Lumerical Software: DEVICE
1 like1,302 views
Powerful semiconductor TCAD device simulation software for the design, analysis and optimization of semiconductor-based optoelectronic components
1 of 14












Recommended
Lumerical Software: FDTD Solutions



Lumerical Software: FDTD SolutionsLumerical Solutions Inc.
?
High performance 3D FDTD-method Maxwell solver for the design, analysis and optimization of nanophotonic devices, processes and materialsLumerical Software: MODE Solutions



Lumerical Software: MODE SolutionsLumerical Solutions Inc.
?
Comprehensive waveguide design environment for the analysis and optimization of planar integrated optical waveguides, components and fibersFiber optics ray theory



Fiber optics ray theorySolo Hermelin
?
Describes Fiber Optics using Optical Ray Theory.
For comments please contact me at solo.hermelin@gmail.com.
For more presentations visit my website at http://www.solohermelin.com.Dpcm ( Differential Pulse Code Modulation )



Dpcm ( Differential Pulse Code Modulation )Mohammed Abdullah
?
This document discusses techniques for image coding and compression, including predicting pixel values from neighboring pixels, encoding differences between actual and predicted values (DPCM), and adapting the mapping of bits to differences over time (ADPCM). DPCM removes redundancy by transmitting only differences between samples, which are normally small. ADPCM varies this mapping dynamically so more bits can be used for rapid changes and fewer for slow changes. Overall the document focuses on prediction-based approaches to reduce image data by exploiting spatial and temporal correlations between pixels.

Antenas microstripFernando Arcos Koronel
?
Este documento describe las antenas microstrip, que consisten en una l®™nea conductora sobre un sustrato diel®¶ctrico. Explica que tienen tama?os de 0.25 a 1 longitud de onda, con frecuencias t®™picas de 400 MHz a 40 GHz. Se usan com®≤nmente en aeronaves, m®Æviles, WLAN y aplicaciones biom®¶dicas debido a su peque?o tama?o, bajo peso y f®¢cil fabricaci®Æn.Cognitive Radio Spectrum Sensing 1586 ppt



Cognitive Radio Spectrum Sensing 1586 pptAnupam Yadav
?
This document discusses cognitive radio spectrum sensing. It begins with an introduction to cognitive radio and the need to more efficiently utilize licensed radio spectrum. It then discusses applications of cognitive radio networks in providing services to users. The document outlines the architecture of cognitive radio networks, including non-cooperative and cooperative architectures. It also discusses different types of spectrum sensing, including energy detection and its mathematical model. It describes an algorithm used for detection of spectrum holes using power spectral density. Simulation results are shown. Finally, references on cognitive radio and spectrum sensing are provided.Ep301



Ep301Muhd Iqwan Mustaffa
?
Upon completion of this chapter, students will be able to:
- Understand the key elements of a communication system including information sources, transmitters, transmission mediums, receivers, and destination equipment.
- Comprehend core concepts such as signals, modulation, noise, interference, and frequency spectrums.
- Learn about various communication system types including radio, broadcasting, and computer networks.Unit 3 SECA1701-microwave measurements.pptx



Unit 3 SECA1701-microwave measurements.pptxPavanVangapally
?
This document provides information about microwave measurements. It discusses the general setup of a microwave bench which includes a signal generator, precision attenuator, variable attenuator, isolator, frequency meter, and crystal detector. It describes how a slotted line can be used to measure standing wave ratio and impedance. It also discusses different microwave measurement devices and techniques for measuring frequency, power, attenuation, VSWR, and dielectric constant. Measurement of low, medium, and high power is described along with how devices like a bolometer, calorimeter, and watt meter are used.optical space division multiplexing



optical space division multiplexingmohammedalimahdi
?
Optical space division multiplexing uses multiple cores or modes in optical fibers to increase transmission capacity. A history of the technology was provided, noting the progression from single mode fibers to coherent detection and polarization multiplexing. Limits with single mode fibers were discussed, along with ways that multi-core and multi-mode fibers can overcome capacity constraints through spatial multiplexing across fiber cores and modes. Recent demonstrations showed record capacities of 57.6 Tb/s over multi-mode fiber and 24 Tb/s over hollow-core fiber. Integration challenges with spatial division multiplexing were also outlined.311 linear modulation



311 linear modulationMohammad Bappy
?
This document discusses linear modulation techniques, specifically amplitude modulation (AM). It describes the main types of AM including double sideband full carrier (DSBFC), double sideband suppressed carrier (DSBSC), and single sideband suppressed carrier (SSBSC). It provides details on how each is generated and transmitted, their advantages and disadvantages, and the basic components and functioning of AM transmitters and receivers.Optical Wavelength converters



Optical Wavelength convertersFAIZAN AHMAD
?
Wavelength converters are devices that convert data from one incoming wavelength to another wavelength. They enable optical channels to be relocated and are achieved using nonlinear optical effects. Wavelength converters are useful in WDM networks for three reasons: 1) data may enter the network at an unsuitable wavelength, 2) converters may improve wavelength utilization on network links, and 3) converters may be needed when networks managed by different entities do not coordinate wavelength allocation. Common types of wavelength converters include optoelectronic, optical gating using cross-gain modulation, and four-wave mixing approaches.Mini Project 2 - Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) Modulator and Demodulator



