03 көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷмқҳкё°м ҖмқҙлЎ н•ҷмҠөмқҙлЎ (мқём§ҖмЈјмқҳ)
- 1. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ м ң 3к°•. көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷмқҳ мқҙлЎ м Ғкё°мҙҲ-2
- 3. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ 1. мқём§ҖмЈјмқҳ н•ҷмҠөмқҙлЎ мқҳ нҠ№м§•кіј көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷм—җ лҜём№ҳлҠ” мӢңмӮ¬м җмқ„ м—ҙкұ°н• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. 2. м •ліҙмІҳлҰ¬ мқҙлЎ м—җ кё°л°ҳмқ„ л‘җкі н•ҷмҠөмқҳ кіјм •м—җ лҢҖн•ҙ м„ӨлӘ…н• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. 3. к°Җл„Өмқҳ мҲҳм—…мӮ¬нғңлҘј кё°л°ҳмңјлЎң мҲҳм—…мқҳ мЈјмҡ” нҷңлҸҷмқ„ м„Өкі„н• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. н•ҷмҠөлӘ©н‘ң
- 4. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ вҖў м•„лһҳмқҳ AмҷҖ BмӨ‘м—җм„ң <ліҙкё°>мҷҖ лӢ®мқҖ кјҙмқҖ л¬ҙм—Үмқёк°Җ? Gasper, K., & Clore, G. L. (2002). Attending to the big picture: Mood and global versus local processing of visual information, Psychological Science, 13, 34-40. <ліҙкё°> <A> <B> Local similarity вҖў negative mood вүҲ 60% вҖў positive/neutral вүҲ 30% Global similarity вҖў negative mood вүҲ 40% вҖў positive/neutral вүҲ 70%
- 6. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ вҖў н•ҷмҠөмқҖ лӢЁмҲңнһҲ мһҗк·№-л°ҳмқ‘мқҳ кё°кі„м Ғ кІ°н•©м—җ мқҳн•ҳм—¬ лӮҳнғҖлӮҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ м•„лӢҲлқј н•ҷмҠөмһҗ лӮҙл¶Җм—җм„ң л°ңмғқн•ҳлҠ” мқём§Җм Ғ кіјм •м—җ мқҳн•ҳм—¬ м„ӨлӘ…н• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. мқём§ҖмЈјмқҳ н•ҷмҠөмқҙлЎ Wax(лӮҷмқё м°Қл“Ҝ, кё°м–өнқ”м Ғмқ„ лӮЁкё°лҠ” кІғ)м—җ 비мң нҳ•нғңмЈјмқҳ мӢ¬лҰ¬н•ҷ(Gestalt Psychology) мқёк°„мқҳ м§Җк°Ғ(perception) кҙҖмӢ¬ м •ліҙмІҳлҰ¬ мқҙлЎ м ҖмһҘкі , м»ҙн“Ён„° л“ұмңјлЎң 비мң 1960л…„лҢҖ мқҙм „ 1960л…„лҢҖ мқҙнӣ„
