Xml unit1
- 1. Introduction to XML Extensible Markup Language
- 2. What is XML âĒ XML stands for eXtensible Markup Language. âĒ A markup language is used to provide information about a document. âĒ Tags are added to the document to provide the extra information. âĒ HTML tags tell a browser how to display the document. âĒ XML tags give a reader some idea what some of the data means.
- 3. What is XML Used For? âĒ XML documents are used to transfer data from one place to another often over the Internet. âĒ XML subsets are designed for particular applications. âĒ One is RSS (Rich Site Summary or Really Simple Syndication ). It is used to send breaking news bulletins from one web site to another. âĒ A number of fields have their own subsets. These include chemistry, mathematics, and books publishing. âĒ Most of these subsets are registered with the W3Consortium and are available for anyoneâs use.
- 4. Advantages of XML âĒ XML is text (Unicode) based. â Takes up less space. â Can be transmitted efficiently. âĒ One XML document can be displayed differently in different media. â Html, video, CD, DVD, â You only have to change the XML document in order to change all the rest. âĒ XML documents can be modularized. Parts can be reused.
- 5. Example of an HTML Document <html> <head><title>Example</title></head. <body> <h1>This is an example of a page.</h1> <h2>Some information goes here.</h2> </body> </html>
- 6. Example of an XML Document <?xml version=â1.0â/> <address> <name>Alice Lee</name> <email>alee@aol.com</email> <phone>212-346-1234</phone> <birthday>1985-03-22</birthday> </address>
- 7. Difference Between HTML and XML âĒ HTML tags have a fixed meaning and browsers know what it is. âĒ XML tags are different for different applications, and users know what they mean. âĒ HTML tags are used for display. âĒ XML tags are used to describe documents and data.
- 8. XML Rules âĒ Tags are enclosed in angle brackets. âĒ Tags come in pairs with start-tags and end-tags. âĒ Tags must be properly nested. â <name><email>âĶ</name></email> is not allowed. â <name><email>âĶ</email><name> is. âĒ Tags that do not have end-tags must be terminated by a â/â. â <br /> is an html example.
- 9. More XML Rules âĒ Tags are case sensitive. â <address> is not the same as <Address> âĒ XML in any combination of cases is not allowed as part of a tag. âĒ Tags may not contain â<â or â&â. âĒ Tags follow Java naming conventions, except that a single colon and other characters are allowed. They must begin with a letter and may not contain white space. âĒ Documents must have a single root tag that begins the document.
- 10. Encoding âĒ XML (like Java) uses Unicode to encode characters. âĒ Unicode comes in many flavors. The most common one used in the West is UTF-8. âĒ UTF-8 is a variable length code. Characters are encoded in 1 byte, 2 bytes, or 4 bytes. âĒ The first 128 characters in Unicode are ASCII. âĒ In UTF-8, the numbers between 128 and 255 code for some of the more common characters used in western Europe, such as ÃĢ, ÃĄ, ÃĨ, or ç. âĒ Two byte codes are used for some characters not listed in the first 256 and some Asian ideographs. âĒ Four byte codes can handle any ideographs that are left. âĒ Those using non-western languages should investigate other versions of Unicode.
- 11. Well-Formed Documents âĒ An XML document is said to be well-formed if it follows all the rules. âĒ An XML parser is used to check that all the rules have been obeyed. âĒ Recent browsers such as Internet Explorer 5 and Netscape 7 come with XML parsers. âĒ Parsers are also available for free download over the Internet. One is Xerces, from the Apache open-source project. âĒ Java 1.4 also supports an open-source parser.
- 12. XML Example Revisited <?xml version=â1.0â/> <address> <name>Alice Lee</name> <email>alee@aol.com</email> <phone>212-346-1234</phone> <birthday>1985-03-22</birthday> </address> âĒ Markup for the data aids understanding of its purpose. âĒ A flat text file is not nearly so clear. Alice Lee alee@aol.com 212-346-1234 1985-03-22 âĒ The last line looks like a date, but what is it for?
