Water caused defects_buildings
- 1. Defects in existing buildings Most buildings are old Most buildings have defects Royal Agricultural College
- 2. Topics covered ŌĆó Defects due to water damage ŌĆó Defects due to biological agents ŌĆó Defects due to mechanical damage Royal Agricultural College
- 3. Why is water a problem? ŌĆó Water is everywhere, you cannot keep it out ŌĆó ŌĆ£Universal solventŌĆØ ŌĆó Water is required for biological activity ŌĆó Water expands when it freezes Royal Agricultural College
- 4. Rust, corrosion Black Spot Mould damage Dissolving of materials Dry rot fungal damage Royal Agricultural Damage to finishes College Frost damage
- 5. ŌĆó Rising damp (ground water) ŌĆó Penetrating damp (rain) ŌĆó Wet services (leaks) ŌĆó Condensation (humidity/dew point) Royal Agricultural College
- 6. Rising damp: remedial work ŌĆó ŌĆ£SolutionsŌĆØ to rising damp problems: ŌĆō Internal ŌĆ£tankingŌĆØ, placing an impervious layer between the wet wall and the interior. ŌĆō Inject a chemical ŌĆ£DPCŌĆØ but these can be ineffective in some situations ŌĆō Insert porous tubes, open to the outside to ventilate the interior of the wall ŌĆō Cut out a course of bricks and insert a full DPC. Royal Expensive and disruptive. Agricultural But it works College
- 7. Cavity wall: rain exclusion Preventing penetrating damp ŌĆó Cavity construction: the cavity is there to drain away penetrating water. ŌĆó Impermeable ŌĆ£rain shieldŌĆØ wall covering, such as metal or plastic sheeting ŌĆ£rain shieldŌĆØ ŌĆó Complete DPC systems often glass or sheet metal around all sides of all openings ŌĆó Good detailing Royal Agricultural ŌĆó Good maintenance College
- 8. Remedial work Overcoat ŌĆó Fix any damage to soaks up rain roofs and openings. ŌĆó Apply a ŌĆ£breathableŌĆØ render, the ŌĆ£over coatŌĆØ principle ŌĆó DONŌĆÖT apply waterproof paints or coatings. This is will not work Moisture dries Royal out in dry Agricultural College periods
- 9. Water damage from services ŌĆó Many problems caused by water are due to leaks from water and central heating pipes ŌĆó Check that what appears to be a leak in a cold pipe or tank is not in fact condensation on the outside of a perfectly sound fitting. Cold water Cold tank Royal Condensation drips Agricultural College
- 10. Condensation ŌĆó The air holds water vapour as a dry gas. ŌĆó The quantity it can hold depends on the air temperature. ŌĆó When the maximum amount is held for the prevailing temperature, the air is ŌĆ£saturatedŌĆØ (100% relative humidity). ŌĆó The temperature at which air becomes saturated by the amount of water it holds is called the ŌĆ£dew pointŌĆØ ŌĆó If further water vapour is added to saturated air, or if the temperature falls, the excess water vapour condenses out as liquid water. Royal Agricultural College
- 11. Surface condensation ŌĆó Surface condensation occurs when the temperature of an internal surface falls below the local dew point temperature. Liquid water condenses out on the surface. ŌĆó Risk of surface condensation is high when ŌĆō internal temperatures drop ŌĆō water vapour increases (in a shower room or kitchen during cooking) Royal Agricultural College
- 12. ŌĆ£Boundary layerŌĆØ of still air The few mm of air adjacent to the surface is held still by friction and acts as an insulating layer. This is more pronounced on the internal surface than on the external, where wind blows the boundary layer away Outside Inside Royal Agricultural College
- 13. Temperature gradient through a wall 20┬░ C in body of room 10┬░ C on surface 5┬░ C outside Air temp drops sharply in boundary layer on a cold wall Outside Royal Inside Agricultural College
- 14. Low dew point scenario Air is holding only a small amount of water (low relative humidity) and so the dew point is low, say 4┬░ C 20┬░ C inside air 10┬░ C on surface 5┬░ C outside Royal Outside Inside Agricultural College
- 15. Low dew point scenario Air is holding only a small amount of water (low relative humidity) and so the dew point is low, say 4┬░ C 20┬░ C inside air 10┬░ C on surface Dew point 4┬░C 5┬░ C outside Low risk of surface condensation Royal Outside Inside Agricultural College
- 16. High dew point scenario Air is holding a large amount of water (high relative humidity) and so the dew point is high, say 12┬░ C 20┬░ C inside air 10┬░ C on surface 5┬░ C outside Royal Agricultural Outside Inside College
- 17. High dew point scenario Air is holding a large amount of water (high relative humidity) and so the dew point is high, say 12┬░ C 20┬░ C inside air Dew point 12┬░C 10┬░ C on surface 5┬░ C outside High risk of surface condensation Royal Agricultural Outside Inside College
- 18. Remedies for surface condensation ŌĆó Reducing water vapour content in the internal air ŌĆō Ventilation ŌĆō Cut down on water generating activities ŌĆō Air conditioning ŌĆó Keeping surfaces warm (i.e above the dew point temperature), but thereŌĆÖs a problemŌĆ” Royal Agricultural College
- 19. Internal insulation can cause interstitial condensation Internal insulation 20┬░ C inside air Thermal gradient temp through wall 5┬░ C outside Inside air temp dew point 12┬░C Outside dew point 4┬░C Royal Agricultural College
- 20. Internal insulation can cause interstitial condensation Internal insulation 20┬░ C inside air Thermal gradient temp through wall Dew point gradient 5┬░ C outside Inside air temp dew point 12┬░C Outside dew point 4┬░C Royal Agricultural College
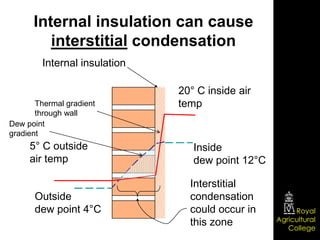
- 21. Internal insulation can cause interstitial condensation Internal insulation 20┬░ C inside air Thermal gradient temp through wall Dew point gradient 5┬░ C outside Inside air temp dew point 12┬░C Interstitial Outside condensation dew point 4┬░C could occur in Royal this zone Agricultural College
- 22. Solution: Vapour barrier on warm side of insulation 20┬░ C inside air temp Dew point 12┬░C 5┬░ C outside air temp Layer impermeable Dew point 4┬░C to water vapour added on warm side: plastic or aluminium foil Royal Agricultural College
- 23. Internal insulation can cause other unexpected problems 20┬░ C inside During freezing weather air temp Temperature gradient without insulation Wall surface temp 2┬░C 0┬░ External air Temp -4┬░C Royal Agricultural College
- 24. Internal insulation can cause other unexpected problems 20┬░ C inside During freezing weather air temp Temperature gradient without insulation Temperature gradient with insulation Wall surface temp 2┬░C 0┬░ External air Temp -4┬░C Royal Agricultural College
- 25. Internal insulation can cause other unexpected problems 20┬░ C inside During freezing weather air temp Temperature gradient without insulation Temperature gradient with insulation Wall surface temp 2┬░C 0┬░ External air Temp -4┬░C Royal The wall is below freezing. Agricultural College If it is wet, it could break
- 26. Summary ŌĆó Liquid water is the damaging agent ŌĆó Determining the source of liquid water is vital to avoid ineffective remedial action ŌĆó The most difficult problems usually result from uncontrolled condensation Royal Agricultural College