Hemibody and total body radiation
Download as PPTX, PDF7 likes1,250 views
This document discusses hemi-body and total body irradiation techniques. Total body irradiation (TBI) delivers a uniform whole body radiation dose and is used as a conditioning regimen before bone marrow transplantation. It was developed in the early 1900s and is now used to treat various cancers and blood disorders. TBI can be delivered using dedicated or modified conventional irradiators. Dosimetry and compensators are used to ensure uniform dose delivery. Adverse effects include nausea, vomiting, pneumonitis and cataracts. Hemi-body irradiation treats only the upper or lower half of the body and has fewer side effects than total body irradiation.
1 of 41
Downloaded 24 times







































Recommended
Srs and sbrt 2 dr.kiran



Srs and sbrt 2 dr.kiranKiran Ramakrishna
╠²
This document discusses the history and techniques of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). It begins by outlining the early development of SRS by Lars Leksell in the 1950s. It then defines key terms like SRS, SBRT, and fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery. The document goes on to discuss the rationale and advantages of SRS/SBRT, including its ability to deliver high radiation doses with steep dose gradients using multiple beams and image guidance. It also covers topics like tumor oxygenation, cell kill mechanisms, and recent technological advances in the field like VMAT, flattening filter free beams, and 4DPARTICLE BEAM RADIOTHERAPY



PARTICLE BEAM RADIOTHERAPYKanhu Charan
╠²
This document discusses various particle beams used in radiation therapy, including their properties and effectiveness. It states that proton beams have superior dose distribution compared to photon beams but lower LET. Neutron beams have high LET properties but poor dose distribution. Heavy charged particle beams like carbon ions have both superior distribution and high LET. BNCT uses boron compounds and neutrons to specifically target tumor cells but is limited by availability and cost. Overall, the document provides an overview of different particle therapies and their advantages over conventional photon radiation.image guided brachytherapy carcinoma cervix



image guided brachytherapy carcinoma cervixIsha Jaiswal
╠²
IMAGE GUIDED BARCHYTHERAPY
AMERICAN BRACHYTHERAPY GUIDELINES
GEC-ESTRO GUIDELINES
LIMITATIONS OF (2 D)RADIOGRAPHIC IMAGING
VOLUMETRIC IMAGING
ADVANCESGap correction



Gap correctionJyoti Bisht
╠²
This document discusses various time-dose models used in radiotherapy, including the Strandqvist, Cohen, NSD, and TDF models. It explains the need for these models to optimize treatment regimes for tumor control while sparing normal tissues. The document also covers gap correction factors used when treatment schedules are interrupted and the various factors that can affect tumor control outcomes due to gaps in treatment. Compensatory methods like accelerated scheduling and increased dosing are presented to account for treatment gaps.Radiotherapy in ca esophagus



Radiotherapy in ca esophagusIsha Jaiswal
╠²
1) The document discusses various radiation techniques for treating cancer of the esophagus including 2D, 3D conformal radiation therapy, IMRT, and IGRT.
2) It covers topics like target volume delineation, field design considerations for different esophageal subsites, and evolution from 2D to 3D treatment planning.
3) While there is no consensus, most contemporary trials use margins of 3-5cm cranially and caudally on the gross tumor with approximately a 2cm radial margin.Hemi body irradiation



Hemi body irradiationNilesh Kucha
╠²
This document discusses hemi body irradiation (HBI) technique used to treat metastatic cancer. HBI involves irradiating only the upper or lower half of the body using parallel opposed radiation fields. It has advantages over total body irradiation like smaller field size and less side effects. HBI is used to palliate widely metastatic disease and as adjuvant therapy for certain cancers. Potential complications include nausea, diarrhea, pneumonitis and hematological effects. The document also provides an overview of cancer registries in India, which systematically collect cancer data to help understand cancer patterns and guide control programs. Population-based and hospital-based registries use active and passive methods to collect data on cancer incidence, stages and survival.TSET



TSETHanuman Doke
╠²
Total skin electron therapy (TSET) is used to treat cutaneous T-cell lymphoma by delivering a uniform dose of radiation to the entire skin surface while sparing underlying organs. It requires large electron fields over the entire body and precise dosimetry. The most common technique uses six electron beams arranged at 60 degree intervals to provide circumferential coverage. Proper field design and calibration are needed to achieve uniform dose across irregular body surfaces and minimize dose from bremsstrahlung x-rays.Icru 38



Icru 38Kiran Ramakrishna
╠²
This document discusses Intra-cavitary Brachytherapy (ICBT) for treating cervical cancer. It describes different historical ICBT systems like Paris, Stockholm, and Manchester systems. It also discusses modern techniques like remote afterloaders and recommendations for reporting absorbed doses and volumes in ICBT. Key points include different dose rates (LDR, MDR, HDR), advantages of remote afterloaders in maintaining geometry and dose distribution, and recommending specifying absorbed dose to the target volume rather than at a single point for ICBT.Proton beam therapy



Proton beam therapyNanditha Nukala
╠²
Proton beam therapy uses protons to treat cancer. It can reduce the dose to healthy tissues compared to photon therapy by depositing most of the energy at a specific depth. Proton therapy has potential applications in tumors near critical structures where dose escalation may improve outcomes. However, more evidence from controlled trials is still needed to demonstrate comparative effectiveness versus other radiation therapies.Total body irradiation



Total body irradiationKiran Ramakrishna
╠²
This document provides information about total body irradiation (TBI). It discusses that TBI uses megavoltage photon beams to destroy the recipient's bone marrow and tumor cells prior to bone marrow transplantation. It is used to treat various diseases like leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. TBI can be delivered at high or low doses, to half the body, or total nodes. Techniques include parallel opposed beams from linear accelerators or cobalt-60 machines. Dosimetry and in vivo dosimetry are important due to the large fields and difficulty achieving uniform dose. Complications can include sterility, secondary cancers, and growth issues.TIME DOSE & FRACTIONATION



TIME DOSE & FRACTIONATIONIsha Jaiswal
╠²
Introduction
Time dose & fractionation
Therapeutic index
Four RŌĆÖs Of Radiobiology
Radiation response
Survival Curves Of Early & Late Responding Cells
Various fractionation schedules
Clinical trials of altered fractionation
Carbon ion therapy



Carbon ion therapyumesh V
╠²
Heavy ion therapy uses ions heavier than helium for radiation therapy. The National Institute of Radiological Sciences in Japan and the GSI in Germany were early adopters of heavy ion therapy using carbon ions. Additional facilities in Japan, China, and Germany have since come online, demonstrating the increasing use of heavy ion therapy globally. Key advantages of heavy ion therapy over photon therapy include improved targeting of tumors and reduced radiation exposure of surrounding healthy tissue.Brachytherapy dosimetry systems .R



