Zigbee Technology
Download as PPTX, PDF2 likes298 views
Technological Standard Created for Control and Sensor Networks Based on the IEEE 802.15.4 Standard High level Communication Operates in Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) and Device-to-Device networks
1 of 23
Downloaded 12 times






















Recommended
Zigbee technology ppt edited



Zigbee technology ppt editedrakeshkumarchary
?
ZigBee is a wireless networking standard focused on low-cost, low-power consumption devices for monitoring and control applications. It uses the IEEE 802.15.4 standard for the physical and MAC layers and provides data rates from 20-250kbps depending on frequency band. ZigBee networks can support hundreds of devices with flexible star, peer-to-peer, or cluster tree topologies and address devices using short or IEEE addresses. The technology is well-suited for wireless control in industrial, commercial, and home automation applications where low data rates and power usage are priorities.Zigbee



ZigbeeWaqarAhmad444
?
What is Zigbee?
this presentation is based on Zigbee
this presentation contains what is zigbee how it works what are their types for what is used how it works introducton contains all the things along with the diagram of zigbee this presentation is very easily understandable..
zigbee architectture is involved
the application of zigbee
the advantages of zigbee
the conclusion of zigbee
it is very helpful for the projects based on home automation security purposes industrial automation... so go through it contains all details about zigbeeZigbee technology



Zigbee technologySrujana Aryasomayajula
?
ZigBee is a wireless technology designed for low-power, short-range communication in personal area networks. It operates on various frequency bands globally. The document discusses ZigBee technology, including its architecture, protocol stack, topologies, algorithms, applications, and future scope. ZigBee aims to provide a low-cost, low-power wireless solution for monitoring and control applications.ZIGBEE TECHNOLOGY ppt



ZIGBEE TECHNOLOGY pptOECLIB Odisha Electronics Control Library
?
The document discusses Zigbee technology, including its history, device types, how it works, uses and future. Zigbee is a wireless technology standard designed for control and sensor networks. It was created by the Zigbee Alliance based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard for low-power wireless networks. Zigbee networks consist of coordinator, router and end devices and can operate using star, tree or mesh topologies to connect small, low-power digital radios. Common applications of Zigbee include home automation, lighting and appliance control.zigbee technology



zigbee technologyDeep Hundal
?
Zigbee is a wireless technology standard used for sensor and control networks. It operates on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard using mesh networking topologies to transmit data over long distances with low power consumption. Zigbee networks consist of coordinator, router, and end devices and are used in applications that require long battery life, security, low data rates and cost such as lighting, HVAC and sensors. Research continues to expand Zigbee's capabilities for use in more devices and markets going forward.ZigBee Technology



ZigBee TechnologyIbrahim Kazanci
?
ZigBee is an IEEE 802.15.4-based specification for personal area networks that uses low power wireless transmissions between devices. It was standardized in 2003 and revised in 2006. ZigBee networks can support up to 65,000 nodes and consume very low amounts of battery power. Common applications of ZigBee include wireless sensor networks, home automation and control, and medical data collection.Zigbee ppt



Zigbee pptPranjul Rastogi
?
Zigbee is a specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols used to create personal area networks from small, low-power digital radios. It operates on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and provides data rates of 250 kbps, 40 kbps, and 20 kbps in different frequency bands. Zigbee devices can transmit data over long distances by passing through a mesh network and has a range of 10-100 meters. The technology targets applications requiring low data transfer rates and long battery life and is often used in industrial automation and home automation through devices like door locks and security sensors.Zigbee ppt



Zigbee pptkondalarao7
?
ZigBee is a wireless networking standard used for control and sensor applications that requires low data rates, low power consumption, and secure networking. It is based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and allows for up to 65,000 nodes to connect in a mesh network topology. ZigBee operates in the 2.4GHz, 868MHz, and 915MHz frequency bands and is designed for use in personal area networks for applications like home automation, lighting control, and wireless sensor networks. Research is ongoing to expand ZigBee's uses in fields like wireless communications and neuroengineering.ZigBee Technology



ZigBee TechnologyNimi T
?
The document introduces ZigBee, a wireless technology standard used for sensor and control networks. ZigBee offers low-cost, low-power wireless connectivity for devices. It uses the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and is intended for applications that require long battery life and secure networking. ZigBee supports mesh networking and can connect thousands of devices together over distances of up to 100 meters. Common applications of ZigBee include wireless light switches, HVAC controls, and other smart home and industrial IoT uses.Zigbee technology presentation



Zigbee technology presentationShamaShaik7
?
Zigbee is a wireless technology standard created for low-power wireless networks. It operates on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and was created by the Zigbee Alliance to define standards for monitoring and control products. Zigbee networks can include thousands of nodes that operate for years on small batteries. It uses low data rates and mesh networking to transmit data over long ranges through multiple connected devices. Common applications of Zigbee technology include wireless light switches, HVAC controls, and sensor networks for utilities and smart homes.zigbee full ppt



zigbee full pptranjitha mudhiraj
?
The document discusses Zigbee, a wireless networking standard based on IEEE 802.15.4. Some key points include:
- Zigbee allows for low-power wireless networks at data rates up to 250 kbps using the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
- It supports mesh networking topologies and can have thousands of nodes with extremely low duty cycles and long battery life.
- Zigbee networks operate using CSMA-CA channel access and can operate in beacon-enabled or non-beacon modes.ZigBee Technology PPT 2.pdf



ZigBee Technology PPT 2.pdfP0608VikasSontakke
?
ZigBee is a wireless networking technology built on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard designed for low-power devices. It enables reliable, cost-effective networks for applications that require low data rates, long battery life, and secure networking. ZigBee is ideal for remote control and automation applications due to its low power consumption and long battery life. The technology uses small, low-power digital radios based on IEEE 802.15.4 and allows self-healing networks to be formed from transceivers. ZigBee networks are secured with 128-bit AES encryption and can connect thousands of devices together wirelessly.Introduction to zigbee



