Multiplex.pptx
0 likes1 view
Multiplexing allows multiple information channels to be transmitted simultaneously over a single transmission medium. There are two main multiplexing methods: frequency division multiplexing (FDM) and time division multiplexing (TDM). FDM divides the available bandwidth into non-overlapping frequency slots, with each slot carrying a single information channel modulated onto a separate carrier frequency. TDM puts information from different channels into separate non-overlapping time slots within a single wider frequency band, allowing multiple users to share the same channel by taking turns.
1 of 8





Recommended
2109986 635316076040095000



2109986 635316076040095000srilaxmi524
Ã˝
The document discusses baseband and modulated communication signals. It defines baseband signals as those that do not use modulation and transmit information in its original form within the baseband frequency range. Modulated signals use carrier waves to shift the information signal to higher frequencies suitable for transmission. The key types of modulation discussed are amplitude modulation (AM), which varies the amplitude of the carrier wave, and angle modulation including frequency modulation (FM) and phase modulation (PM), which vary the frequency or phase of the carrier. Common applications of baseband signals include telephony and digital data transmission over copper wires, while modulated signals are required for wireless transmission through free space using radio frequencies.Tham khao ofdm tutorial



Tham khao ofdm tutorialTrần Đức Mạnh
Ã˝
OFDM is a digital multi-carrier modulation technique that divides the available spectrum into multiple orthogonal subcarriers. It allows high spectral efficiency by spacing the carriers to maintain orthogonality even when their spectra overlap. The document provides an intuitive explanation of OFDM using analogies like a shower head vs faucet and multiple smaller trucks vs one large truck. It explains how OFDM provides resistance to interference by spreading data across orthogonal subcarriers rather than a single carrier. The key concept of orthogonality allows the subcarriers to overlap without interference by ensuring the area under one subcarrier's frequency multiplied by another is always zero.Ofdm



OfdmRasim Levashov
Ã˝
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) is a digital multi-carrier modulation technique that divides the available bandwidth into multiple orthogonal subcarriers.
- OFDM provides advantages over traditional Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) by making the subcarriers orthogonal, allowing them to overlap without interference and achieving higher spectral efficiency.
- The document provides an example of how OFDM works by taking a bit stream and mapping bits in groups of four to four orthogonal subcarriers at frequencies of 1, 2, 3, and 4 Hz using BPSK modulation before combining them to generate the OFDM signal.Ofdm tutorial



Ofdm tutorialPrashant Sengar
Ã˝
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) is a digital multi-carrier modulation technique that divides the available bandwidth into multiple orthogonal subcarriers.
- OFDM provides advantages over traditional Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) by making the subcarriers orthogonal, allowing them to overlap without interference and achieving higher spectral efficiency.
- The document provides an example of how OFDM works by taking a bit stream and mapping bits in groups of four to four orthogonal subcarriers at frequencies of 1, 2, 3, and 4 Hz using BPSK modulation before combining them to generate the OFDM signal.MULTIPLEXING_AND_DEMULTIPLEXING (2).pdf



MULTIPLEXING_AND_DEMULTIPLEXING (2).pdfClarkLinogaoFelisild
Ã˝
Multiplexing allows multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously over a single communication channel by combining the signals. There are two main types of multiplexing: frequency-division multiplexing (FDM), which divides the channel bandwidth into smaller frequency bands, and time-division multiplexing (TDM), which allocates time slots to each signal in turn. At the receiving end, a demultiplexer separates the signals back into their individual channels. Multiplexing techniques such as FDM and TDM have made technologies like cable TV and telephone networks feasible by efficiently increasing transmission capacity.Frequency translation



Frequency translationMOHAMMAD AKRAM
Ã˝
In this ppt we learn about the method of frquency translation.How it can be done , what are their benefits etc.Introduction to Modulation and Demodulation.pptx



Introduction to Modulation and Demodulation.pptxNiharranjanAdit
Ã˝
1) The document discusses various modulation techniques used in communication systems including amplitude modulation (AM), frequency modulation (FM), phase modulation (PM), pulse amplitude modulation (PAM), frequency-shift keying (FSK), phase-shift keying (PSK), and their derivatives.
2) It explains the basic concepts of modulation such as using a message signal to control parameters of a carrier signal to transmit information.
3) Key modulation types covered are AM, which varies the amplitude of a carrier signal; FSK and PSK, which are used for digital modulation by shifting the frequency or phase of a carrier.Analog communication