Mini Project 2 - Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) Modulator and DemodulatorAIMST University
?
This document outlines a laboratory project on frequency shift keying (FSK) modulation and demodulation. The objectives are to generate an FSK modulated signal using a modulator circuit with a 555 timer IC and transmit binary data, and to demodulate the FSK signal using a demodulator circuit with a 565 phase locked loop. Students will construct the circuits according to the specifications, test them, and write a report explaining FSK theory and operations, describing the printed circuit board fabrication and assembly, and presenting the results.Wireless Channel Impairment Mitigation Techniques



Wireless Channel Impairment Mitigation Techniquesmohammedalimahdi
?
There are many types of wireless channel impairments such as noise, path loss, shadowing, and fading and impairment Mitigation techniques should be adopted according to system requirements and channel environments.
Dtmf signaling



Dtmf signalingk sekhar
?
The document describes implementing DTMF (dual-tone multi-frequency) detection using the Goertzel algorithm in an FPGA. It proposes using the Goertzel algorithm as an area-efficient solution compared to using an ASIC or FFT. The key steps of the Goertzel algorithm are described for detecting the presence of DTMF tones from a signal. The algorithm is further optimized by modifying it based on the matched filter concept.Radar 2009 a 11 waveforms and pulse compression



Radar 2009 a 11 waveforms and pulse compressionForward2025
?
The document describes a lecture on radar waveforms and pulse compression. It introduces matched filters and how they are implemented by convolving a reflected echo with a time-reversed transmit pulse. This maximizes the signal-to-noise ratio. Pulse compression techniques like linear frequency modulation and phase coding are then discussed, which allow the use of longer pulses that increase energy while maintaining high range resolution. The goal is to reduce the high peak power needs of short pulses for applications like airborne radar.OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-1



OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-1Asif Iqbal
?
This document provides information about light propagation through optical fibers. It begins by defining an optical fiber as a cylindrical waveguide made of glass that uses total internal reflection to transmit light. It then discusses the fiber's core and cladding layers and the conditions needed for total internal reflection. The key points covered include:
- Light propagation is guided through the fiber core by total internal reflection at the core-cladding interface.
- Only rays entering the fiber core within the acceptance angle will continue propagating through total internal reflection.
- Electromagnetic mode theory is needed to fully understand light propagation in fibers. Discrete modes exist that are solutions to Maxwell's equations.
- The evanescent field that penetrates the cl

Fibra clase 2PITU Avalos
?
Este documento describe las fibras ®Æpticas, incluyendo su estructura b®¢sica, modos de propagaci®Æn, atenuaci®Æn, dispersi®Æn y tipos. Explica que una fibra ®Æptica est®¢ constituida principalmente por un n®≤cleo y un revestimiento, y que la luz se gu®™a a lo largo del n®≤cleo por reflexi®Æn total interna. Tambi®¶n cubre factores que afectan la atenuaci®Æn como la absorci®Æn y el scattering de Rayleigh, as®™ como los diferentes tipos de dispersi®Æn como la intermodal, crom®¢tica y por polarizaci®Æn modal.Radar signal processing



Radar signal processingMustahid Ali
?
RADAR uses radio waves to detect distant objects. It transmits pulses and measures properties of the reflected pulses, including range, angles, size, and speed of targets. RADAR signal processing involves measuring distance using transit time or frequency modulation, measuring speed using Doppler effect, and reducing interference through techniques like moving target indication and constant false alarm rate processing. The signal processor separates targets from clutter based on Doppler shifts and amplitude. RADAR has military, navigation, and civilian applications including air traffic control and law enforcement.Laser Frequency Response with Optisystems



Laser Frequency Response with OptisystemsLouise Antonio
?
This report discusses the frequency response of a directly modulated laser. It describes how a carrier generator was used to create 298 channels with 25 MHz separations from 50 MHz as input to a laser diode. The laser's frequency response was then displayed using an RF spectrum analyzer. Nonlinearities in the laser were observed at higher amplitudes of the carrier generator input, changing the frequency response from a flat magnitude up to 2 GHz to one with kinks. Components of the simulation like the carrier generator, RFSA, laser and OSA are also outlined.

Antenas e suas aplica??es caps1&2 270114_17h55m (1)Pedro Henrique de Medeiros Leite
?
1) O documento apresenta os principais tipos e aplica??es de antenas, incluindo antenas de fio, de abertura, de refletor, de lente e planares.
2) Os par?metros principais de antenas s?o descritos, como diagramas de radia??o, imped?ncia, ganho, diretividade e polariza??o.
3) M®¶todos num®¶ricos s?o usados para calcular a pot®∫ncia radiada a partir dos diagramas de radia??o das antenas.optical sources keiser.ppt



optical sources keiser.pptsrividyaL1
?
The document discusses optical sources for fiber optic communications, including light emitting diodes (LEDs) and laser diodes. It describes the basic structures and operating principles of LEDs and laser diodes. LEDs have a wide spectral width and beam width, while lasers can achieve coherent, highly directional beams with narrow spectral width using stimulated emission in an optical cavity. The document covers considerations for optical sources used in fiber communications and reviews semiconductor physics concepts relevant to LED and laser operation.5 pulse compression waveform