Brachytherapy dosimetry systems .Rraazvarma
╠²
This document provides information about brachytherapy dosimetry systems. It discusses different brachytherapy treatment techniques including intracavitary, interstitial, and permanent vs. temporary implants. Common radionuclides used in brachytherapy are described. Dosimetry systems for interstitial and intracavitary brachytherapy like Patterson-Parker, Quimby, Paris, Manchester, Stockholm, and ICRU systems are summarized. Key aspects of these systems including reference points, volumes, and dose specifications are highlighted.ICRU CONCEPT



ICRU CONCEPTKanhu Charan
╠²
The ICRU was conceived in 1925 to propose a unit for measuring radiation in medicine. It is now responsible for defining units of measure for radiation quantities and developing recommendations on their safe application. The ICRU works with committees to publish reports on topics like radiation therapy, dosimetry, and protection. Its goals are to evaluate data on ionizing radiation and maintain contacts to benefit radiation science.Rrecent advances in linear accelerators [MR linac]![Rrecent advances in linear accelerators [MR linac]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Rrecent advances in linear accelerators [MR linac]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Rrecent advances in linear accelerators [MR linac]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Rrecent advances in linear accelerators [MR linac]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Rrecent advances in linear accelerators [MR linac]Upasna Saxena
╠²
Brief description of evolution of linear accelerators- and elaboration of online adaptive radiotherapy and MRLinacImage Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)



Image Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)Teekendra Singh Faujdar
╠²
This document discusses Image Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT). It begins by explaining that radiotherapy has traditionally used imaging for treatment planning and execution when the target is not on the surface. It then describes various IGRT technologies, dividing them into non-radiation based systems like ultrasound, cameras, electromagnetic tracking and MRI; and radiation based systems like EPID, CBCT, fan beam KVCT and MVCT. These systems provide improved target localization and allow for corrections. IGRT aims to reduce errors and improve precision of radiotherapy.Plan evaluation in Radiotherapy- Dr Kiran



Plan evaluation in Radiotherapy- Dr KiranKiran Ramakrishna
╠²
This document discusses various methods used to evaluate radiotherapy treatment plans, including physical and biological parameters. Physically, plans are evaluated using isodose curves, dose distribution statistics, differential and cumulative dose-volume histograms (DVHs). Target coverage should be within 95-100% of the prescribed dose. Biologically, tumor control probability (TCP) and normal tissue complication probability (NTCP) models are used. The therapeutic ratio and index compare the dose required for tumor control versus normal tissue complications. NTCP models include Lyman-Kutcher-Burman and critical element/volume models. Plan evaluation ensures target doses are adequate while respecting organ tolerance doses.Interstitial BT Principles



Interstitial BT PrinciplesYamini Baviskar
╠²
This document provides an overview of interstitial brachytherapy principles and concepts. It discusses the history and evolution of brachytherapy sources from radium to modern radioactive sources like iridium-192. Key concepts covered include dose rate calculations, implant systems like the Paris system, and factors that influence dose distribution from a radioactive source like distance, absorption and scattering. The document also describes temporary and permanent brachytherapy sources and different methods of source application including preloading, afterloading and remote afterloading.Treatment plannings i kiran



Treatment plannings i kiranKiran Ramakrishna
╠²
Isodose curves depict absorbed dose distributions and variations in volume and planes. They join points of equal dose. Isodose charts show the variation in dose as a function of depth and transverse distance from the central beam axis. Factors like beam energy, field size, and distance affect isodose curve shape through penumbra and dose deposition. Multiple beams are often needed to adequately treat tumors while sparing surrounding tissues. Beam arrangements, weights, and modifiers must be optimized for each plan.BASICS RADIOBIOLOGY FOR RADIOTHERAPY



BASICS RADIOBIOLOGY FOR RADIOTHERAPYNik Noor Ashikin Nik Ab Razak
╠²
The document discusses key concepts in radiobiology relevant for radiotherapy. It defines important treatment volumes including the gross tumour volume (GTV), clinical target volume (CTV), planning target volume (PTV), treated volume (TV), irradiated volume (IV), and organs at risk (OARs). It also describes biological factors that influence radiation effects on tissues, known as the "5 Rs": repair, repopulation, reoxygenation, redistribution, and radiosensitivity. Fractionated radiotherapy takes advantage of these factors to maximize tumor cell kill while minimizing damage to normal tissues.ICRU 38 nayana



ICRU 38 nayanaNAYANA KRISHNAN
╠²
The document summarizes recommendations from ICRU Report 38 regarding dose specification, reporting, and volumes for intracavitary brachytherapy for gynecological cancers. It discusses:
1. Historical dose reporting systems like milligram-hours and Point A/B and introduces the concept of a reference volume receiving 60Gy.
2. Factors to report like treatment technique, time-dose patterns, and doses to organs at risk.
3. Volumes for reporting like the treated volume, high-dose volume, irradiated volume, and Point A volume.
4. Recommendations for specifying and reporting doses in a standardized way to allow comparison between different brachytherapy proceduresRole of SBRT in lung cancer



Role of SBRT in lung cancerDrAyush Garg
╠²
SBRT is a precise form of radiation therapy that delivers very high ablative doses of radiation to tumors in a small number of fractions. It has become the standard of care for early stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSC LC) that is not surgically resectable. Key aspects of SBRT planning and delivery include delineating targets and organs at risk on imaging, determining appropriate dose and fractionation based on tumor location, using motion management strategies to account for tumor motion, precise daily image guidance, and ensuring dose constraints are met to minimize risks to critical structures like the spinal cord. SBRT provides superior local tumor control compared to conventional fractionation for early stage NSCLC with a favorable toxicity profile.Icru 50,62,83 volume deliniation



Icru 50,62,83 volume deliniationalthaf jouhar
╠²
The document discusses guidelines from the International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) for prescribing, recording, and reporting intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). It describes the different target volumes and organs at risk that must be delineated for treatment planning according to ICRU reports 50, 62, and 83. These include the gross tumor volume, clinical target volume, planning target volume, internal target volume, treated volume, and irradiated volume. Factors such as margins for internal motion and patient setup must be considered when defining volumes. Dose specifications, dose-volume histograms, conformity, and homogeneity are also discussed. Proper delineation of volumes and standardization of dose reporting are emphasized.Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy



Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapyfondas vakalis
╠²
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) uses advanced technology to deliver high ablative doses of radiation to tumors in a precise manner. SBRT has been shown to be effective in treating various tumor types with acceptable toxicity. However, long term toxicity requires further study. New techniques aim to reduce treatment margins and account for organ motion to minimize dose to surrounding healthy tissues while ensuring accurate dose delivery to the tumor. SBRT shows promise but further prospective clinical trials are needed to fully evaluate efficacy and safety.physics and clinical aspects of interstitial brachytherapy



physics and clinical aspects of interstitial brachytherapyVIMOJ JANARDANAN NAIR
╠²
The document summarizes interstitial brachytherapy, including indications, contraindications, isotopes used, and details of various planning systems like Paterson-Parker, Quimby, Paris, and computer-based systems. It discusses dose rates, types of implants, applicators, volume definition, and dosimetry parameters like reference isodose and uniformity criteria for different planning approaches.Image Guided Radiotherapy



Image Guided RadiotherapySheetal R Kashid
╠²
1. Dr. Sheetal R Kashid presented on the use of IGRT for head and neck cancers and central nervous system tumors at TMH.
2. IGRT uses image guidance to precisely position patients and correct for setup errors, allowing for accurate radiation delivery while minimizing dose to surrounding healthy tissues.
3. At TMH, IGRT is performed using CBCT, EPID, and offline protocols to correct for systematic and random errors in head and neck and neuro-oncology patients.Fractionated radiation and dose rate effect



Fractionated radiation and dose rate effectParag Roy
╠²
Fractionated radiation and the dose-rate effect can impact cell survival through mechanisms like sublethal damage (SLD) repair and cell cycle redistribution. SLD repair occurs as double-strand breaks are rejoined after radiation exposure. At lower dose rates, more SLD can be repaired between fractions, improving cell survival. However, very low dose rates may instead reduce survival if cells become frozen in radiosensitive phases of the cell cycle. The dose-rate effect varies between cell types and depends on factors like oxygenation and ability to progress through the cell cycle after radiation.COMPLETE OVERVIEW ON ADAPTIVE RADIOTHERAPY OVER DAILY IMAGE GUIDED RADIOTHERAPY



COMPLETE OVERVIEW ON ADAPTIVE RADIOTHERAPY OVER DAILY IMAGE GUIDED RADIOTHERAPYSubrata Roy
╠²
Adaptive Radiotherapy is a closed-loop radiation treatment process where the treatment plan can be modified using a systematic feedback of measurements, Intending to improve radiation treatment by systematically monitoring treatment variations and incorporating them to re-optimize the treatment plan early on during the course of treatment.
Total body irradiation



Total body irradiationBharat Mistary
╠²
Total body irradiation (TBI) is a form of radiotherapy used prior to bone marrow transplants to reduce the risk of transplant rejection and destroy any remaining cancer cells. TBI techniques use large photon fields, usually from cobalt-60 machines or LINACs, to irradiate the entire body. Common techniques include opposing anterior-posterior beams or lateral beams. Precise dosimetry is required due to the large fields and total body exposure, with dose uniformity targets of within ┬▒10% across the body. In vivo dosimetry using TLD or diodes is also employed to verify accurate dose delivery. Early side effects from TBI include fatigue, nausea, hair loss and skin irritation due to the whole body irradiationMore Related Content
What's hot (20)
Proton beam therapy



Proton beam therapyNanditha Nukala
╠²
Proton beam therapy uses protons to treat cancer. It can reduce the dose to healthy tissues compared to photon therapy by depositing most of the energy at a specific depth. Proton therapy has potential applications in tumors near critical structures where dose escalation may improve outcomes. However, more evidence from controlled trials is still needed to demonstrate comparative effectiveness versus other radiation therapies.Total body irradiation



Total body irradiationKiran Ramakrishna
╠²
This document provides information about total body irradiation (TBI). It discusses that TBI uses megavoltage photon beams to destroy the recipient's bone marrow and tumor cells prior to bone marrow transplantation. It is used to treat various diseases like leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. TBI can be delivered at high or low doses, to half the body, or total nodes. Techniques include parallel opposed beams from linear accelerators or cobalt-60 machines. Dosimetry and in vivo dosimetry are important due to the large fields and difficulty achieving uniform dose. Complications can include sterility, secondary cancers, and growth issues.TIME DOSE & FRACTIONATION



TIME DOSE & FRACTIONATIONIsha Jaiswal
╠²
Introduction
Time dose & fractionation
Therapeutic index
Four RŌĆÖs Of Radiobiology
Radiation response
Survival Curves Of Early & Late Responding Cells
Various fractionation schedules
Clinical trials of altered fractionation
Carbon ion therapy



Carbon ion therapyumesh V
╠²
Heavy ion therapy uses ions heavier than helium for radiation therapy. The National Institute of Radiological Sciences in Japan and the GSI in Germany were early adopters of heavy ion therapy using carbon ions. Additional facilities in Japan, China, and Germany have since come online, demonstrating the increasing use of heavy ion therapy globally. Key advantages of heavy ion therapy over photon therapy include improved targeting of tumors and reduced radiation exposure of surrounding healthy tissue.Brachytherapy dosimetry systems .R



Brachytherapy dosimetry systems .Rraazvarma
╠²
This document provides information about brachytherapy dosimetry systems. It discusses different brachytherapy treatment techniques including intracavitary, interstitial, and permanent vs. temporary implants. Common radionuclides used in brachytherapy are described. Dosimetry systems for interstitial and intracavitary brachytherapy like Patterson-Parker, Quimby, Paris, Manchester, Stockholm, and ICRU systems are summarized. Key aspects of these systems including reference points, volumes, and dose specifications are highlighted.ICRU CONCEPT



ICRU CONCEPTKanhu Charan
╠²
The ICRU was conceived in 1925 to propose a unit for measuring radiation in medicine. It is now responsible for defining units of measure for radiation quantities and developing recommendations on their safe application. The ICRU works with committees to publish reports on topics like radiation therapy, dosimetry, and protection. Its goals are to evaluate data on ionizing radiation and maintain contacts to benefit radiation science.Rrecent advances in linear accelerators [MR linac]![Rrecent advances in linear accelerators [MR linac]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Rrecent advances in linear accelerators [MR linac]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Rrecent advances in linear accelerators [MR linac]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Rrecent advances in linear accelerators [MR linac]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Rrecent advances in linear accelerators [MR linac]Upasna Saxena
╠²
Brief description of evolution of linear accelerators- and elaboration of online adaptive radiotherapy and MRLinacImage Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)