Analog communicationA. Shamel
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of analog signal communication systems. It discusses how baseband signals need to be modulated to higher frequencies suitable for transmission over a channel. It introduces multiplexing as a way to send multiple signals simultaneously. It describes the main types of analog modulation: amplitude modulation (AM), frequency modulation (FM), and phase modulation (PM). It compares AM and FM and discusses their advantages and disadvantages. It also provides a brief overview of noise in communication systems and how it can degrade performance.Communication systems



Communication systemsUmang Gupta
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of key concepts in communications systems, including:
1) It describes the basic components of a communications system including the input/output transducers, transmitter, channel, and receiver.
2) It discusses different types of signals that can be transmitted through a channel including analog modulation techniques like AM, FM and PM as well as digital modulation.
3) It provides an overview of electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum used for wireless communication. Unit-II Data Communication.ppt



Unit-II Data Communication.pptshloksharma1315
Ã˝
This document discusses various methods for compressing analog and digital data. It begins by explaining why analog signals are modulated, such as to allow for more efficient transmission. It then covers analog to digital conversion techniques like pulse code modulation (PCM). On the digital side, it discusses lossless compression methods like run-length encoding, Huffman encoding, and Lempel-Ziv encoding. Lossy compression techniques like JPEG and MPEG are also summarized. The document aims to provide an overview of different data compression strategies.Multiplexing



MultiplexingNaveed Ahmed
Ã˝
Multiplexing is a technique used to combine multiple signals into one signal over a shared medium. There are different types of multiplexing including frequency division multiplexing (FDM), time division multiplexing (TDM), and wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). In FDM, the medium is divided by frequency into channels, with each signal given its own unique frequency. In TDM, the medium is divided over time into time slots that are assigned to different signals on a timed schedule. Multiplexing allows more efficient use of transmission bandwidth and is used widely in telecommunications including telephone networks and radio/television broadcast.EC6651 COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING UNIT 1



EC6651 COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING UNIT 1RMK ENGINEERING COLLEGE, CHENNAI
Ã˝
AM – Frequency spectrum – vector representation – power relations – generation of AM – DSB, DSB/SC, SSB, VSB AM Transmitter & Receiver; FM and PM – frequency spectrum – power relations : NBFM & WBFM, Generation of FM and DM, Armstrong method & Reactance modulations : FM & PM frequency.
EVM Degradation in LTE systems by RF Filtering 



EVM Degradation in LTE systems by RF Filtering criterion123
Ã˝
This document discusses OFDM, OFDMA, and SC-FDMA techniques used in LTE. It explains that LTE uses OFDM for the downlink to transmit over multiple narrow subcarriers to overcome multipath fading. OFDMA is used to enable time-frequency scheduling by allocating users to subsets of subcarriers. SC-FDMA is used for the uplink instead of OFDMA to reduce high peak-to-average power ratios. Resource blocks, which are the smallest allocable units, occupy 180kHz frequency bandwidth and 0.5ms time slots. Filter selection impacts error vector magnitude, and filters should have wide bandwidth and stable frequency response even at high temperatures to avoid signal distortion near band edgesDigital Pulse Modulation techniques.pptx



Digital Pulse Modulation techniques.pptxUmaM987983
Ã˝
Digital Pulse Modulation PPT includes all digital pulse modulation techniquesAnalog and digital communications. Electronic Course.pptx



Analog and digital communications. Electronic Course.pptxkeemjupiter
Ã˝
Analog and digital communications. Electronic Course03 linear mod



03 linear modntpc08
Ã˝
This document summarizes linear carrier wave modulation techniques used in telecommunication systems. It discusses amplitude modulation (AM), double sideband modulation (DSB), and single sideband modulation (SSB). It describes how these modulation techniques work in both the time and frequency domains. It also covers topics like modulators, detectors, envelope detection, and power efficiency of different modulation methods.Introduction to Communication Systems 3



Introduction to Communication Systems 3slmnsvn
Ã˝
This document discusses amplitude modulation (AM) and detection. It begins by introducing AM, including its use of a carrier signal to transmit a baseband message signal. It describes how AM varies the amplitude of the carrier based on the message signal. The document then discusses envelope detection used at the receiver to recover the original message signal. It also introduces double sideband suppressed carrier AM, which removes the carrier component to increase power efficiency, requiring a product detector instead of envelope detection.Pcm



Pcmmanish katara
Ã˝
1. PCM uses time division multiplexing to transmit multiple telephone calls over a single transmission line by sampling each call and transmitting the samples in brief time slots.
2. During sampling, the amplitude of an analog signal is measured at regular intervals and assigned a digital code. This process is called quantization and results in quantization distortion from approximating the original signal.
3. Non-uniform quantization, called companding, is used to provide more quantization levels for smaller amplitudes that are more common in speech, improving the signal-to-noise ratio across all amplitudes.Chapter-8_Multiplexing.pptx