- 7. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ вҖў лӮҙм Ғ мӮ¬кі кіјм •мқ„ к°•мЎ° вҖў мҳӨмҠӨлІЁмқҳ мң мқҳлҜён•ҷмҠө мқҙлЎ вҖў к°Җл„Өмқҳ көҗмҲҳмқҙлЎ вҖў н•ҷмҠөлӮҙмҡ©мқҳ мЎ°м§Ғнҷ”, кі„м—ҙнҷ” мқҙлЎ мқ„ м •көҗнҷ” мқём§ҖмЈјмқҳ н•ҷмҠөмқҙлЎ мқҳ мҳҒн–Ҙ
- 8. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ вҖў "лӢЁкё° кё°м–ө"мқҖ м„ёмғҒмқ„ м–ҙл–»кІҢ мқҙн•ҙн• к№Ң? вҖў лҲҲ лң¬ мһҘлӢҳ? мҪ”м•һм—җм„ң лҢҖнҷ”н•ҳлҚҳ мӮ¬лһҢмқҙ л°”лҖҢм–ҙлҸ„ лҲҲм№ҳ лӘ»мұ„лҠ” мқҙмң вҖў кёҙ мҲ«мһҗлҘј лҚ” мһҳ кё°м–өн•ҳлҠ” л°©лІ•, 'мІӯнӮ№' вҖў лӢ№мӢ мқҖ лӘҮ к°ңлӮҳ кё°м–өн• мҲҳ мһҲмқ„к№Ң? кё°м–өл Ҙ н–ҘмғҒ нҢҒ! вҖў кіөл¶Җмқҳ мҷ•лҸ„ - мқём§Җ м„ёкі„лҠ” лғүм—„н•ҳлӢӨ мқём§ҖмЈјмқҳ н•ҷмҠөмқҙлЎ кҙҖл Ё мҳҒмғҒ
- 9. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ м •ліҙмІҳлҰ¬мқҙлЎ лӢЁкё°кё°м–өкі , мһ‘м—…кё°м–ө, нҷңм„ұнҷ”кё°м–ө (Short Term(Working, Activated) Memory) вҖў мқјм°Ём Ғ мһ‘м—…лҢҖ, мһ„мӢңм Ғ кё°м–өкі лҰ¬ вҖў мӨ‘м•ҷ нҶөм ңм Ғ мһ‘м—…лҢҖ мһҘкё° кё°м–өкі (Long Term Memory) вҖў мҳҒкө¬м Ғ м ҖмһҘкі вҖў л¬ҙмқҳмӢқм Ғ нҡҢлЎңл§қ
- 10. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ н•ҷмҠөмқ„ лҸ•лҠ” м „лһө(н–үлҸҷмЈјмқҳ) вҖў м—°н•© вҖў л°ҳліө вҖў ліҙмғҒ
- 11. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ н•ҷмҠөмқ„ лҸ•лҠ” м „лһө(мқём§ҖмЈјмқҳ) вҖў л°ҳліөмқҖ мӨ‘мҡ”н•ҳм§Җл§Ң, л¬ҙн•ңм • л°ҳліөн•ҙлҸ„ кё°м–өн•ҳм§Җ лӘ»н• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. вҖў ліҙмғҒмқ„ нҶөн•ҙм„ңлҸ„ мҡ°лҰ¬мқҳ кё°м–ө мІҙкі„лҠ” мһ‘лҸҷн•ҳм§Җ м•ҠлҠ”лӢӨ. вҖў кё°м–өмқҖ мғқк°Ғмқҳ мһ”м—¬л¬ј, мқҳлҜёлҘј мғқк°Ғн•ҳкІҢ н•ҳмһҗ. вҖў н•ҷмҠөмһҗл“Өмқҳ мһ…мһҘм—җм„ң мқҳлҜёлҘј мғқк°Ғн•ҳлҸ„лЎқ лҸ•мһҗ. вҖў мқём§ҖмІҳлҰ¬кіјм •м—җ лҢҖн•ң мқҙн•ҙлҘј кё°л°ҳмңјлЎң мҲҳм—…мқ„ кө¬м„ұн•ҳмһҗ. вҖў мқҳлҜё м—ҶлҠ” м •ліҙлҠ” м Ғм Ҳн•ң кё°м–өмҲ мқ„ нҷңмҡ©н•ҳмһҗ.