Image Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)Teekendra Singh Faujdar
╠²
This document discusses Image Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT). It begins by explaining that radiotherapy has traditionally used imaging for treatment planning and execution when the target is not on the surface. It then describes various IGRT technologies, dividing them into non-radiation based systems like ultrasound, cameras, electromagnetic tracking and MRI; and radiation based systems like EPID, CBCT, fan beam KVCT and MVCT. These systems provide improved target localization and allow for corrections. IGRT aims to reduce errors and improve precision of radiotherapy.Plan evaluation in Radiotherapy- Dr Kiran



Plan evaluation in Radiotherapy- Dr KiranKiran Ramakrishna
╠²
This document discusses various methods used to evaluate radiotherapy treatment plans, including physical and biological parameters. Physically, plans are evaluated using isodose curves, dose distribution statistics, differential and cumulative dose-volume histograms (DVHs). Target coverage should be within 95-100% of the prescribed dose. Biologically, tumor control probability (TCP) and normal tissue complication probability (NTCP) models are used. The therapeutic ratio and index compare the dose required for tumor control versus normal tissue complications. NTCP models include Lyman-Kutcher-Burman and critical element/volume models. Plan evaluation ensures target doses are adequate while respecting organ tolerance doses.Interstitial BT Principles



Interstitial BT PrinciplesYamini Baviskar
╠²
This document provides an overview of interstitial brachytherapy principles and concepts. It discusses the history and evolution of brachytherapy sources from radium to modern radioactive sources like iridium-192. Key concepts covered include dose rate calculations, implant systems like the Paris system, and factors that influence dose distribution from a radioactive source like distance, absorption and scattering. The document also describes temporary and permanent brachytherapy sources and different methods of source application including preloading, afterloading and remote afterloading.Treatment plannings i kiran



Treatment plannings i kiranKiran Ramakrishna
╠²
Isodose curves depict absorbed dose distributions and variations in volume and planes. They join points of equal dose. Isodose charts show the variation in dose as a function of depth and transverse distance from the central beam axis. Factors like beam energy, field size, and distance affect isodose curve shape through penumbra and dose deposition. Multiple beams are often needed to adequately treat tumors while sparing surrounding tissues. Beam arrangements, weights, and modifiers must be optimized for each plan.BASICS RADIOBIOLOGY FOR RADIOTHERAPY



BASICS RADIOBIOLOGY FOR RADIOTHERAPYNik Noor Ashikin Nik Ab Razak
╠²
The document discusses key concepts in radiobiology relevant for radiotherapy. It defines important treatment volumes including the gross tumour volume (GTV), clinical target volume (CTV), planning target volume (PTV), treated volume (TV), irradiated volume (IV), and organs at risk (OARs). It also describes biological factors that influence radiation effects on tissues, known as the "5 Rs": repair, repopulation, reoxygenation, redistribution, and radiosensitivity. Fractionated radiotherapy takes advantage of these factors to maximize tumor cell kill while minimizing damage to normal tissues.ICRU 38 nayana



ICRU 38 nayanaNAYANA KRISHNAN
╠²
The document summarizes recommendations from ICRU Report 38 regarding dose specification, reporting, and volumes for intracavitary brachytherapy for gynecological cancers. It discusses:
1. Historical dose reporting systems like milligram-hours and Point A/B and introduces the concept of a reference volume receiving 60Gy.
2. Factors to report like treatment technique, time-dose patterns, and doses to organs at risk.
3. Volumes for reporting like the treated volume, high-dose volume, irradiated volume, and Point A volume.
4. Recommendations for specifying and reporting doses in a standardized way to allow comparison between different brachytherapy proceduresRole of SBRT in lung cancer



Role of SBRT in lung cancerDrAyush Garg
╠²
SBRT is a precise form of radiation therapy that delivers very high ablative doses of radiation to tumors in a small number of fractions. It has become the standard of care for early stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSC LC) that is not surgically resectable. Key aspects of SBRT planning and delivery include delineating targets and organs at risk on imaging, determining appropriate dose and fractionation based on tumor location, using motion management strategies to account for tumor motion, precise daily image guidance, and ensuring dose constraints are met to minimize risks to critical structures like the spinal cord. SBRT provides superior local tumor control compared to conventional fractionation for early stage NSCLC with a favorable toxicity profile.Icru 50,62,83 volume deliniation



Icru 50,62,83 volume deliniationalthaf jouhar
╠²
The document discusses guidelines from the International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) for prescribing, recording, and reporting intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). It describes the different target volumes and organs at risk that must be delineated for treatment planning according to ICRU reports 50, 62, and 83. These include the gross tumor volume, clinical target volume, planning target volume, internal target volume, treated volume, and irradiated volume. Factors such as margins for internal motion and patient setup must be considered when defining volumes. Dose specifications, dose-volume histograms, conformity, and homogeneity are also discussed. Proper delineation of volumes and standardization of dose reporting are emphasized.Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy



Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapyfondas vakalis
╠²
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) uses advanced technology to deliver high ablative doses of radiation to tumors in a precise manner. SBRT has been shown to be effective in treating various tumor types with acceptable toxicity. However, long term toxicity requires further study. New techniques aim to reduce treatment margins and account for organ motion to minimize dose to surrounding healthy tissues while ensuring accurate dose delivery to the tumor. SBRT shows promise but further prospective clinical trials are needed to fully evaluate efficacy and safety.physics and clinical aspects of interstitial brachytherapy



physics and clinical aspects of interstitial brachytherapyVIMOJ JANARDANAN NAIR
╠²
The document summarizes interstitial brachytherapy, including indications, contraindications, isotopes used, and details of various planning systems like Paterson-Parker, Quimby, Paris, and computer-based systems. It discusses dose rates, types of implants, applicators, volume definition, and dosimetry parameters like reference isodose and uniformity criteria for different planning approaches.Image Guided Radiotherapy



Image Guided RadiotherapySheetal R Kashid
╠²
1. Dr. Sheetal R Kashid presented on the use of IGRT for head and neck cancers and central nervous system tumors at TMH.
2. IGRT uses image guidance to precisely position patients and correct for setup errors, allowing for accurate radiation delivery while minimizing dose to surrounding healthy tissues.
3. At TMH, IGRT is performed using CBCT, EPID, and offline protocols to correct for systematic and random errors in head and neck and neuro-oncology patients.Fractionated radiation and dose rate effect



Fractionated radiation and dose rate effectParag Roy
╠²
Fractionated radiation and the dose-rate effect can impact cell survival through mechanisms like sublethal damage (SLD) repair and cell cycle redistribution. SLD repair occurs as double-strand breaks are rejoined after radiation exposure. At lower dose rates, more SLD can be repaired between fractions, improving cell survival. However, very low dose rates may instead reduce survival if cells become frozen in radiosensitive phases of the cell cycle. The dose-rate effect varies between cell types and depends on factors like oxygenation and ability to progress through the cell cycle after radiation.COMPLETE OVERVIEW ON ADAPTIVE RADIOTHERAPY OVER DAILY IMAGE GUIDED RADIOTHERAPY



