1 of 7
Download to read offline





Ad
Recommended
Cva ppt
Cva pptVinod Sankoju
Ã˝
This document provides an analysis of the business process outsourcing industry in India. It includes an introduction to BPO in India, a SWOT analysis identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats, profiles of five major BPO companies including information on their establishment, revenue and websites, a financial comparison of the five companies over five years, findings from the financial comparison, and a conclusion on the future prospects of the BPO industry in India.Stroke (cva)
Stroke (cva)numeyko
Ã˝
A stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain is blocked or ruptures, interrupting blood flow and oxygen to the brain. This causes brain cells to die. The main types of stroke are ischemic, caused by a clot blocking an artery, and hemorrhagic, caused by a ruptured blood vessel. Risk factors include hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, smoking, obesity, and head injuries. Symptoms include sudden numbness, weakness, confusion, trouble seeing or walking. Diagnosis involves CT scans, MRI, or lumbar puncture. Treatment includes medications, surgery, and rehabilitation to regain functions and prevent complications.Cva
Cva000 07
Ã˝
A stroke, or cerebrovascular accident (CVA), occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, causing brain cells to die from lack of oxygen. The most common causes of stroke are thrombosis, where a clot blocks a blood vessel, and embolism, where a traveling clot blocks a vessel. Less common is hemorrhage, where a blood vessel ruptures in the brain. Risk factors include age, hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, and smoking. Symptoms vary depending on the affected brain region but can include paralysis, difficulty speaking, and mental status changes. Treatment involves stabilizing the patient, treating the underlying cause, and rehabilitation to regain lost functions.Beroerte
BeroerteMaasstad Ziekenhuis
Ã˝
Een beroerte wordt ook wel een CVA genoemd, ofwel een Cerebro Vasculair Accident. Dit kan zowel een bloeding in de hersenen als een herseninfarct (bijvoorbeeld door een bloedprop) betekenen.
Een veelgebruikte term is ook TIA, ofwel een Transient Ischemisch Attack. Deze term betekent per definitie dat de symptomen binnen 24 uur verdwenen zijn en is altijd een infarct.Cva In Huisartspraktijk
Cva In HuisartspraktijkLucien Engelen
Ã˝
Presentatie gehouden bij Symposium Acute Zorg Anders op 5 maart 2009 van Acute Zorgregio Oost.Presentationon cva
Presentationon cvatahav kershio
Ã˝
This document discusses the challenges in nursing care for patients experiencing a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) or stroke. It begins by defining a CVA as a sudden loss of brain function caused by disrupted blood flow to the brain. The document then covers the types, risk factors, clinical manifestations, investigations, and management of strokes. It emphasizes the nursing priorities of initial treatment to prevent further deterioration, ongoing risk assessment, and interventions to address impaired mobility, vital signs, nutrition, and more. The overall goal of nursing management is to control symptoms, prevent complications, and optimize recovery through a coordinated, multidisciplinary approach.Cva
CvaNursing Path
Ã˝
This document discusses cerebrovascular disorders such as stroke. It begins by defining cerebrovascular disorders as any functional abnormality of the central nervous system caused by disrupted blood supply to the brain. Stroke is the primary cerebrovascular disorder. The document then covers the anatomy of the nervous system, definitions of stroke, risk factors, types of stroke (ischemic and hemorrhagic), clinical manifestations, diagnostic findings, and management approaches including medical, surgical, and nursing considerations.Basic Anatomy & Pathophysiology of ischemic stroke
Basic Anatomy & Pathophysiology of ischemic strokeAjay Kumar
Ã˝
This document discusses the anatomy, pathophysiology, and factors related to ischemic stroke. It begins by outlining the arterial supply of the brain and clinical findings associated with occlusion of the anterior, middle, and posterior cerebral arteries. It then explains key aspects of cerebral blood flow such as normal rates, autoregulation, and thresholds for ischemia and infarction. Finally, it lists several factors that can influence the occurrence of ischemic stroke such as the rate and duration of reduced blood flow, collateral circulation, systemic conditions, and temperature and glucose levels.2013.stroke areyouready
2013.stroke areyoureadySLNI_KC_2012
Ã˝
1) Strokes occur when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, causing brain cells to die rapidly over time.
