WIP Flow: A Card system for Production Planning and Control
- 1. Card Based Production Planning &Control (PPC) System Presented by [Ibrahim Mohammed]
- 2. Problem Statement Q: How can we quote realistic delivery times for Customer Order? Ans: ŌĆó A system to keep stock and estimate current workload and shop through-put ŌĆó A system to sequence product transformation ŌĆó A system to monitor and control product transformation
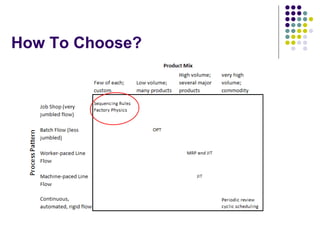
- 5. Workload Control (WLC) Concept ŌĆó ŌĆ£Based on creating predictable and short through-put times for each critical work stationŌĆØ ŌĆó ŌĆ£predictable throughput times are important for a good timing of order releases, for quoting realistic delivery times, and for good timing of capacity adjustments.ŌĆØ
- 6. SYSTEM COMPONENTS 1. Loop of Cards between the Shop Floor and the Planning Office 2. Card Display Boards 3. Order Guiding Form 4. Support Staff
- 7. How it Works (Phases) ŌĆó Order Entry Phase ŌĆó Process Planning Phase ŌĆó Job Release Phase ŌĆó Job Execution Phase (Shop Floor) ŌĆó Monitoring and Control
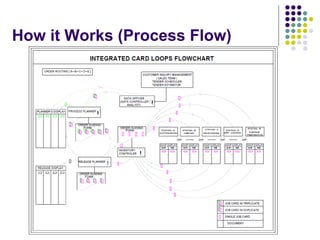
- 8. How it Works (Process Flow) .
- 9. Demo (Today: Jan-01) Jobs Simulation: ŌĆó Mickey Sculpture ŌĆó Oryx Sculpture ŌĆó Tweety Bird Cage ŌĆó AWR Farmhouse Pot Type 4 ŌĆó KZ Doha Airplane Turbine ŌĆó Uniflora Pot Type 1 ŌĆó VM Accessories Risers ŌĆó LMG Feature Wall Cutouts ŌĆó Frit Panels
- 10. Demo (Order Entry: Easter Eggs) .
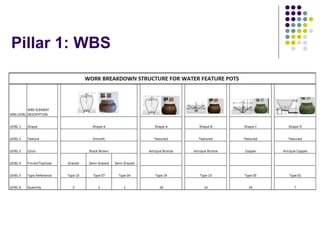
- 11. Fundamentals (Axioms) Pillar 1: WBS ŌĆó Customer orders (products) can be broken down into sub-components that can be routed independently, and produced as a set of basic operations Pillar 2: Routing/Operations Sequence ŌĆó Each subcomponent can be designed as a sequence of simple, repetitive operations Pillar 3: Shop Design/Structure ŌĆó The shop floor is designed to integrate human labor and machine ŌĆó Shop is divided into work centers i.e. where and when an operation must be performed ŌĆó Shop operations are categorized by work centers ŌĆó Job dispatching rules/Job processing rules are established Pillar 4: Training ŌĆó Training in skills and teamwork
- 12. Pillar 1: WBS .
- 13. Pillar 2: Routing/Operations Sequence Cutting Room ŌåÆ Carving ŌåÆ Modeling (Application of Clay) ŌåÆ Modeling (Detailing of Clay) ŌåÆ Metal Fabrication (Steel Framework) ŌåÆ Mold Making ŌåÆ GRP (Casting) ŌåÆ GRP (Tooling/Stamping) ŌåÆ Metal Fabrication (Base Plate) ŌåÆ Surface preparation ŌåÆ Renderring JOB ROUTING Each Job Route = 1 Job Card ŌåÆ 1 Job Stage Each Job Card = Complete List of Operation at a Job Stage
- 14. Pillar 2: Routing/Operations Sequence ID WORK CENTRE 1 Cutting Room 2 Carving 3 Modeling 4 Modeling 8 GRP (Tooling) 9 Metal Fabrication 10 Surface Prep. 11 Artistry Apply Top Coat paint on sculpture and base plate 12 Paint Finishing 6 7 GRP (casting) Apply Epoxy Primer to base Plate Paint base plate Attach metal baseplate to feet of sculpture, as in drawing Wash out excess wax, carry out light sanding of smooth areas, apply primer make rendering of the sculpture as per reference image provided and approved pantone colors Mold Making5 Metal Fabrication Fabricate Metal Framing for Sculpture Fabricate metal baseplate for sculpture Demarcate the model with forex cards according to the number of parts of the mold required Make rubber mold with hard backing of each part of the After curing is completed, release the mold by removing the model, then degrease the mold by washing with soap and pressurised water Cast the product in 2 layer GRP + Metel Frame (Armature) After curing is complete, release product from mold Trim out excess material on the product along the line of DETAILS OF OPERATIONS Cut EPS model of product to scale of 1:1 Assemble and carve out shape of product, by hand Mold clay on the EPS model Imprint body details of sculpture onto the clay molded on the EPS model Apply wax over the entire surface area of the model
- 15. Pillar 3: Shop Design/Structure WORK CENTER FOREMAN TEAM LEADER 1 TEAM MEMBER 1 TEAM MEMBER 2 TEAM MEMBER 3 TEAM MEMBER 4 TEAM LEADER 2 TEAM MEMBER 1 TEAM MEMBER 2 TEAM MEMBER 3 TEAM MEMBER 4 ’ü¼Team Structure (unit of organization) ’ü¼Operations Categories (basis of categorization)
- 17. Resource Requirement Process Planning Phase ŌĆó Process Planner Job Release Phase ŌĆó Release Planner Shop Floor ŌĆó WIP-Inventory Controller Monitoring and Control Phase ŌĆó Planning Data Officer (Data Control and Analysis) ***most importantly: PLANNING ROOM
- 18. What the Card System Does ŌĆó Reduces uncertainty in the control decision by using feedback loops that update the current situation on the shop floor in real time ŌĆó Coordinate the flow of products through the system ŌĆó Coordinate the flow of products in accordance with the availability of transforming resources ŌĆó Reduce waiting waste i.e. free up capacity
- 19. What the card System Does Not Do ŌĆó Does not ensure quality- ensuring quality is the job of Total Quality Mgt. (TQM) or Six Sigma ŌĆó Does not improve efficiency of material transformation process- this is the job of design and engineering ŌĆó Does not improve efficiency of an operation itself- this is the job of motion studies, improved job design, or improved product design ŌĆó Does not make unreliable machines reliable- this is the job of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) ŌĆó Does not reduce transportation waste ŌĆó Does not solve the problem of multiple points of control ŌĆó Does not solve the problem of ŌĆ£Jaldi JaldiŌĆØ ŌĆó Does not solve the problem of cashflow/material approval
- 20. Scaling Up ŌĆó Integration of QC Function ŌĆó Integration of Sales/Marketing Function ŌĆó Integration of Materials Inventory/Store ŌĆó Automation

![Card Based Production
Planning &Control (PPC)
System
Presented by [Ibrahim Mohammed]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cardsystemforppc-190924060833/85/WIP-Flow-A-Card-system-for-Production-Planning-and-Control-1-320.jpg)