abdelwahab alsammak_Chapter 1-Internet concepts.ppt
- 2. Introduction ’ü« Over the past century and a half, important technological developments have created a global environment that is drawing the people of the world closer and closer together. ’ü« Currently, we are in the information Age, where magnifying the computation power is an essential Goal.
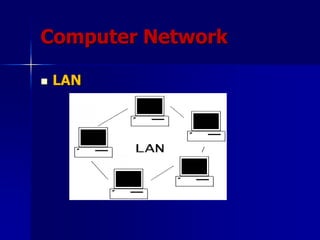
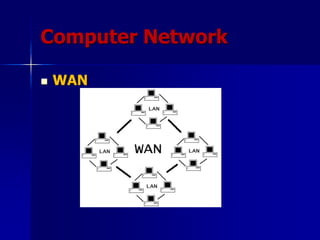
- 5. Computer Network ’ü« Allow us to generate exchange, share and manipulate information in an uncountable number of ways.
- 6. What is the Internet? ’ü« Internet is a specific interconnected network that connects computers all over the world using a common set of interconnection standards or protocols.
- 7. Connecting to a Network Vs Communicating over a network ’ü« When Connect to the Internet requires special hardware such as: ’ü« Modem ŌĆō short for modulator / demodulator - which connects computers using a standard telephone line ’ü« Network interface card (NIC) ŌĆō which connects computers using a special type of network cabling.
- 8. Connecting to a Network Vs Communicating over a network ’ü« In order to communicate with another computer over a network, you must do two things: 1- Use the set of rules governing communication over the network, called a protocol. Your computer will generally handle this. 2- Know the address of the computer you want to communicate with. There are two types of network addresses: ŌĆō Medium access control (MAC) address which is used inside a single network ŌĆō Internet protocol (IP) address which is used on the Internet
- 9. World Wide Web ’ü« The World Wide Web (web for short or www) is a collection of interlinked multimedia documents that are stored on the Internet and accessed using a common protocol (HTTP). ’ü« So, what is the relation between the internet and the World Wide Web? ŌĆō World Wide Web (WWW) is an Internet based software application. ’ü« Other Internet applications are: ŌĆō Email ŌĆō ftp (file transfer protocol) ŌĆō Messenger
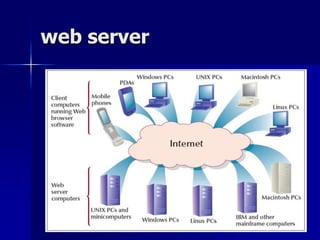
- 10. web server ’ü« is a computer programs that delivers (serves) content web pages, using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol HTTP. ’ü« The term web server can also refer to a computer connected to the Internet that contains files their owners have made available publicly through their Internet connections.
- 11. Web Client ’ü« When you use your Internet connection to become part of the Web, your computer becomes a Web client in a worldwide network called a client/server network. ’ü« Web browsers are software that you run on your computer to make it work as a Web client
- 12. web server
- 13. Web servers ’ü« Apache HTTP Server which occupies (69.01%) of the general use. It is developed in 1994 by Rob McCool. ’ü« It is Available for free charge. ’ü« It Runs on operating systems including FreeBSD-UNIX, HP-UX, Linux, Microsoft Windows, SCO-UNIX and Solaris
- 14. Web servers ’ü« Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) which occupies (23.26%) of the general use. ’ü« It comes bundled with Microsoft Windows Server operating system. ’ü« It runs on Windows 2003 Server and Windows XP.
- 15. Web servers ’ü« Sun Java System Web Server (JSWS) (former names are Sun One, iPlanet Enterprise Server and Netscape Enterprise Server) (0.86%)
- 16. HTML ’ü« HTML is a standard language used on the Web to format documents. ’ü« HTML uses codes (tags) to tell the Web browser software how to display text. ’ü« HTML document is defined as a text file that contains HTML tags. ’ü« When a Web browser displays an HTML document, it is referred to as a Web page.