Chapter-8_Multiplexing.pptxMDTahsinAmin3
Ã˝
Frequency division multiplexing (FDM) allows multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously across a single communication channel by assigning each signal a unique frequency band. At the receiving end, filters separate the signals by frequency for delivery. FDM is commonly used in telephone networks and cellular systems. Time division multiplexing (TDM) transmits signals in sequential time slots allocated in a repeating frame. Synchronous TDM pre-assigns slots while statistical TDM dynamically allocates slots. TDM is used in digital transmission and SONET networks. Multiplexing techniques improve bandwidth utilization by allowing multiple users to share transmission capacity.Wireless communication



Wireless communicationMukesh Chinta
Ã˝
This presentation deals with topics such as Electromagnetic Spectrum, Wireless Propagation, Signals, Signal propagation effects, Spread spectrum and cellular systems. communication system lec3



communication system lec3ZareenRauf1
Ã˝
What is communication?
Information Transfer Modulation
Communication System
Input/output Device Transmitter Channel
Noise Receiver
Simplex and duplex communication
Lec am modulation



Lec am modulationSarah Krystelle
Ã˝
Modulation involves modifying a carrier signal with a modulating signal to make it suitable for transmission. There are two main types of modulation: analog and digital. Analog modulation includes amplitude modulation (AM), where the amplitude of the carrier wave varies with the modulating signal. AM can take different forms such as double sideband suppressed carrier (DSBSC) and single sideband (SSB) to improve power and bandwidth efficiency.dspppt.pptx



dspppt.pptxAbhishekKumar129104
Ã˝
1. The presentation discusses frequency translation, modulation techniques, signal detection, and overranging issues. It covers topics like frequency multiplexing, modulation, amplitude shift keying (ASK), phase shift keying (PSK), and frequency shift keying (FSK).
2. Frequency translation involves translating a signal from one frequency range to another. This allows combining multiple signals into a single channel and making antenna sizes practical. Modulation involves modifying a carrier wave with an information signal.
3. Digital modulation techniques covered include ASK, PSK, and FSK. In ASK, amplitude is changed to indicate bits. In PSK, phase is shifted. In FSK, frequency is altered to represent bits. DigitalCommunication Theory - Angle Modulation .pdf



Communication Theory - Angle Modulation .pdfRajaSekaran923497
Ã˝
This document discusses angle modulation techniques, specifically frequency modulation (FM) and phase modulation (PM). It defines these terms and discusses the key aspects of narrowband and wideband FM. Narrowband FM has a modulation index below 1, while wideband FM is above 0.5. Carson's rule provides an estimate for the bandwidth of an FM signal. FM can be demodulated using a frequency discriminator or phase-locked loop (PLL). The PLL performs better in noise. Wideband FM transmission is used for broadcast to transmit high quality audio over a large bandwidth.Frequency modulation2



Frequency modulation2Sarah Krystelle
Ã˝
This document discusses frequency modulation (FM) and provides details about:
1) FM can be used for both analog and digital data transmission by varying the instantaneous frequency of a carrier wave.
2) In analog FM the carrier frequency varies continuously, while in digital FM it shifts abruptly between discrete frequency states.
3) FM bandwidth depends on the modulation index, with higher indices resulting in wider bandwidth signals classified as wideband FM.analog communication system for undergraduate .pdf



analog communication system for undergraduate .pdfAlaAwouda
Ã˝
This document provides an outline and introduction to the concepts of analog and digital communication systems. It discusses key topics such as modulation techniques, signal systems, bandwidth, and noise. Modulation techniques covered include amplitude modulation, frequency modulation, phase modulation, amplitude shift keying, frequency shift keying, and phase shift keying. It also discusses pulse code modulation, differential pulse code modulation, delta modulation, and adaptive delta modulation. Production of amplitude modulated signals using a block diagram approach is described.slidesgo-driving-sustainability-the-green-computing-challenge-in-iot-20240514...



slidesgo-driving-sustainability-the-green-computing-challenge-in-iot-20240514...DedyWahyuHerdiyanto
Ã˝
driving-sustainability-the-green-computing-challenge-in-iotMore Related Content
Similar to Multiplex.pptx (20)
Communication systems