Introduction to zigbeeAmit Dixit
?
ZigBee is a wireless technology standard created for low-power wireless networks. It uses small, low-power digital radios to transmit data over short distances. ZigBee networks are commonly used in wireless control and monitoring applications that require long battery life, such as home automation and industrial control systems. ZigBee operates on open global standards and has low manufacturing costs, making it suitable for a wide range of wireless control and monitoring applications.Zigbee technology ppt



Zigbee technology pptijaranjani
?
A wireless technological device which is popular for extremely low power, and low bit rate wireless PAN technology called Ą°zigBeeĄą.
Zigbee Presentation



Zigbee PresentationMaathu Michael
?
zigbee is a new wireless technolgy Designed for low power consumption allowing batteries to essentially last for ever....
Zigbee abstract



Zigbee abstractKadaSuraj
?
Zigbee is a low power wireless technology standard developed as a specification based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. It was accepted by the Zigbee Alliance, a consortium of over 300 companies, in 2004. Zigbee devices can transmit data over longer distances by passing data through a mesh network of intermediate devices to reach more distant ones without a centralized controller. The technology is intended to be simpler and less expensive than other wireless standards like Bluetooth.Zigbee technology [autosaved]![Zigbee technology [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zigbeetechnologyautosaved-140716030459-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Zigbee technology [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zigbeetechnologyautosaved-140716030459-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Zigbee technology [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zigbeetechnologyautosaved-140716030459-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Zigbee technology [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zigbeetechnologyautosaved-140716030459-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Zigbee technology [autosaved]vandjadhav
?
This seminar report provides an overview of ZigBee technology. It defines ZigBee as a wireless networking standard intended for low-power devices. The report outlines ZigBee's key characteristics including low cost, low power consumption, mesh networking topology, and built-in security. It also describes ZigBee's protocol stack and compares it to other wireless technologies like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. Common applications of ZigBee technology include home automation, wireless sensor networks, and industrial control.5 g technology



5 g technologyKaran Poshattiwar
?
This document provides an overview of 5G wireless technology. It discusses how 5G represents the next major phase in mobile telecommunications, offering speeds up to 1 Gbps which is 10 times faster than 4G. The presentation covers the evolution from 1G to 5G networks, the key architecture and hardware/software components of 5G including open wireless architecture and open transport protocol. It also outlines some of the main features, advantages, and applications of 5G technology.Zigbee- The Future of Data Communications



Zigbee- The Future of Data CommunicationsArkaprava Sadhu
?
Zigbee is a technological standard designed for control and sensor networks based on IEEE 802.15.4. The standard is developed and promoted by the Zigbee Alliance. Vodafone's NB-IoT Rollout



Vodafone's NB-IoT RolloutDuncan Purves
?
Vodafone's NB-IoT Rollout -?presentation by John Tuersley, ?Vodafone Group Technology at the IoT Thames Valley Meetup on 8th May, 2019.
https://www.meetup.com/Internet-of-Things-Thames-Valley/Z wave



Z waveReena Arya
?
Z-wave?is a protocol used for wireless communication mainly in?home-automation.?This protocols caters needs of residential control and automation market which effectively and smartly control lighting,?security systems.
Gifi technology full seminar report



Gifi technology full seminar reportSusheel Marati
?
GI-FI (Gigabit Fidelity) or Giga bit wireless refers to wireless communication at a data rate of more than one billion bits (gigabits) per second. GI-FI offers some advantages over WI-FI, a similar wireless technology. In that it offers faster information rate in GBPS, less power consumption and low cost for short range transmission as compare to current technology. GI-FI consists of a chip which has facility to deliver short-range multi gigabit data transfer in a local environment and compared to other technologies in the market it is ten times faster. GI-FI has the data transfer speed up to 5 GBPS within a short-range of 10 metres. It operates in 60 GHZ frequency band. GI-FI is developed on an integrated wireless transceiver chip. It has both transmitter and receiver, integrated on a single chip which is fabricated using the CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) process and it also consists of a small antenna. GI-FI allows transferring large videos, audio files, data files etc. within few seconds.LPWAN for IoT



LPWAN for IoTInfiswift Solutions
?
Overview of which LPWAN technologies (LoRa, Sigfox, Weightless, etc.) are right for various IoT applications. Clear look at the pros and cons of each technology.Zigbee technology



Zigbee technologySerma Pavi
?
ZigBee is a wireless technology standard developed for low-cost, low-power wireless networks for applications like home automation and industrial control. It uses small, low-power digital radios to form mesh networks that can self-heal and scale to thousands of devices. ZigBee networks are reliable, secure, and interoperable, allowing devices from different manufacturers to communicate. Common applications of ZigBee include smart energy, lighting controls, HVAC systems, medical devices, and more due to its ability to run for years on inexpensive batteries.WiGig PPT



WiGig PPTSeminar Links
?
WiGig or IEEE 802.11ad, uses 60GHz spectrum to reach theoretical speeds as high as 7Gbps (bits per second), over a shorter range than today's Wi-Fi technologies. That's a lot more speed: The fastest Wi-Fi system, 802.11ac, tops out at just over 1Gbps.ZIGBEE.pptx



ZIGBEE.pptxssuser04c2e3
?
Zigbee is a wireless technology standard used for low-power wireless networks. It operates on frequencies including 2.4 GHz, 900 MHz, and 868 MHz. Zigbee uses mesh networking and supports up to 65,000 devices with low data rates between 20-250 kbps. Common applications include home automation, lighting, and sensor networks. The Zigbee Alliance develops Zigbee standards and specifications.Zigbee technolgy 