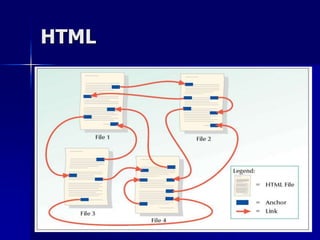
- 17. HTML ’ü« One of the most important features of html is HTML anchor tag ’ü« create Hypertext links. ’ü« Hypertext links can connect HTML documents together or can connect one part of HTML document to another part. ’ü« When hyperlinks connect to Multimedia files , it is called Hypermedia links.
- 18. HTML
- 19. HTML ’ü« Having a collection of linked Web pages with a common theme or focus is called a website. ’ü« Each website should have a main or home page to start the web site from.
- 20. Domain Name Addressing ’ü« Each computer on the Web is given a unique identification number called Internet Protocol Address or (IP). ’ü« Remembering IP addresses are hard to remember ’ü« IP address may also be assigned a host or domain name.
- 21. Domain Name Addressing ’ü« Domain name are unique name associated with specific IP address by a program that runs on an Internet host computer. ’ü« This program is called DNS (Domain Name System ) software. ’ü« Domain Name Software or (DNS) is an Internet service that translates domain names into IP addresses.
- 22. Domain Name Addressing ’ü« Every time you use a domain name, a DNS service must translate the name into the corresponding IP address. ’ü« For example, the domain name www.example.com might translate to 198.105.232.4. ’ü« The host computer that runs the DNS service or software is called Domain name server or DNS server.
- 23. Domain Name Addressing ’ü« The last part of domain name is called its top-level domain (TLD).
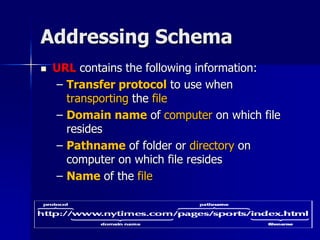
- 24. Addressing Schema ’ü« How to tell the browser the needed information to allocate the wanted web site to be displayed. ’ü« The Addressing schema = uniform resource allocator (URL) ’ü« URLs, or Uniform Resource Locators, are the schema by which documents or data are addressed in the World Wide Web.
- 25. Addressing Schema ’ü« URL contains the following information: ŌĆō Transfer protocol to use when transporting the file ŌĆō Domain name of computer on which file resides ŌĆō Pathname of folder or directory on computer on which file resides ŌĆō Name of the file
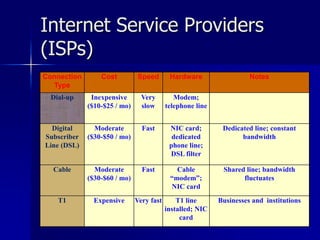
- 26. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) ’ü« ISP is a company that offers its customer access to the Internet. ’ü« The ISP connects to its customers using a data transmission technology appropriate for delivering Internet Protocol datagrams ŌĆō dial-up ŌĆō DSL ŌĆō cable modem ŌĆō wireless ŌĆō dedicated high-speed interconnects.
- 27. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) ’ü« ISPs charge persons for a fee and provide the following services: ŌĆō Adding your computer to the ISPŌĆÖs network, allowing you to communicate with other computers on the Internet ŌĆō Giving your computer an IP address, allowing other computers on the Internet to communicate with you ŌĆō Providing you access to a DNS server.
- 28. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) Connection Type Cost Speed Hardware Notes Dial-up Inexpensive ($10-$25 / mo) Very slow Modem; telephone line Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Moderate ($30-$50 / mo) Fast NIC card; dedicated phone line; DSL filter Dedicated line; constant bandwidth Cable Moderate ($30-$60 / mo) Fast Cable ŌĆ£modemŌĆØ; NIC card Shared line; bandwidth fluctuates T1 Expensive Very fast T1 line installed; NIC card Businesses and institutions
- 29. The Structure of the Internet ’ü« To understand how to get an IP address from a URL, we need to understand the basic structure of the Internet. root com org net edu bellsouth yahoo w3c hypercon kctcs uky www www mail www
- 30. Who Structuring the Internet? ’ü« Networks from corporations, commercial firms, and other companies ’ü« Telephone companies ’ü« Cable companies ’ü« Satellite companies ’ü« Government
- 31. who is controlling the internet? ’ü« generally speaking there is no single entity controls or owns the Internet. ’ü« The Internet is a public, cooperative, and independent network.
