Windows 8 store apps development
- 1. For Windows Phone developers
- 2. Agenda ’éŚ Introduction. ’éŚ Main features. ’éŚ Design &UX. ’éŚ Performance best practice.
- 3. Windows 8 ?
- 4. Windows 8 ’éŚ Windows 8 basically for : ’éŚ Home and business desktops. ’éŚ Laptops. ’éŚ Tablets. ’éŚ Home theater PCs.
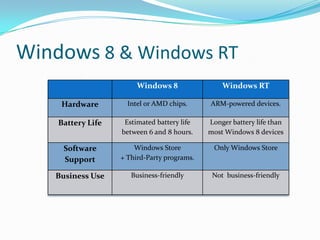
- 5. Windows 8 & Windows RT Windows 8 Windows RT Hardware Intel or AMD chips. ARM-powered devices. Battery Life Estimated battery life between 6 and 8 hours. Longer battery life than most Windows 8 devices Software Support Windows Store + Third-Party programs. Only Windows Store Business Use Business-friendly Not business-friendly
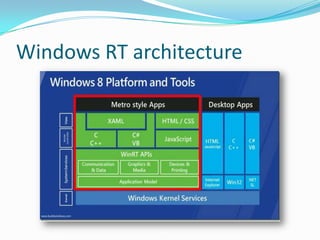
- 7. Windows 8 Store Apps ’éŚ Multiple Views. ’éŚ Touch and pen input. ’éŚ Use tiles instead of icons. ’éŚ Different UI and controls. ’éŚ Windows Store.
- 8. Where are you? Desktop Application Developers Windows Phone Developers
- 9. What is new ? How can I use it?
- 10. Main Features ’éŚ Snapping and orientation. ’éŚ New XAML controls. ’éŚ Contracts. ’éŚ Live tiles. ’éŚ Toast notifications. ’éŚ Lock screen notifications. ’éŚ Background tasks
- 11. Main Features ’éŚ Navigation. ’éŚ Geolocation. ’éŚ Storage. ’éŚ Context menus. ’éŚ File association. ’éŚ Camera capture. ’éŚ Sensors. ’éŚ Application life cycle.
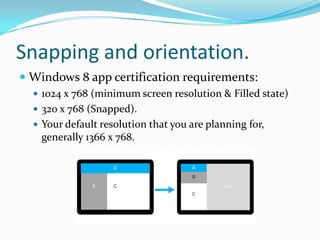
- 12. Snapping and orientation. ’éŚ Windows 8 app certification requirements: ’éŚ 1024 x 768 (minimum screen resolution & Filled state) ’éŚ 320 x 768 (Snapped). ’éŚ Your default resolution that you are planning for, generally 1366 x 768.
- 13. New XAML Controls ’éŚ Different Navigation controls. ’éŚ New Controls: ’éŚ App Bar ’éŚ Flip View ’éŚ Grid View ’éŚ Progress Ring ’éŚ Semantic Zoom ’éŚ Web View
- 14. App Bar ’éŚ The Bottom AppBar ’éŚ Left : context-specific commands. ’éŚ Right : universal commands. ’éŚ The Top AppBar ’éŚ Navigation ’éŚ Other purposes. ’éŚ 202 default AppBar button Styles.
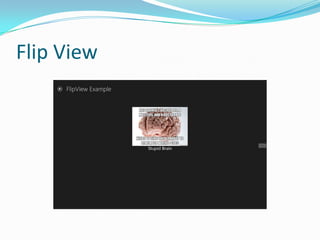
- 15. Flip View
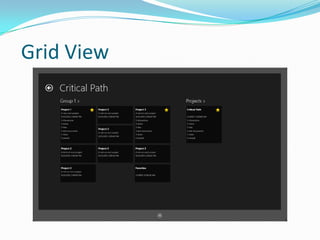
- 16. Grid View
- 17. Progress Ring
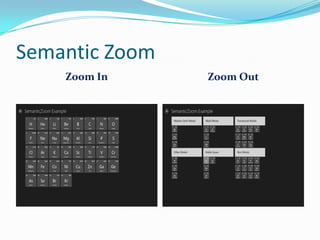
- 18. Semantic Zoom Zoom In Zoom Out
- 19. Web View
- 20. Contracts ’éŚ Contracts = Agreement. ’éŚ Settings Contract. ’éŚ Search Contract. ’éŚ Share Contract. ’éŚ File Picker Contract. ’éŚ Play To Contract.
- 21. Settings Contract ’éŚ Add handler to Settings pane open request. ’éŚ Create new Settings Command. ’éŚ Handle all of the cases for Popup. ’éŚ DO NOT wait for save. ’éŚ DO NOT wait to confirm
- 22. Search Contract ’éŚ Add Search Contract Template. ’éŚ What would users expect to search for in my app? ’éŚ Add your search results for Search Page. ’éŚ Define search suggestions. ’éŚ Forced Search by Keystrokes.