COMPLETE OVERVIEW ON ADAPTIVE RADIOTHERAPY OVER DAILY IMAGE GUIDED RADIOTHERAPYSubrata Roy
╠²
Adaptive Radiotherapy is a closed-loop radiation treatment process where the treatment plan can be modified using a systematic feedback of measurements, Intending to improve radiation treatment by systematically monitoring treatment variations and incorporating them to re-optimize the treatment plan early on during the course of treatment.
Similar to Hemibody and total body radiation (20)
Total body irradiation



Total body irradiationBharat Mistary
╠²
Total body irradiation (TBI) is a form of radiotherapy used prior to bone marrow transplants to reduce the risk of transplant rejection and destroy any remaining cancer cells. TBI techniques use large photon fields, usually from cobalt-60 machines or LINACs, to irradiate the entire body. Common techniques include opposing anterior-posterior beams or lateral beams. Precise dosimetry is required due to the large fields and total body exposure, with dose uniformity targets of within ┬▒10% across the body. In vivo dosimetry using TLD or diodes is also employed to verify accurate dose delivery. Early side effects from TBI include fatigue, nausea, hair loss and skin irritation due to the whole body irradiationTBI



TBIAparna Attoor
╠²
Total Body Irradiation (TBI) is given
to prepare (condition) the patientŌĆÖs body for bone marrow or stem cell transplant.
It is a special radio therapeutic technique
that delivers to a patientŌĆÖs whole body, a
uniform dose within (+/-)10% of the
prescribed dose.Time dose & fractionation relationship 



Time dose & fractionation relationship Amin Amin
╠²
This document discusses time, dose, and fractionation in radiation therapy. It begins by introducing the aims of delivering precisely measured radiation doses to tumors while minimizing damage to normal tissues. It then discusses tumor lethal dose, tissue tolerance factors, and how normal tissue tolerance limits the maximum dose that can be delivered. The document covers dose, time, and fractionation as treatment factors. It reviews several historical time-dose models including Strandquist lines, Cohen's model, Fowler's work, Ellis' NSD equation, and the linear quadratic model which is still commonly used today. It also notes limitations of some early empirical models.Re Radiation



Re RadiationDr.Rashmi Yadav
╠²
- Reirradiation or retreatments after initial radiotherapy is possible for 10% of cancer patients who experience a second cancer. However, if the radiation tolerance of a normal organ or tissue was exceeded in the initial treatment, reirradiation cannot be done safely.
- Early-responding tissues like skin generally recover better than late-responding tissues like fibrosis and can tolerate reirradiation with reduced doses. Spinal cord and lung data from rodent and monkey studies show some reirradiation is possible. Kidney and bladder do not recover from late damage.
- Clinical studies on reirradiation are limited but show it can provide local control and possibly survival for head and neck cancers, though with high risks of toxicity and functionalRadiotherapy in ENT



Radiotherapy in ENTYousuf Choudhury
╠²
This document discusses the history and techniques of radiotherapy in ENT. It begins with the discovery of x-rays in 1895 and progresses to modern technologies like IMRT, IGRT, proton beam therapy and SBRT. It covers the physics, biology and mechanisms of radiation therapy. Key aspects of radiotherapy for head and neck cancers like dosimetry, fractionation schedules, acute and chronic toxicities are summarized. Newer conformal techniques aim to reduce normal tissue damage while adequately treating tumors.1.radiation of h&n tumors



1.radiation of h&n tumorswww.ffofr.org - Foundation for Oral Facial Rehabilitiation
╠²
This document discusses radiation therapy for head and neck tumors. It covers the biologic effects of radiation, different modalities like external beam radiation therapy and brachytherapy, and fractionation schedules. Changes in radiation therapy over time are also reviewed, including increased doses, use of chemotherapy with radiation (chemoRT), and intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). The document discusses both acute and long term tissue effects of radiation therapy and increasing post-treatment morbidity as techniques have advanced.Particle beam ŌĆō proton,neutron & heavy ion therapy



Particle beam ŌĆō proton,neutron & heavy ion therapyAswathi c p
╠²
particle therapy is advanced external beam therapy used to treat cancer , which uses beams of protons or other charged particles such as helium, carbon or other ions instead of photons. charged particles have different depth-dose distributions compared to photons. They deposit most of their energy in the last final millimeters of their trajectory (when their speed slows). This results in a sharp and localized peak of dose, known as the Bragg peak.ICRU 83



ICRU 83apollo seminar group
╠²
This seminar is presented as a part of weekly journal club and seminar presented in Apollo Hospital,Kolkata Department of Radiation Oncology.This seminar is moderated by Dr Tanweer Shahid.Understanding Radiation Units and Quantities, MDIRT Nchanji Nkeh Keneth



Understanding Radiation Units and Quantities, MDIRT Nchanji Nkeh KenethNchanji Nkeh Keneth
╠²
Ionising Radiations, Meaurement, Radiation Units and Quantities
Understanding effects of Ionising radiations. Credit to IAEA for lectureRadiotherapy In Early Breast Cancer



Radiotherapy In Early Breast CancerDr.T.Sujit :-)
╠²
This document summarizes the use of radiotherapy in early breast cancer treatment. It discusses how breast-conserving therapy with radiotherapy is as effective as mastectomy, and how radiotherapy reduces local recurrence when used as part of breast-conserving surgery for ductal carcinoma in situ. It also describes different radiotherapy techniques for early invasive breast cancer including whole breast irradiation, tumor bed boosts, and accelerated partial breast irradiation.INTRA OPERATIVE RADIOTHERAPY-DR ANDREA R SALINS



INTRA OPERATIVE RADIOTHERAPY-DR ANDREA R SALINSDr Andrea R Salins
╠²
INTRA OPERATIVE RADIOTHERAPY-BY DR ANDREA R SALINSTherapeutic nuclear medicine



Therapeutic nuclear medicineSabari Kumar
╠²
Therapeutic nuclear medicine uses radionuclides to treat various conditions like hyperthyroidism and thyroid cancer. Common isotopes used include iodine-131, phosphorus-32, and strontium-89. Administration procedures and internal dosimetry calculations are important considerations. The MIRD formalism provides a framework for calculating absorbed dose to target regions from radioactive sources. Key factors include cumulative activity, residence time, and absorbed fraction. Assumptions of uniform activity distribution and average absorbed dose are limitations but the MIRD approach is simple and easy to use.Medical uses of ionising radiation



