Polimorfizmin ilaç stabilitesine etkisi
- 1. POLİMORFİZMİN İLAÇ STABİLİTESİNE ETKİSİ Ecz.Sema Arısoy Ankara Üniversitesi Eczacılık Fakültesi Farmasötik Teknoloji Anabilim Dalı
- 2. KRİSTALİNİTE Atom, iyon ya da molekülleri belli bir düzene göre sı- ralanmış maddelere saydam buz anlamına gelen kristal adı verilmiştir. Gerçek bir kristalde birim hücreler üç boyutlu düzlemde belli bir kristal örgüsü oluşturacak şekilde düzenli olarak tekrarlanarak yığılır. Farmasötik amaçla kullanılan organik ve inorganik bileşiklerin bir veya birden fazla kristalen şekli bulunur. Bir bileşiğin en iyi bilinen kristalen şekilleri polimorflar ve solvatlardır.
- 3. Bir katı etkin maddenin kristal morfolojisi ve iç moleküler düzeni hem kütle (bulk) hem de fizikokimyasal özelliklerini etkiler. Bu fizikokimya sal özellikler akış özelliklerinden kimyasal stabiliteye kadar geniş bir aralığı kapsar. Farmasötik amaçla kullanılan organik ve inorganik bileşiklerin bir veya birden fazla kristalen şekli bulunur. Bir bileşiğin en iyi bilinen kristalen şekilleri polimorflarve solvatlardır.
- 4. Farklı polimorflar ve solvatlar, kristal yığılması, moleküler diziliş, örgü enerjisi ve entropi açı- sından farklılık gösterirler. Bundan dolayı, dansite, sertlik, tablet haline gelebilme, kırma indisi, erime noktası, entalpi ve füzyon, buhar basıncı, çözünürlük, çözünme hızı gibi fiziksel özellikler, termodinamik ve kinetik özellikler bakımından farklılıklar da görülür.
- 5. SOLVATLAR Solvatlar yalancı polimorflar (pseudopolimorf) olarak da bilinirler ve stokiyometrik veya non-stokiyometrik oranda solvan moleküllerinin kristal örgü içine veya moleküller arası boşluklara yerleşmesi sonucu oluşurlar. içerikli bileşik (inclusion compound) ve klatrat olarak adlandırılan non-stokiyometrik bileşikler, kristal örgü- sü içinde hapsedilmiş solvan molekülleri içerir.
- 6. Genelde bu bileşikler tekrarlanabilirliklerinin olmaması nedeniyle ürün geliştirme çalışmalarında tercih edilmez. Solvatlar, non-solvat olan tiplerine göre daha yüksek çözünürlük ve çözünme hızı göstermekle birlikte farmasötik alanda çok fazla kullanılmazlar.
- 7. AMORF ŞEKİLLER Kristal olmayan şekillerdir. Komşu moleküller arasında kısa mesafeli moleküler diziliş, yani kısa mesafeli bir düzen söz konusudur. Diğer bir deyişle kristalen şekle göre moleküller rastgele yer almaktadır. Halbuki kristalen yapıdaki bileşiklerde atom veya moleküller üç boyutlu düzlemde tekrarlanan bir şekilde dizilmişlerdir ve uzun mesafeli moleküler diziliş görülmektedir
- 8. Amorf şekiller genel olarak kristalen şekle göre daha yüksek termodinamik enerjiye sahiptirler, fiziksel ve kimyasal açıdan daha az dayanıklıdırlar. Bu nedenle de çözünürlükleri ve çözünme hızları daha yüksektir. Amorf şekillerin hazırlanması için çöktürme, liyofilizasyon, püskürterek kurutma, katı dispersiyon hazırlama veya hızlı soğutma gibi yöntemler kullanılabilir. Ayrıca öğütme, toz etme ve yaş granülasyon gibi kimyasal veya fiziksel zorlama gibi işlemler de amorf katının oluşumuna yol açar. İşlem
- 9. İlk yapılması gereken işlem, katı bileşiğin kristalen ya da amorf yapıda olup olmadığının belirlenmesidir. Saklama sırasında amorf şekiller daha dayanıklı şekillere dönüşmek eğilimindedir. Termodinamik açıdan bu instabilité probleminin, işlem sırasında veya dozaj şeklinin içinde oluşması amorf şekillerle çalışmanın en büyük sakıncasıdır.
