Xml intro1
- 2. Definition ’éŚ XML stands for EXtensible Markup Language ’éŚ XML is a markup language much like HTML ’éŚ XML was designed to carry data, to transport and store data, not to display data ’éŚ XML tags are not predefined. You must define your own tags ’éŚ XML is designed to be self-descriptive The best description of XML is: ŌĆ£XML is a software and hardware-independent tool for carrying informationŌĆØ.
- 3. XML & HTML ’éŚ XML is not a replacement for HTML. ’éŚ XML and HTML were designed with different goals: ŌŚ” XML was designed to transport and store data, with focus on what data is ŌŚ” HTML was designed to display data, with focus on how data looks ŌŚ” HTML is about displaying information, while XML is about carrying information.
- 4. First Example <note> <to>Tove</to> <from>Jani</from> <heading>Reminder</heading> <body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body> </note> ’éŚ The note above is quite self-descriptive. It has sender and receiver information, it also has a heading and a message body.
- 5. XML Tags ’éŚ The tags in the example above (like <to> and <from>) are not defined in any XML standard. These tags are "invented" by the author of the XML document. ’éŚ That is because the XML language has no predefined tags. ’éŚ The tags used in HTML are predefined. HTML documents can only use tags defined in the HTML standard (like <p>, <h1>, etc.). ’éŚ XML allows the author to define his/her own tags and his/her own document structure.
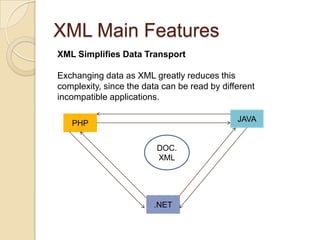
- 6. XML Main Features XML Simplifies Data Transport Exchanging data as XML greatly reduces this complexity, since the data can be read by different incompatible applications. JAVA PHP DOC. XML .NET
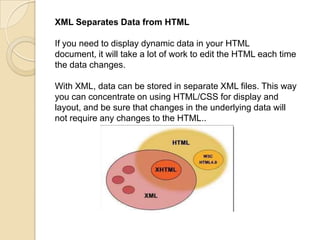
- 7. XML Separates Data from HTML If you need to display dynamic data in your HTML document, it will take a lot of work to edit the HTML each time the data changes. With XML, data can be stored in separate XML files. This way you can concentrate on using HTML/CSS for display and layout, and be sure that changes in the underlying data will not require any changes to the HTML..
- 8. XML Makes Your Data More Available Different applications can access your data, not only in HTML pages, but also from XML data sources. With XML, your data can be available to all kinds of "reading machines" (Handheld computers, voice machines, news feeds, etc), and make it more available for blind people, or people with other disabilities.
- 9. XML Simplifies Platform Changes XML data is stored in text format. This makes it easier to expand or upgrade to new operating systems, new applications, or new browsers, without losing data. XML Simplifies Data Sharing In the real world, computer systems and databases contain data in incompatible formats.
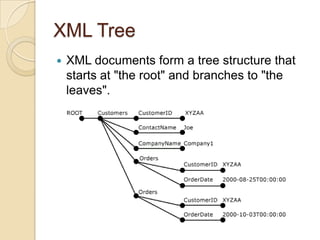
- 10. XML Tree ’éŚ XML documents form a tree structure that starts at "the root" and branches to "the leaves".
- 11. Tree Structure ’éŚ XML documents must contain a root element. This element is "the parent" of all other elements. ’éŚ The elements in an XML document form a document tree. The tree starts at the root and branches to the lowest level of the tree. ’éŚ All elements can have sub elements (child elements). <root> <child> <subchild attribute=ŌĆØvalueŌĆØ>.....</subchild> </child> </root>
- 12. XML Syntax Rules ’éŚ All XML Elements Must Have a Closing Tag. ’éŚ XML Tags are Case Sensitive. ’éŚ XML Elements Must be Properly Nested. ’éŚ XML Documents Must Have a Root Element. ’éŚ XML Attribute Values Must be Quoted. <root> <child> <subchild attribute=ŌĆØvalueŌĆØ>value #1</subchild> </child> </root>
- 13. XML Elements ’éŚ An XML element is everything from (including) the element's start tag to (including) the element's end tag. An element can contain: ŌŚ” other elements ŌŚ” text ŌŚ” attributes ŌŚ” or a mix of all of the above...