- 32. who is controlling the internet? ’ü« Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN). Its task is to manage the logistics of Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and domain names. ’ü« World Wide Web Consortium (W3C): Its task is to develop and tests advanced Internet technologies.
- 33. steps followed to retrieve a certain page through the internet ’ü« http://www.feng.benha.edu/staff/ahmed/index.html ’ü« http stands for hypertext transfer protocol, the protocol for retrieving web pages ’ü« www is the name of the server (with a specific IP address) ’ü« feng is a subdomain of benha ’ü« benha is the subdomain of edu ’ü« edu is the top level domain ’ü« /staff/ahmed/ is the name of the folder (or directory) on the server where the page is stored. This part of the URL is called the path. ’ü« index.html is the name of the file we want to see
- 34. Example ISP is BellSouth (www.bellsouth.com If you try to reach www.kctcs.edu
- 35. The Client-Server Relationship ’ü« Now you located the computer you wish to communicate (remote host or server) ’ü« Your machine is a local host or client ’ü« Client request web pages from the server ’ü« Web pages are written in HTML (text + multimedia) ’ü« Received web pages are read by web browsers (IE, FireFoxŌĆ”)
- 36. HTML Example <HTML> <BODY> <CENTER> <B> Hello, World! </B> </CENTER> <BR> <FONT COLOR=ŌĆ£REDŌĆØ> This text is red. </FONT> <BR> <A href=ŌĆ£www.kctcs.eduŌĆØ> Go to kctcs.edu. </A> </BODY> </HTML>
- 37. HTML Example Hello, World! This text is red. Go to kctcs.edu.
- 38. More on Browsers ’ü« The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) has tried to establish standards for HTML that all browsers should support. ’ü« A good web page designer will test his or her page in several browsers before publishing it.
- 39. Main Elements of Web Browsers
- 40. Main Elements of Web Browsers History
- 41. Hyperlinks: ŌĆō The true power of HTML lies in the use of hyperlinks. ŌĆō Most browsers render hyperlinked text in blue and underline it. ŌĆō Hyperlinked graphics have a blue border. ŌĆō The browserŌĆÖs status bar shows the URL of the resource linked to by the hyperlink. ŌĆō The browser changes the cursor, usually to a hand.
- 42. Browser cache ’ü« In the interest of speed, most browsers will cache web pages the first time they are visited. ’ü« On subsequent visits, it displays the cached copy instead of requesting the page from the server. ’ü« If you do not believe you are seeing the most up-to-date information, click your browserŌĆÖs Refresh or Reload button to force the browser to request the page from the server.
- 43. Browser Cookies ŌĆóSome web sites appear to ŌĆ£rememberŌĆØ your preferences on subsequent visits. ŌĆóThis is accomplished in one of two ways: ŌĆó A server-side database stores your preferences. When you visit the site, you enter a username and password, and your preferences are loaded from the database. ŌĆó On your first visit, the site silently places a small text file (called a cookie) on your hard drive. This file contains your preferences and is automatically loaded by the site when you visit
- 44. Search Engines ’ü« Allows the user to type in a word or phrase to search for, then returns results that it determines most closely match the userŌĆÖs request. ’ü« The userŌĆÖs request is called a query. Each individual result is called a hit. ’ü« Some popular search engines are Yahoo, Google and AltaVista
- 45. Search Engines ’ü« Search engines are constantly updating their ŌĆ£knowledgeŌĆØ of information on the Internet using spiders. ’ü« Spiders are programs that crawl the Internet (i.e. follow all possible links and reporting the information found there back to the search engine.). ’ü« Some search engines do not use spiders. Instead, they query many other search engines and combine the list of hits. These engines are called meta-search engines. Some popular meta-search engines are Dogpile, MetaCrawler, and Excite.
- 46. Email ’ü« To send and receive email, you need an email account. ’ü« An email address of the form username@domainname.tld. ’ü« Mail storage where your incoming messages are stored. (ISP ŌĆ£10MŌĆØ- and web mails ŌĆ£2GŌĆØ)
- 47. File Transfer ŌĆó Files can be transferred from one computer to another over the Internet using the file transfer protocol (FTP). ŌĆóThe process of transferring a file from a remote host to your local machine is called downloading. ŌĆóThe process of transferring a file from your local machine is called uploading. ŌĆóMost browsers natively support downloading, but uploading often requires a special utility called an FTP client.
