Larflast
- 1. 1/15/2010 Ontology-Centered Personalized Presentation of Intelligent Tutoring Systems Knowledge Extracted Knowledge based systems - ontologies From the Web Student modeling Reasoning for: Student diagnosis Stefan Trausan-Matu, UPB, ROMANIA Explanations generation Daniele Maraschi, LIRMM, FRANCE Lesson planning Stefano Cerri, LIRMM, FRANCE Intelligent interfaces Ontologies Ontologies - Concepts The central part of the domain ontology is a "An ontology is a specification of a taxonomically organized knowledge base of conceptualization....That is, an ontology is a concepts: description (like a formal specification of a Security program) of the concepts and relationships Bond that can exist for an agent or a community of Share agents" (Gruber) OrdinaryShare PreferenceShare Stock Ontologies used in ITSs Student model Domain Keeps track of the concepts known, unknown or wrongly known by the student (Dimitrova, Self, Tutoring Brna, 2000) Human-computer interfacing Inferred from results at tests or from interaction Lexical (visited web pages, topics searched etc.) Upper Level Is usually defined in relation with the domain ontology (concept net, Bayesian net) 1
- 2. 1/15/2010 Fragment of a learner’s model Personalized web pages (Dimitrova, Self, Brna, 2000) Are adapted to each users': know(ogi,secondary_market,[b_def],u_1_d_2,1). knowledge - ITS student model know(ogi,negotiated_market,[b_def],u_1_d_2,1). learning style not_know(ogi,open_market,[b_def],u_1_d_2,1). not_know(ogi,primary_market,[b_def],u_1_d_2,1). psychological profile know(ogi,money_market,[b_def],u_1_d_2,1). goals (e.g. lists of concepts to be learned) not_know(ogi,primary_market,[a_def],u_1_d_2,2). level (novice, expert) know(ogi,negotiated_market,[a_def],u_1_d_2,2). preferences (e.g. style of web pages) context of interaction ITS on the Web - Problems of Browsing for Learning Known ideas Intelligent search of relevant material Huge amount of information Knowledge extraction Permanent appearance of new information XML Metadata Disorientation Personalization Adaptive hypermedia New ideas in our approach Solutions Permanent updating of information according to The generated web pages include latest newly published web pages, discovered by information gathered by search agents agents Use semantic editors for annotation Assuring the sense of the whole Dynamically generate coherent structures of web The structure of the web pages should reflect the pages that conceptual map of the domain – the Ontology reflect the domain ontology, Facilitation of understanding are filtered according to the learner’s model, Browsing a holistic, understandable structure may contain latest information, induce a flow state include metaphors according to intentionality Use metaphors (especially in CALL) 2
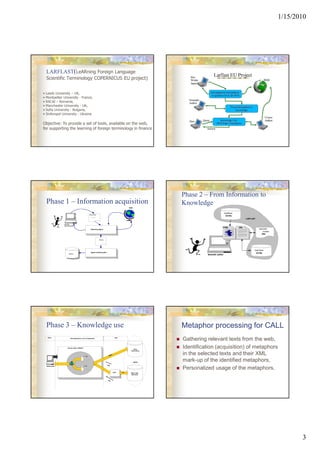
- 3. 1/15/2010 LARFLAST(LeARning Foreign Language Scientific Terminology COPERNICUS EU project) • Leeds University – UK, • Montpellier University - France, • RACAI – Romania, • Manchester University - UK, • Sofia University - Bulgaria, • Sinferopol University - Ukraine Objective: To provide a set of tools, available on the web, for supporting the learning of foreign terminology in finance Phase 2 – From Information to Phase 1 – Information acquisition Knowledge WEB DataBase Keywords list XHTML <?xml version="1.0"?> <..> LARFLAST Inserting Search keywords HTML XML Searching Agent Semantic models XML URLs list Data Base Agent collecting data Database XHTML Semantic author Phase 3 – Knowledge use Metaphor processing for CALL Client Web applications server d'application Data Gathering relevant texts from the web, Servlet engine TOMCAT Other Identification (acquisition) of metaphors informations XML in the selected texts and their XML MySQL mark-up of the identified metaphors, XSL Personalized usage of the metaphors. Web browser eXist JDBC Native XML Data base 3
- 4. 1/15/2010 Stocks defined in ontologies Metaphors are often used to give insight in what a concept means "stock" is AKO "securitiy", "Stocks are very sensitive creatures" "capital", "asset" or “possession“ “stock” has attributes “owner”, (New York Stock Exchange web page … http://www.nyse.com/). Semantic editing (Trausan, 2000) LARFLAST Dynamic generation of personalized web pages Runs from an Apache servlet Adapts to the learner’s model, transferred from another web site Parameterized, easy to configure for new patterns of web pages and structures Includes relevant metaphors and texts from a corpus 4
- 5. 1/15/2010 5
- 6. 1/15/2010 Conclusions Serenditipous search, annotation, and use of information The domain ontology used for: serendipitous search XML semantic annotation retrieval of relevant metaphors structuring the dynamically generated web pages including knowledge in the web pages Conclusions (cont.) Other approaches Holistic character that assure the coherence Adaptive hypermedia (deBra, Brusilovsky, Houser) local policies like flexible link sorting, of the presentation, with direct effects on hiding or disabling or by conditionally showing the learning process – study with Sofia text fragments etc. University students Planning the content of the presented material Metaphor identification, annotations, and (Vassilieva; Siekmann, Benzmuller, and all) local decisions based on the learner model. usage – intentionality (Trausan 2000) – other approaches: Lakoff & Johnson, D. They miss a holistic character! Fass, J. Martin Other approaches The permanent inclusion of new information gathered and annotated from the web is another novel feature, not included in other systems. Existing approaches only provide intelligent recommendation of interesting web pages, according to the user profile (Breese, Heckerman, Kadie; Lieberman) They do not permit the inclusion of relevant facts in the structure of ontology-centred structure. 6


![1/15/2010
Fragment of a learner’s model Personalized web pages
(Dimitrova, Self, Brna, 2000)
Are adapted to each users':
know(ogi,secondary_market,[b_def],u_1_d_2,1). knowledge - ITS student model
know(ogi,negotiated_market,[b_def],u_1_d_2,1).
learning style
not_know(ogi,open_market,[b_def],u_1_d_2,1).
not_know(ogi,primary_market,[b_def],u_1_d_2,1). psychological profile
know(ogi,money_market,[b_def],u_1_d_2,1). goals (e.g. lists of concepts to be learned)
not_know(ogi,primary_market,[a_def],u_1_d_2,2). level (novice, expert)
know(ogi,negotiated_market,[a_def],u_1_d_2,2).
preferences (e.g. style of web pages)
context of interaction
ITS on the Web -
Problems of Browsing for Learning Known ideas
Intelligent search of relevant material
Huge amount of information Knowledge extraction
Permanent appearance of new information XML Metadata
Disorientation Personalization
Adaptive hypermedia
New ideas in our approach Solutions
Permanent updating of information according to The generated web pages include latest
newly published web pages, discovered by information gathered by search agents
agents Use semantic editors for annotation
Assuring the sense of the whole Dynamically generate coherent structures of web
The structure of the web pages should reflect the pages that
conceptual map of the domain – the Ontology reflect the domain ontology,
Facilitation of understanding are filtered according to the learner’s model,
Browsing a holistic, understandable structure may contain latest information,
induce a flow state include metaphors according to intentionality
Use metaphors (especially in CALL)
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/larflast-100907170821-phpapp01/85/Larflast-2-320.jpg)