YCIS_Forensic_Image Enhancement and Edge detection.pptx
- 1. Part 2: Digital Image Processing using Python :Image Enhancement and Edge detection Dr. Sharmila S. More Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science MIT Art's Commerce and Science College Alandi (D),Pune-15
- 2. Topics to be Covered¡ Image Enhancement and Edge detection Python How are we using Python in DIP
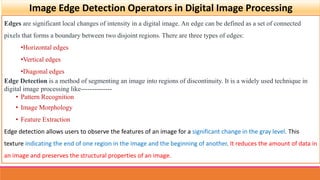
- 3. Image Edge Detection Operators in Digital Image Processing Edges are significant local changes of intensity in a digital image. An edge can be defined as a set of connected pixels that forms a boundary between two disjoint regions. There are three types of edges: ?Horizontal edges ?Vertical edges ?Diagonal edges Edge Detection is a method of segmenting an image into regions of discontinuity. It is a widely used technique in digital image processing like-------------- ? Pattern Recognition ? Image Morphology ? Feature Extraction Edge detection allows users to observe the features of an image for a significant change in the gray level. This texture indicating the end of one region in the image and the beginning of another. It reduces the amount of data in an image and preserves the structural properties of an image.
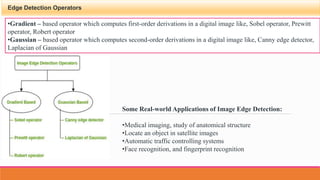
- 4. Edge Detection Operators ?Gradient ¨C based operator which computes first-order derivations in a digital image like, Sobel operator, Prewitt operator, Robert operator ?Gaussian ¨C based operator which computes second-order derivations in a digital image like, Canny edge detector, Laplacian of Gaussian Some Real-world Applications of Image Edge Detection: ?Medical imaging, study of anatomical structure ?Locate an object in satellite images ?Automatic traffic controlling systems ?Face recognition, and fingerprint recognition
- 5. Sobel Operator: It is a discrete differentiation operator. It computes the gradient approximation of image intensity function for image edge detection. At the pixels of an image, the Sobel operator produces either the normal to a vector or the corresponding gradient vector. It uses two 3 x 3 kernels or masks which are convolved with the input image to calculate the vertical and horizontal derivative approximations respectively ¨C Advantages: 1.Simple and time efficient computation 2.Very easy at searching for smooth edges Limitations: 1.Diagonal direction points are not preserved always 2.Highly sensitive to noise 3.Not very accurate in edge detection 4.Detect with thick and rough edges does not give appropriate results
- 6. Prewitt Operator: This operator is almost similar to the sobel operator. It also detects vertical and horizontal edges of an image. It is one of the best ways to detect the orientation and magnitude of an image. It uses the kernels or masks ¨C Advantages: 1.Good performance on detecting vertical and horizontal edges 2.Best operator to detect the orientation of an image Limitations: 1.The magnitude of coefficient is fixed and cannot be changed 2.Diagonal direction points are not preserved always
- 7. Marr-Hildreth Operator or Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG): It is a gaussian-based operator which uses the Laplacian to take the second derivative of an image. This really works well when the transition of the grey level seems to be abrupt. It works on the zero-crossing method i.e when the second-order derivative crosses zero, then that particular location corresponds to a maximum level. It is called an edge location. Here the Gaussian operator reduces the noise and the Laplacian operator detects the sharp edges. The Gaussian function is defined by the formula: Advantages: Easy to detect edges and their various orientations 1.There is fixed characteristics in all directions Limitations: 1.Very sensitive to noise 2.The localization error may be severe at curved edges 3.It generates noisy responses that do not correspond to edges, so-called ¡°false edges¡±
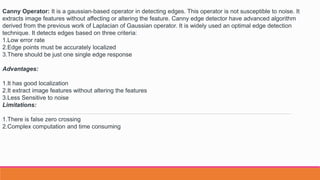
- 8. Canny Operator: It is a gaussian-based operator in detecting edges. This operator is not susceptible to noise. It extracts image features without affecting or altering the feature. Canny edge detector have advanced algorithm derived from the previous work of Laplacian of Gaussian operator. It is widely used an optimal edge detection technique. It detects edges based on three criteria: 1.Low error rate 2.Edge points must be accurately localized 3.There should be just one single edge response Advantages: 1.It has good localization 2.It extract image features without altering the features 3.Less Sensitive to noise Limitations: 1.There is false zero crossing 2.Complex computation and time consuming
- 9. THANK YOU