- 10. HİDRATLAR Eğer kristal örgü içine, hidrojen bağları yaparak ilave olan solvan su ise hidrat olarak tanımlanırlar. Yapı içindeki bu hidrojen bağları kristalin yapışmasına ve bunun sonucunda anhidrat (susuz) şekle göre daha yavaş çözünme hızı göstermesine ve emiliminin azalmasına neden olur. Genellikle etkin maddelerin hidrat formlarının çözü- nürlüğü, çözünme hızı ve biyoyararlanımı susuz şekle göre daha düşüktür.
- 11. POLİMORFİZM Kristalen polimorflar, aynı kimyasal yapıya, ancak farklı iç kristal örgüsüne sahip olan katı bileşiklerdir. Genel olarak gerçek polimorflar iki gruba ayrılır. 1) Enantiyotropik polimorflar: Sıcaklık veya basınç değişikliği durumlarında bir polimorf diğer bir polimorfa geri dönüşlü olarak değişir. 2) Monotropik polimorflar: İki polimorf arasındaki değişim geri dönüşsüzdür.
- 12. OLUŞMA KOŞULLARI a) Farklı hız ve sıcaklıklarda farklı solvanlardan kristalizasyon b) Çöktürme c) Uçurma d) Erimiş kütleden kristalizasyon e) Öğütme ve baskı f) Liyofilizasyon g) Püskürterek kurutma
- 13. Farklı kristal yapının oluşması etkin maddenin kristallenmesi sırasında en az iki farklı iç moleküler düzenleme olasılığı sonucunda ortaya çıkar. Genellikle polimorfların erime noktası en düşük olan şekli dayanıksızdır; diğer polimorflar ise metastabl olup, stabl şekle dönüşme eğilimindedir. Farmasötik açıdan metastabl formlar daha çok tercih edilir.
- 14. Önformülasyon çalışmaları boyunca 25°C'de dayanıklı olan formun belirlenmesi çok önemlidir. Stabilité çalış- maları boyunca kullanılan ve imalat işlemlerinde (kurutma, toz etme) uygulanan sıcaklıklarda polimorfik dönüşümlerin olup olmadığının saptanması da önem taşır. Polimorfların raf ömrü süresince dayanıklı olmaları gerekir. Farklı polimorfların yapılarında gözlenen farklı kristal yapılar, çözünürlük ve çözünme profillerinde farklılığa yol açabilir.Bu durum özellikle katı ilaç şekillerinde ve süspansiyonlarda problem yaratabilir.
- 15. Polimorfik dönüşümün gerçekleştiği geçiş sıcaklığın saptanmasında Van't Hoff eşitliğinden faydalanılır. Ge- çiş sıcaklığı, çözünürlüğe karşı mutlak sıcaklığın tersinin grafiğe geçirilmesiyle elde edilen doğrunun uzatılması (ekstrapole edilmesi) ile tahmin edilir. Tablet ve kapsül gibi katı ilaç şekilleri için de partikül büyüklüğü, nem ve yardımcı maddelerin etkisine bağlı olarak benzer problemler ortaya çıkabilir.
- 16. Metastabl polimorfların dozaj şekli içindeki stabilitesini incelemek için, içinde stabl polimorfun çekirdeğini içeren ve içermeyen ilk prototip formülasyonda çeşitli faktörlerin etkisi tek tek gözden geçirilmelidir. Bir bileşiğin polimorfiarı, erime noktası, çözünürlük, dansite, optik ve elektriksel özellikler, buhar basıncı ve katı hal stabiliteleri açısından farklı özelliklere sahiptir. Bir bileşiğin polimorfik özellik göstermesi formülasyon, biyofarmasötik ve kimyasal işlemler bakımından önemlidir.
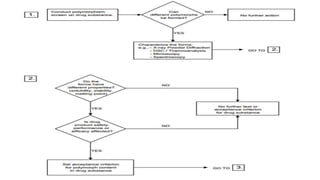
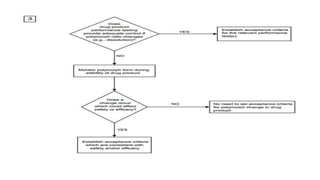
- 17. KLAVUZLAR ICH Q6 ya göre tanım; Polimorfizm: İlaç etken maddesinin değişik kristalin formlarının bulunmasıdır. Solvat, hidrat (psödopolimorf) ve amorf formları gibi formları bulunur.
- 20. KAYNAKLAR 1. Modern farmasötik teknoloji, Önformülasyon, Sevgi Takka, Füsun Acartürk, İlbeyi Ağabeyoğlu, Nevin Çelebi, Tuncer Değim, Zelihagül Değim. 2. ICH Q6