Zigbee technolgy Haricharan Palakurthi
?
Zigbee is a wireless networking standard that uses low power digital radio signals to connect devices together wirelessly. It operates in the 2.4GHz, 915MHz, and 868MHz frequency bands. Zigbee networks can include full-function devices, reduced-function devices, and coordinators that route data. Devices communicate using the CSMA-CA channel access method to check for clear channels before transmitting data. Zigbee provides low power consumption, low data rates, and high security making it suitable for applications like home automation and sensor networks.Introduction of iot



Introduction of iotsandeepkraggarwal
?
The document provides an introduction to Internet of Things (IoT). It defines IoT as comprising things that have unique identities and are connected to the Internet. It notes that while many existing devices like mobile phones are already connected, the focus of IoT is on traditionally unconnected devices like thermostats and sensors being networked. Experts forecast that by 2020 there will be 50 billion devices connected to the Internet. The document then discusses various aspects of IoT including the physical and logical design, enabling technologies, communication models, and deployment templates.Zigbeepresentation



ZigbeepresentationDivya korrapati
?
It is designed for low power consumption allowing batteries to essentially last for ever
ZigBee makes possible completely networked homes where all devices are able to communicate and be controlled by a single unitZig Bee



Zig BeeVishwa Mohan
?
The document provides an overview of the ZigBee wireless protocol. It discusses that ZigBee is a low power, low cost wireless standard targeted for automation and remote control applications. It then covers ZigBee features such as mesh networking, security, reliability and interoperability. The document also summarizes the ZigBee protocol stack including the physical, MAC and network layers and different device types in ZigBee networks.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
ZigBee Technology



ZigBee TechnologyNimi T
?
The document introduces ZigBee, a wireless technology standard used for sensor and control networks. ZigBee offers low-cost, low-power wireless connectivity for devices. It uses the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and is intended for applications that require long battery life and secure networking. ZigBee supports mesh networking and can connect thousands of devices together over distances of up to 100 meters. Common applications of ZigBee include wireless light switches, HVAC controls, and other smart home and industrial IoT uses.Zigbee technology presentation



Zigbee technology presentationShamaShaik7
?
Zigbee is a wireless technology standard created for low-power wireless networks. It operates on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and was created by the Zigbee Alliance to define standards for monitoring and control products. Zigbee networks can include thousands of nodes that operate for years on small batteries. It uses low data rates and mesh networking to transmit data over long ranges through multiple connected devices. Common applications of Zigbee technology include wireless light switches, HVAC controls, and sensor networks for utilities and smart homes.zigbee full ppt



zigbee full pptranjitha mudhiraj
?
The document discusses Zigbee, a wireless networking standard based on IEEE 802.15.4. Some key points include:
- Zigbee allows for low-power wireless networks at data rates up to 250 kbps using the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
- It supports mesh networking topologies and can have thousands of nodes with extremely low duty cycles and long battery life.
- Zigbee networks operate using CSMA-CA channel access and can operate in beacon-enabled or non-beacon modes.ZigBee Technology PPT 2.pdf



ZigBee Technology PPT 2.pdfP0608VikasSontakke
?
ZigBee is a wireless networking technology built on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard designed for low-power devices. It enables reliable, cost-effective networks for applications that require low data rates, long battery life, and secure networking. ZigBee is ideal for remote control and automation applications due to its low power consumption and long battery life. The technology uses small, low-power digital radios based on IEEE 802.15.4 and allows self-healing networks to be formed from transceivers. ZigBee networks are secured with 128-bit AES encryption and can connect thousands of devices together wirelessly.Introduction to zigbee



Introduction to zigbeeAmit Dixit
?
ZigBee is a wireless technology standard created for low-power wireless networks. It uses small, low-power digital radios to transmit data over short distances. ZigBee networks are commonly used in wireless control and monitoring applications that require long battery life, such as home automation and industrial control systems. ZigBee operates on open global standards and has low manufacturing costs, making it suitable for a wide range of wireless control and monitoring applications.Zigbee technology ppt



Zigbee technology pptijaranjani
?
A wireless technological device which is popular for extremely low power, and low bit rate wireless PAN technology called Ą°zigBeeĄą.
Zigbee Presentation



Zigbee PresentationMaathu Michael
?
zigbee is a new wireless technolgy Designed for low power consumption allowing batteries to essentially last for ever....
Zigbee abstract



Zigbee abstractKadaSuraj
?
Zigbee is a low power wireless technology standard developed as a specification based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. It was accepted by the Zigbee Alliance, a consortium of over 300 companies, in 2004. Zigbee devices can transmit data over longer distances by passing data through a mesh network of intermediate devices to reach more distant ones without a centralized controller. The technology is intended to be simpler and less expensive than other wireless standards like Bluetooth.Zigbee technology [autosaved]![Zigbee technology [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zigbeetechnologyautosaved-140716030459-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Zigbee technology [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zigbeetechnologyautosaved-140716030459-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Zigbee technology [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zigbeetechnologyautosaved-140716030459-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Zigbee technology [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/zigbeetechnologyautosaved-140716030459-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Zigbee technology [autosaved]vandjadhav
?
This seminar report provides an overview of ZigBee technology. It defines ZigBee as a wireless networking standard intended for low-power devices. The report outlines ZigBee's key characteristics including low cost, low power consumption, mesh networking topology, and built-in security. It also describes ZigBee's protocol stack and compares it to other wireless technologies like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. Common applications of ZigBee technology include home automation, wireless sensor networks, and industrial control.5 g technology



5 g technologyKaran Poshattiwar
?
This document provides an overview of 5G wireless technology. It discusses how 5G represents the next major phase in mobile telecommunications, offering speeds up to 1 Gbps which is 10 times faster than 4G. The presentation covers the evolution from 1G to 5G networks, the key architecture and hardware/software components of 5G including open wireless architecture and open transport protocol. It also outlines some of the main features, advantages, and applications of 5G technology.Zigbee- The Future of Data Communications