5 pulse compression waveformSolo Hermelin
?
Describes Pulse Compression in Radar Systems.
For comments please contact me at solo.hermelin@gmail.com.
For more presentations on different subjects visit my website at http://solohermelin.com.
Since some figures were not downloaded, I recommend to see this presentation on my website under RADAR Folder, Signal Processing subfolder.Optical networking



Optical networkingFawzi Mohammed Hassan
?
Optical networking technologies provide high-speed, high-bandwidth data transmission over long distances using fiber optic cables. Key technologies include passive optical networks (PON) for access networks, SONET/SDH for metro networks, and dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) for long-haul transport networks. DWDM works by transmitting multiple optical signals simultaneously on different wavelengths over the same fiber, vastly increasing network capacity. Proper layer-2 encapsulation is required to transport layer-3 protocols like IP over DWDM.Electronics Quiz



Electronics QuizNaveen Kumar
?
This document appears to be a quiz containing multiple choice questions related to electronics and electrical engineering. There are 50 questions in total across common, buzzer, and final rounds. The quiz was created by Naveen Kumar and contains questions testing knowledge of concepts like circuits, resistors, capacitors, transistors, logic gates, and more.Photo-detector by GIRISH HARMUKH



Photo-detector by GIRISH HARMUKHGIRISH HARMUKH
?
This document discusses different types of photodetectors. It describes photoconductive detectors like light dependent resistors (LDRs) and junction photodetectors including p-n photodiodes, PIN photodiodes, avalanche photodiodes, and Schottky photodiodes. PIN photodiodes are presented as an improvement over p-n photodiodes by having a larger depletion region for higher quantum efficiency. Avalanche photodiodes provide internal gain through impact ionization. Schottky photodiodes have a high speed due to being majority carrier devices. Phototransistors are also discussed as providing gain. Applications mentioned include fiber optics, cameras, medical devices, barcodes, and security systemsTo Calculate the Maximum LOS Coverage



To Calculate the Maximum LOS CoverageJustin MA (ÒRºŒ≤˝)
?
This paper to introduce how to calculate the maximum LOS distance for a known radio tower with the local altitude.WiMax - Technology & Architecture



WiMax - Technology & Architecturesashar86
?
The document discusses WiMAX technology and architecture. It provides an overview of the IEEE 802.16 standard, operating frequencies, data rates, network components, and services supported. The key components of a WiMAX network include the subscriber stations, access service network with base stations, connectivity service network with AAA and DHCP servers, and network service provider layer which offers various applications and services to subscribers.Introduction to radar



Introduction to radarUlsah T N
?
Radar was originally developed for military purposes during World War 2 to detect ships and airplanes. Scientists later discovered that radar could also detect precipitation, making it an essential tool for weather prediction. There are two main types of radar: pulse radar which uses pulse transmission to determine range and continuous wave radar which relies on the Doppler effect. Key radar components include the transmitter, receiver, antenna, and display unit. Radar systems can be classified by their primary mission as search, tracking, or weather surveillance radars. Common examples include air search radars, long range surveillance radars, and tracking radars used in aircraft.Improving Engagement with CRM Software for Instance Agents



Improving Engagement with CRM Software for Instance AgentsInsurance Tech Services
?
A tailored CRM that helps insurance agents streamline interactions, enhance engagement, and drive growth through automation and centralized data. Visit https://www.damcogroup.com/insurance/crm-software for more details!Intranet Examples That Are Changing the Way We Work



Intranet Examples That Are Changing the Way We WorkBizPortals Solutions
?
In today°Øs workplace, staying connected is more important than ever. Whether teams are remote, hybrid, or back in the office, communication and collaboration are at the heart of getting things done. But here°Øs the truth °™ outdated intranets just don°Øt cut it anymore.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
optical space division multiplexing



optical space division multiplexingmohammedalimahdi
?
Optical space division multiplexing uses multiple cores or modes in optical fibers to increase transmission capacity. A history of the technology was provided, noting the progression from single mode fibers to coherent detection and polarization multiplexing. Limits with single mode fibers were discussed, along with ways that multi-core and multi-mode fibers can overcome capacity constraints through spatial multiplexing across fiber cores and modes. Recent demonstrations showed record capacities of 57.6 Tb/s over multi-mode fiber and 24 Tb/s over hollow-core fiber. Integration challenges with spatial division multiplexing were also outlined.311 linear modulation



311 linear modulationMohammad Bappy
?
This document discusses linear modulation techniques, specifically amplitude modulation (AM). It describes the main types of AM including double sideband full carrier (DSBFC), double sideband suppressed carrier (DSBSC), and single sideband suppressed carrier (SSBSC). It provides details on how each is generated and transmitted, their advantages and disadvantages, and the basic components and functioning of AM transmitters and receivers.Optical Wavelength converters