Communication systemsUmang Gupta
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of key concepts in communications systems, including:
1) It describes the basic components of a communications system including the input/output transducers, transmitter, channel, and receiver.
2) It discusses different types of signals that can be transmitted through a channel including analog modulation techniques like AM, FM and PM as well as digital modulation.
3) It provides an overview of electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum used for wireless communication. Unit-II Data Communication.ppt



Unit-II Data Communication.pptshloksharma1315
Ã˝
This document discusses various methods for compressing analog and digital data. It begins by explaining why analog signals are modulated, such as to allow for more efficient transmission. It then covers analog to digital conversion techniques like pulse code modulation (PCM). On the digital side, it discusses lossless compression methods like run-length encoding, Huffman encoding, and Lempel-Ziv encoding. Lossy compression techniques like JPEG and MPEG are also summarized. The document aims to provide an overview of different data compression strategies.Multiplexing



MultiplexingNaveed Ahmed
Ã˝
Multiplexing is a technique used to combine multiple signals into one signal over a shared medium. There are different types of multiplexing including frequency division multiplexing (FDM), time division multiplexing (TDM), and wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). In FDM, the medium is divided by frequency into channels, with each signal given its own unique frequency. In TDM, the medium is divided over time into time slots that are assigned to different signals on a timed schedule. Multiplexing allows more efficient use of transmission bandwidth and is used widely in telecommunications including telephone networks and radio/television broadcast.EC6651 COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING UNIT 1



EC6651 COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING UNIT 1RMK ENGINEERING COLLEGE, CHENNAI
Ã˝
AM – Frequency spectrum – vector representation – power relations – generation of AM – DSB, DSB/SC, SSB, VSB AM Transmitter & Receiver; FM and PM – frequency spectrum – power relations : NBFM & WBFM, Generation of FM and DM, Armstrong method & Reactance modulations : FM & PM frequency.
EVM Degradation in LTE systems by RF Filtering 



EVM Degradation in LTE systems by RF Filtering criterion123
Ã˝
This document discusses OFDM, OFDMA, and SC-FDMA techniques used in LTE. It explains that LTE uses OFDM for the downlink to transmit over multiple narrow subcarriers to overcome multipath fading. OFDMA is used to enable time-frequency scheduling by allocating users to subsets of subcarriers. SC-FDMA is used for the uplink instead of OFDMA to reduce high peak-to-average power ratios. Resource blocks, which are the smallest allocable units, occupy 180kHz frequency bandwidth and 0.5ms time slots. Filter selection impacts error vector magnitude, and filters should have wide bandwidth and stable frequency response even at high temperatures to avoid signal distortion near band edgesDigital Pulse Modulation techniques.pptx



Digital Pulse Modulation techniques.pptxUmaM987983
Ã˝
Digital Pulse Modulation PPT includes all digital pulse modulation techniquesAnalog and digital communications. Electronic Course.pptx



Analog and digital communications. Electronic Course.pptxkeemjupiter
Ã˝
Analog and digital communications. Electronic Course03 linear mod



03 linear modntpc08
Ã˝
This document summarizes linear carrier wave modulation techniques used in telecommunication systems. It discusses amplitude modulation (AM), double sideband modulation (DSB), and single sideband modulation (SSB). It describes how these modulation techniques work in both the time and frequency domains. It also covers topics like modulators, detectors, envelope detection, and power efficiency of different modulation methods.Introduction to Communication Systems 3



Introduction to Communication Systems 3slmnsvn
Ã˝
This document discusses amplitude modulation (AM) and detection. It begins by introducing AM, including its use of a carrier signal to transmit a baseband message signal. It describes how AM varies the amplitude of the carrier based on the message signal. The document then discusses envelope detection used at the receiver to recover the original message signal. It also introduces double sideband suppressed carrier AM, which removes the carrier component to increase power efficiency, requiring a product detector instead of envelope detection.Pcm



Pcmmanish katara
Ã˝
1. PCM uses time division multiplexing to transmit multiple telephone calls over a single transmission line by sampling each call and transmitting the samples in brief time slots.
2. During sampling, the amplitude of an analog signal is measured at regular intervals and assigned a digital code. This process is called quantization and results in quantization distortion from approximating the original signal.
3. Non-uniform quantization, called companding, is used to provide more quantization levels for smaller amplitudes that are more common in speech, improving the signal-to-noise ratio across all amplitudes.Chapter-8_Multiplexing.pptx



Chapter-8_Multiplexing.pptxMDTahsinAmin3
Ã˝
Frequency division multiplexing (FDM) allows multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously across a single communication channel by assigning each signal a unique frequency band. At the receiving end, filters separate the signals by frequency for delivery. FDM is commonly used in telephone networks and cellular systems. Time division multiplexing (TDM) transmits signals in sequential time slots allocated in a repeating frame. Synchronous TDM pre-assigns slots while statistical TDM dynamically allocates slots. TDM is used in digital transmission and SONET networks. Multiplexing techniques improve bandwidth utilization by allowing multiple users to share transmission capacity.Wireless communication