Zigbee- The Future of Data CommunicationsArkaprava Sadhu
?
Zigbee is a technological standard designed for control and sensor networks based on IEEE 802.15.4. The standard is developed and promoted by the Zigbee Alliance. Vodafone's NB-IoT Rollout



Vodafone's NB-IoT RolloutDuncan Purves
?
Vodafone's NB-IoT Rollout -?presentation by John Tuersley, ?Vodafone Group Technology at the IoT Thames Valley Meetup on 8th May, 2019.
https://www.meetup.com/Internet-of-Things-Thames-Valley/Z wave



Z waveReena Arya
?
Z-wave?is a protocol used for wireless communication mainly in?home-automation.?This protocols caters needs of residential control and automation market which effectively and smartly control lighting,?security systems.
Gifi technology full seminar report



Gifi technology full seminar reportSusheel Marati
?
GI-FI (Gigabit Fidelity) or Giga bit wireless refers to wireless communication at a data rate of more than one billion bits (gigabits) per second. GI-FI offers some advantages over WI-FI, a similar wireless technology. In that it offers faster information rate in GBPS, less power consumption and low cost for short range transmission as compare to current technology. GI-FI consists of a chip which has facility to deliver short-range multi gigabit data transfer in a local environment and compared to other technologies in the market it is ten times faster. GI-FI has the data transfer speed up to 5 GBPS within a short-range of 10 metres. It operates in 60 GHZ frequency band. GI-FI is developed on an integrated wireless transceiver chip. It has both transmitter and receiver, integrated on a single chip which is fabricated using the CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) process and it also consists of a small antenna. GI-FI allows transferring large videos, audio files, data files etc. within few seconds.LPWAN for IoT



LPWAN for IoTInfiswift Solutions
?
Overview of which LPWAN technologies (LoRa, Sigfox, Weightless, etc.) are right for various IoT applications. Clear look at the pros and cons of each technology.Zigbee technology



Zigbee technologySerma Pavi
?
ZigBee is a wireless technology standard developed for low-cost, low-power wireless networks for applications like home automation and industrial control. It uses small, low-power digital radios to form mesh networks that can self-heal and scale to thousands of devices. ZigBee networks are reliable, secure, and interoperable, allowing devices from different manufacturers to communicate. Common applications of ZigBee include smart energy, lighting controls, HVAC systems, medical devices, and more due to its ability to run for years on inexpensive batteries.WiGig PPT



WiGig PPTSeminar Links
?
WiGig or IEEE 802.11ad, uses 60GHz spectrum to reach theoretical speeds as high as 7Gbps (bits per second), over a shorter range than today's Wi-Fi technologies. That's a lot more speed: The fastest Wi-Fi system, 802.11ac, tops out at just over 1Gbps.ZIGBEE.pptx



ZIGBEE.pptxssuser04c2e3
?
Zigbee is a wireless technology standard used for low-power wireless networks. It operates on frequencies including 2.4 GHz, 900 MHz, and 868 MHz. Zigbee uses mesh networking and supports up to 65,000 devices with low data rates between 20-250 kbps. Common applications include home automation, lighting, and sensor networks. The Zigbee Alliance develops Zigbee standards and specifications.Zigbee technolgy 



Zigbee technolgy Haricharan Palakurthi
?
Zigbee is a wireless networking standard that uses low power digital radio signals to connect devices together wirelessly. It operates in the 2.4GHz, 915MHz, and 868MHz frequency bands. Zigbee networks can include full-function devices, reduced-function devices, and coordinators that route data. Devices communicate using the CSMA-CA channel access method to check for clear channels before transmitting data. Zigbee provides low power consumption, low data rates, and high security making it suitable for applications like home automation and sensor networks.Introduction of iot



Introduction of iotsandeepkraggarwal
?
The document provides an introduction to Internet of Things (IoT). It defines IoT as comprising things that have unique identities and are connected to the Internet. It notes that while many existing devices like mobile phones are already connected, the focus of IoT is on traditionally unconnected devices like thermostats and sensors being networked. Experts forecast that by 2020 there will be 50 billion devices connected to the Internet. The document then discusses various aspects of IoT including the physical and logical design, enabling technologies, communication models, and deployment templates.Similar to Zigbee Technology (20)
Zigbeepresentation



ZigbeepresentationDivya korrapati
?
It is designed for low power consumption allowing batteries to essentially last for ever
ZigBee makes possible completely networked homes where all devices are able to communicate and be controlled by a single unitZig Bee



Zig BeeVishwa Mohan
?
The document provides an overview of the ZigBee wireless protocol. It discusses that ZigBee is a low power, low cost wireless standard targeted for automation and remote control applications. It then covers ZigBee features such as mesh networking, security, reliability and interoperability. The document also summarizes the ZigBee protocol stack including the physical, MAC and network layers and different device types in ZigBee networks.The Differences of between ZigBee and Bluetooth technologies



The Differences of between ZigBee and Bluetooth technologiesCan KAYA
?
ZigBee and Bluetooth are wireless network technologies but they have key differences. ZigBee is intended for low data rate, long battery life applications like sensor networks and home automation. It has a range of 10-100m, very low power consumption, supports large networks, and a long battery life. Bluetooth is intended for cable replacement between devices like phones, laptops, and headsets within 10m. It has higher data rates but also higher power consumption and shorter battery life than ZigBee.Techincal Seminar.pptx



Techincal Seminar.pptxPAVANguests
?
The document provides an overview of Zigbee technology. It discusses that Zigbee is a wireless technology standard developed for low-cost, low-power networks including machine-to-machine and internet of things applications. The document outlines the history of Zigbee's development, describes the different device types in Zigbee networks, and explains how Zigbee networks function in terms of topology, protocol layers, and device roles. It also reviews the advantages of Zigbee such as low data rates and power consumption as well as future projections for widespread adoption in home automation and other applications.Wireless standards 



