Yarn & Fabric Formation by Sukhvir Sabharwal
- 1. Processing of Cotton YARN & FABRIC FORMATION By:-Sukhvir Sabharwal B-Tech 2007 Batch TITS Bhiwani (INDIA)
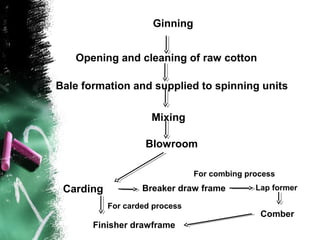
- 2. Ginning Opening and cleaning of raw cotton Bale formation and supplied to spinning units Mixing Blowroom For combing process Carding Breaker draw frame Lap former For carded process Comber Finisher drawframe
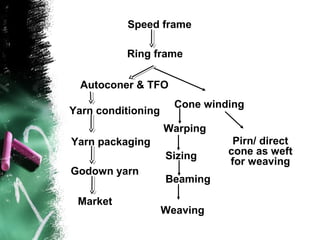
- 3. Speed frame Ring frame Autoconer & TFO Cone winding Yarn conditioning Warping Yarn packaging Pirn/ direct Sizing cone as weft for weaving Godown yarn Beaming Market Weaving
- 4. Ginning ŌĆó Ginning is the separation of seed from seed cotton ŌĆó Recovery of clean lint. The process requires a dryer, a gin saw or some other type of separation devices. ŌĆó The clean lint is then compacted and tied with a bale wrap. ŌĆó It is finally weighed and stored.
- 5. Opening and Cleaning of Raw Cotton ŌĆó The object of this process is to blend cotton so as to obtain uniform raw material, remove leaf dirt and fresh, open up the fibres after they have been compressed in the bale ŌĆó To deliver a clean uniform product in a suitable form to the nextstage.
- 6. Blow room ŌĆó The blow room machinery performs function of opening hard pressed bales of cotton and cleaning the cotton of impurities
- 7. Carding ŌĆó In carding, the lap is attenuated into a sliver (about 100 draft) ŌĆó The fibres made parallel for the next stage.
- 8. Drawing ŌĆó Drawing evens the sliver. ŌĆó It attenuate the sliver to desired count ŌĆó Doubling reduces mass CV
- 9. Roving ŌĆó Roving further attenuates the sliver to above 7 draft. ŌĆó It makes the sliver useful to make yarn
- 10. Spinning ŌĆó There are two main types of spinning: ring spinning and open-end or break spinning. ŌĆó In ring spinning the roving is further attenuated by roller drafting to the fineness of the yarn required, usually a draft of about 20 ŌĆó and at the sametime twist is applied to give the yarn the necessary strength. ŌĆó Full bobbins may be manually or automatically doffed.
- 11. Cone winding ŌĆó Cone winding facilitates subsequent processing by rewinding yarn onto a large package ŌĆó and removing faults.
- 13. Weaving technology covers: ŌĆó ¶Ćü║ Preparatory Weaving process ŌĆó ¶Ćü║ Types of Yarn Packages ŌĆó ¶Ćü║ Yarn Winding ŌĆó ¶Ćü║ Winding Machines ŌĆó ¶Ćü║ Warp Preparation ŌĆó ¶Ćü║ Weaving as a Fabric Formation Process ŌĆó ¶Ćü║ Weaving Operations ŌĆó ¶Ćü║ Picking Mechanisms
- 14. Preparatory Weaving Processes ¶Ćü║ Yarn Preparation ¶Ćü║ Warp preparation ¶Ćü║ Warp Installation ¶Ćü║ Weft Preparation
- 15. TYPE OF CONE
- 16. Warping ŌĆó To make bigger package to supply warp yarn ŌĆó Yarn with uniform tension
- 17. Sizing ŌĆó The purpose of sizing to increase weaving resistance ŌĆó Resistance against abrasion
- 18. Drawing in ŌĆó The drawing-in of the sized warp threads through the heddles, reeds and drop-wires of the loom ŌĆó May be done either manually by a pair of workers
- 19. Weaving ŌĆó Interlace between two sets of yarn ŌĆó Weaving is the crossing of yarns at right angles or strips of other materials to produce a flat, more or less compact surface.
- 20. Woven fabrics
- 22. Woven structures Plain weave
- 23. Woven structures Twill weave Twill weave, the secondbasic weave, is characterized by diagonal lines running at angles varying between 15┬░ and 75┬░. A twill weave is denoted by using numbers above and bellow a line (such as 2/1 twill which may be interpreted as two up and one down in the shedding sequence).
- 24. Woven structure Satin and Sateen weave Sateen weave is the third basic weave, in which the interlacing points are arranged in a similar way to twill weaves but without showing the twill line. The satin weave is warp face weave and the sateen is a filling face weave. Fig. Shows 5 ends (Harness) satin. In this case, the repeat is on 5 ends x 5 picks.
- 25. Selvages