Medical uses of ionising radiationAmin Amin
╠²
Medical uses of ionizing radiation include radiotherapy, medical imaging like CT scans and X-rays, and nuclear medicine. Radiotherapy uses radiation to treat cancer and can involve external beam techniques like 3D conformal radiation therapy (3D CRT), intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT), stereotactic radiosurgery, and brachytherapy. Emerging techniques like proton beam therapy further improve radiation targeting and dose distribution. Precise imaging guidance and computer planning help deliver high radiation doses safely and effectively to tumors while avoiding nearby healthy tissues.Radiobiologia aplicada a f├Łsica m├®dica e suas aplica├¦├Ąes



Radiobiologia aplicada a f├Łsica m├®dica e suas aplica├¦├Ąeslarachavest3
╠²
Radiobiologia aplicada a f├Łsica m├®dica - aplica├¦├Ąespatient dose management in angiography king saud unversity.pdf



patient dose management in angiography king saud unversity.pdfnaima SENHOU
╠²
This document discusses patient dose management in angiography procedures. It defines key radiation terms like exposure, absorbed dose, equivalent dose and effective dose. It explains radiation units like Gray, Sievert and Dose Area Product. Factors influencing patient dose like equipment settings, patient positioning, tube angulation, magnification and collimation are described. Methods to minimize dose like reducing beam-on time, increasing source-to-patient distance and using automatic exposure control are provided. The use of diagnostic reference levels to promote radiation dose optimization is also summarized.FACTORS AFFECTING PATIENT DOSE IN RADIOLOGICAL EXAMINATIONS.pptx



FACTORS AFFECTING PATIENT DOSE IN RADIOLOGICAL EXAMINATIONS.pptxNomeh Henry
╠²
The presentation explained in details various factors affecting patient's dose during radiological examinations.Recently uploaded (20)
One Health Rabies Control in Indonesia_APCAT meeting May 2022.pptx



One Health Rabies Control in Indonesia_APCAT meeting May 2022.pptxWahid Husein
╠²
What is FAO doing to support rabies control programmes in Indonesia using One Health approachIMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINE



IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINERelianceNwosu
╠²
This presentation emphasizes the role of immunodiagnostics and Immunotherapy. Correlation of vitamin D level with prediabetes status_Dr Ahmed Al Montasir_f...



Correlation of vitamin D level with prediabetes status_Dr Ahmed Al Montasir_f...zilkerapurbo
╠²
Correlation of vitamin D level with prediabetes statusLocal Anesthetic Use in the Vulnerable Patients



Local Anesthetic Use in the Vulnerable PatientsReza Aminnejad
╠²
Local anesthetics are a cornerstone of pain management, but their use requires special consideration in vulnerable groups such as pediatric, elderly, diabetic, or obese patients. In this presentation, weŌĆÖll explore how factors like age and physiology influence local anesthetics' selection, dosing, and safety. By understanding these differences, we can optimize patient care and minimize risks.
MLS 208 - UNIT 1- Lecture Notes - ETANDO AYUK - SANU - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 1- Lecture Notes - ETANDO AYUK - SANU - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
╠²
Unit 1: Introduction to Histological and Cytological techniques
’éĘ Differentiate histology and cytology
’éĘ Overview on tissue types
’éĘ Function and components of the compound light microscope
’éĘ Overview on common Histological Techniques:
o Fixation
o Grossing
o Tissue processing
o Microtomy
o Staining
o Mounting
’éĘ Application of histology and cytologyThe influence of birth companion in mother care and neonatal outcome



The influence of birth companion in mother care and neonatal outcomeLokesh Kumar Sharma
╠²
this content related to birth companionship, role of birth companion in care of mother and neonatal Non-Invasive ICP Monitoring for Neurosurgeons



Non-Invasive ICP Monitoring for NeurosurgeonsDhaval Shukla
╠²
This presentation delves into the latest advancements in non-invasive intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring techniques, specifically tailored for neurosurgeons. It covers the importance of ICP monitoring in clinical practice, explores various non-invasive methods, and discusses their accuracy, reliability, and clinical applications. Attendees will gain insights into the benefits of non-invasive approaches over traditional invasive methods, including reduced risk of complications and improved patient outcomes. This comprehensive overview is designed to enhance the knowledge and skills of neurosurgeons in managing patients with neurological conditions.
Invasive systems are commonly used for monitoring intracranial pressure (ICP) in traumatic brain injury (TBI) and are considered the gold standard. The availability of invasive ICP monitoring is heterogeneous, and in low- and middle-income settings, these systems are not routinely employed due to high cost or limited accessibility. The aim of this presentation is to develop recommendations to guide monitoring and ICP-driven therapies in TBI using non-invasive ICP (nICP) systems.
Rabies Bali 2008-2020_WRD Webinar_WSAVA 2020_Final.pptx



Rabies Bali 2008-2020_WRD Webinar_WSAVA 2020_Final.pptxWahid Husein
╠²
A decade of rabies control programmes in Bali with support from FAO ECTAD Indonesia with Mass Dog Vaccination, Integrated Bite Case Management, Dog Population Management, and Risk Communication as the backbone of the programmesPRODUCTION OF HB VACCINE AND INTERFERONS BY rDNA - Copy.pptx



PRODUCTION OF HB VACCINE AND INTERFERONS BY rDNA - Copy.pptxkarishmaduhijod1
╠²
APPLICATION of RECOMBINANAT DNA TECHNOLOGY : IN THE PRODUCTION OF HEPATITIS B VACCINE ,INSULIN and INTERFERONAcute & Chronic Inflammation, Chemical mediators in Inflammation and Wound he...



Acute & Chronic Inflammation, Chemical mediators in Inflammation and Wound he...Ganapathi Vankudoth
╠²
A complete information of Inflammation, it includes types of Inflammation, purpose of Inflammation, pathogenesis of acute inflammation, chemical mediators in inflammation, types of chronic inflammation, wound healing and Inflammation in skin repair, phases of wound healing, factors influencing wound healing and types of wound healing.Biography of Dr. Vincenzo Giordano



Biography of Dr. Vincenzo GiordanoDr. Vincenzo Giordano
╠²
Dr. Vincenzo Giordano began his medical career 2011 at Aberdeen Royal Infirmary in the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery. Here, he performed complex adult cardiothoracic surgical procedures, significantly enhancing his proficiency in patient critical care, as evidenced by his FCCS certification.MORPHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF PNEUMONIA.....



MORPHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF PNEUMONIA.....maheenmazhar021
╠²
This presentation provides a detailed exploration of the morphological and microscopic features of pneumonia, covering its histopathology, classification, and clinical significance. Designed for medical students, pathologists, and healthcare professionals, this lecture differentiates bacterial vs. viral pneumonia, explains lobar, bronchopneumonia, and interstitial pneumonia, and discusses diagnostic imaging patterns.
¤ÆĪ Key Topics Covered:
Ō£ģ Normal lung histology vs. pneumonia-affected lung
Ō£ģ Morphological changes in lobar, bronchopneumonia, and interstitial pneumonia
Ō£ģ Microscopic features: Fibroblastic plugs, alveolar septal thickening, inflammatory cell infiltration
Ō£ģ Stages of lobar pneumonia: Congestion, Red hepatization, Gray hepatization, Resolution
Ō£ģ Common causative pathogens (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Mycoplasma, etc.)
Ō£ģ Clinical case study with diagnostic approach and differentials
¤ö¼ Who Should Watch?
This is an essential resource for medical students, pathology trainees, and respiratory health professionals looking to enhance their understanding of pneumoniaŌĆÖs morphological aspects.HER2-Targeting Therapy in HER2+ MBC With and Without CNS Metastases: Selectio...



HER2-Targeting Therapy in HER2+ MBC With and Without CNS Metastases: Selectio...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair and Presenters Sara A. Hurvitz, MD, FACP, Carey K. Anders, MD, FASCO, and Vyshak Venur, MD, discuss metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer in this CME/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£Fine-Tuning the Selection and Sequencing of HER2-Targeting Therapies in HER2-Positive MBC With and Without CNS Metastases: Expert Guidance on How to Individualize Therapy Based on Latest Evidence, Disease Features, Treatment Characteristics, and Patient Needs and Preferences.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/4f8sUs7. CME/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until March 2, 2026.HUMAN SEXUALITY AND SEXUAL RESPONCE CYCLE



HUMAN SEXUALITY AND SEXUAL RESPONCE CYCLEdaminipatel37
╠²
It is all about topic of obg for new semester students Stability of Dosage Forms as per ICH Guidelines



Stability of Dosage Forms as per ICH GuidelinesKHUSHAL CHAVAN
╠²
This presentation covers the stability testing of pharmaceutical dosage forms according to ICH guidelines (Q1A-Q1F). It explains the definition of stability, various testing protocols, storage conditions, and evaluation criteria required for regulatory submissions. Key topics include stress testing, container closure systems, stability commitment, and photostability testing. The guidelines ensure that pharmaceutical products maintain their identity, purity, strength, and efficacy throughout their shelf life. This resource is valuable for pharmaceutical professionals, researchers, and regulatory experts.legal Rights of individual, children and women.pptx



legal Rights of individual, children and women.pptxRishika Rawat
╠²
A legal right is a claim or entitlement that is recognized and protected by the law. It can also refer to the power or privilege that the law grants to a person. Human rights include the right to life and liberty, freedom from slavery and torture, freedom of opinion and expression, the right to work and educationphysiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation ž│žżž¦┘ä.pptx



physiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation ž│žżž¦┘ä.pptxamralmohammady27
╠²
┘ä┘ł ž╣┘åž»┘ā ┘䞦ž© ž¬┘łž© žŻ┘ł ž¬ž¦ž©┘䞬 ┘üž¦┘ä
power point show
┘ć┘Ŗ┘å┘üž╣┘ā ž¼ž»ž¦ ┘ü┘Ŗ ┘ģž▒ž¦ž¼ž╣ž® ž│ž▒┘Ŗž╣ž® ┘ä┘Ŗ┘äž® ž¦┘䞦┘ģž¬žŁž¦┘å
┘łž¦┘ä┘ä┘Ŗ ┘Ŗ┘éž»ž▒ ┘Ŗž╣┘ģ┘ä žŁž¦ž¼ž® ┘Ŗž╣┘ģ┘ä┘枦
┘łž┤┘āž▒ž¦ ┘ä┘äž»┘āž¬┘łž▒ž® ┘å┘łž¦┘ä ž╣┘ä┘ē ž¬ž¼┘ģ┘Ŗž╣ž® žŻž│ž”┘äž® ž¦┘äž©┘Ŗ┘łMLS 208 - UNIT 1- Lecture Notes - ETANDO AYUK - SANU - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 1- Lecture Notes - ETANDO AYUK - SANU - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
╠²
Acute & Chronic Inflammation, Chemical mediators in Inflammation and Wound he...



Acute & Chronic Inflammation, Chemical mediators in Inflammation and Wound he...Ganapathi Vankudoth
╠²
HER2-Targeting Therapy in HER2+ MBC With and Without CNS Metastases: Selectio...