Wireless communicationMukesh Chinta
Ã˝
This presentation deals with topics such as Electromagnetic Spectrum, Wireless Propagation, Signals, Signal propagation effects, Spread spectrum and cellular systems. communication system lec3



communication system lec3ZareenRauf1
Ã˝
What is communication?
Information Transfer Modulation
Communication System
Input/output Device Transmitter Channel
Noise Receiver
Simplex and duplex communication
Lec am modulation



Lec am modulationSarah Krystelle
Ã˝
Modulation involves modifying a carrier signal with a modulating signal to make it suitable for transmission. There are two main types of modulation: analog and digital. Analog modulation includes amplitude modulation (AM), where the amplitude of the carrier wave varies with the modulating signal. AM can take different forms such as double sideband suppressed carrier (DSBSC) and single sideband (SSB) to improve power and bandwidth efficiency.dspppt.pptx



dspppt.pptxAbhishekKumar129104
Ã˝
1. The presentation discusses frequency translation, modulation techniques, signal detection, and overranging issues. It covers topics like frequency multiplexing, modulation, amplitude shift keying (ASK), phase shift keying (PSK), and frequency shift keying (FSK).
2. Frequency translation involves translating a signal from one frequency range to another. This allows combining multiple signals into a single channel and making antenna sizes practical. Modulation involves modifying a carrier wave with an information signal.
3. Digital modulation techniques covered include ASK, PSK, and FSK. In ASK, amplitude is changed to indicate bits. In PSK, phase is shifted. In FSK, frequency is altered to represent bits. DigitalCommunication Theory - Angle Modulation .pdf



Communication Theory - Angle Modulation .pdfRajaSekaran923497
Ã˝
This document discusses angle modulation techniques, specifically frequency modulation (FM) and phase modulation (PM). It defines these terms and discusses the key aspects of narrowband and wideband FM. Narrowband FM has a modulation index below 1, while wideband FM is above 0.5. Carson's rule provides an estimate for the bandwidth of an FM signal. FM can be demodulated using a frequency discriminator or phase-locked loop (PLL). The PLL performs better in noise. Wideband FM transmission is used for broadcast to transmit high quality audio over a large bandwidth.Frequency modulation2



Frequency modulation2Sarah Krystelle
Ã˝
This document discusses frequency modulation (FM) and provides details about:
1) FM can be used for both analog and digital data transmission by varying the instantaneous frequency of a carrier wave.
2) In analog FM the carrier frequency varies continuously, while in digital FM it shifts abruptly between discrete frequency states.
3) FM bandwidth depends on the modulation index, with higher indices resulting in wider bandwidth signals classified as wideband FM.analog communication system for undergraduate .pdf



analog communication system for undergraduate .pdfAlaAwouda
Ã˝
This document provides an outline and introduction to the concepts of analog and digital communication systems. It discusses key topics such as modulation techniques, signal systems, bandwidth, and noise. Modulation techniques covered include amplitude modulation, frequency modulation, phase modulation, amplitude shift keying, frequency shift keying, and phase shift keying. It also discusses pulse code modulation, differential pulse code modulation, delta modulation, and adaptive delta modulation. Production of amplitude modulated signals using a block diagram approach is described.More from DedyWahyuHerdiyanto (7)
slidesgo-driving-sustainability-the-green-computing-challenge-in-iot-20240514...



slidesgo-driving-sustainability-the-green-computing-challenge-in-iot-20240514...DedyWahyuHerdiyanto
Ã˝
driving-sustainability-the-green-computing-challenge-in-iotslidesgo-efficient-strategies-for-green-computing-202405140856401UdC.pdf



slidesgo-efficient-strategies-for-green-computing-202405140856401UdC.pdfDedyWahyuHerdiyanto
Ã˝
Green Computing BasicELECTRIC GENERATION SYSTEM FROM RENEWABLE ENERGY AND INTELLEGENCE.pptx



ELECTRIC GENERATION SYSTEM FROM RENEWABLE ENERGY AND INTELLEGENCE.pptxDedyWahyuHerdiyanto
Ã˝
just some presentation IoT Pertemuan 1.pptx