- 48. File Transfer To download with an Internet browser,
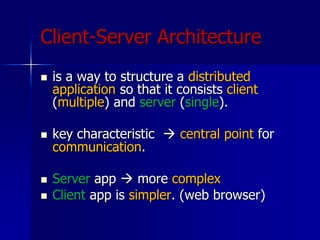
- 49. Client-Server Architecture ’ü« is a way to structure a distributed application so that it consists client (multiple) and server (single). ’ü« key characteristic ’āĀ central point for communication. ’ü« Server app ’āĀ more complex ’ü« Client app is simpler. (web browser)
- 50. Client-Server Architecture ’ü« The server runs on a port (standard=80) and network IP address (need to be known) that is known to the client module. ’ü« The server need not be configured with any information about the clients. (many->one) ’ü« The clients only need to know the IP address of the computer on which the server is running
- 51. ’ü« Client server ’āĀ simplicity and ease of maintenance ’ü« It has one drawback ŌĆö It does not utilize the computing power of the client computers.
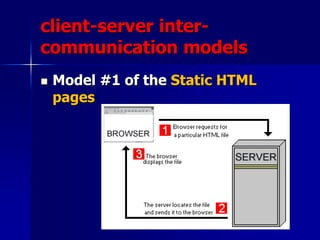
- 52. client-server inter- communication models ’ü« Model #1 of the Static HTML pages
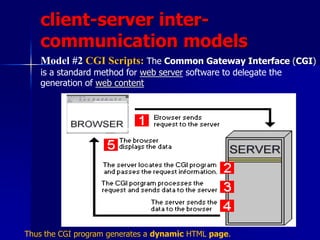
- 53. client-server inter- communication models Model #2 CGI Scripts: The Common Gateway Interface (CGI) is a standard method for web server software to delegate the generation of web content Thus the CGI program generates a dynamic HTML page.
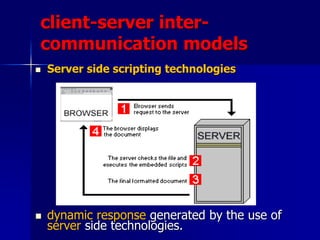
- 54. client-server inter- communication models ’ü« Server side scripting technologies ’ü« dynamic response generated by the use of server side technologies.
- 55. There are many server side technologies today: Active Server Pages (ASP): A Microsoft technology. ASP pages typically have the extension .asp. Personal Home Pages (PHP): An open source technology. PHP pages typically have .php, .phtml or .php3 file name extensions. Java Server Pages: .jsp pages contain Java code. With these server technologies it has become easier to maintain Web pages especially helpful for a large web site. The developer needs to embed the server-side language code inside the HTML page. This code is passed to the appropriate interpreter which processes these instructions and generates the final HTML displayed by the browser Server side scripting technologies
- 56. Peer-to-Peer Architecture ’ü« More complex ’ü« Each computer need to know the network addresses others. ’ü« propagating changes to the different software modules is harder. ’ü« result in much more scalable applications.
- 58. Instant Messaging ’ü« Instant Messaging (IM) where software applications, such as MSN Messenger or AOL Instant Messenger ’ü« While most vendors offer a free version of their IM software others have begun to focus on enterprise versions of IM software as business and corporations have moved towards implementing IM as a standard communications tool for business.
- 59. Affinity Communities ŌĆ½ž¦┘ä┘ģž¼ž¬┘ģž╣ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘鞦ž▒ž©ŌĆ¼ ’ü« based around file-sharing ’ü« Napster. Affinity Communities are based on users collaborating and searching other user's computers for information and files.
- 60. Static vs. Dynamic pages ’ü« In Static pages, the contents (text/ links/ images) are the same each time it is delivered by the web server. WebServer Client 1 Author writes HTML 2 Client requests page 3 Web server locates .htm file HTML stream returned to browser 4 5 Browser processes page
- 61. Static vs. Dynamic pages ’ü« Server-side Dynamic Page Delivery Web Server Client 1 Author writes instructions 2 Client requests page 3 Web server locates instructions file HTML stream returned to browser 5 6 Browser processes page 4 Web server processes instructions to create HTML Client-side Dynamic Page Delivery