Optical Wavelength convertersFAIZAN AHMAD
?
Wavelength converters are devices that convert data from one incoming wavelength to another wavelength. They enable optical channels to be relocated and are achieved using nonlinear optical effects. Wavelength converters are useful in WDM networks for three reasons: 1) data may enter the network at an unsuitable wavelength, 2) converters may improve wavelength utilization on network links, and 3) converters may be needed when networks managed by different entities do not coordinate wavelength allocation. Common types of wavelength converters include optoelectronic, optical gating using cross-gain modulation, and four-wave mixing approaches.Mini Project 2 - Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) Modulator and Demodulator



Mini Project 2 - Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) Modulator and DemodulatorAIMST University
?
This document outlines a laboratory project on frequency shift keying (FSK) modulation and demodulation. The objectives are to generate an FSK modulated signal using a modulator circuit with a 555 timer IC and transmit binary data, and to demodulate the FSK signal using a demodulator circuit with a 565 phase locked loop. Students will construct the circuits according to the specifications, test them, and write a report explaining FSK theory and operations, describing the printed circuit board fabrication and assembly, and presenting the results.Wireless Channel Impairment Mitigation Techniques



Wireless Channel Impairment Mitigation Techniquesmohammedalimahdi
?
There are many types of wireless channel impairments such as noise, path loss, shadowing, and fading and impairment Mitigation techniques should be adopted according to system requirements and channel environments.
Dtmf signaling



Dtmf signalingk sekhar
?
The document describes implementing DTMF (dual-tone multi-frequency) detection using the Goertzel algorithm in an FPGA. It proposes using the Goertzel algorithm as an area-efficient solution compared to using an ASIC or FFT. The key steps of the Goertzel algorithm are described for detecting the presence of DTMF tones from a signal. The algorithm is further optimized by modifying it based on the matched filter concept.Radar 2009 a 11 waveforms and pulse compression



Radar 2009 a 11 waveforms and pulse compressionForward2025
?
The document describes a lecture on radar waveforms and pulse compression. It introduces matched filters and how they are implemented by convolving a reflected echo with a time-reversed transmit pulse. This maximizes the signal-to-noise ratio. Pulse compression techniques like linear frequency modulation and phase coding are then discussed, which allow the use of longer pulses that increase energy while maintaining high range resolution. The goal is to reduce the high peak power needs of short pulses for applications like airborne radar.OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-1



OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-1Asif Iqbal
?
This document provides information about light propagation through optical fibers. It begins by defining an optical fiber as a cylindrical waveguide made of glass that uses total internal reflection to transmit light. It then discusses the fiber's core and cladding layers and the conditions needed for total internal reflection. The key points covered include:
- Light propagation is guided through the fiber core by total internal reflection at the core-cladding interface.
- Only rays entering the fiber core within the acceptance angle will continue propagating through total internal reflection.
- Electromagnetic mode theory is needed to fully understand light propagation in fibers. Discrete modes exist that are solutions to Maxwell's equations.
- The evanescent field that penetrates the cl

Fibra clase 2PITU Avalos
?
Este documento describe las fibras ®Æpticas, incluyendo su estructura b®¢sica, modos de propagaci®Æn, atenuaci®Æn, dispersi®Æn y tipos. Explica que una fibra ®Æptica est®¢ constituida principalmente por un n®≤cleo y un revestimiento, y que la luz se gu®™a a lo largo del n®≤cleo por reflexi®Æn total interna. Tambi®¶n cubre factores que afectan la atenuaci®Æn como la absorci®Æn y el scattering de Rayleigh, as®™ como los diferentes tipos de dispersi®Æn como la intermodal, crom®¢tica y por polarizaci®Æn modal.Radar signal processing



Radar signal processingMustahid Ali
?
RADAR uses radio waves to detect distant objects. It transmits pulses and measures properties of the reflected pulses, including range, angles, size, and speed of targets. RADAR signal processing involves measuring distance using transit time or frequency modulation, measuring speed using Doppler effect, and reducing interference through techniques like moving target indication and constant false alarm rate processing. The signal processor separates targets from clutter based on Doppler shifts and amplitude. RADAR has military, navigation, and civilian applications including air traffic control and law enforcement.Laser Frequency Response with Optisystems



Laser Frequency Response with OptisystemsLouise Antonio
?
This report discusses the frequency response of a directly modulated laser. It describes how a carrier generator was used to create 298 channels with 25 MHz separations from 50 MHz as input to a laser diode. The laser's frequency response was then displayed using an RF spectrum analyzer. Nonlinearities in the laser were observed at higher amplitudes of the carrier generator input, changing the frequency response from a flat magnitude up to 2 GHz to one with kinks. Components of the simulation like the carrier generator, RFSA, laser and OSA are also outlined.