IoT Pertemuan 1.pptxDedyWahyuHerdiyanto
Ã˝
Dokumen tersebut membahas tentang konsep Internet of Things (IoT) dimulai dari asal mula telemetri, layer dan protokol komunikasi IoT, teknologi jaringan nirkabel seperti LoRa dan jaringan sensor nirkabel, serta penerapannya dalam bidang pertanian.Presentation Philipine.pptx



Presentation Philipine.pptxDedyWahyuHerdiyanto
Ã˝
Indonesia has great potential for wind power generation due to its location between two oceans and continents. However, as of 2015 only 0.01% of wind potential was being utilized, producing just 3.1 MW of electricity. While the Indonesian government has implemented rules to develop wind power plants in strategic locations, utilization remains low due to various challenges.slidesgo-driving-sustainability-the-green-computing-challenge-in-iot-20240514...



slidesgo-driving-sustainability-the-green-computing-challenge-in-iot-20240514...DedyWahyuHerdiyanto
Ã˝
Recently uploaded (20)
US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
Ã˝
Preface: The ReGenX Generator innovation operates with a US Patented Frequency Dependent Load Current Delay which delays the creation and storage of created Electromagnetic Field Energy around the exterior of the generator coil. The result is the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs any magnitude of Positive Electro-Mechanical Work at infinite efficiency on the generator's Rotating Magnetic Field, increasing its Kinetic Energy and increasing the Kinetic Energy of an EV or ICE Vehicle to any magnitude without requiring any Externally Supplied Input Energy. In Electricity Generation applications the ReGenX Generator innovation now allows all electricity to be generated at infinite efficiency requiring zero Input Energy, zero Input Energy Cost, while producing zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions, zero Air Pollution and zero Nuclear Waste during the Electricity Generation Phase. In Electric Motor operation the ReGen-X Quantum Motor now allows any magnitude of Work to be performed with zero Electric Input Energy.
Demonstration Protocol: The demonstration protocol involves three prototypes;
1. Protytpe #1, demonstrates the ReGenX Generator's Load Current Time Delay when compared to the instantaneous Load Current Sine Wave for a Conventional Generator Coil.
2. In the Conventional Faraday Generator operation the created Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Negative Work at infinite efficiency and it reduces the Kinetic Energy of the system.
3. The Magnitude of the Negative Work / System Kinetic Energy Reduction (in Joules) is equal to the Magnitude of the created Electromagnetic Field Energy (also in Joules).
4. When the Conventional Faraday Generator is placed On-Load, Negative Work is performed and the speed of the system decreases according to Lenz's Law of Induction.
5. In order to maintain the System Speed and the Electric Power magnitude to the Loads, additional Input Power must be supplied to the Prime Mover and additional Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft.
6. For example, if 100 Watts of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >100 Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
7. If 1 MW of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >1 MW Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
8. Generally speaking the ratio is 2 Watts of Mechanical Input Power to every 1 Watt of Electric Output Power generated.
9. The increase in Drive Shaft Mechanical Input Power is provided by the Prime Mover and the Input Energy Source which powers the Prime Mover.
10. In the Heins ReGenX Generator operation the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Positive Work at infinite efficiency and it increases the Kinetic Energy of the system.Optimization of Cumulative Energy, Exergy Consumption and Environmental Life ...



Optimization of Cumulative Energy, Exergy Consumption and Environmental Life ...J. Agricultural Machinery
Ã˝
Optimal use of resources, including energy, is one of the most important principles in modern and sustainable agricultural systems. Exergy analysis and life cycle assessment were used to study the efficient use of inputs, energy consumption reduction, and various environmental effects in the corn production system in Lorestan province, Iran. The required data were collected from farmers in Lorestan province using random sampling. The Cobb-Douglas equation and data envelopment analysis were utilized for modeling and optimizing cumulative energy and exergy consumption (CEnC and CExC) and devising strategies to mitigate the environmental impacts of corn production. The Cobb-Douglas equation results revealed that electricity, diesel fuel, and N-fertilizer were the major contributors to CExC in the corn production system. According to the Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) results, the average efficiency of all farms in terms of CExC was 94.7% in the CCR model and 97.8% in the BCC model. Furthermore, the results indicated that there was excessive consumption of inputs, particularly potassium and phosphate fertilizers. By adopting more suitable methods based on DEA of efficient farmers, it was possible to save 6.47, 10.42, 7.40, 13.32, 31.29, 3.25, and 6.78% in the exergy consumption of diesel fuel, electricity, machinery, chemical fertilizers, biocides, seeds, and irrigation, respectively. Structural QA/QC Inspection in KRP 401600 | Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3)...