2) Regional networks allow for over 1,000 stroke patients to be treated annually from over 80 regional hospitals via helicopter or ambulance.
3) Determining the exact time of onset, or "time last known well", is crucial for determining appropriate interventions, as certain treatments must be administered within a specific time window to be effective. Guidelines for management of acute stroke
Guidelines for management of acute strokesankalpgmc8
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of stroke types, pathophysiology, investigations, and management guidelines. It discusses the three main types of stroke: ischemic, intracerebral hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. For ischemic stroke, it describes the ischemic core and penumbra. It outlines the emergency evaluation of acute ischemic stroke including vital signs, blood tests, imaging, and scales like the NIH Stroke Scale. Management strategies discussed include thrombolysis, antiplatelet/anticoagulation drugs, neuroprotective agents, and surgical interventions. Complications like cerebral edema and their management are also summarized.Cerebrovascular disease (CVA / Stroke)
Cerebrovascular disease (CVA / Stroke)Richard Brown
Ã˝
1) The document discusses strokes (cerebrovascular accidents or CVAs), their causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
2) Strokes are caused by disturbances in the vascular system and can be ischemic (caused by clot or blockage) or hemorrhagic (caused by bleeding).
3) Common symptoms of strokes include weakness or numbness on one side of the body, speech problems, and visual issues. The specific symptoms depend on the area of the brain affected.Stroke
StrokeCarlos Rene Espino de la Cueva
Ã˝
The document discusses stroke, including risk factors, signs and symptoms, and the importance of rapid treatment. It outlines the "Stroke Chain of Survival and Recovery" which includes early detection, emergency dispatch, pre-hospital transport and management, emergency department triage, evaluation and specific therapies, and fibrinolytic drug therapy. Rapid recognition of stroke, emergency medical response, and treatment are critical to limiting neurological damage and improving patient outcomes.Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)
Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)Tosca Torres
Ã˝
This document provides information about cerebrovascular accidents (strokes), including:
1. Strokes occur when blood supply to the brain is disrupted, causing brain cells to die from lack of oxygen and nutrients.
2. There are two main types of strokes - ischemic (lack of blood flow) and hemorrhagic (bleeding in the brain).
3. Signs and symptoms of strokes vary depending on the area of the brain affected but may include weakness, confusion, vision problems, and headaches.More Related Content
Viewers also liked (8)
Cva
CvaNursing Path
Ã˝
This document discusses cerebrovascular disorders such as stroke. It begins by defining cerebrovascular disorders as any functional abnormality of the central nervous system caused by disrupted blood supply to the brain. Stroke is the primary cerebrovascular disorder. The document then covers the anatomy of the nervous system, definitions of stroke, risk factors, types of stroke (ischemic and hemorrhagic), clinical manifestations, diagnostic findings, and management approaches including medical, surgical, and nursing considerations.Basic Anatomy & Pathophysiology of ischemic stroke
Basic Anatomy & Pathophysiology of ischemic strokeAjay Kumar
Ã˝
This document discusses the anatomy, pathophysiology, and factors related to ischemic stroke. It begins by outlining the arterial supply of the brain and clinical findings associated with occlusion of the anterior, middle, and posterior cerebral arteries. It then explains key aspects of cerebral blood flow such as normal rates, autoregulation, and thresholds for ischemia and infarction. Finally, it lists several factors that can influence the occurrence of ischemic stroke such as the rate and duration of reduced blood flow, collateral circulation, systemic conditions, and temperature and glucose levels.2013.stroke areyouready
2013.stroke areyoureadySLNI_KC_2012
Ã˝
1) Strokes occur when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, causing brain cells to die rapidly over time.
2) Regional networks allow for over 1,000 stroke patients to be treated annually from over 80 regional hospitals via helicopter or ambulance.
