Year 10 ict computing essentials
- 2. Operating Systems • Operating System is a program that controls the computer and enables it to run applications software. It allows the computer to manage its internal resources. • Allows the computer system to manage its own resources (disks, monitor, keyboard, and printer). • It runs the basic computer operations - it tells the hardware what to do and how, and when to do it. Applications software cannot run without system software. • Common desktop operating system software includes: • MS Windows – provides an easy interface between the computer and the user. It uses pictures (graphical representations) which look like push buttons on the screen and you can use the mouse to press them. This interface is known as a Graphical User Interface (GUI). • MS Windows comes in a variety of versions. It has been updated over the years to make it more powerful and easier to use. • Macintosh Operating System (Mac OS) – is the standard operating for Apple Corporation’s Macintosh computers. Like Windows, the MAC OS has a GUI interface. • Linux • Unix • OS/2 Warp • Tablets and smartphones also include operating systems that provide a GUI and can run applications (Android, iOS (for iPads & iPhones), and Windows Phone). These operating systems are developed specifically for portable devices and therefore are designed around touchscreen input. • •
- 3. Operating Systems •Applications software are programs that help the user carry out specific tasks on the computer. •Application software falls into two categories: •Tailor-made (or custom-written) software •Off-the-Shelf (or packaged) software
- 4. Operating Systems • Off-the-shelf software includes: • Word-processing programs (e.g. MS Word, Writer) – used to prepare text-based documents such as letters, memos, reports etc. • • Spreadsheet programs (e.g. MS Excel, Calc) – used to analyse and summarise numerical data. Spreadsheets are commonly used in accounting environments to prepare balance sheets and financial reports. • • Database programs (e.g. MS Access, Base) – used to organise and manage large quantities of data. Databases enable efficient manipulation of data. • • Presentation graphics programs (e.g. MS PowerPoint, Impress) – used to organise text and numeric data in an appropriate format to be displayed to a group of people. Typically presentations are used in the preparation of on-screen displays, overhead transparencies and 35mm slides. •
- 5. Operating Systems • Photoediting programs (e.g. MS PhotoEditor, Adobe PhotoShop, GIMP) – used to alter images and graphics. These programs are used to change the size of pictures, crop pictures, adjust the colours of pictures etc. • Desktop publishing programs (e.g. MS Publisher, Adobe InDesign) – used to prepare high quality printed material e.g. flyers, invitations, posters, reports, magazines, and books. • Internet Web Browsers (e.g. MS Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Opera) – used to locate and display information at Web sites. Browsers display Web pages with text, graphics, sounds and video-clips. • Communications software (e.g. MS Outlook, Mozilla Thunderbird) – used for the transmission of electronic messages or documents between different computers. • Social Networking websites (e.g. Facebook, LinkedIn) – allow users to be part of a virtual community. These websites provide users with simple tools to create a custom profile with text and pictures. A typical profile includes basic information about the user, photo albums, videos and comments published by the user. People use social networking sites to add friends, send messages to other users, and leave comments directly on friends' profiles. Some people join special interest groups on social networking sites. • Mobile applications (or mobile apps) – are software programs designed to run on smartphones, tablets and other mobile devices. These programs are usually available through application distribution platforms (e.g. Apple App Store, Google Play, Windows Phone Store etc.). Some mobile apps are free, while others must be bought. Mobile apps include email, calendar, contacts, weather information, location based services, banking, order-tracking and ticket purchases. •
- 6. Internet Research - Software •End-User Licence Agreement •Software Licences: •Proprietary software •Open source •Trial version •Shareware •Freeware
- 8. Purposes of a network
- 9. Data Transfer Rate • How fast data is transferred from one location to another • • Data is transmitted in characters or collections of bits. The transmission speed of data is measured in: • bps – stands for bits per second. 8 bits = 1 character kbps – 1000 bits per second • mbps – 1,000,000 bits per second • gbps – 1,000,000,000 bits per second.
- 10. Internet Connections • Dialup connection • Broadband connection • ADSL • Cable broadband • Wi-Fi • WiMax • Mobile phone • Satellite broadband
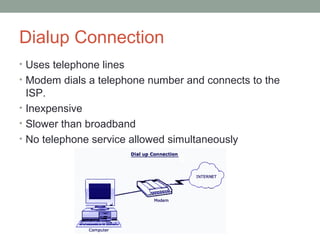
- 11. Dialup Connection • Uses telephone lines • Modem dials a telephone number and connects to the ISP. • Inexpensive • Slower than broadband • No telephone service allowed simultaneously
- 12. Broadband connection • Permanent connection to the internet • Computer is more prone to hacking • Flat-rate monthly fee • Fast data transfer between computers connected to the internet
- 13. ADSL (Asynchronous Digital Subscriber Line) •Uses a modem and a telephone line to connect to the internet •The telephone line can be used simultaneously •Faster than dial-up connection •Downloading is faster than outgoing data
- 14. Cable broadband • Uses a modem and the cabling infrastructure used for cable TV • The cable modem connects to the computer via a local area network (LAN) • Incoming data (downloading) is significantly faster than outgoing data (uploading). • The cost of a cable connection is similar to an ADSL connection.
- 15. Wi-Fi •Uses radio transmitters and receivers to link computers •Public areas provide wireless local area network hotspots •Many smart phones support wireless connectivity
- 16. WiMax • A wireless communications standard similar to Wi-Fi, but supports a far greater range of coverage • WiMAX station can cover a range of up to 50km Satellite broadband • An Internet connection that requires the installation of a special satellite dish.
- 17. Protected & Open Wireless Network • Wireless networks appear only if your laptop has a wireless network adapter and driver installed and the adapter is enabled. • Protected/secure or open • Wireless networks that do not have security enabled (i.e. open networks) will be identified with a yellow shield icon.
- 18. Password policies • At least 6 characters long • It should consist of both upper and lower case letters and also one or more numbers • Date of birth, phone number and words found in dictionaries do not constitute a good password • Passwords should be changed regularly
- 19. Firewall • A system designed to prevent unauthorised access to your computer system when connected to Internet •Filters information coming through the Internet connection • If an incoming packet of information is flagged by the filters, it is not allowed through
- 20. Backing Up Data •Copying of data files to a secondary storage medium as a precaution in case the first medium fails. •Regularly • At least two backups • Off-site storage •Special-purpose backup utility program