Wireless standards Ajay Suresh
?
This document provides an overview of Bluetooth and Zigbee wireless technologies. It discusses Bluetooth standards, classes, software, and applications. Bluetooth was developed in 1994 and operates at 2.45GHz using frequency hopping. Zigbee was created for low-power wireless sensor and control networks. It has a layered architecture based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and supports three device types: coordinator, full function device, and reduced function device. The document compares Zigbee to Bluetooth and other wireless protocols, outlines Zigbee characteristics and applications, and concludes that Zigbee will likely be the basis for future home networking solutions.Zigbee technology2



Zigbee technology2Presentaionslive.blogspot.com
?
Zigbee is a wireless networking standard used for low-power digital radios in personal area networks. It uses small, low-power digital radios designed for use in wireless sensor and control networks. Zigbee devices include coordinators, routers, and end devices. Coordinators manage the network, routers relay data, and end devices can only communicate with their parent node. Zigbee uses mesh networking topologies to allow for redundancy and multiple communication paths. Its software architecture is built on top of the IEEE 802.15.4 standard and includes network, application, and device object layers. Zigbee networks are initialized by coordinators searching for channels and assigning PAN IDs to start the network for other devicesMain document



Main documentN.CH Karthik
?
ZigBee is a wireless communication standard that uses small, low-power digital radios to transmit data over short distances. It is intended to be simpler and cheaper than other wireless personal area network (WPAN) technologies like Bluetooth. The ZigBee standard defines protocols for sensing, monitoring and control applications that require transmission of small data packets over longer battery life and secure networking. The document discusses ZigBee's low-power and low-cost characteristics that make it suitable for wireless sensor networks. It also describes ZigBee's network topologies, frame structure, security features and other technical specifications.ZIGBEE TRANSMITTER FOR IOT WIRELESS DEVICES



ZIGBEE TRANSMITTER FOR IOT WIRELESS DEVICESVLSICS Design
?
The rapid development in wireless networking has been witnessed in past several years, which aimed on high speed and long range applications. There are different protocol standards used for the short range wireless communication namely the Bluetooth, ZigBee, Wimax and Wi-Fi. Among these standards ZigBee is based on IEEE 802.15.4 protocol can meet a wider variety of real industrial needs due to its long-term battery operation and reliability of the mesh networking architecture. The increasing demand for low data rate and low power networking led to the development of ZigBee technology. This technology was developed for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPAN), directed at control and military applications, where low cost, low data rate, and more battery life were main requirements. This paper presents VerilogHDL simulation of the Top level module (Cyclic Redundancy Check, Bit-to-Symbol block, Symbol-to-Chip block, OQPSK block and Pulse shaping) of the ZigBee transmitter for IoT applications.Zigbee Transmitter for IoT Wireless Devices



Zigbee Transmitter for IoT Wireless DevicesVLSICS Design
?
This document describes the design and implementation of a ZigBee transmitter for Internet of Things applications. It discusses the various components of the ZigBee transmitter including the cyclic redundancy check block, bit-to-symbol block, symbol-to-chip block, offset quadrature phase shift keying modulator, and pulse shaping block. It also provides details on the medium access control layer frame format and physical layer specifications that are used in the ZigBee transmitter design. The design is implemented in Verilog HDL and simulates the top level modules of the ZigBee transmitter.CSE-Zigbee-ppt.pptx



CSE-Zigbee-ppt.pptxguruprasad605534
?
This document provides an overview of zigbee technology. It discusses the history and introduction of zigbee, the different device types in a zigbee network including coordinators, routers, and end devices. It describes how zigbee works using different topologies like star, tree, and mesh. It discusses the layers of zigbee including the physical, MAC, and network/application support layers. Examples are given of uses in home automation, smart metering, and smart grids. The conclusion states that zigbee is well-suited for low data rate, low power wireless applications and will continue growing in the future for uses in homes and industries.6-IoT protocol.pptx



6-IoT protocol.pptxPratik Gohel
?
The document discusses several key protocols used in IoT applications:
1. Bluetooth, Zigbee, WirelessHART and Z-Wave are discussed as short-range wireless protocols suitable for personal area networks.
2. Long-range wide area network protocols discussed include LoRaWAN, LTE-M and NB-IoT which are designed for low-power wide area networks supporting millions of devices over large areas.
3. IEEE 802.11ah is presented as an alternative for energy-efficient WiFi designed for IoT applications in the sub-1GHz spectrum to provide longer range than typical WiFi.Zigbee



ZigbeeGuruprasad816984
?
Zigbee is a wireless communication standard used for home automation and industrial applications. It allows for low-cost, low-power wireless mesh networks that can connect various electronics like lighting, HVAC, sensors and more. There are three device types in Zigbee - coordinators, routers and end devices. Zigbee uses star, tree and mesh topologies to connect devices in a network. It operates in the 2.4GHz band and uses low power for long battery life, making it suitable for wireless control and sensor applications. Zigbee is expected to be widely used for home automation, smart metering and smart grid applications in the future.053744r00 Zb Mwg 2005 09 11 Zig Bee Alliance Tutorial 



053744r00 Zb Mwg 2005 09 11 Zig Bee Alliance Tutorial voracle
?
The document discusses ZigBee, a wireless technology standard focused on low-power wireless networks. It provides an overview of ZigBee capabilities including its ability to form large mesh networks of thousands of devices with long battery life. Applications discussed include home automation, industrial controls, and asset tracking where ZigBee's low-power and low-cost features are beneficial. The ZigBee Alliance aims to promote interoperability through standardization and certification.IoT _protocols.ppt