Structural QA/QC Inspection in KRP 401600 | Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3)...slayshadow705
Ã˝
This presentation provides an in-depth analysis of structural quality control in the KRP 401600 section of the Copper Processing Plant-3 (MOF-3) in Uzbekistan. As a Structural QA/QC Inspector, I have identified critical welding defects, alignment issues, bolting problems, and joint fit-up concerns.
Key topics covered:
✔ Common Structural Defects – Welding porosity, misalignment, bolting errors, and more.
✔ Root Cause Analysis – Understanding why these defects occur.
✔ Corrective & Preventive Actions – Effective solutions to improve quality.
✔ Team Responsibilities – Roles of supervisors, welders, fitters, and QC inspectors.
✔ Inspection & Quality Control Enhancements – Advanced techniques for defect detection.
üìå Applicable Standards: GOST, KMK, SNK ‚Äì Ensuring compliance with international quality benchmarks.
üöÄ This presentation is a must-watch for:
‚úÖ QA/QC Inspectors, Structural Engineers, Welding Inspectors, and Project Managers in the construction & oil & gas industries.
‚úÖ Professionals looking to improve quality control processes in large-scale industrial projects.
üì¢ Download & share your thoughts! Let's discuss best practices for enhancing structural integrity in industrial projects.
Categories:
Engineering
Construction
Quality Control
Welding Inspection
Project Management
Tags:
#QAQC #StructuralInspection #WeldingDefects #BoltingIssues #ConstructionQuality #Engineering #GOSTStandards #WeldingInspection #QualityControl #ProjectManagement #MOF3 #CopperProcessing #StructuralEngineering #NDT #OilAndGasdecarbonization steel industry rev1.pptx



decarbonization steel industry rev1.pptxgonzalezolabarriaped
Ã˝
Webinar Decarbonization steel industryWireless-Charger presentation for seminar .pdf



Wireless-Charger presentation for seminar .pdfAbhinandanMishra30
Ã˝
Wireless technology used in chargerEnv and Water Supply Engg._Dr. Hasan.pdf



Env and Water Supply Engg._Dr. Hasan.pdfMahmudHasan747870
Ã˝
Core course, namely Environment and Water Supply Engineering. Full lecture notes are in book format for the BSc in Civil Engineering program. Integration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...



Integration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...ASHISHDESAI85
Ã˝
Combining 3D printing with Internet of Things (IoT) enables the creation of smart, connected, and customizable objects that can monitor, control, and optimize their performance, potentially revolutionizing various industries. oT-enabled 3D printers can use sensors to monitor the quality of prints during the printing process. If any defects or deviations from the desired specifications are detected, the printer can adjust its parameters in real time to ensure that the final product meets the required standards.Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
Ã˝
Welcome to the March 2025 issue of WIPAC Monthly the magazine brought to you by the LinkedIn Group WIPAC Monthly.
In this month's edition, on top of the month's news from the water industry we cover subjects from the intelligent use of wastewater networks, the use of machine learning in water quality as well as how, we as an industry, need to develop the skills base in developing areas such as Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence.
Enjoy the latest editionTaykon-Kalite belgeleri



Taykon-Kalite belgeleriTAYKON
Ã˝
Kalite Politikamız
Taykon Çelik için kalite, hayallerinizi bizlerle paylaştığınız an başlar. Proje çiziminden detayların çözümüne, detayların çözümünden üretime, üretimden montaja, montajdan teslime hayallerinizin gerçekleştiğini gördüğünüz ana kadar geçen tüm aşamaları, çalışanları, tüm teknik donanım ve çevreyi içine alır KALİTE.The Golden Gate Bridge a structural marvel inspired by mother nature.pptx



The Golden Gate Bridge a structural marvel inspired by mother nature.pptxAkankshaRawat75
Ã˝
The Golden Gate Bridge is a 6 lane suspension bridge spans the Golden Gate Strait, connecting the city of San Francisco to Marin County, California.
It provides a vital transportation link between the Pacific Ocean and the San Francisco Bay.
Frankfurt University of Applied Science urkunde



Frankfurt University of Applied Science urkundeLisa Emerson
Ã˝
Duplicate Frankfurt University of Applied Science urkunde, make a Frankfurt UAS degree.US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
Ã˝
Optimization of Cumulative Energy, Exergy Consumption and Environmental Life ...