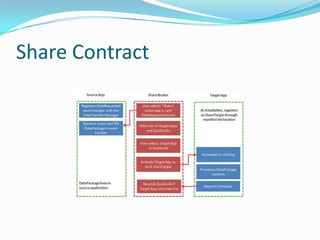
- 23. Share Contract
- 24. Share Contract ’éŚ Types of content: ’éŚ Unformatted Plain Text ’éŚ Link ’éŚ Formatted Content / HTML ’éŚ Files ’éŚ Single Image ’éŚ Custom Data Format
- 25. Share Contract ’éŚ Share Target REQs: ’éŚ Add the Share Target declaration. ’éŚ Add method to handle when the Share Target is activated. ’éŚ Handle Target Page to work with share data.
- 26. File Picker Contract File open picker File save picker
- 27. File Picker Contract ’éŚ Specific Type (s) or any. ’éŚ Define start location. ’éŚ View mode (List/Thumbnail). ’éŚ Retrieve one or multiple. ’éŚ Folder Picker.
- 28. Play To Contract ’éŚ Share content from your computer to a television, another computer, or an Xbox 360. ’éŚ A Play To source. ’éŚ A play To target.
- 29. Live Tiles ’éŚ A relationship with your user. ’éŚ Small & Large tiles. ’éŚ You must ALWAYS have a small tile. ’éŚ XML templates. ’éŚ Secondary Tiles. ’éŚ Turn live tile off.
- 30. Toast Notification ’éŚ YOU NEED TO KNOW THIS INFORMATION RIGHT NOW! ’éŚ XML Templates. ’éŚ Long duration toasts. ’éŚ Setting the audio (9 files only).
- 31. Lock Screen Notifications ’éŚ Badge & Text. ’éŚ Updated from a Background Agent. ’éŚ Only ONE opportunity to ask the user for permission. ’éŚ Glyph or number.
- 32. Background Tasks ’éŚ The code that runs when your app doesnŌĆÖt. ’éŚ Windows Runtime Component. ’éŚ Must implement IBacKgroundTask. ’éŚ Declare Background Tasks in package.appxmanifest file. ’éŚ Register your background task.
- 33. Navigation ’éŚ Frame.Navigate. ’éŚ Go Home! ’éŚ Passing data between Pages. ’éŚ Cashing pages.
- 34. Geolocation ’éŚ Useful for: ’éŚ Line of Business Apps. ’éŚ Games. ’éŚ Maps. ’éŚ Travel. ’éŚ Exercise. ’éŚ Updating Manifest. ’éŚ Getting geolocation data when it changes.
- 36. Storage ’éŚ NO System.Data. ’éŚ You have 4 Solutions: ’éŚ Services(Azure). ’éŚ IndexedDB ’éŚ Third party (SQLite). ’éŚ Application Settings: ’éŚ Local. ’éŚ Roaming.
- 37. SQLite ’éŚ Relational database management system contained in a small Cprogramming library. ’éŚ Stores the entire database as a single cross-platform file on a host machine. ’éŚ DoesnŌĆÖt support all the SQL features
- 38. SQLite ’éŚ Get it from Extension Manager. ’éŚ Add references to your project. ’éŚ Target only one Package. ’éŚ Add sqlite-net package
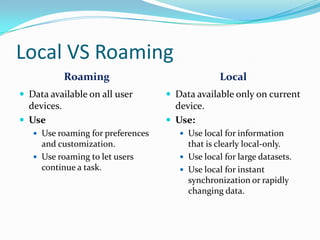
- 39. Local VS Roaming Roaming Local ’éŚ Data available on all user devices. ’éŚ Use ’éŚ Use roaming for preferences and customization. ’éŚ Use roaming to let users continue a task. ’éŚ Data available only on current device. ’éŚ Use: ’éŚ Use local for information that is clearly local-only. ’éŚ Use local for large datasets. ’éŚ Use local for instant synchronization or rapidly changing data.
- 40. Context Menu ’éŚ Right-click on something you couldnŌĆÖt select. ’éŚ Steps: ’éŚ determine the position of the clicked element. ’éŚ Create context menu and add commands . ’éŚ Show popup. ’éŚ Only six commands. ’éŚ Text box context menus.
- 41. File association ’éŚ Registering our app with Windows 8 as an app that opens files of a certain type. ’éŚ Suitable for Editor apps (Text, photo,ŌĆ”). ’éŚ Open your own extension files.
- 42. Camera Capture ’éŚ Updating Manifest ’éŚ User permission. ’éŚ Create CameraCaptureUI object. ’éŚ CaptureFileAsync to get photo or video. ’éŚ Setup video settings (Max duration/format type/Max Resolution).