IoT _protocols.pptrohitbansal761378
?
The document discusses several Internet of Things (IoT) data link protocols, including IEEE 802.15.4, WirelessHART, Z-Wave, Bluetooth Low Energy, Zigbee Smart Energy, DASH7, LTE-A, LoRaWAN, and DECT/ULE. It provides details on their network architectures, medium access control methods, and suitability for various IoT applications.Wireless notice board using zigbee



Wireless notice board using zigbeeAvinash Reddy Penugonda
?
This document describes a wireless notice board project using ZigBee technology. The system uses an AT89S52 microcontroller interfaced with an LCD, Max232 for RS-232 communication, and ZigBee modules. Power is supplied through a transformer, rectifier, and voltage regulator. Software includes Keil C51 and XCTU. Applications include information display in public places. Improvements could include adding more receivers, LED displays, and multi-lingual support. The project aims to automate notice distribution wirelessly.Characteristics of the 6 wireless protocols



Characteristics of the 6 wireless protocolsAntenna Manufacturer Coco
?
After the read, you will learn the characteristics of the 6 wireless protocols IEEE protocols: LoRa, NB-IoT, ZigBee, Wi-Fi, BLE, WiMax.
In the field of IoT, a wide range of communication technologies wireless protocols exist simultaneously. In terms of transmission distance, there are BLE, WI-FI, ZigBee, sub1G, etc., which are widely used in the context of local wireless networks, such as wearable, home, and enterprise applications.
ZigBee technology.pptx



ZigBee technology.pptxAjaySahre
?
ZigBee is a wireless networking technology built on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard designed for low-power wireless networks. It was created to satisfy the need for an inexpensive, low-power, reliable, and secure wireless standard for monitoring and control applications. The ZigBee Alliance develops the ZigBee standard and its applications. ZigBee operates on three frequency bands and uses CSMA-CA to reduce interference. There are three device types - coordinator, router, and end device. ZigBee supports star, mesh, and peer-to-peer topologies and is well-suited for wireless sensor networks due to its low power consumption.ZIG BEE PRESENTATION..pptx



ZIG BEE PRESENTATION..pptxRayateAbhay
?
This document provides an overview of Zigbee wireless technology. It discusses that Zigbee is an open global standard for wireless personal area networks designed for low data rate, low power consumption applications. It then covers the objectives, literature survey, how Zigbee works including topology, layers and block diagram. The advantages are listed as long battery life, remote management capabilities. Limitations include lack of security and cost of replacement. Applications discussed are home automation, wireless sensor networks, industrial control and medical data collection. The conclusion states there is increasing demand for Zigbee applications and it provides low power specifications for wireless devices.IoT Communication Protocols, Socket Programming with Python, MQTT & HTTP



IoT Communication Protocols, Socket Programming with Python, MQTT & HTTPAnshu Pandey
?
Notes on IoT COmmunication protocols like Wifi, Bluetooth, Sigfox, XBee, LoraWAN. A complete description and python code for socket programming, TCP client, and Server, UDP Client, and Server. HTTP v/s MQTT. MQTT Python programming for raspberry piRecently uploaded (20)
DAO UTokyo 2025 DLT mass adoption case studies IBM Tsuyoshi Hirayama (Æ―É―Ōã)



DAO UTokyo 2025 DLT mass adoption case studies IBM Tsuyoshi Hirayama (Æ―É―Ōã)Tsuyoshi Hirayama
?
DAO UTokyo 2025
|ūĐīóŅ§ĮéóŅ§h ĨÖĨíĨÃĨŊĨÁĨ§Đ`ĨóŅÐūŋĨĪĨËĨ·ĨĒĨÆĨĢĨÖ
https://utbciii.com/2024/12/12/announcing-dao-utokyo-2025-conference/
Session 1 :DLT mass adoption
IBM Tsuyoshi Hirayama (Æ―É―Ōã)Cloud of everything Tech of the 21 century in Aviation



Cloud of everything Tech of the 21 century in AviationAssem mousa
?
AI, Block chain, Digital Currency, Cloud, Cloud of Things, Tactile Internet, Digital Twins, IOT, AR, VR, MR, U commerce, data and robotics."
Formal Methods: Whence and Whither? [Martin Fr?nzle Festkolloquium, 2025]![Formal Methods: Whence and Whither? [Martin Fr?nzle Festkolloquium, 2025]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/mf2025-250305164811-a0930761-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Formal Methods: Whence and Whither? [Martin Fr?nzle Festkolloquium, 2025]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/mf2025-250305164811-a0930761-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Formal Methods: Whence and Whither? [Martin Fr?nzle Festkolloquium, 2025]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/mf2025-250305164811-a0930761-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Formal Methods: Whence and Whither? [Martin Fr?nzle Festkolloquium, 2025]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/mf2025-250305164811-a0930761-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Formal Methods: Whence and Whither? [Martin Fr?nzle Festkolloquium, 2025]Jonathan Bowen
?
Alan Turing arguably wrote the first paper on formal methods 75 years ago. Since then, there have been claims and counterclaims about formal methods. Tool development has been slow but aided by MooreĄŊs Law with the increasing power of computers. Although formal methods are not widespread in practical usage at a heavyweight level, their influence as crept into software engineering practice to the extent that they are no longer necessarily called formal methods in their use. In addition, in areas where safety and security are important, with the increasing use of computers in such applications, formal methods are a viable way to improve the reliability of such software-based systems. Their use in hardware where a mistake can be very costly is also important. This talk explores the journey of formal methods to the present day and speculates on future directions.
TrustArc Webinar - Building your DPIA/PIA Program: Best Practices & Tips