Optimization of Cumulative Energy, Exergy Consumption and Environmental Life ...J. Agricultural Machinery
Ã˝
Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
Ã˝
Multiplex.pptx
- 1. Multiplex Dedy Wahyu Herdiyanto Komunikasi Nirkabel RF D4 TRE
- 2. INTRODUCTION TO MULTIPLEXING ÔÇ¥ Multiplexing is used for the transmission of a plurality of information channels over a single transmission medium. ÔÇ¥ Multiplexing is a process that combines several signals for simultaneous transmission on one transmission channel. ÔÇ¥ An information channel may be a telephone voice channel, data channel, or a channel carrying image information. ÔÇ¥ There are essentially two generic methods of multiplexing information channels: ÔÇ¥ In the frequency domain; we call this frequency division multiplex (FDM). ÔÇ¥ In the time domain, which we call time division multiplex (TDM)
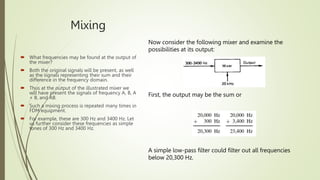
- 3. Mixing  What frequencies may be found at the output of the mixer?  Both the original signals will be present, as well as the signals representing their sum and their difference in the frequency domain.  Thus at the output of the illustrated mixer we will have present the signals of frequency A, B, A + B, and AB.  Such a mixing process is repeated many times in FDM equipment.  For example, these are 300 Hz and 3400 Hz. Let us further consider these frequencies as simple tones of 300 Hz and 3400 Hz. Now consider the following mixer and examine the possibilities at its output: First, the output may be the sum or A simple low-pass filter could filter out all frequencies below 20,300 Hz.
- 4.  Now imagine that instead of two frequencies, we have a continuous spectrum of frequencies between 300 Hz and 3400 Hz (i.e., we have the voice channel). We represent the spectrum as a triangle: As a result of the mixing process (translation) we have another triangle, as follows: When we take the sum, as we did previously, and filter out all other frequencies, we say we have selected the upper sideband. Therefore we have a triangle facing to the right, and we call this an upright or erect sideband. We can also take the difference, such that This is called an inverted sideband. To review, when we take the sum, we get an erect sideband. When we take the difference, frequencies invert and we have an inverted sideband represented by a triangle facing left. Again, this modulation technique is called single-sideband suppressed carrier (SSBSC). It is a type of amplitude modulation (AM). With conventional AM, the modulation produces two sidebands, an upper sideband and a lower sideband, symmetrical on either side of the carrier. Each sideband carries the information signal. If we tune to 870 kHz on the AM dial, 870 kHz is the frequency of the RF carrier, and its sidebands fall on either side, where each sideband is about 7.5 kHz wide. Thus a radio station on the AM dial requires about 15 kHz of spectrum bandwidth.
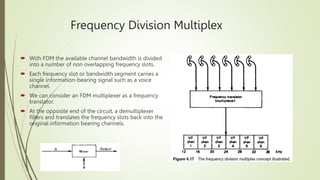
- 5. Frequency Division Multiplex  With FDM the available channel bandwidth is divided into a number of non overlapping frequency slots.  Each frequency slot or bandwidth segment carries a single information-bearing signal such as a voice channel.  We can consider an FDM multiplexer as a frequency translator.  At the opposite end of the circuit, a demultiplexer filters and translates the frequency slots back into the original information bearing channels.
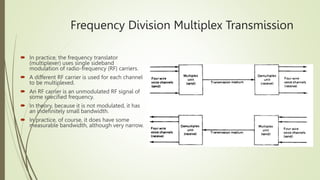
- 6. Frequency Division Multiplex Transmission  In practice, the frequency translator (multiplexer) uses single sideband modulation of radio-frequency (RF) carriers.  A different RF carrier is used for each channel to be multiplexed.  An RF carrier is an unmodulated RF signal of some specified frequency.  In theory, because it is not modulated, it has an indefinitely small bandwidth.  In practice, of course, it does have some measurable bandwidth, although very narrow.
- 7. Time Division Multiplexing ÔÇ¥ A more modern method of multiplexing is TDM, which puts different messages, for example, PCM words from different users, in non overlapping time slots. ÔÇ¥ Each user channel uses a wider frequency band but only a small fraction of time. ÔÇ¥ In addition to the user channels, framing information is needed for the switching circuit at the receiver that separates the user channels (time slots) in the demultiplexer. ÔÇ¥ When the demultiplexer detects the frame synchronization word, it knows that this is the start of a new frame and the next time slot contains the information of user channel 1. ÔÇ¥ This method of TDM is used in high-capacity transmission systems such as optical line systems but also in digital cellular networks where we call it time-division multiple access (TDMA). ÔÇ¥ One user occupies one time slot of a frame, and the time-division principle allows multiple users to access the network at the same time using the same carrier frequency.
- 8. Differences between FDM and FDM












