Writing Proofs (Direct and Indirect) PPT.pptx
- 1. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lesson, you will be able to: ’ü▒ make direct or indirect proofs of a given situation; and ’ü▒ apply the theorems, postulates, properties of equality, properties of congruence in
- 3. MATH-TIONARY
- 4. MATH-TIONARY
- 5. MATH-TIONARY
- 6. MATH-TIONARY
- 7. Suppose you and your friend Rachel are going to an art festival. When you get there, you are the only ones there. Rachel looks at you and says, ''If the art festival is today, there would be hundreds of people here, so it can't be today.ŌĆśŌĆÖ You take out your tickets, look at the date and say, ''The
- 8. As it turns out, your argument is an example of a DIRECT PROOF, and Rachel's argument is an example
- 9. DIRECT PROOF assumes that the hypothesis of a conjecture is true, and then uses a series of logical deductions to INDIRECT PROOF relies on a contradiction to prove a given conjecture by assuming the conjecture is not true, and then running into a
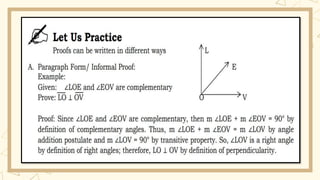
- 10. WAYS IN WRITING PROOFS A. Direct Proofs which can be in the following forms: 1. Paragraph form, which is an informal proof 2. Two-column Form, which is a formal proof 3. Flow Chart Form, also a formal proof
- 11. Postulate ŌĆō is statement that is accepted without proof. Theorem ŌĆō is a statement accepted after it is proved deductively.
- 12. To perform a direct proof, we use the following steps: 1. Identify the hypothesis and conclusion of the conjecture you're trying to prove 2. Assume the hypothesis to be true 3. Use definitions, properties, theorems, etc. to make a series of deductions that eventually prove the conclusion of the conjecture to be true 4. State that by direct proof, the conclusion of Consider your arguments again. In your argument (direct proof), you use the fact that the tickets say that the art festival is tomorrow to prove that the art festival can't be today. You use a direct proof by using logical deductions
- 13. Method of Indirect Proofs But to perform an indirect proof, we use a different process which includes the following steps: 1. Assume the opposite of the conjecture, or assume that the conjecture is false 2. Try to prove your assumption directly until you run into a contradiction
- 14. In Rachel's argument (indirect proof), she starts by assuming the opposite of the original conjecture, which is that the festival is not today. That is, she starts with ''If the art festival was today'', then she says, ''there would be hundreds of people here.ŌĆśŌĆÖ This is a contradiction, since you and Rachel are the only ones there.
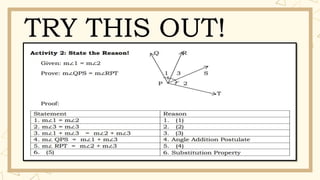
- 17. TRY THIS OUT!
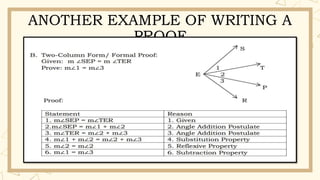
- 18. ANOTHER EXAMPLE OF WRITING A PROOF
- 19. TRY THIS OUT!