- 13. Expanded Example <?xml version = â1.0â ?> <address> <name> <first>Alice</first> <last>Lee</last> </name> <email>alee@aol.com</email> <phone>123-45-6789</phone> <birthday> <year>1983</year> <month>07</month> <day>15</day> </birthday> </address>
- 14. XML Files are Trees address name email phone birthday first last year month day
- 15. XML Trees âĒ An XML document has a single root node. âĒ The tree is a general ordered tree. â A parent node may have any number of children. â Child nodes are ordered, and may have siblings. âĒ Preorder traversals are usually used for getting information out of the tree.
- 16. Validity âĒ A well-formed document has a tree structure and obeys all the XML rules. âĒ A particular application may add more rules in either a DTD (document type definition) or in a schema. âĒ Many specialized DTDs and schemas have been created to describe particular areas. âĒ These range from disseminating news bulletins (RSS) to chemical formulas. âĒ DTDs were developed first, so they are not as comprehensive as schema.
- 17. Document Type Definitions âĒ A DTD describes the tree structure of a document and something about its data. âĒ There are two data types, PCDATA and CDATA. â PCDATA is parsed character data. â CDATA is character data, not usually parsed. âĒ A DTD determines how many times a node may appear, and how child nodes are ordered.
- 18. DTD for address Example <!ELEMENT address (name, email, phone, birthday)> <!ELEMENT name (first, last)> <!ELEMENT first (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT last (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT email (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT phone (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT birthday (year, month, day)> <!ELEMENT year (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT month (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT day (#PCDATA)>
- 19. Schemas âĒ Schemas are themselves XML documents. âĒ They were standardized after DTDs and provide more information about the document. âĒ They have a number of data types including string, decimal, integer, boolean, date, and time. âĒ They divide elements into simple and complex types. âĒ They also determine the tree structure and how many children a node may have.
- 20. Schema for First address Example <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1" ?> <xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xs:element name="address"> <xs:complexType> <xs:sequence> <xs:element name="name" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name="email" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name="phone" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name="birthday" type="xs:date"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element> </xs:schema>
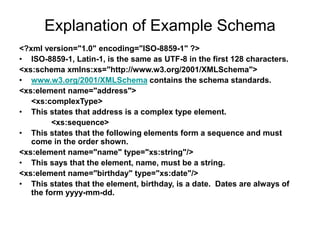
- 21. Explanation of Example Schema <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1" ?> âĒ ISO-8859-1, Latin-1, is the same as UTF-8 in the first 128 characters. <xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> âĒ www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema contains the schema standards. <xs:element name="address"> <xs:complexType> âĒ This states that address is a complex type element. <xs:sequence> âĒ This states that the following elements form a sequence and must come in the order shown. <xs:element name="name" type="xs:string"/> âĒ This says that the element, name, must be a string. <xs:element name="birthday" type="xs:date"/> âĒ This states that the element, birthday, is a date. Dates are always of the form yyyy-mm-dd.
- 22. XSLT Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations âĒ XSLT is used to transform one xml document into another, often an html document. âĒ The Transform classes are now part of Java 1.4. âĒ A program is used that takes as input one xml document and produces as output another. âĒ If the resulting document is in html, it can be viewed by a web browser. âĒ This is a good way to display xml data.
- 23. A Style Sheet to Transform address.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"> <xsl:template match="address"> <html><head><title>Address Book</title></head> <body> <xsl:value-of select="name"/> <br/><xsl:value-of select="email"/> <br/><xsl:value-of select="phone"/> <br/><xsl:value-of select="birthday"/> </body> </html> </xsl:template> </xsl:stylesheet>
- 24. The Result of the Transformation Alice Lee alee@aol.com 123-45-6789 1983-7-15
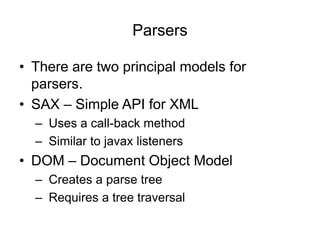
- 25. Parsers âĒ There are two principal models for parsers. âĒ SAX â Simple API for XML â Uses a call-back method â Similar to javax listeners âĒ DOM â Document Object Model â Creates a parse tree â Requires a tree traversal
- 26. References âĒ Elliotte Rusty Harold, Processing XML with Java, Addison Wesley, 2002. âĒ Elliotte Rusty Harold and Scott Means, XML Programming, OâReilly & Associates, Inc., 2002. âĒ W3Schools Online Web Tutorials, http://www.w3schools.com.