitat loss that have led to population declines. Tables show the number of species in major taxonomic groups and the conservation status of different animal species found in Pakistan. The document also describes the different vegetation zones and their characteristic wildlife.Iucn



Iucnvagh sarman
╠²
The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) is an international organization working in nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. It is involved in data gathering, research, field projects, lobbying and education. It is best known for compiling and publishing the Red List which assesses the conservation status of species worldwide. IUCN's mission is to influence societies to conserve nature and ensure sustainable use of natural resources.Biosphere Reserves



Biosphere ReservesManideep Raj
╠²
A description of the logistics of declaring biosphere reserves in India along with the role of different zones and their functionsWildlife in india



Wildlife in indiaprasadvagal
╠²
This document discusses wildlife conservation in India. It notes that India is home to significant biodiversity and many threatened species. National parks and wildlife sanctuaries aim to preserve this wildlife, while the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 and Project Tiger provide legal protections. However, habitat loss and fragmentation from human activities like deforestation, grazing, and infrastructure development threaten Indian wildlife. Increased awareness and community involvement are important for effective long-term conservation.Wild life



Wild lifeBahuddin Zakariya University, Multan
╠²
The document discusses the history and importance of wildlife conservation in Pakistan. It begins with the founding of the Society for the Promotion of Nature Reserves in 1912 in London, which aimed to identify and protect areas for wildlife. It then describes the various ecosystems and species of plants and animals found across Pakistan, from mammals like the snow leopard and markhor, to insects and birds. The document emphasizes the economic, nutritional, recreational, scientific, and ecological benefits of wildlife for humans. However, threats from population growth, agriculture, hunting, and habitat loss have endangered many species and ecosystems in Pakistan. Strong laws and protected areas are needed to promote biodiversity and conserve Pakistan's valuable wildlife.Wildlife management techniques and methods of wildlife conservation



Wildlife management techniques and methods of wildlife conservationAnish Gawande
╠²
Wildlife Conservation is the practice of protecting wild plant and animal species and their habitat. Wildlife plays an important role in balancing the environment and provides stability to different natural processes of nature. The goal of wildlife conservation is to ensure that nature will be around for future generations to enjoy and also to recognize the importance of wildlife and wilderness for humans and other species alike. Many nations have government agencies and NGO's dedicated to wildlife conservation, which help to implement policies designed to protect wildlife. Numerous independent non-profit organizations also promote various wildlife conservation causes.
Wildlife conservation has become an increasingly important practice due to the negative effects of human activity on wildlife. An endangered species is defined as a population of a living species that is in the danger of becoming extinct because the species has a very low or falling population, or because they are threatened by the varying environmental or prepositional parameters.Elephant project sites



Elephant project sitesRuchika Kulshrestha
╠²
The document discusses elephant reserves in India. It notes that elephants require large areas and optimal forest conditions to survive. It outlines the goals of Project Elephant, launched in 1992, which are to protect elephants, their habitats, and corridors. Project Elephant aims to ensure the long-term survival of wild elephant populations through various conservation activities like habitat restoration, addressing human-elephant conflict, research, and awareness programs. It also lists the 28 elephant reserves across India where Project Elephant is being implemented.Iucn red list



Iucn red listHarshraj Shinde
╠²
The IUCN Red List is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of species. It uses a set of criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and publishes its assessments. Major goals are to convey the urgency of conservation and provide information to guide actions to conserve biological diversity. Key findings from assessments over the years have shown increasing numbers of threatened species, including many moving into critically endangered categories. Major taxonomic groups like corals, amphibians, and mammals are particularly at risk.Protected area network :Biosphere reserves 



Protected area network :Biosphere reserves Almas Tamake
╠²
Protected areas are a cornerstone of in situ conservation and include national parks, bioreserves, and sanctuaries. They are managed areas dedicated to protecting biodiversity. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has established seven categories of protected areas and guidelines for their management. India has over 600 protected areas covering a variety of ecosystems and hosting many endangered species. These areas help maintain biodiversity through conserving habitats and genetic diversity. Biosphere reserves specifically aim to balance conservation and sustainable development through zoning of areas for strict protection and various levels of human involvement. India has established 18 biosphere reserves recognized for their unique biodiversity and ecosystems.Territoriality



TerritorialityHaider Ali Malik
╠²
Territorial behaviour are the methods by which an animal, or group of animals, protects its territory from incursions by others of its species.
Protected Areas of Pakistan. 