3) Determining the exact time of onset, or "time last known well", is crucial for determining appropriate interventions, as certain treatments must be administered within a specific time window to be effective. Guidelines for management of acute stroke
Guidelines for management of acute strokesankalpgmc8
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of stroke types, pathophysiology, investigations, and management guidelines. It discusses the three main types of stroke: ischemic, intracerebral hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. For ischemic stroke, it describes the ischemic core and penumbra. It outlines the emergency evaluation of acute ischemic stroke including vital signs, blood tests, imaging, and scales like the NIH Stroke Scale. Management strategies discussed include thrombolysis, antiplatelet/anticoagulation drugs, neuroprotective agents, and surgical interventions. Complications like cerebral edema and their management are also summarized.Cerebrovascular disease (CVA / Stroke)
Cerebrovascular disease (CVA / Stroke)Richard Brown
Ã˝
1) The document discusses strokes (cerebrovascular accidents or CVAs), their causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
2) Strokes are caused by disturbances in the vascular system and can be ischemic (caused by clot or blockage) or hemorrhagic (caused by bleeding).
3) Common symptoms of strokes include weakness or numbness on one side of the body, speech problems, and visual issues. The specific symptoms depend on the area of the brain affected.Stroke
StrokeCarlos Rene Espino de la Cueva
Ã˝
The document discusses stroke, including risk factors, signs and symptoms, and the importance of rapid treatment. It outlines the "Stroke Chain of Survival and Recovery" which includes early detection, emergency dispatch, pre-hospital transport and management, emergency department triage, evaluation and specific therapies, and fibrinolytic drug therapy. Rapid recognition of stroke, emergency medical response, and treatment are critical to limiting neurological damage and improving patient outcomes.Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)
Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)Tosca Torres
Ã˝
This document provides information about cerebrovascular accidents (strokes), including:
1. Strokes occur when blood supply to the brain is disrupted, causing brain cells to die from lack of oxygen and nutrients.
2. There are two main types of strokes - ischemic (lack of blood flow) and hemorrhagic (bleeding in the brain).
3. Signs and symptoms of strokes vary depending on the area of the brain affected but may include weakness, confusion, vision problems, and headaches.CVA
- 2. ÔÅΩ plotse aandoening van de hersenbloedvaten ÔÅΩ 4 soorten CVA: ‚ó¶ de hersentrombose ‚ó¶ de hersenembolie ‚ó¶ de hersenbloeding ‚ó¶ de bloeding onder de hersenvliezen
- 3. ÔÅΩ Algemene oorzaken van een CVA: ‚ó¶ Atherosclerose: bloedvaten vernauwen ‚ó¶ Hoge bloeddruk: beschadiging vaatwand ÔÅΩ Specifieke oorzaken van een CVA: ‚ó¶ Trombose: bloedvatafsluiting in de kleinere bloedvaten ‚ó¶ Embolie: bloedklonter die bloedtoevoer van hersenen stopt ‚ó¶ Te veel stollingsfactoren in bloed
- 4. ÔÅΩ Specifieke oorzaken van een bloeding: ‚ó¶ Verzwakte vaatwand ‚ó¶ Aangeboren vaatafwijkingen ‚ó¶ Schedeltrauma ‚ó¶ Schedelfractuur heeft groot bloedvat beschadigd ‚ó¶ Bloedingen in een vaatrijke tumor
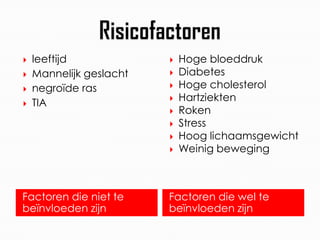
- 5.  leeftijd  Hoge bloeddruk  Mannelijk geslacht  Diabetes  negroïde ras  Hoge cholesterol  Hartziekten  TIA  Roken  Stress  Hoog lichaamsgewicht  Weinig beweging Factoren die niet te Factoren die wel te beïnvloeden zijn beïnvloeden zijn
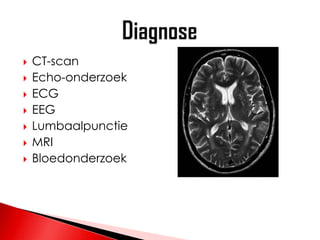
- 6. ÔÅΩ CT-scan ÔÅΩ Echo-onderzoek ÔÅΩ ECG ÔÅΩ EEG ÔÅΩ Lumbaalpunctie ÔÅΩ MRI ÔÅΩ Bloedonderzoek
