Nosocomial Gram negative Infections
Gram-negative bacteria commonly cause nosocomial infections like pneumonia and bloodstream infections in debilitated patients. Enterobacteriaceae are the most frequent causes, while non-fermenters like Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter predominate in critically ill patients. Mortality from gram-negative infections remains high, especially with certain multidrug-resistant pathogens. Inappropriate antibiotic therapy, which can include incorrect dosing or use when not indicated, increases morbidity, mortality and resistance. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases and AmpC beta-lactamases are important resistance mechanisms in key pathogens like K. pneumoniae and Enterobacter species. Carbapenems remain the preferred treatment for infections caused by extended


















Recommended




























































More Related Content
What's hot (15)






























Similar to Nosocomial Gram negative Infections (20)








































Recently uploaded (20)


















































Nosocomial Gram negative Infections
- 1. NOSOCOMIAL GRAM-NEGATIVE INFECTIONS Mohamed Ahmed Badheeb, MBBS.
- 2. FACTS Gram-negative bacteria are typically non-pathogenic in the immunocompetent host. This is especially true of the Enterobacteriaceae and the non-fermentative gram- negative bacilli. However, in the debilitated host, gram-negative bacteria can become significant pathogens Gram-negative pathogens are common in both nosocomial pneumonia and bloodstream infections, two of the most difficult nosocomial infections to manage. Enterobacteriaceae are the most common cause of gram-negative nosocomial infection; however, non-fermentors, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter species, are predominant pathogens in the critically ill.
- 3. Mortality Mortality rates for gram-negative bacteremia have not changed dramatically since the era before antibiotic drugs. Patients with nosocomial ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) have higher mortality rates than similar patients without VAP, but the impact is greatest for certain high-risk pathogens, such as Acinetobacter species, P. aeruginosa, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. There are several independent risk factors for mortality, including - The presence of hepatic, renal, or cardiac failure. - Diabetes mellitus. - Age older than 60 years. - Corticosteroid use; antineoplastic therapy. - Neutropenia - Shock.
- 4. Appropriate Versus Inappropriate Therapy Inappropriate antimicrobial therapy remains a significant problem in treating nosocomial infection. Inappropriate antibiotic therapy can be defined in several terms, including; ŌĆó antimicrobial use when it is not indicated. ŌĆó Use of an antibiotic regimen that does not have activity against the causative pathogen. ŌĆó Incorrect dosing ŌĆó Wrong administration route. The consequences of inappropriate use can be significant, including increased rates of morbidity and mortality, and increased resistance.
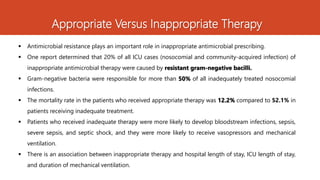
- 5. Appropriate Versus Inappropriate Therapy ’é¦ Antimicrobial resistance plays an important role in inappropriate antimicrobial prescribing. ’é¦ One report determined that 20% of all ICU cases (nosocomial and community-acquired infection) of inappropriate antimicrobial therapy were caused by resistant gram-negative bacilli. ’é¦ Gram-negative bacteria were responsible for more than 50% of all inadequately treated nosocomial infections. ’é¦ The mortality rate in the patients who received appropriate therapy was 12.2% compared to 52.1% in patients receiving inadequate treatment. ’é¦ Patients who received inadequate therapy were more likely to develop bloodstream infections, sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock, and they were more likely to receive vasopressors and mechanical ventilation. ’é¦ There is an association between inappropriate therapy and hospital length of stay, ICU length of stay, and duration of mechanical ventilation.
- 7. Antibiotics Resistance !!!! Antibiotic-resistant gram-negative bacilli infection is more commonly associated with resistance to empiric antibiotic therapy, requiring treatment change. The most important gram-negative resistance issues affecting nosocomial infections are ’é¦ Extended-spectrum b-lactamases (ESBLs) in K. pneumoniae, E. coli, Enterobacter species, and Proteus mirabilis. ’é¦ Cephalosporin and extended spectrum penicillin resistance mediated by AmpC b-lactamase found in Enterobacter species and Citrobacter freundii; and multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa, Acinetobacter species, and S. maltophilia. (AKA;
- 8. Factors That Promote Antimicrobial Resistance ’é¦ Health Care Setting Factors Many factors may be responsible for the increasing incidence of gram- negative infection. Transmission of antibiotic-resistant pathogens in the acute care setting is common. ŌĆó A variety of health care workers participate in managing acutely ill patients. ŌĆó Handwashing or other aseptic techniques are not uniformly or effectively practiced throughout the health care setting.