Protected Areas of Pakistan. Mishkat Noor
╠²
This document provides information on protected areas in Pakistan. It defines protected areas and notes that Pakistan has four types: national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, game reserves, and community-controlled hunting areas. It lists the number of each type of protected area by province. National parks are described as set aside for scenic and wildlife protection. Several major national parks are highlighted, including the largest - Central Karakoram National Park. Wildlife sanctuaries are areas where public access is restricted to protect flora and fauna. Game reserves allow controlled hunting.Wildlife sanctuaries and National Park in India



Wildlife sanctuaries and National Park in IndiaJamia Millia Islamia
╠²
This document provides information on various wildlife sanctuaries and national parks in India through a presentation by Aditya Ranjan. It discusses that wildlife sanctuaries are protected areas where animals can live naturally, and India has over 442 such sanctuaries home to thousands of species. National parks are areas protected for conservation that allow recreation and education, and India's first was Jim Corbett National Park. The presentation then gives multi-paragraph descriptions of several prominent national parks in India, including their locations, features, and the wildlife found there.Wildlife management - threats to wildlife



Wildlife management - threats to wildlifeAnish Gawande
╠²
There are few places left on the planet where the impact of people has not been felt. We have explored and left our footprint on nearly every corner of the globe. As our population and needs grow, we are leaving less and less room for wildlife.
Wildlife are under threat from many different kinds of human activities, from directly destroying habitat to spreading invasive species and disease. Most ecosystems are facing multiple threats. Each new threat puts additional stress on already weakened ecosystems and their wildlife.
project tiger,project lion,crocodile breeding



project tiger,project lion,crocodile breedingPriyanka Jaipal
╠²
Project Tiger and Project Gir Lion are wildlife conservation programs in India that focus on single species and their habitats. Project Tiger, started in 1973, aims to protect tigers and increase their population in tiger reserves. It helped increase tigers from 1,200 to 3,500 but the population later dropped to 1,411. Project Gir Lion, started in 1965, focuses on the last wild population of Asiatic lions in Gir Forest. It has increased lions from 285 to over 500. Both projects use technologies like mapping and GIS modeling to monitor populations and habitats.Red list categories



Red list categoriesShekhar Tidke
╠²
Species are organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classifies species into different categories based on extinction risk. The IUCN Red List evaluates thousands of species and subspecies to convey the urgency of conservation and help reduce extinction. Species are classified into groups including Extinct, Critically Endangered, Endangered, Vulnerable, Near Threatened, Least Concern, Data Deficient, and Not Evaluated based on population decline, size, distribution and other risk factors.Wildlife Corridors



Wildlife CorridorsSimu Dulai
╠²
Wildlife corridors are areas of habitat that connect separate areas of similar habitat and allow animal movement and gene flow between populations. They are important for maintaining biodiversity as they help counteract the effects of habitat loss and fragmentation. Effective corridors should be wide and maintain natural vegetation and habitat. They enable species migration and support genetic diversity. Management aims to enhance habitat quality and protect ecological processes within corridors. The Siju-Rewak Corridor in India links two protected areas and preserves an important elephant crossing point along the Simsang River.wildlife conservation



wildlife conservationapoorvkumar9277
╠²
This document summarizes a presentation on wildlife conservation in India. It discusses India's biodiversity, defining wildlife conservation and importance. It outlines causes of wildlife destruction like habitat loss, poaching, and fragmentation. Specific endangered species are highlighted. The document also reviews India's past wildlife, current status, government role in conservation like the Wildlife Protection Act and Project Tiger, and provides recommendations.Optimal Foraging Theory (OFT)



Optimal Foraging Theory (OFT)Tikeshkumar7
╠²
Presentation on Optimal Foraging Theory (a behavioral ecology model that helps predict how an animal behaves when searching for food).National and international agencies involved in wildlife conservation and ma...