Antenas e suas aplica??es caps1&2 270114_17h55m (1)Pedro Henrique de Medeiros Leite
?
1) O documento apresenta os principais tipos e aplica??es de antenas, incluindo antenas de fio, de abertura, de refletor, de lente e planares.
2) Os par?metros principais de antenas s?o descritos, como diagramas de radia??o, imped?ncia, ganho, diretividade e polariza??o.
3) M®¶todos num®¶ricos s?o usados para calcular a pot®∫ncia radiada a partir dos diagramas de radia??o das antenas.optical sources keiser.ppt



optical sources keiser.pptsrividyaL1
?
The document discusses optical sources for fiber optic communications, including light emitting diodes (LEDs) and laser diodes. It describes the basic structures and operating principles of LEDs and laser diodes. LEDs have a wide spectral width and beam width, while lasers can achieve coherent, highly directional beams with narrow spectral width using stimulated emission in an optical cavity. The document covers considerations for optical sources used in fiber communications and reviews semiconductor physics concepts relevant to LED and laser operation.5 pulse compression waveform



5 pulse compression waveformSolo Hermelin
?
Describes Pulse Compression in Radar Systems.
For comments please contact me at solo.hermelin@gmail.com.
For more presentations on different subjects visit my website at http://solohermelin.com.
Since some figures were not downloaded, I recommend to see this presentation on my website under RADAR Folder, Signal Processing subfolder.Optical networking



Optical networkingFawzi Mohammed Hassan
?
Optical networking technologies provide high-speed, high-bandwidth data transmission over long distances using fiber optic cables. Key technologies include passive optical networks (PON) for access networks, SONET/SDH for metro networks, and dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) for long-haul transport networks. DWDM works by transmitting multiple optical signals simultaneously on different wavelengths over the same fiber, vastly increasing network capacity. Proper layer-2 encapsulation is required to transport layer-3 protocols like IP over DWDM.Electronics Quiz



Electronics QuizNaveen Kumar
?
This document appears to be a quiz containing multiple choice questions related to electronics and electrical engineering. There are 50 questions in total across common, buzzer, and final rounds. The quiz was created by Naveen Kumar and contains questions testing knowledge of concepts like circuits, resistors, capacitors, transistors, logic gates, and more.Photo-detector by GIRISH HARMUKH



Photo-detector by GIRISH HARMUKHGIRISH HARMUKH
?
This document discusses different types of photodetectors. It describes photoconductive detectors like light dependent resistors (LDRs) and junction photodetectors including p-n photodiodes, PIN photodiodes, avalanche photodiodes, and Schottky photodiodes. PIN photodiodes are presented as an improvement over p-n photodiodes by having a larger depletion region for higher quantum efficiency. Avalanche photodiodes provide internal gain through impact ionization. Schottky photodiodes have a high speed due to being majority carrier devices. Phototransistors are also discussed as providing gain. Applications mentioned include fiber optics, cameras, medical devices, barcodes, and security systemsTo Calculate the Maximum LOS Coverage



To Calculate the Maximum LOS CoverageJustin MA (ÒRºŒ≤˝)
?
This paper to introduce how to calculate the maximum LOS distance for a known radio tower with the local altitude.WiMax - Technology & Architecture



WiMax - Technology & Architecturesashar86
?
The document discusses WiMAX technology and architecture. It provides an overview of the IEEE 802.16 standard, operating frequencies, data rates, network components, and services supported. The key components of a WiMAX network include the subscriber stations, access service network with base stations, connectivity service network with AAA and DHCP servers, and network service provider layer which offers various applications and services to subscribers.Introduction to radar



Introduction to radarUlsah T N
?
Radar was originally developed for military purposes during World War 2 to detect ships and airplanes. Scientists later discovered that radar could also detect precipitation, making it an essential tool for weather prediction. There are two main types of radar: pulse radar which uses pulse transmission to determine range and continuous wave radar which relies on the Doppler effect. Key radar components include the transmitter, receiver, antenna, and display unit. Radar systems can be classified by their primary mission as search, tracking, or weather surveillance radars. Common examples include air search radars, long range surveillance radars, and tracking radars used in aircraft.Recently uploaded (20)
Improving Engagement with CRM Software for Instance Agents



Improving Engagement with CRM Software for Instance AgentsInsurance Tech Services
?
A tailored CRM that helps insurance agents streamline interactions, enhance engagement, and drive growth through automation and centralized data. Visit https://www.damcogroup.com/insurance/crm-software for more details!Intranet Examples That Are Changing the Way We Work



Intranet Examples That Are Changing the Way We WorkBizPortals Solutions
?
In today°Øs workplace, staying connected is more important than ever. Whether teams are remote, hybrid, or back in the office, communication and collaboration are at the heart of getting things done. But here°Øs the truth °™ outdated intranets just don°Øt cut it anymore.Shortcomings of EHS Software ®C And How to Overcome Them



Shortcomings of EHS Software ®C And How to Overcome ThemTECH EHS Solution
?
Shortcomings of EHS Software°™and What Overcomes Them
What you'll learn in just 8 slides:
- ? Why most EHS software implementations struggle initially
- ? 3 common pitfalls: adoption, workflow disruption, and delayed ROI
- ?? Practical solutions that deliver long-term value
- ? Key features: centralization, security, affordability
- ? Why the pros outweigh the cons
Perfect for HSE heads, plant managers, and compliance leads!
#EHS #TECHEHS #WorkplaceSafety #EHSCompliance #EHSManagement #ehssoftware #safetysoftwareList Unfolding - 'unfold' as the Computational Dual of 'fold', and how 'unfol...



