WIRES AND CABLES -building services t.y.b.arch.
- 1. D.Y. PATIL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING S.Y.B.ARCH BUILDING SERVICES-II Presented by-Prof. A. S. Pandharpatte DYPCOAT
- 2. WIRES AND CABLES ŌĆó Electrical wiring uses insulated conductors. ŌĆó Wires and cables are rated, by the circuit voltage, temperature and environmental conditions in which they are used. ŌĆó International Electro technical Commission is attempting to standardize wiring amongst member countries. ŌĆó Colour codes are used to distinguish wires- line, neutral and ground.
- 3. WIRES AND CABLES ŌĆó An electrical cable is made up of two or more wires, running side by side and bonded , twisted, braided together to form a single assembly , the ends of which can be connected to two devices, enabling the transfer of electrical signals from one device to another. ŌĆó Long distance communication takes place over undersea cables . ŌĆó Power cables are used for bulk transmission of alternating and direct current power, using high voltage cable.
- 4. WIRES AND CABLES ŌĆó Wire is a single electrical conductor, whereas a cable is a group of wires wrapped in sheathing . ŌĆó Whether indoors or outdoors, proper wire and cable installation is important to ensure smooth electricity supply . ŌĆó Each wire and cable should be installed carefully from the fuse box to the outlets , fixtures and appliances. ŌĆó The National Electrical Code (NEC) and Local Building Code regulate the manner of installation and the types of wires and cables for various electrical applications.
- 5. Size of wire according to BIS ŌĆó In India, wire sizes are typically specified according to the standards set by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). ŌĆó The wire size is primarily determined by its cross-sectional area, which is specified in square millimeters (mm┬▓). The commonly used size of wire according to BIS standards include: ŌĆó 1.0 mm┬▓: This size is often used for lighting circuits and smaller loads. ŌĆó 1.5 mm┬▓: Commonly used for general-purpose electrical wiring in homes and small installations. The current rating is around 10 amps ŌĆó 2.5 mm┬▓: Suitable for higher current-carrying capacity applications, such as power outlets and larger loads. The current rating is around 16 amps ŌĆó 4.0 mm┬▓ and above: Used for heavy-duty applications, industrial installations, and circuits with high current requirements. ŌĆó Current ratings are based on typical household wiring standards and may vary based on specific electrical codes and regulations in different regions.
- 6. ŌĆó Wire Lettering: ŌĆó The letters THHN, THWN,THW and XHHN, represent the main insulation types of individual wires. ŌĆó T ŌĆō Thermoplastic Insulation. ŌĆó H ŌĆō Heat Resistance ŌĆó HH ŌĆō High heat resistance (up to 194 degrees) ŌĆó W- Suitable for wet locations ŌĆó N- Nylon coating, resistant to oil / gas ŌĆó X ŌĆō Synthetic polymer that is flame resistant.
- 7. ŌĆó TYPES OF WIRES: ŌĆó 1) TRIPLEX WIRES: They are usually used in single phase service drop conductors, between the power pole and weather heads. ŌĆó They are made up of two, insulated aluminum wires, wrapped with a third bare wire which is used as common neutral. ŌĆó 2) MAIN FEEDER WIRES: They are the wires that connect, the service weather head to the house. ŌĆó They are made with stranded or solid THHN wire and the cable installed is 25 % more than the load required. TRIPLEX service drop cable
- 8. ŌĆó The current rating of a feeder is called the ampacity and the National Electric Code (NEC) requires that a 25% margin (to accommodate overloads) be applied when sizing conductors. The 25% margin is applied as follows: ŌĆó When a feeder supplies a combination of continuous and non- continuous nonmotor load, its ampacity shall not be less than 125% of the continuous load plus 100% of the non-continuous load. ŌĆó When a feeder supplies several motors, its ampacity shall not be less than 125% of the largest motor load plus 100% of the remaining motor load. ŌĆó When a feeder supplies a mixture of motor and non-motor load the two foregoing criteria should be applied to each component and their results summed.
- 10. WIRES AND CABLES ŌĆó 3) PANEL FFED WIRES: They are black insulated THHN wire. These are used to power, the main junction box and circuit breaker panels. ŌĆó 4) NON METALLIC SHEATHED WIRES: Used in homes and have 2-3 conductors, each with plastic insulation and a bare ground wire. The individual wires are covered with another layer of non metallic sheathing.
- 11. WIRES AND CABLES ŌĆó 5) SINGLE STRAND WIRES: Also uses THHN wire, though there are other variants. Each wire is separate and multiple wires can be drawn together through a pipe easily. These wires are the most popular choice for layouts that use pipes to contain wires. ŌĆó TYPES OF ELCTRICAL CABLES: ŌĆó 1) NON METALLIC SHEATHED CABLE: They are known as NM cables. They feature a flexible plastic jacket with 2 or 4 wires and a bare wire for grounding.
- 12. WIRES AND CABLES ŌĆó 2) UNDERGROUND FEEDER CABLE: They are similar to NM cables but instead of each wire being individually wrapped in thermoplastic , wires are grouped together and embedded with the flexible material. They are water resistant. ŌĆó 3) METALLIC SHEATHED CABLE: Known as armoured or BX cables, they are used to supply mains electricity or for large appliances. They feature 3 plain stranded copper wires that are insulated with cross linked polythene, PVC bedding, and a black PVC sheathing. BX cables and steel wire sheathing are used for outdoor applications.
- 13. WIRES AND CABLES ŌĆó 4) UNSHIELDED TWISTED PAIR: (UTP cables) This type consists of two wires that are twisted together. The individual wires are not insulated which makes this cable perfect for signal transmission and video applications. They are used in telephones , security cameras and data network. ŌĆó 5) RIBBON CABLE: Used in computers and peripherals. Wires run parallel to each other on a flat plane. They can handle low voltage applications. ŌĆó 6) DIRECT BURIED CABLES: (DBCŌĆÖS ) Specially designed coaxial or bundled fiber optic cables, which do not require sheathing, insulation or piping, before being buried underground. They have layers of banded metal sheathing. Used for transmission or communication requirements.
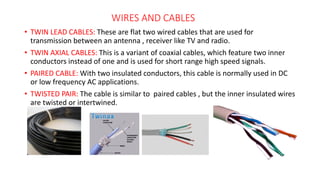
- 14. WIRES AND CABLES ŌĆó TWIN LEAD CABLES: These are flat two wired cables that are used for transmission between an antenna , receiver like TV and radio. ŌĆó TWIN AXIAL CABLES: This is a variant of coaxial cables, which feature two inner conductors instead of one and is used for short range high speed signals. ŌĆó PAIRED CABLE: With two insulated conductors, this cable is normally used in DC or low frequency AC applications. ŌĆó TWISTED PAIR: The cable is similar to paired cables , but the inner insulated wires are twisted or intertwined.