Ct chest type
- 2. CT Types 1. Standard 2. High Resolution 3. Low Dose 4. CT Angio
- 3. Axial lung window Coronal C+ arterial phase Normal CT chest
- 4. STANDARD CT ’éĪ Slice thickness: 3-10 mm ’éĪ scans a large volume, very quickly ’éĪ Covers the full lung ’éĪ +/- contrast ’üČIndications ’éĪ CXR abnormality ’éĪ Pleural and mediastinal abnormalities ’éĪ Lung cancer staging ’éĪ F/U metastases ’éĪ Empyema vs abscess
- 6. HIGH RESOLUTION (HRCT) It is used in the diagnosis of various health problems, though most commonly for lung disease. It involves the use of special computed tomography scanning techniques to assess the lung parenchyma. STANDARD CT HRCT
- 7. HIGH RESOLUTION (HRCT) ’éŚ narrow x-ray beam collimation: 1-1.3mm vs. conventional 3-10mm ’éŚ cross sections are further apart: 10 mm ’éŚ high definition images of lung parenchyma: vessels, airspaces, airway and interstitium ’éŚ No contrast
- 8. HIGH RESOLUTION (HRCT) ’üČ Indications ’éĪ Hemoptysis ’éĪ Diffusely abnormal CXR ’éĪ Normal CXR with abnormal PFTŌĆÖs ’éĪ Baseline for pts with diffuse lung disease ’éĪ Solitary pulmonary nodules ’éĪ Reversible (active) vs. non-reversible (fibrotic) lung disease ’éĪ Lung biopsy guide ’éĪ F/U known lung disease ’éĪ Assess Rx response
- 9. LOW DOSE
- 10. Baseline Findings - ELCAP ’āś According to ( Early Lung Cancer Action Program) ’üČLow dose CT greatly increases the likelihood of detection of NCN and early lung cancer compared with chest radiography ’éĪ NCN: 3 times as commonly ’éĪ Malignant tumors: 4 times as commonly ’éĪ Stage I tumors: 6 times as commonly
- 11. Low-dose CT: Lung cancer
- 12. LOW DOSE ŌĆó Premise: lower dose radiation will not reduce the diagnostic functionality of the scan (eg. 250 mAs ŌĆ║ 50 mAs) ŌĆó Detail is decreased ’üČUses ’éĪ Screening ŌĆō ongoing trials ’üČF/U ŌĆō infections ŌĆō post lung transplant ŌĆō metastases
- 13. ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA) ŌĆó contrast injected into peripheral vein ŌĆó injection timing/rate controlled automatically ŌĆó dye is where you want it during scan ŌĆó replaced conventional catheter angiogram ’üČ Indications ’éĪ Pulmonary embolism ’éĪ Aortic aneurysms ’éĪ Aortic dissection ’üČ Risks ’éĪ Iodinated contrast: ŌĆō Allergic/ nephrotoxic
- 14. 69- year old female with shortness of breath ANGIOGRAPHY (CTA)
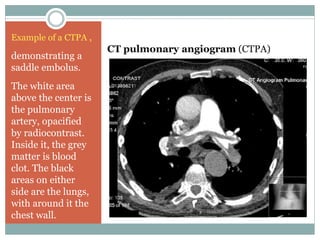
- 15. CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) Example of a CTPA , demonstrating a saddle embolus. The white area above the center is the pulmonary artery, opacified by radiocontrast. Inside it, the grey matter is blood clot. The black areas on either side are the lungs, with around it the chest wall.
- 16. References 1. https://radiopaedia.org/cases/normal-ct-chest 2. http://www.slideshare.net/divitto1/approach-to-ct-chest-578 3. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High-resolution_computed_tomography 4. http://slideplayer.com/slide/download/ 5. Henschke et al, Lancet 1999; 354:99-105 6. I-ELCAP is an international, collaborative group consisting of experts on lung cancer and related issues from around the world. ’ā╝ Made by; Abdullah Salem Al-habeeb