- 9. Factors That Promote Antimicrobial Resistance ’é¦ Patient-specific Factors Many patient-specific factors increase the infection risk with antimicrobial-resistant pathogens. Acutely ill patients, especially those in the ICU. ŌĆó Require invasive monitoring and therapeutic devices. ŌĆó Intensive care unit patients commonly have severe underlying clinical conditions, such as immunosuppression, cancer, malnutrition, organ failure, and prior interaction with the health care system. Patients with severe disease have longer hospital and ICU stays. Late-onset nosocomial infections among patients in the ICU are more likely to be associated with an antimicrobial-resistant pathogen.
- 11. - ESBL - SPICE organisms Specific Resistance Mechanisms
- 12. General Overview ’é¦ Beta-lactamases are enzymes that open the beta-lactam ring, inactivating the antibiotic. ’é¦ TEM-1 and TEM-2 are the most common plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases in gram- negative bacteria, including Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, they hydrolyze penicillins and narrow spectrum cephalosporins, such as cephalothin or cefazolin. However, they are not effective against higher generation cephalosporins with an oxyimino side chain, such as cefotaxime, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, or cefepime. ’é¦ There are different varities for ESBL, including: ’ā╝ SHV beta-lactamases, hydrolyze beta-lactams such as penicillins and narrow spectrum. ’ā╝ CTX-M beta-lactamases, hydrolyze cefotaxime than other oxyimino-beta-lactam substrates (eg, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, or cefepime). ’ā╝ OXA beta-lactamases, hydrolyze oxacillin and related anti-staphylococcal penicillins.
- 13. Extended-spectrum b-Lactamase ’é¦ Extended-spectrum b-lactamases are b-lactamases capable of hydrolyzing penicillins, broad- and extended spectrum cephalosporins that contain the oxyimino side chain, and monobactams, and are inhibited by clavulanic acid. ’é¦ Extended-spectrum b-lactamases have been isolated from a variety of Enterobacteriaceae, as well as P. aeruginosa. Originally, they were found inK. pneumoniae and E. coli, but are now common in other gram-negative organisms such as the Enterobacter species. ’é¦ Genes that code for ESBL are carried on plasmids and can be transferred easily from one organism to another. Extended-spectrum b-lactamase-producing organisms remain susceptible to cephamycins (cefoxitin and cefotetan). The frequency of fluoroquinolone resistance is higher in ESBL-producing organisms than among non-ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae or E. coli.
- 14. TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR ESBL Preferred agents ŌĆö The preferred, proven therapeutic options for severe infections caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing organisms are carbapenems (imipenem, meropenem, doripenem, and ertapenem). The combination cephalosporin-beta-lactamase inhibitor agents (ceftolozane-tazobactam and ceftazidime- avibactam) and the broad-spectrum tetracycline eravacycline appear promising, although data on their clinical efficacy are too limited at this time to recommend their routine use, and it is not clear that they provide additional benefit over carbapenems. For complicated UTI, plazomicin is another option that can be active against ESBL-producing isolates that are resistant to other aminoglycosides. For simple cystitis, oral fosfomycin and nitrofurantoin are other potential options that may retain activity against ESBL- producing isolates.
- 15. TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR ESBL
- 16. AmpC-type b-Lactamase AmpC beta-lactamases (AmpC) are enzymes which convey resistance to penicillins, second and third generation cephalosporins and cephamycins. However, they do not convey resistance to fourth generation cephalosporins. The genes for these enzymes occur naturally in some bacteria species as so-called chromosomal AmpC (e.g. in E. coli, but not in Salmonella up to now). The important thing is the increasing number of AmpC genes localised outside the chromosome on so-called plasmids, which is why they are often referred to as ŌĆØplasmidic AmpCŌĆØ (pAmpC). They ensure the constant formation of the enzyme and lie on transmissible gene sections. These can be exchanged between bacteria of the same type or of different types (horizontal gene transfer)
- 17. AmpC-type b-Lactamase and SPICE organisms Most Enterobacteriaceae carry AmpC cephalosporinases, but these enzymes are considered clinically problematic in the so-called SPICE organisms (Serratia, indole-positive Proteus, Citrobacter, and Enterobacter, as well as Providencia, Morganella, and Hafnia). AmpC-mediated b-lactamase confers resistance to first-, second-, and third generation cephalosporins, in addition to monobactams, such as aztreonam, and to some penicillins.
- 19. Thanks!