National and international agencies involved in wildlife conservation and ma...Noor Zada
╠²
The document discusses several national agencies involved in wildlife conservation and management in Pakistan. It describes 5 key organizations: 1) Society for Conservation and Protection of Environment (SCOPE) which focuses on water/sanitation and social mobilization projects. 2) Bioresource Research Center (BRC) which works to curb bear baiting. 3) Zoological Survey Department which conducts wildlife surveys and has a natural history museum. 4) Pakistan Animal Welfare Society (PAWS) which coordinates animal rescues and adoptions. 5) Pakistan Museum of Natural History which exhibits the natural history of Pakistan across various galleries.Wildlife management - habit, habitat, territory & niche of animals



Wildlife management - habit, habitat, territory & niche of animalsAnish Gawande
╠²
The document discusses various concepts related to animal behavior including habit, habitat, territory, niche, herbivores, carnivores, solitary animals, packs, and herds.
It defines habit as aspects of animal behavior or structure. Habitat is described as the physical area where a species lives, defined by factors like temperature and rainfall. Territory refers to the area an animal defends against others of its species. Niche is the role a species plays in its ecosystem, such as how it obtains energy.
Herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores are discussed in detail. Examples of solitary animal behaviors and specific pack behaviors in species like wolves are provided. Herds are describedSimilar to Wildlife conservation (20)
Biodiversity and wildlife



Biodiversity and wildlifeStudy
╠²
The document discusses biodiversity and wildlife conservation. It defines biodiversity as the variety of life forms on Earth, including species, ecosystems, and genes. There are three main types of biodiversity: species diversity, ecosystem diversity, and genetic diversity. Biodiversity provides both consumptive value through resources like food and medicine, and non-consumptive value through benefits like recreation and research. Wildlife faces threats from habitat loss, overexploitation, invasive species, pollution, climate change, and more. India is home to significant biodiversity and many endangered species. The government plays an important role in wildlife conservation through laws and programs like Project Tiger to protect threatened species and their habitats.Wildlifeconservationsuryanshsinghppt 140714000450-phpapp02



Wildlifeconservationsuryanshsinghppt 140714000450-phpapp02Prateek Gupta
╠²
This presentation discusses wildlife conservation in India. It covers the key laws and organizations related to wildlife protection, including the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, the Forest Conservation Act of 1980, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature. The document outlines the main threats to wildlife such as habitat loss and pollution, and emphasizes the importance of conservation efforts like protected areas and breeding programs.WILDLIFE THREATS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT IN INDIA.pptx



WILDLIFE THREATS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT IN INDIA.pptxramkumarlodhi3
╠²
threats to wildlife and managementwildlife



wildlifesng123
╠²
The document discusses the history and principles of wildlife conservation. It outlines how wildlife conservation aims to protect endangered species and habitats for future generations. Principles that guide wildlife management in North America include treating wildlife as public resources and eliminating commercial markets for game. The document also discusses the World Conservation Strategy developed in 1980 which provided a framework for national and international conservation actions and priorities.International Agencies Involved in Conservation & Management of Wildlife



International Agencies Involved in Conservation & Management of WildlifeSyed Muhammad Khan
╠²
A brief introduction to some of the most important international agencies involved in conservation and management of wildlife.Online assignment



Online assignmentgayathrideviaj
╠²
The document discusses different types of protected areas in India that conserve biodiversity - biosphere reserves, wildlife sanctuaries, national parks, and zoos. It provides background on India's biodiversity and lists threats like habitat loss. Biosphere reserves aim to conserve biodiversity and support sustainable development. Wildlife sanctuaries and national parks protect habitats and species. The document lists several biosphere reserves, wildlife sanctuaries, and national parks in Kerala. Zoos provide ex-situ conservation of endangered species.15277 biodiversity updated