TrustArc Webinar - Building your DPIA/PIA Program: Best Practices & TipsTrustArc
?
Understanding DPIA/PIAs and how to implement them can be the key to embedding privacy in the heart of your organization as well as achieving compliance with multiple data protection / privacy laws, such as GDPR and CCPA. Indeed, the GDPR mandates Privacy by Design and requires documented Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) for high risk processing and the EU AI Act requires an assessment of fundamental rights.
How can you build this into a sustainable program across your business? What are the similarities and differences between PIAs and DPIAs? What are the best practices for integrating PIAs/DPIAs into your data privacy processes?
Whether you're refining your compliance framework or looking to enhance your PIA/DPIA execution, this session will provide actionable insights and strategies to ensure your organization meets the highest standards of data protection.
Join our panel of privacy experts as we explore:
- DPIA & PIA best practices
- Key regulatory requirements for conducting PIAs and DPIAs
- How to identify and mitigate data privacy risks through comprehensive assessments
- Strategies for ensuring documentation and compliance are robust and defensible
- Real-world case studies that highlight common pitfalls and practical solutionsTechnology use over time and its impact on consumers and businesses.pptx



Technology use over time and its impact on consumers and businesses.pptxkaylagaze
?
In this presentation, I will discuss how technology has changed consumer behaviour and its impact on consumers and businesses. I will focus on internet access, digital devices, how customers search for information and what they buy online, video consumption, and lastly consumer trends.
AIXMOOC 2.3 - Modelli di reti neurali con esperimenti di addestramento



AIXMOOC 2.3 - Modelli di reti neurali con esperimenti di addestramentoAlessandro Bogliolo
?
Lezione tenuta da Alessandro Bogliolo nell'ambito del MOOC dell'UniversitĻĪ di Urbino dedicato a LLMs e IA generativa
https://mooc.uniurb.it/aixmooc FinTech - US Annual Funding Report - 2024.pptx



FinTech - US Annual Funding Report - 2024.pptxTracxn
?
US FinTech 2024, offering a comprehensive analysis of key trends, funding activities, and top-performing sectors that shaped the FinTech ecosystem in the US 2024. The report delivers detailed data and insights into the region's funding landscape and other developments. We believe this report will provide you with valuable insights to understand the evolving market dynamics.L01 Introduction to Nanoindentation - What is hardness



L01 Introduction to Nanoindentation - What is hardnessRostislavDaniel
?
Introduction to NanoindentationTechnology use over time and its impact on consumers and businesses.pptx



Technology use over time and its impact on consumers and businesses.pptxkaylagaze
?
In this presentation, I explore how technology has changed consumer behaviour and its impact on consumers and businesses. I will focus on internet access, digital devices, how customers search for information and what they buy online, video consumption, and lastly consumer trends.Unlock AI Creativity: Image Generation with DALLĄĪE



Unlock AI Creativity: Image Generation with DALLĄĪEExpeed Software
?
Discover the power of AI image generation with DALLĄĪE, an advanced AI model that transforms text prompts into stunning, high-quality visuals. This presentation explores how artificial intelligence is revolutionizing digital creativity, from graphic design to content creation and marketing. Learn about the technology behind DALLĄĪE, its real-world applications, and how businesses can leverage AI-generated art for innovation. Whether you're a designer, developer, or marketer, this guide will help you unlock new creative possibilities with AI-driven image synthesis.World Information Architecture Day 2025 - UX at a Crossroads



World Information Architecture Day 2025 - UX at a CrossroadsJoshua Randall
?
User Experience stands at a crossroads: will we live up to our potential to design a better world? or will we be co-opted by Ą°product managementĄą or another business buzzword?
Looking backwards, this talk will show how UX has repeatedly failed to create a better world, drawing on industry data from Nielsen Norman Group, Baymard, MeasuringU, WebAIM, and others.
Looking forwards, this talk will argue that UX must resist hype, say no more often and collaborate less often (you read that right), and become a true profession ĄŠ in order to be able to design a better world.30B Images and Counting: Scaling Canva's Content-Understanding Pipelines by K...



30B Images and Counting: Scaling Canva's Content-Understanding Pipelines by K...ScyllaDB
?
Scaling content understanding for billions of images is no easy feat. This talk dives into building extreme label classification models, balancing accuracy & speed, and optimizing ML pipelines for scale. You'll learn new ways to tackle real-time performance challenges in massive data environments.Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation (Preview)



Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation (Preview)nick896721
?
Early Adopter's Guide to AI Moderation preview by User Interviews.Gojek Clone Multi-Service Super App.pptx



Gojek Clone Multi-Service Super App.pptxV3cube
?
Gojek Clone is a versatile multi-service super app that offers ride-hailing, food delivery, payment services, and more, providing a seamless experience for users and businesses alike on a single platform.Replacing RocksDB with ScyllaDB in Kafka Streams by Almog Gavra



Replacing RocksDB with ScyllaDB in Kafka Streams by Almog GavraScyllaDB
?
Learn how Responsive replaced embedded RocksDB with ScyllaDB in Kafka Streams, simplifying the architecture and unlocking massive availability and scale. The talk covers unbundling stream processors, key ScyllaDB features tested, and lessons learned from the transition.Backstage Software Templates for Java Developers



Backstage Software Templates for Java DevelopersMarkus Eisele
?
As a Java developer you might have a hard time accepting the limitations that you feel being introduced into your development cycles. Let's look at the positives and learn everything important to know to turn Backstag's software templates into a helpful tool you can use to elevate the platform experience for all developers.Build with AI on Google Cloud Session #4



Build with AI on Google Cloud Session #4Margaret Maynard-Reid
?
This is session #4 of the 5-session online study series with Google Cloud, where we take you onto the journey learning generative AI. YouĄŊll explore the dynamic landscape of Generative AI, gaining both theoretical insights and practical know-how of Google Cloud GenAI tools such as Gemini, Vertex AI, AI agents and Imagen 3. SMART SENTRY CYBER THREAT INTELLIGENCE IN IIOT



SMART SENTRY CYBER THREAT INTELLIGENCE IN IIOTTanmaiArni
?
SMART SENTRY CYBER THREAT INTELLIGENCE IN IIOTFl studio crack version 12.9 Free Download