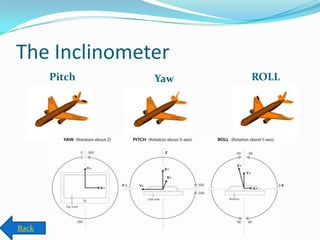
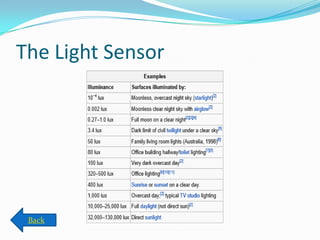
- 43. Sensors ’éŚ The Compass. ’éŚ The Light Sensor. ’éŚ The Accelerometer. ’éŚ The Gyro meter. ’éŚ The Inclinometer.
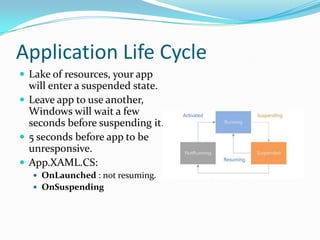
- 44. Application Life Cycle ’éŚ Lake of resources, your app will enter a suspended state. ’éŚ Leave app to use another, Windows will wait a few seconds before suspending it. ’éŚ 5 seconds before app to be unresponsive. ’éŚ App.XAML.CS: ’éŚ OnLaunched : not resuming. ’éŚ OnSuspending
- 45. Welcome to store apps world !
- 46. Design & UX ’éŚ Content Before Chrome. ’éŚ Using The Windows 8 Silhouette. ’éŚ Navigation Patterns. ’éŚ Fluid Motion. ’éŚ Make Touch a Priority.
- 47. Content Before Chrome ’éŚ The focus is content ’éŚ STOP MAKING BUTTONS! ’éŚ Could this live in an application bar?
- 48. Using The Windows 8 Silhouette
- 49. Navigation Patterns ’éŚ DONOT use the ŌĆ£everywhere navigationŌĆØ pattern. ’éŚ Hierarchical Navigation ’éŚ Master/detail structure. ’éŚ Semantic Zoom ’éŚ Branching not flat.
- 50. Hub Navigation Pattern ’éŚ Hub pages : ’éŚ Entry point. ’éŚ WhatŌĆÖs new and available. ’éŚ Section Page: ’éŚ Second level. ’éŚ Individual items. ’éŚ Detail pages: ’éŚ Third level. ’éŚ Details of individual items.
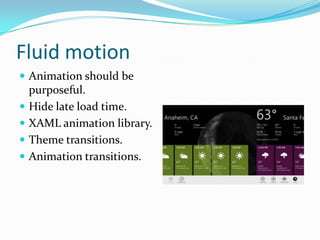
- 51. Fluid motion ’éŚ Animation should be purposeful. ’éŚ Hide late load time. ’éŚ XAML animation library. ’éŚ Theme transitions. ’éŚ Animation transitions.
- 52. Make a touch priority ’éŚ A ŌĆ£tapŌĆØ and a ŌĆ£clickŌĆØ in Windows 8 are the same. ’éŚ Clickable larger than 48 x 48 pixels. ’éŚ Optimal places to put your buttons and content.
- 53. How to use resources Sparingly ?
- 54. Performance best practices ’éŚ Minimize Application Startup. ’éŚ Optimize loading XAML. ’éŚ Load, store, and display large sets of data efficiently. ’éŚ Access the file system efficiently. ’éŚ Keep the UI thread responsive. ’éŚ Keep your app fast when you use interop.
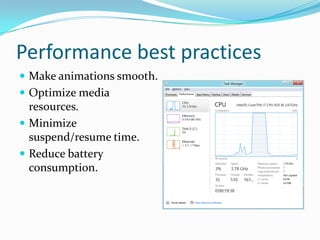
- 55. Performance best practices ’éŚ Make animations smooth. ’éŚ Optimize media resources. ’éŚ Minimize suspend/resume time. ’éŚ Reduce battery consumption.
- 56. Minimize Application Startup ’éŚ Start time: ’éŚ Less than one second (Excellent). ’éŚ Less than 5 seconds (Good). ’éŚ Greater than 5 seconds (Poor). ’éŚ Minimize managed assemblies in the startup ’éŚ Two small assemblies instead one large. ’éŚ Load locally instead web requests. ’éŚ Disk operations are faster than network operations.
- 57. Optimize loading XAML ’éŚ Start Page: ’éŚ DonŌĆÖt reference for controls and resources in other files. ’éŚ DonŌĆÖt include page specific XAML in appŌĆÖs resource dictionary. ’éŚ Optimize element count: ’éŚ Avoid unnecessary elements. ’éŚ Remove hidden elements or set the Visibility property to Collapsed. ’éŚ Same vector = an image.