HER2-Targeting Therapy in HER2+ MBC With and Without CNS Metastases: Selectio...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Hemibody and total body radiation
- 1. HEMIBODY & TOTAL BODY IRRADIATION Dr. Dhiman Das 2nd year resident. Dept. of Radiotherapy Medical College & Hospital kolkata
- 2. Total Body Irradiation ŌĆó TBI is a special radiotherapy technique that delivers to a patients whole body a dose uniform to within +/- 10% of the prescribed dose. ŌĆó It is performed as conditioning regime
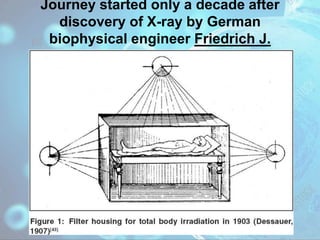
- 3. Journey started only a decade after discovery of X-ray by German biophysical engineer Friedrich J. Dessauer
- 4. ŌĆó In 1907, Alad├Īr Elfer,a medical professor in Hungary, reported his experience using a TBI technique . ŌĆó Arthur C. Heublein, in collaboration with Gioacchino Failla, is credited with the development of the first TBI unit in North America, located at Memorial Hospital in New York City.
- 5. ŌĆó In 1959, a kidney was successfully transplanted between dizygotic twins after TBI at exposures of up to 450 R. ŌĆó In 1957, Nobel laureate E. Donnall Thomas first reported the use of bone marrow infusion in humans following whole body irradiation or chemotherapy, and less than 1 year later he published his experience in using TBI with exposures up to 600 R followed by bone marrow transplantation.
- 6. Diseases treated with TBI ŌĆó Malignant ŌĆō Leukaemia. ŌĆō Aplastic anaemia. ŌĆō Lymphoma. ŌĆō Multiple Myeloma. ŌĆó Non Malignant ŌĆō Autoimmune Diseases. ŌĆō Inborn errors of metabolism. ŌĆō Aplastic anaemia
- 7. Mode of Action 1. Cytotoxicity-Destroy the bone marrow & tumour cells of the recipient. 2. Immunosuppression-Immunosuppress the patient sufficiently.
- 8. ŌĆó auto-SCT ŌĆō cytotoxicity ŌĆó allo-SCT ŌĆō cytotoxicity ŌĆō immunosuppression
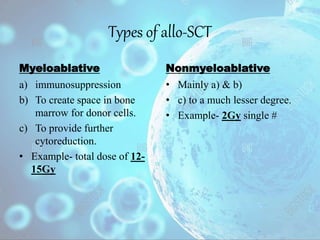
- 9. Types of allo-SCT Myeloablative a) immunosuppression b) To create space in bone marrow for donor cells. c) To provide further cytoreduction. ŌĆó Example- total dose of 12- 15Gy Nonmyeloablative ŌĆó Mainly a) & b) ŌĆó c) to a much lesser degree. ŌĆó Example- 2Gy single #
- 10. Types of TBI TOTAL DOSE NO. OF # 1.HIGH DOSE TBI 12Gy 1-6 2.LOW DOSE TBI 10-15cGy/# 10-15 3.TOTAL NODAL IRRADIATION 40Gy 20
- 11. TBI based regime vs Chemotherapy alone
- 12. To conclude.. ŌĆó TBI ŌĆó Pros. ’āś Access to sanctuary sites ’āś Controllable dose delivery. ŌĆó Cons. ’āś Interstitial pneumonitis. ’āś Catarct. ’āś Endocrine deficiency ŌĆó Chemotherapy. ŌĆó Pros. ’āś No special arrangements needed like TBI ŌĆó Cons. ’āś Hepatic VOD/SOS.(BuCy) ’āś Haemorrhagic cystitis.(BuCy) ’āś Seizures.(oral busalphan)
- 13. Mode of Delivery A. Dedicated irradiator. B. Modified conventional irradiator.
- 14. A. Dedicated Irradiators. 1. Treatment at extended SSD.
- 16. 2.Treatment at standard SSD after the CoŌüČ┬░collimator is removed.
- 17. B.Modified Conventional Irradiator. 1.Treatment with a translational beam
- 18. 2.Treatment with a sweeping beam.
- 20. Choice of Technique ŌĆó Depends on- ’āśAvailable equipment ’āśPhoton beam energy ’āśMaximum possible field size ’āśTreatment distance ’āśDose rate ’āśPatient dimension
- 21. Choice of Beam Energy
- 22. Choice of Portals 1. AP/PA. o Pros ŌĆō a) Better dose uniformity along the longitudinal body axis. b) Convenient for treating small children. o Cons-patient positioning (other than standing upright) may pose problem. ’āś Developed in Memorial Sloan Kattering hospital,New York. ’āś Shielding (Dusenbery & Gerbi)- Lung,kidney, Brain.
- 24. 2.Bilateral TBI ŌĆó Pros- ŌĆō More comfortable to the patient. ŌĆó Cons- ŌĆō Greater variation in body thickness along the path of the beam.
- 26. Patient positioning ŌĆó Semifetal position(khan et al.) ŌĆó Arms are positioned laterally to follow the body contour. ŌĆó Arms should shadow the lungs, not the Spinal Column. ŌĆó Pt set-up. ŌĆó SAD
- 27. ŌĆó Compensators are designed for H&N ,lungs,legs. ŌĆó Reference thickness for compensator is the lateral diameter of the body at the level
- 28. Compensator Design ŌĆó Challenges ŌĆō ŌĆō Large variation in body thickness. ŌĆō Lack of complete body immobilisation. ŌĆō Internal tissue heterogeneities.
- 29. Compensator Thickness along a ray line a) Tissue deficit, compared to the reference depth at the prescription point. b) Material(density). c) Distance from the point of compensation. d) Depth of the point of compensation. e) Field size. f) Beam energy.
- 30. Thickness Ratio(Žä) ŌĆó The required thickness of a tissue equivalent compensator that gives the same dose at the point of interest as would a bolus of thickness equal to the tissue deficit. ŌĆó For TBI an average value of 0.7 provides good approximation of all beam energies & compensation conditions.
- 31. Formulae to obtain compensator thickness 1. ŌĆó Tc=comp thickness ŌĆó TD=tissue deficit ŌĆó ╬Īc=density of comp 2. ŌĆó I/I╠ź=doses before & after comp added. ŌĆó T(Aß┤┐dß┤┐) &T(A d)=TPR for ref body section & sectn to be compensated.
- 33. Dosimetry A.Directly ŌĆó By using a 0.6cmߥī Farmer- type ionisation chamber placed in a 40cmߥī water phantom. ŌĆó By placing TLD capsule/chips in strategic locations in body.(in-vivo dosimetry) B.Indirectly ŌĆó By using this formula.
- 34. Adverse effects In nonmyeloablative regimen Acute ’ā╝Nausea ’ā╝Vomiting Long term ’ā╝cataract
- 35. Adverse effects In myeloablative regimens Acute ’ā╝ Nausea, Vomiting ’ā╝ mucositis ’ā╝ Diarrhoea ’ā╝ Xerostomia ’ā╝ Headache ’ā╝ Fever ’ā╝ HTN ’ā╝ Reversible alopecia ’ā╝ Parotiditis Long-term ’ā╝ Lung-interstitial pneumonitis. ’ā╝ Lens-cataract. ’ā╝ Growth & gonadal & Endocrine effects. ’ā╝ Liver-VOD & SOS ’ā╝ Kidney. ’ā╝ 2┬░ cancers.
- 36. HEMI BODY IRRADIATION ŌĆó INDICATIONS- ŌĆō To alleviate symptoms in metastatic diseases. ŌĆō Delaying progression of existing asymptomatic mets. ŌĆō Defers development of new mets.
- 37. Difference with TBI ŌĆó Different therapeutic goal. ŌĆó Smaller field size. ŌĆó Lesser side effects
- 38. Technique ŌĆó Bottom of L4 separates uper & lower half. ŌĆó A/P parallal opposed fields. ŌĆó Patients positioned with vertical beam allowing coverage of hemibody. ŌĆó Necessary shielding. ŌĆó Dose prescribed to mid-plane of the patient at the central axis of the beam.
- 39. Dose ŌĆó Upper HBI-6Gy ŌĆó Lower HBI-8Gy Rx for other half ŌĆó Wait for 6-8 weeks.
- 40. Side effects ’āśNausea ,vomiting(M/C) ’āśFatigue. ’āśCough, breathlessness. ’āśInterstitial pneumonitis. ’āśReversible alopecia ’āśDry mouth, stomatitis. ’āśParotid swelling.