Fl studio crack version 12.9 Free Downloadkherorpacca127
?
https://ncracked.com/7961-2/
Note: >>?? Please copy the link and paste it into Google New Tab now Download link
The ultimate guide to FL Studio 12.9 Crack, the revolutionary digital audio workstation that empowers musicians and producers of all levels. This software has become a cornerstone in the music industry, offering unparalleled creative capabilities, cutting-edge features, and an intuitive workflow.
With FL Studio 12.9 Crack, you gain access to a vast arsenal of instruments, effects, and plugins, seamlessly integrated into a user-friendly interface. Its signature Piano Roll Editor provides an exceptional level of musical expression, while the advanced automation features empower you to create complex and dynamic compositions.Zigbee Technology
- 2. ? Introduction ? History ? Device Types ? How Zigbee Works ? Layer of Zigbee Networks ? Stack Architecture ? Topologies ? Uses ? Applications ? Future ? Conclusion
- 4. ? Technological Standard Created for Control and Sensor Networks ? Based on the IEEE 802.15.4 Standard ? High level Communication ? Operates in Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) and Device-to-Device networks ? Created by the ZigBee Alliance ? Connectivity between small packet devices ? Control of lights, switches, thermostats, appliances, etc.
- 5. ? ZigBee-style networks began to be conceived about 1998, when many engineers realized that both WiFi and Bluetooth were going to be unsuitable for many applications. In particular, many engineers saw a need for self-organizing ad-hoc digital radio networks. ? The IEEE 802.15.4 standard was completed in May 2003. ? The ZigBee specifications were ratified on 14 December 2004. ? The ZigBee Alliance announces public availability of Specification 1.0 on 13 June 2005.
- 6. There are three different types of ZigBee device: ? ZigBee coordinator (ZC) ? ZigBee Router (ZR) ? ZigBee End Device (ZED)
- 7. ? ZigBee coordinator (ZC): The most capable device, the coordinator forms the root of the network tree and might bridge to other networks. There is exactly one ZigBee coordinator in each network. It is able to store information about the network, including acting as the repository for security keys.
- 8. ? ZigBee Router (ZR): Routers can act as an intermediate router, passing data from other devices. ? ZigBee End Device (ZED): Contains just enough functionality to talk to its parent node (either the coordinator or a router); it cannot relay data from other devices. It requires the least amount of memory, and therefore can be less expensive to manufacture than a ZR or ZC.
- 9. ? Low cost ? Low power consumption ? Low data rate ? Relatively short transmission range ? Scalability and reliability ? Flexible protocol design suitable for many applications
- 10. ? 65,536 network (client) nodes ? 27 channels over 2 bands ? 250Kbps data rate ? Optimized for timing-critical applications and power management ? Full Mesh Networking Support Network coordinator Full Function node Reduced Function node Communications flow Virtual links šÝšÝßĢ 10
- 11. ? Topology Star Cluster Tree Mesh ? Network coordinator, routers, end devices
- 12. ? Network and Application Support layer ? Physical (PHY) layer ? Media access control (MAC) layer
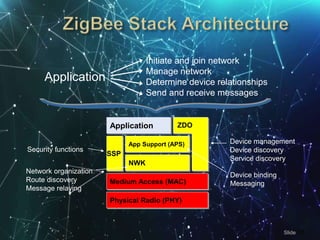
- 13. Application Initiate and join network Manage network Determine device relationships Send and receive messages Physical Radio (PHY) Medium Access (MAC) Application ZDO NWK App Support (APS) SSP Security functions Network organization Route discovery Message relaying Device binding Messaging Device management Device discovery Service discovery šÝšÝßĢ 13
- 14. ? Different topologies as illustrated below: star, peer-to- peer, mesh
- 15. ? Star Topology ? Advantage ? Easy to synchronize ? Low latency ? Disadvantage ? Small scale
- 16. ? Mesh Topology ? Advantage ? Robust multihop communication ? Network is more flexible ? Lower latency ? Disadvantage ? Route discovery is costly ? Needs storage for routing table
- 17. ? Cluster Tree ? Advantage ? Low routing cost ? Allow multihop communication ? Disadvantage ? Route reconstruction is costly ? Latency may be quite long
- 18. ? Optimized for different applications ? ZigBee ? Smaller packets over large network ? Mostly Static networks with many, infrequently used devices ? Home automation, toys, remote controls, etc. ? Bluetooth ? Larger packets over small network ? AdĐ\hoc networks ? File transfer ? Screen graphics, pictures, handsfree audio, Mobile phones, headsets, PDAs, etc.
- 19. In all of its uses, zigbee offers four inherent, beneficial characteristics: ? Low cost: ? Range and obstruction issue avoidance: ? Multisource products: ? Low power consumption:
- 20. PERSONAL HEALTH CARE HOME AUTOMATION CONSUMER ELECTRONIC PC & PERIPHERALS consoles portables educational TOYS & GAMES INDUSTRIAL & COMMERCIAL monitors sensors automation control monitors diagnostics sensors security HVAC lighting closures mouse keyboard joystick TV VCR DVD/CD Remote control APPLICATIONS
- 21. ? A recent analyst report issued by West Technology Research Solutions estimates that by the year 2008, "annual shipments for ZigBee chipsets into the home automation segment alone will exceed 339 million units," and will show up in "light switches, fire and smoke detectors, thermostats, appliances in the kitchen, video and audio remote controls, landscaping, and security systems." ? Futurists are sure to hold ZigBee up and say, "See, I told you so".
- 22. ? ZigBee is one of the global standards of communication protocol formulated by the relevant task force. ? ZigBee is the newest and provides specifications for devices that have low data rates, consume very low power and are thus characterized by long battery life.
Editor's Notes
- #2: 1