15277 biodiversity updatedEajaz Khan
╠²
India has significant biodiversity with over 50,000 plant varieties, 1,000 mango varieties, and 500 pepper varieties domestically cultivated. Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms and includes genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. India contains several biodiversity hotspots like the Western Ghats and parts of the Himalayas. Threats to Indian biodiversity include habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, and overexploitation. Conservation efforts include protected areas like national parks and wildlife sanctuaries as well as ex situ methods such as botanical gardens, zoos, and gene banks. India has significant biodiversity at risk due to threats, so conservation is important.Presentation on wildlife - Akib Sumon



Presentation on wildlife - Akib SumonAkib Sumon
╠²
This document discusses wildlife biodiversity in Bangladesh. It defines wildlife and biodiversity, noting that biodiversity describes the variety of life on Earth across animals, plants, and microorganisms. The importance of biodiversity is explained, such as maintaining ecosystem balance and providing resources for humans. Major threats to Bangladesh's biodiversity are identified as natural calamities, habitat loss, pollution, and poaching. The document outlines strategies for protecting wildlife, including establishing sanctuaries and reserves, reforestation, reducing pollution and waste dumping, and increasing public education around conservation.Biodiversity protection



Biodiversity protectionrajdeepjadeja
╠²
This document discusses biodiversity and its importance. It notes that biodiversity is declining rapidly, with thousands of species going extinct each year. Biodiversity is essential for ecosystem functions like water and air purification. Conservation strategies include legislation, in-situ and ex-situ conservation efforts, recording indigenous knowledge, community participation, and international agreements. Local communities depend on biodiversity for their livelihoods and cultures. Overall biodiversity conservation is crucial for environmental health and human well-being.Biodiversity conservation strategies



Biodiversity conservation strategiesVarshini3
╠²
Conservation of Biodiversity is the need of the hour. Awareness is a must for biodiversity conservation.Various strategies of conservation are included in the presentation.Human impact on wildlife



Human impact on wildlifePriyanka Priya
╠²
This document summarizes the impact of human activity on wildlife. It defines wildlife as non-domesticated animals and explains that carefully managed populations can be conserved indefinitely. It then outlines some threats to wildlife like habitat loss, pollution, hunting and introduction of exotic species. The document discusses India's efforts to conserve wildlife through national parks, sanctuaries, biosphere reserves, and legal protections. It provides examples of protected areas in India and conservation measures taken, highlighting the importance of breeding programs, prevention of hunting, and enforcement of wildlife laws.Need for conservation of forest and wildlife in an ecosystem 



Need for conservation of forest and wildlife in an ecosystem Vichu Vichu
╠²
Habitat destruction, overexploitation, poaching, and climate change are major threats to wildlife. Habitat destruction decreases the areas where wildlife can live and fragments habitats. Overexploitation harvests animals and plants faster than populations can recover. Poaching targets endangered species for illegal wildlife trade. Climate change leads to habitat destruction and impacts species ranges through changing conditions. Conservation efforts include afforestation, controlling fires, regulating forest resource use, and developing protected areas while controlling hunting and overexploitation to preserve biodiversity.Ppt for sharing



Ppt for sharingvijetaarora
╠²
The document summarizes information about endangered species and the steps governments of four countries - India, USA, UAE, and Ukraine - are taking to protect endangered animals. It discusses endangered animals in each country, including the Bengal tiger in India, monarch butterfly in USA, Arabian leopard in UAE, and Alpine shrew in Ukraine. It then outlines some of the key measures taken by the governments, such as establishing reserves, enacting wildlife protection laws, providing financial assistance for conservation, and participating in international agreements like CITES.VCE Environmental Science Unit 3: Biodiversity and conservation management.



