World War I - part 1
- 2. The M.A.I.N. Causes of WWI
- 3. MilitarismMilitarism: fascination with military power and the glory of warLed to Arms Race When a nation built up its military, its enemies saw it as a move toward warEx. Germany built up its navy to compete with Great Britain’s navy, causing tension between the two countries
- 4. AlliancesAlliances: agreements between countries to help each other during wartimeAlliances pulled many countries into the war
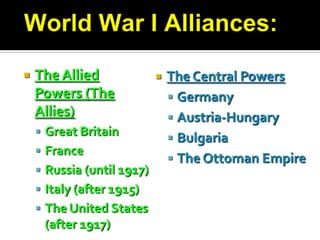
- 5. :World War I Alliances:The Allied Powers (The Allies)Great BritainFranceRussia (until 1917)Italy (after 1915)The United States (after 1917)The Central PowersGermanyAustria-HungaryBulgariaThe Ottoman Empire
- 6. ImperialismImperialism: building empires by expanding territory and gaining coloniesCompetition for colonies led to intense rivalries among the European powersEx. Germany and Italy wanted to create empires that would compete with those of Great Britain and France
- 7. NationalismNationalism: strong feelings of pride and unity among a particular group of peopleWorsened rivalries between European powersLed nations to seek to create empires or break away from them
- 8. Led to ethnic and ideological differences between nationsTrouble in the Balkans (multi-ethnic region of Southeastern Europe)Serbia wanted to take control of BosniaAustria-Hungary took over BosniaArchduke Franz Ferdinand (the heir to the throne of Austria-Hungary) was assassinated by a Serbian terroristAustria-Hungary declared war on Serbia