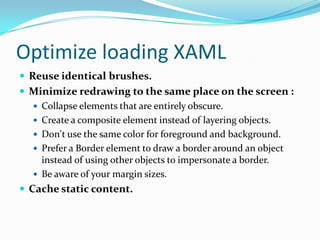
- 58. Optimize loading XAML ’éŚ Reuse identical brushes. ’éŚ Minimize redrawing to the same place on the screen : ’éŚ Collapse elements that are entirely obscure. ’éŚ Create a composite element instead of layering objects. ’éŚ Don't use the same color for foreground and background. ’éŚ Prefer a Border element to draw a border around an object instead of using other objects to impersonate a border. ’éŚ Be aware of your margin sizes. ’éŚ Cache static content.
- 59. Load, store, and display large sets of data efficiently ’éŚ Use UI virtualization to create only visible items: ’éŚ Wrap Grid . ’éŚ Virtualizing StackPanel. ’éŚ Keep item templates simple. ’éŚ Use item template selectors only as needed. ’éŚ Load subsets of data: ’éŚ Incremental data virtualization: (ISupportIncrementalLoading.) ’éŚ Random access data virtualization: (INotifyCollectionChanged and IObservableVector)
- 60. Access the file system efficiently ’éŚ Only retrieve needed properties not all. ’éŚ Windows Runtime stream adapters data buffer . ’éŚ DonŌĆÖt use buffer for low-latency reads and writes and large blocks out of the underlying
- 61. Keep the UI thread responsive ’éŚ Use asynchronous APIs. ’éŚ Async /Await ’éŚ Offload work to background threads. ’éŚ Calculating of computer AI in a game
- 62. Keep your app fast when you use interop
- 63. Make Animations Smooth ’éŚ Use independent instead of dependent animations . Dependant animations Independent animations ’āśUI thread creates the animation tree. ’āśEach frame is generated on the UI thread and sent individually to the compositor. ’āśCompositor renders the scene. ’āś UI thread creates the animation tree. ’āś Compositor takes over and runs the animation.
- 64. Make Animations Smooth Independent animations Dependant Animations ’āś Object animations using key frames ’āś Zero-duration animations ’āś Canvas.Left and Canvas.Top ’āś UIElement.Opacity ’āś SolidColorBrush.Color ’āś Render Transform ’āś Projection ’āś Clip ’āś EnableDependentAnimation property. ’āś BitmapCache independent animations considered dependent because the cache must be rerasterized for each frame.
- 65. Make Animations Smooth ’éŚ Don't animate a WebView : ’éŚ Swap it with a WebViewBrush for the duration of the animation . ’éŚ Use infinite animations sparingly . ’éŚ Adding ahandler for CompositionTarget.Rendering is similar to running an infinite animation. ’éŚ Use the animation library: (Windows.UI.Xaml.Media.Animation )
- 66. Optimize media resources ’éŚ Release media streams. ’éŚ Display full screen video playback when possible. ’éŚ Put other elements to the side of embedded video. ’éŚ Delay setting the source for a MediaElement . ’éŚ Set MediaElement.PosterSource. ’éŚ Match video resolution with device resolution. ’éŚ Choose recommended formats.(MP4,MP3,H.264)
- 67. Optimize media resources ’éŚ Scale images to the appropriate size : ’éŚ DecodePixelWidth & DecodePixelHeight instead width and height. ’éŚ Use GetThumbnailAsync for thumbnails. ’éŚ Decode images once.
- 68. Minimize suspend/resume time ’éŚ Serialize only when necessary . ’éŚ Use Xml Serializer: ’éŚ The lowest serialization and deserialization times ’éŚ Reduce memory footprint: ’éŚ Freeing as much memory as possible at suspension ’éŚ Release resources.
- 69. Reduce battery consumption ’éŚ Remove unnecessarily timers . ’éŚ DonŌĆÖt use animations in snap view. ’éŚ Reducing the frequency at which you poll for new info using web services.
- 70. References ’éŚ Windows RT. ’éŚ 31 days of Windows 8. ’éŚ Windows 8 Samples. ’éŚ Local Database in Windows Store app. ’éŚ Windows 8 APP UX. ’éŚ Performance best practice for Windows Store Apps. ’éŚ Windows Store Investigation. ’éŚ Code reuse between WP 8 and Windows 8.
- 72. App bar button styles Back
- 73. Glyphs Back
- 79. Avoid unnecessary elements. Bad Code <Grid> <!-- BAD CODE DO NOT USE.--> <Rectangle Fill="Black"/> <!-- BAD CODE DO NOT USE.--> </Grid> <!-- BAD CODE DO NOT USE.--> Best Practice <Grid Background="Black" /> Back