List Unfolding - 'unfold' as the Computational Dual of 'fold', and how 'unfol...Philip Schwarz
?
In this deck we look at the following:
* how unfolding lists is the computational dual of folding lists
* different variants of the function for unfolding lists
* how they relate to the iterate functionMarketing And Sales Software Services.pptx



Marketing And Sales Software Services.pptxjulia smits
?
Marketing and Sales Software Services refer to digital solutions designed to streamline, automate, and enhance a company°Øs marketing campaigns and sales processes. These services include tools for customer relationship management (CRM), email marketing, lead generation, sales analytics, campaign tracking, and more°™helping businesses attract, engage, and convert prospects more efficiently.zOS CommServer support for the Network Express feature on z17



zOS CommServer support for the Network Express feature on z17zOSCommserver
?
The IBM z17 has undergone a transformation with an entirely new System I/O hardware and architecture model for both storage and networking. The z17 offers I/O capability that is integrated directly within the Z processor complex. The new system design moves I/O operations closer to the system processor and memory. This new design approach transforms I/O operations allowing Z workloads to grow and scale to meet the growing needs of current and future IBM Hybrid Cloud Enterprise workloads. This presentation will focus on the networking I/O transformation by introducing you to the new IBM z17 Network Express feature.
The Network Express feature introduces new system architecture called Enhanced QDIO (EQDIO). EQDIO allows the updated z/OS Communications Server software to interact with the Network Express hardware using new optimized I/O operations. The new design and optimizations are required to meet the demand of the continuously growing I/O rates. Network Express and EQDIO build the foundation for the introduction of advanced Ethernet and networking capabilities for the future of IBM Z Hybrid Cloud Enterprise users.
The Network Express feature also combines the functionality of both the OSA-Express and RoCE Express features into a single feature or adapter. A single Network Express port supports both IP protocols and RDMA protocols. This allows each Network Express port to function as both a standard NIC for Ethernet and as an RDMA capable NIC (RNIC) for RoCE protocols. Converging both protocols to a single adapter reduces Z customers°Ø cost for physical networking resources. With this change, IBM Z customers can now exploit Shared Memory Communications (SMC) leveraging RDMA (SMC-R) technology without incurring additional hardware costs.
In this session, the speakers will focus on how z/OS Communications Server has been updated to support the Network Express feature. An introduction to the new Enhanced QDIO Ethernet (EQENET) interface statement used to configure the new OSA is provided. EQDIO provides a variety of simplifications, such as no longer requiring VTAM user defined TRLEs, uses smarter defaults and removes outdated parameters. The speakers will also cover migration considerations for Network Express. In addition, the operational aspects of managing and monitoring the new OSA and RoCE interfaces will be covered. The speakers will also take you through the enhancements made to optimize both inbound and outbound network traffic. Come join us, step aboard and learn how z/OS Communications Server is bringing you the future in network communications with the IBM z17 Network Express feature. VFP-Report-Copy-Data-Environment details



VFP-Report-Copy-Data-Environment detailsmanojbkalla
?
VFP-Report-Copy-Data-Environment details.
I am MCTS - (Microsoft Certified Tech. Specialist).
I had started my journey with COBOL, dbaseIII+, Clipper, Foxpro - DOS/WIndows/Visual, VB6.
My 130+ Articles on .NET : https://www.c-sharpcorner.com/members/manoj-kalla3
My YouTube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/@manojkalla4174/playlists
Total 200+ Videos on Visual Foxpro.
My Medium Article : https://medium.com/@manojkalla
Ahmedabad Information Technology IT college Syllabus for BCA, MCA and online teaching for Asp.Net MVC, Asp.Net Core, Java, C Language, C++ Language, Entity Framework, Linq To SQL, Android.
The Maharaja Sayajirao University (M.S. University), Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Open University (BAOU), Indus University (IU), Ahmedabad courses and G.L.S. Institute Of Computer Application (GLSICA), Gujarat University online courses BCA, MCA and BTech, MTech online.
Mehsana Information Technology IT college Syllabus for BCA, MCA.
Mehsana online teaching for Asp.Net MVC, Asp.Net Core, Java, C Language, C++ Language, Entity Framework, Linq To SQL, Android.
Yashwantrao Chavan Maharashtra Open University (YCMOU) course online training institute.
YCMOU Java Notes, YCMOU Android Training, YCMOU Java Training, YCMOU Linux Course, YCMOU syllabus online Training insitute, YCMOU C++ Notes, YCMOU C++ online training, YCMOU C++ online tutor.
YCMOU BCA tutor , YCMOU BCA training,
Bharati Vidyapeeth University (BVP) courses online training ,
Bharati Vidyapeeth University (BVP) courses online tutor,
Bharati Vidyapeeth University (BVP) courses BCA online training ,
Bharati Vidyapeeth University (BVP) courses BTECH online tutor,
Angular online tutor in malad mumbai,
Angular online tutor in kandivali mumbai,
Angular online tutor in bhayandar mumbai,
Angular online tutor in vapi gujrat,
Angular online tutor in surat gujrat,
Angular online tutor in baroda gujrat,
Angular online tutor in vadodara gujrat,
Angular online tutor in indore MP,
Angular online tutor in bhopal MP,
Angular online tutor in nashik maharashtra,
Angular online tutor in pune maharashtra,
Angular online training institute in Bandra Mumbai,
Angular online training institute in mehsana Gujrat,
Angular online tutor in malad mumbai,
Angular online tutor in kandivali mumbai,
Angular online tutor in bhayandar mumbai,
Angular online tutor in vapi gujrat,
Angular online tutor in surat gujrat,
Angular online tutor in baroda gujrat,
Angular online tutor in vadodara gujrat,
Angular online tutor in indore MP,
Angular online tutor in bhopal MP,
Angular online tutor in nashik maharashtra,
Angular online tutor in pune maharashtra,
Angular online training institute in Bandra Mumbai,
Angular online training institute in mehsana Gujrat,
AI-ASSISTED METAMORPHIC TESTING FOR DOMAIN-SPECIFIC MODELLING AND SIMULATION