- 14. XML Naming Rules ’éŚ XML elements must follow these naming rules: ŌŚ” Names can contain letters, numbers, and other characters ŌŚ” Names cannot start with a number or punctuation character ŌŚ” Names cannot start with the letters xml (or XML, or Xml, etc) ŌŚ” Names cannot contain spaces ŌŚ” Any name can be used, no words are reserved
- 15. XML Elements are Extensible ŌĆó XML elements can be extended to carry more information. <note> <to>Tove</to> <from>Jani</from> <body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body> </note> <note> <date>2008-01-10</date> <to>Tove</to> <from>Jani</from> <heading>Reminder</heading> <body>Don't forget me this weekend!</body> </note>
- 16. XML Attributes ’éŚ XML elements can have attributes, just like HTML. ’éŚ Attributes provide additional information about an element. ’éŚ In HTML, attributes provide additional information about elements: <img src=/slideshow/xml-intro1/14579383/"computer.gif"> <a href="demo.asp"> ’éŚ In the example below, the file type is irrelevant to the data, but can be important to the software that wants to manipulate the element: <file type="gif">computer.gif</file>
- 17. XML Attributes Must be Quoted ’éŚ Either single or double quotes can be used. For a person's sex, the person element can be written like this: <person sex="female"> ’éŚ or like this: <person sex='female'> ’éŚ If the attribute value itself contains double quotes you can use single quotes, like in this example: <gangster name='George "Shotgun" Ziegler'> ’éŚ or you can use character entities: <gangster name="George " Shotgun" Ziegler">
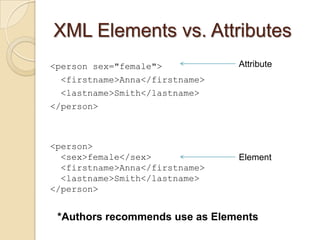
- 18. XML Elements vs. Attributes <person sex="female"> Attribute <firstname>Anna</firstname> <lastname>Smith</lastname> </person> <person> <sex>female</sex> Element <firstname>Anna</firstname> <lastname>Smith</lastname> </person> *Authors recommends use as Elements
- 19. Using XML Attributes ’éŚ Some of the problems with using attributes are: ŌŚ” attributes cannot contain multiple values (elements can) ŌŚ” attributes cannot contain tree structures (elements can) ŌŚ” attributes are not easily expandable (for future changes) ’éŚ Attributes are difficult to read and maintain. Use elements for data. Use attributes for information that is not relevant to the data. Example using only attributes: <note day="10" month="01" year="2008" to="Tove" from="Jani" heading="Reminder" body="Don't forget me this weekend!ŌĆ£> </note>
- 20. XML Validation XML with correct syntax is "Well Formed" XML. ŌĆó A "Well Formed" XML document has correct XML syntax. ŌĆó Use the correct syntax rules. ŌĆó XML documents must have a root element ŌĆó XML elements must have a closing tag ŌĆó XML tags are case sensitive ŌĆó XML elements must be properly nested ŌĆó XML attribute values must be quoted
- 21. XML validated against a DTD is "Valid" XML. ŌĆó A "Valid" XML document is a "Well Formed" XML document, which also conforms to the rules of a Document Type Definition (DTD)
- 22. The purpose of a DTD is to define the structure of an XML document. It defines the structure with a list of legal elements: <!DOCTYPE note XML DTD [ <!ELEMENT note (to,from,heading,body)> <!ELEMENT to (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT from (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT heading (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT body (#PCDATA)> ]> W3C supports an XML-based alternative to DTD: <xs:element name="note"> XML <xs:complexType> <xs:sequence> <xs:element name="to" type="xs:string"/> Schema <xs:element name="from" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name="heading" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name="body" type="xs:string"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element>
- 23. Viewing XML Files ’éŚ Raw XML files can be viewed in all major browsers. ’éŚ If an erroneous XML file is opened, the browser will report the error. ’éŚ The XML document will be displayed with color-coded root and child elements. A plus (+) or minus sign (-) to the left of the elements can be clicked to expand or collapse the
- 24. Displaying XML with CSS ’éŚ With CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) you can add display information to an XML document. ’éŚ It is possible to use CSS to format an XML document. ’éŚ LetŌĆÖs see an example of how to use a CSS style sheet to format an XML document.
- 25. THANKSŌĆ”ŌĆ” And letŌĆÖs build together some XML ’üŖ


















![The purpose of a DTD is to define the structure
of an XML document. It defines the structure
with a list of legal elements:
<!DOCTYPE note
XML DTD [
<!ELEMENT note
(to,from,heading,body)>
<!ELEMENT to (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT from (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT heading (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT body (#PCDATA)>
]>
W3C supports an XML-based alternative to
DTD:
<xs:element name="note">
XML <xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="to" type="xs:string"/>
Schema <xs:element name="from" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="heading" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="body" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xmlintro1-121003165233-phpapp01/85/Xml-intro1-22-320.jpg)