VCE Environmental Science Unit 3: Biodiversity and conservation management.Peter Phillips M.Ed.
╠²
Learning intentions:
To understand how biodiversity is identified and managed in Australia.
Success Criteria:
Be able to apply categories of conservation status and describe how degree of threat is determined.
Know the three biodiversity categories and how they relate to each other.
Be able to explain how remnant vegetation, corridors and conservation reserves can be used to support biodiversity.
Describe Global, Australian and Victorian legislation and conventions and a current biodiversity issue which refers to each.Biodiversity & Conservation



Biodiversity & Conservationnabeelmano66
╠²
This document discusses biodiversity and its importance. It defines biodiversity as the variety of life on Earth, including species, genes, and ecosystems. It describes three levels of biodiversity: genetic diversity within species, species diversity within communities, and ecosystem diversity across landscapes. Some key threats to biodiversity mentioned are habitat loss and degradation, poaching, and human-wildlife conflicts. The document also discusses biodiversity hotspots and criteria for identifying them. Both in-situ and ex-situ conservation approaches are outlined. In-situ involves protecting habitats through reserves, while ex-situ involves maintaining species outside their natural habitats in zoos and botanical gardens. The importance of biodiversity conservation is emphasized for maintaining ecosystem1-151024123924-lva1-app6891.pdf



1-151024123924-lva1-app6891.pdfibforver
╠²
This document discusses biodiversity, its levels and types, values, hotspots, threats, and conservation methods. It defines biodiversity as the variety of life on Earth, including genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. It notes two biodiversity hotspots in India, the Indo-Burma region and Western Ghats. Major threats include habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflicts. Conservation approaches involve both in-situ methods like protected areas, and ex-situ methods such as botanical gardens, zoos, and gene banks.Wild life conservation



Wild life conservationAbasaheb Garware College, Department of Zoology, Karve road. Pune-4
╠²
The document discusses wildlife conservation in India. It defines wildlife and explains that wildlife conservation preserves ecosystem stability and provides many benefits. Threats to wildlife include habitat loss, pollution, hunting, and introduction of exotic species. The document outlines various protected areas in India like national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, biosphere reserves and measures taken for wildlife conservation including breeding programs, legal provisions like the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, and the roles of organizations like IUCN.Biodiversity at risk



Biodiversity at riskwja10255
╠²
Scientists warn that the current mass extinction of species is human-caused. The major drivers of extinction are habitat loss, invasive species, pollution, overharvesting, hunting and poaching. Some areas like tropical rainforests have exceptionally high biodiversity and endemic species. Conservation efforts include captive breeding programs, preserving genetic material, protecting ecosystems, and establishing protected areas and regulations like the U.S. Endangered Species Act and the international CITES treaty. However, balancing conservation with human needs and development remains an ongoing challenge.Biodiversity.pptx



Biodiversity.pptxVaibhavPawar130
╠²
This document discusses biodiversity, including its levels, values, hotspots, threats, and methods of conservation. It defines biodiversity as the variety of living organisms on Earth, including different ecosystems. Biodiversity exists at genetic, species, and ecosystem levels and provides values such as food, medicine, fuel and social/cultural importance. Two biodiversity hotspots in India are described that contain many endemic species but are highly threatened. The main threats to biodiversity are habitat loss and degradation, poaching, and human-wildlife conflicts. Conservation methods include in-situ conservation of species within protected natural areas, and ex-situ conservation in zoos, botanical gardens, and gene banks.Biodiversity



BiodiversityDr. Priyanka Wandhe
╠²
This presentation discusses biodiversity in India. It begins by defining biodiversity as the variety of life on Earth, including genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. India is considered a megadiversity nation with high numbers of endemic species. Biodiversity provides both direct value through resources and indirect value through ecosystem services. However, biodiversity in India faces threats from habitat loss, poaching, and other human activities. Conservation efforts focus on both in-situ methods within protected areas as well as ex-situ methods like zoos and seed banks. Key biodiversity hotspots in India are the Indo-Burma and Western Ghats regions.Recently uploaded (20)
Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoy



Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoyEconomic and Social Research Institute
╠²
NAPD Annual Symposium
ŌĆ£Equity in our Schools: Does the system deliver for all young people?ŌĆØBISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH



BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHcoacharyasetiyaki
╠²
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHBß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
╠²
https://app.box.com/s/ij1ty3vm7el9i4qfrr41o756xycbahmgChapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdf



Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdfRommel Regala
╠²
This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18



Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide weŌĆÖll discuss on the effective product variant management in Odoo 18. Odoo concentrates on managing product variations and offers a distinct area for doing so. Product variants provide unique characteristics like size and color to single products, which can be managed at the product template level for all attributes and variants or at the variant level for individual variants.Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptx



Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptxNidhiSharma495177
╠²
Research Publication & Ethics contains a chapter on Intellectual Honesty and Research Integrity.
Different case studies of intellectual dishonesty and integrity were discussed.Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptx



Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptxKhurshid Ahmed Ansari
╠²
Validity is an important characteristic of a test. A test having low validity is of little use. Validity is the accuracy with which a test measures whatever it is supposed to measure. Validity can be low, moderate or high. There are many factors which affect the validity of a test. If these factors are controlled, then the validity of the test can be maintained to a high level. In the power point presentation, factors affecting validity are discussed with the help of concrete examples.Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptx



Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptxRomaSmart1
╠²
Computers have revolutionized various sectors, including education, by enhancing learning experiences and making information more accessible. This presentation, "Computer Hardware for Educational Computing," introduces the fundamental aspects of computers, including their definition, characteristics, classification, and significance in the educational domain. Understanding these concepts helps educators and students leverage technology for more effective learning.How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss the one click RFQ Cancellation in odoo 18. One-Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 is a feature that allows users to quickly and easily cancel Request for Quotations (RFQs) with a single click.Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatBß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
╠²
Wildlife conservation
- 1. By: Group:1 ID: 130501, 130502, 130504,130505,130506,130508,130509 ,130510,130511,130512,130513 A presentation on Principles and Roles of Wildlife Conservation
- 2. Content ’āś Definition of Wildlife ’āś Wildlife Conservation & its goals ’āś Principles of wildlife conservation ’āś Roles of Wildlife Conservation ’āś Biodiversity Status ’āś Major causes of endangerment ’āś Conservation measures ’āś Recommendations
- 3. Meaning of wildlife Legal definition: According to Bangladesh wildlife preservation amendment act, 1974, Wildlife means any vertebrate, creature other than human beings and animals of usually domestic species or fish and includes till eggs of birds and reptiles. ’āś Example: lion, deer, crocodiles, whales, trees etc. ’ü▒ Wildlife refers to living organisms (flora and fauna) in their natural habitats. ’üČ But cultivated plants and domesticated animals are not included in wildlife!
- 4. Wildlife Conservation is the practice of protecting wild plant and animal species and their habitats. Goals of Wildlife Conservation ’āś To ensure that nature will be around for future generations to enjoy and also to recognize the importance of wildlife and wilderness for humans and other species alike. Conservation: Wise use of natural resources, without wasting them.
- 5. Principles of wildlife conservation ’āśProtect the Breeding Stock ’āśHarvest the "Surplus" Wisely ’āśBalance Animals and Habitat Protect the Breeding Stock ’āśŌĆ£Breeding stockŌĆØ is a term used to describe the appropriate mixture of young and adult animals needed to maintain a population. ’āśIt is the task of the wildlife managers to determine how many animals are surplus in a game population and to protect the remaining animals.
- 6. Harvest the surplus wisely ’āśThe ŌĆ£surplusŌĆØ animals refer to those animals that exceed the carrying capacity. ’āśWildlife managers want to carefully remove the surplus to allow the harvest animals to grow so hunters can get the most meat possible from the harvest.
- 7. Balance Animals and Habitat ’āśLands and vegetation are an important part of sustaining a habitat but can be harmed when the number of animals using an area is too much for the land to support. Rate = 80 million new people/year + New York City every month + Germany every year + United States every 3.7 years
- 8. ’üČTo protect wildlife and wilderness from being extincted. ’üČTo maintain the ecological balance. ’üČTo protect the biodiversity from being destroyed. ’üČTo provide excellent economic benefits (eg.horns,skin etc.) Roles of Wildlife Conservation
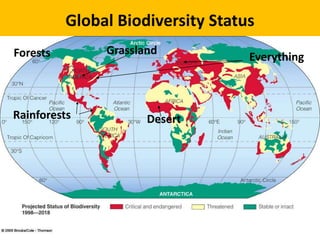
- 9. Global Biodiversity Status Forests Grassland Rainforests Desert Everything
- 12. ’āśMost critical factor in species extinction. ’āśThere is now 20% less forest cover than existed 300 years ago.
- 13. ŌĆó Another major cause of animal species extinction. ŌĆó Poaching and illegal trade in animals are US$2 billion to $3 billion.
- 14. ’āśPet Trade ’āśFur Trade ’āśMeat Trade ’āśBody Parts Trade ’āśTrade for Biomedical Research
- 15. Arms 3 Wildlife 2 Narcotic 1 Arms Narcotic wildlife Value of the trade ’ü▒ Wildlife trade as given by international enforcement agencies is second only to narcotics in the illegal area. ’ü▒ Wildlife crime is therefore the second largest illegal occupation in the world.
- 16. More Factors ŌĆó Climate change / Global warming ŌĆó Disease ŌĆó Pollution ŌĆó Fires ŌĆó Natural disasters ŌĆó Introduced (Invasive) Species ŌĆó Farmer / Rancher Shootings
- 17. Source : Wildlife protection society of India
- 18. Conservation measures The conservation strategies should include the following programmes and policies: ’āśProtection of threatened/useful plants and animals species living in natural habitats, zoological and botanical gardens, seed gene, tissue culture and DNA banks. ’āśPreservation of critical habitats of animal and plant species plus the management of life supporting systems in the surrounding habitats. ’āśHunting and international trade in wild animals and plants products should be regulated and a strict vigil should be maintained upon these actions. ’āśRole of government and NGOs in spreading awareness programmes among common people about values of wildlife and itŌĆÖs conservation.
- 19. IUCN(International Union for Conservation of Nature) ŌĆó The organization publishes the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, which assesses the conservation status of species. ŌĆó It works for the enlistment and preservation of endangered species of plants and animals. Now known as the World Conservation Union, it aims to impart information about the distribution and status of threatened species, develop awareness about the importance of threatened biodiversity and guide their conservation programmes and actions.
- 20. International rules and laws Many nations have reached bilateral/multilateral agreements and have framed rules and regulations for protection and conservation of wildlife. Some of these are: ’āś Africanconventionontheconservationofnaturalresources,1968. ’āś Convention of wetlands of international importance (ramsar convention), 1971. ’āś Conservationandprotectionoftheworldcultureandnationalheritageact, 1972.
- 21. Wildlife conservation rules and laws in Bangladesh ’üČNo separate policy for wildlife management in Bangladesh. ’ā╝ Bangladesh Wild Life (Preservation) Order, 1973. ’ā╝ Forest Policy 1994. ’ā╝ Wildlife (Conservation and Security) Act, 2012. ’ā╝ National Forestry Policy, 2016 (final draft). ’ā╝ Cetacean management plan. ’ā╝ Bangladesh Tiger Action Plan, 2009-17.
- 22. How Can We Help?
- 23. Recommendations ’āś Love for Earth ,Nature & Animals. ’āśConservation laws for wildlife/forest practiced properly. ’āśStrict actions against ,who do not abide laws. ’āśNon industrial activities besides reserve forest.
- 24. STOP BUYING WILDLIFE PRODUCTS & CONSERVE NATURE