AI-ASSISTED METAMORPHIC TESTING FOR DOMAIN-SPECIFIC MODELLING AND SIMULATIONmiso_uam
?
AI-ASSISTED METAMORPHIC TESTING FOR DOMAIN-SPECIFIC MODELLING AND SIMULATION (plenary talk at ANNSIM'2025)
Testing is essential to improve the correctness of software systems. Metamorphic testing (MT) is an approach especially suited when the system under test lacks oracles, or they are expensive to compute. However, building an MT environment for a particular domain (e.g., cloud simulation, automated driving simulation, production system simulation, etc) requires substantial effort.
To alleviate this problem, we propose a model-driven engineering approach to automate the construction of MT environments, which is especially useful to test domain-specific modelling and simulation systems. Starting from a meta-model capturing the domain concepts, and a description of the domain execution environment, our approach produces an MT environment featuring comprehensive support for the MT process. This includes the definition of domain-specific metamorphic relations, their evaluation, detailed reporting of the testing results, and the automated search-based generation of follow-up test cases.
In this talk, I presented the approach, along with ongoing work and perspectives for integrating intelligence assistance based on large language models in the MT process. The work is a joint collaboration with Pablo G®Æmez-Abajo, Pablo C. Ca?izares and Esther Guerra from the miso research group and Alberto N®≤?ez from UCM.
ICDL FULL STANDARD 2025 Luisetto mauro - Academia domani- 55 HOURS LONG pdf



ICDL FULL STANDARD 2025 Luisetto mauro - Academia domani- 55 HOURS LONG pdfM. Luisetto Pharm.D.Spec. Pharmacology
?
.Why-Choose-an-Authorised-Microsoft-Reseller.pptx



Why-Choose-an-Authorised-Microsoft-Reseller.pptxMichael cole
?
Choosing an authorized Microsoft reseller ensures that your business gets authentic software, professional licensing guidance, and constant technical support.Certified resellers offer secure deployment, compliance with Microsoft standards, and tailored cloud solutions °™ helping businesses maximize ROI, reduce risks, and stay up to date with the latest Microsoft innovations.How John started to like TDD (instead of hating it) (ViennaJUG, June'25)



How John started to like TDD (instead of hating it) (ViennaJUG, June'25)Nacho Cougil
?
Let me share a story about how John (a developer like any other) started to understand (and enjoy) writing Tests before the Production code.
We've all felt an inevitable "tedium" when writing tests, haven't we? If it's boring, if it's complicated or unnecessary? Isn't it? John thought so too, and, as much as he had heard about writing tests before production code, he had never managed to put it into practice, and even when he had tried, John had become even more frustrated at not understanding how to put it into practice outside of a few examples katas ??°·?
Listen to this story in which I will explain how John went from not understanding Test Driven Development (TDD) to being passionate about it... so much that now he doesn't want to work any other way ? ! He must have found some benefits in practising it, right? He says he has more advantages than working in any other way (e.g., you'll find defects earlier, you'll have a faster feedback loop or your code will be easier to refactor), but I'd better explain it to you in the session, right?
PS: Think of John as a random person, as if he was even the speaker of this talk ? !
---
Presentation shared at ViennaJUG, June'25
Feedback form:
https://bit.ly/john-like-tdd-feedback Multiple Platforms of Unity Game Development.pdf



Multiple Platforms of Unity Game Development.pdfNova Carter
?
Unity Game Development stands out for its unparalleled flexibility across multiple platforms, making it a top choice for developers aiming to reach a broad audience. With Unity, creators can build a game once and deploy it seamlessly across mobile devices, desktops, gaming consoles, web browsers, and even AR/VR systems. This multi-platform capability reduces development costs and effort while ensuring consistent performance and user experience across devices. Whether targeting casual mobile gamers or console enthusiasts, Unity empowers developers to scale their games effectively and maintain a competitive edge in today°Øs diverse gaming landscape.Custom Software Development: Types, Applications and Benefits.pdf



Custom Software Development: Types, Applications and Benefits.pdfDigital Aptech
?
Discover the different types of custom software, their real-world applications across industries, and the key benefits they offer. Learn how tailored solutions improve efficiency, scalability, and business performance in this comprehensive overview.Issues in AI Presentation and machine learning.pptx



Issues in AI Presentation and machine learning.pptxJalalkhan657136
?
A simple presentation about issues in artificial intelligence or ai and machine learning Key Characteristics of High-Performing Insurance Broker Software



Key Characteristics of High-Performing Insurance Broker SoftwareInsurance Tech Services
?
Insurance broker software enables brokers to streamline and simplify client management. It is a comprehensive solution to boost productivity and consolidate business data. Let°Øs have a look at the features that every good insurance broking software must possess. Explore more - https://www.damcogroup.com/insurance/brokeredge-broker-management-softwareOptimising Claims Management with Claims Processing Systems



Optimising Claims Management with Claims Processing SystemsInsurance Tech Services
?
A Claims Processing System enhances customer satisfaction, efficiency, and compliance by automating the claims lifecycle°™enabling faster settlements, fewer errors, and greater transparency. Explore More - https://www.damcogroup.com/insurance/claims-management-softwareAI Alternative - Discover the best AI tools and their alternatives



AI Alternative - Discover the best AI tools and their alternativesAI Alternative
?
AIAlternative.co is a comprehensive directory designed to help users discover, compare, and evaluate AI tools across various domains. Its primary goal is to assist individuals and businesses in finding the most suitable AI solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Key Features
- Curated AI Tool Listings: The platform offers detailed information on a wide range of AI tools, including their functionalities, use cases, and alternatives. This allows users to make informed decisions based on their requirements.
- Alternative Suggestions: For each listed AI tool, aialternative.co provides suggestions for similar or alternative tools, facilitating easier comparison and selection.
- Regular Updates: The directory is consistently updated to include the latest AI innovations, ensuring users have access to the most current tools available in the market.
Browse All Tools here: https://aialternative.co/ICDL FULL STANDARD 2025 Luisetto mauro - Academia domani- 55 HOURS LONG pdf



ICDL FULL STANDARD 2025 Luisetto mauro - Academia domani- 55 HOURS LONG pdfM. Luisetto Pharm.D.Spec. Pharmacology
?
Lumerical Software: DEVICE
- 1. DEVICE PRODUCT OVERVIEW ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC1
- 2. Lumerical Solutions Products ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC2 FDTD Solutions NANOPHOTONIC SOLVER (2D/3D) MODE Solutions WAVEGUIDE DESIGN ENVIRONMENT spatial distribution of charge carriers optical generation rate of charge carriers INTERCONNECT PHOTONIC INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SIMULATOR DEVICE CHARGE TRANSPORT SOLVER (2D/3D) System Level Component Level: Optical Component Level: Electrical
- 3. Lumerical Product Overview All Lumerical products share common features ? Parameter sweep and optimization framework ? Concurrent computing on multiple computers ? Broad operating system support ? Windows, Linux, MAC ? HPC on Amazon EC2 ? Powerful scripting language ? MATLAB integration ? Technical support from product specialists ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC3
- 4. DEVICE Robust industry proven 2D/3D drift-diffusion solver ? Accurately determine distribution and flow of electrical charge ? Integrate optical stimulus in electrical simulations Automated finite element mesh generation ? Optimized based on electrical and optical profiles ? Efficient simulation of arbitrary 2D/3D geometries ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC4
- 5. Applications ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC5 CMOS Image Sensors Photodetectors Electro-Optic Modulators THz Resonant Modulators Photovoltaic Devices MOSFETs
- 6. DEVICE Key Features Specialized for optoelectronic design and analysis ? Accelerate optoelectronic R&D Complete 2D/3D electrical simulation ? DC steady state ? Adaptive time-step transient Adaptive finite element mesh technology Integrated visual material model database ? Predefined and custom models for semiconductors ? Heterostructure support Interoperates with Lumerical optical solvers for electro-optic and photosensitive device simulations ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC6
- 7. DEVICE Workflow 1. Define materials 2. Define geometry 3. Define doping 4. Define contacts 5. Define simulation region and mesh 6. Define monitors 7. Run simulation 8. Visualize and analyze results 9. (Optional) Run parameter sweep and optimization ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC7
- 8. DEVICE Workflow ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC8 Define materials Define geometry
- 9. DEVICE Workflow ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC9 Define doping Define contacts
- 10. DEVICE Workflow ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC10 Define simulation region and mesh Define monitors
- 11. DEVICE Workflow ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC11 Run simulation Visualize and analyze results
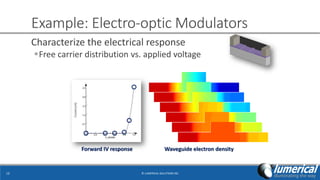
- 12. Example: Electro-optic Modulators ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC12 Characterize the electrical response ?Free carrier distribution vs. applied voltage Waveguide electron densityForward IV response
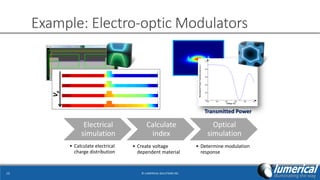
- 13. Example: Electro-optic Modulators ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC13 Electrical simulation ? Calculate electrical charge distribution Calculate index ? Create voltage dependent material Optical simulation ? Determine modulation response Va Transmitted Power
- 14. Questions? support@lumerical.com Sales Inquiries: sales@lumerical.com Contact your local Lumerical representative Start your free 30 day trial today www.lumerical.com Contact Us Connect with Lumerical www.lumerical.com ? LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC14