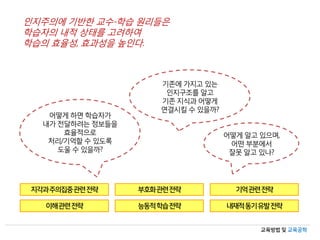
- 12. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ кё°мЎҙм—җ к°Җм§Җкі мһҲлҠ” мқём§Җкө¬мЎ°лҘј м•Ңкі кё°мЎҙ м§ҖмӢқкіј м–ҙл–»кІҢ м—°кІ°мӢңнӮ¬ мҲҳ мһҲмқ„к№Ң? м–ҙл–»кІҢ м•Ңкі мһҲмңјл©°, м–ҙл–Ө л¶Җ분м—җм„ң мһҳлӘ» м•Ңкі мһҲлӮҳ? м–ҙл–»кІҢ н•ҳл©ҙ н•ҷмҠөмһҗк°Җ лӮҙк°Җ м „лӢ¬н•ҳл ӨлҠ” м •ліҙл“Өмқ„ нҡЁмңЁм ҒмңјлЎң мІҳлҰ¬/кё°м–өн• мҲҳ мһҲлҸ„лЎқ лҸ„мҡё мҲҳ мһҲмқ„к№Ң? л¶Җнҳёнҷ”кҙҖл Ём „лһө кё°м–өкҙҖл Ём „лһө мқҙн•ҙкҙҖл Ём „лһө лҠҘлҸҷм Ғн•ҷмҠөм „лһө лӮҙмһ¬м ҒлҸҷкё°мң л°ңм „лһө м§Җк°ҒкіјмЈјмқҳ집мӨ‘кҙҖл Ём „лһө мқём§ҖмЈјмқҳм—җ кё°л°ҳн•ң көҗмҲҳ-н•ҷмҠө мӣҗлҰ¬л“ӨмқҖ н•ҷмҠөмһҗмқҳ лӮҙм Ғ мғҒнғңлҘј кі л Өн•ҳм—¬ н•ҷмҠөмқҳ нҡЁмңЁм„ұ, нҡЁкіјм„ұмқ„ лҶ’мқёлӢӨ.
- 13. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ вҖў н•ҷмҠөмқҳ лӮҙм Ғ мЎ°кұҙ мқҙнӣ„мқҳ н•ҷмҠөм—җ н•„мҲҳм Ғмқҙкұ°лӮҳ ліҙмЎ°м Ғмқё кІғ н•ҷмҠөмһҗк°Җ мқҙлҜё мҠөл“қн•ң лҠҘл Ҙл“Өмқҳ нҡҚл“қ л°Ҹ м ҖмһҘ, лӮҙм Ғ мқём§Җкіјм • вҖў м„ мҲҳн•ҷмҠөлҠҘл Ҙ(Gagne & Briggs, 1979) н•ҷмҠөмқҙ м„ұкіөм ҒмңјлЎң мқјм–ҙлӮҳкё° мң„н•ҙ н•„мҡ”н•ң кІғ н•„мҲҳм Ғ м„ мҲҳн•ҷмҠөлҠҘл Ҙ(мғҲлЎңмҡҙ н•ҷмҠөмқҳ нҶөн•©м Ғ л¶Җ분мңјлЎңм„ң нҠ№м •н•ң лҠҘл Ҙ) ліҙмЎ°м Ғ м„ мҲҳн•ҷмҠөлҠҘл Ҙ(мғҲлЎңмҡҙ н•ҷмҠөмқҳ кіјм •мқ„ лҸ•лҠ” л¶Җк°Җм Ғмқё лҠҘл Ҙ) к°Җл„Өмқҳ 9к°Җм§Җ мҲҳм—…мӮ¬нғң(9 events)
- 14. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ н•ҷмҠөмқҳ лӮҙм Ғ мқём§Җкіјм •
- 15. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ вҖў н•ҷмҠөмқҳ лӮҙм Ғ мқём§Җкіјм •кіј мҷём Ғ мЎ°кұҙ н•ҷмҠөмқҳ мҷём Ғ мЎ°кұҙ лӮҙм Ғ мқём§Җкіјм • мқём§Җкіјм • н•ҳмң„мҡ”мҶҢ мҷём Ғ мЎ°кұҙ н•ҷмҠөмқ„ мң„н•ң мӨҖ비 мЈјмқҳ집мӨ‘ мЈјмқҳлҘј 집мӨ‘мӢңнӮҙ кё°лҢҖ лӘ©н‘ңлҘј мЈјм§ҖмӢңнӮҙ мһ¬мғқ м„ мҲҳм§ҖмӢқмқ„ мһҗк·№мӢңнӮҙ м •ліҙ/кё°мҲ мқҳ нҡҚл“қкіј мҲҳн–ү м„ нғқм Ғ м§Җк°Ғ н•ҷмҠөмһҗлЈҢлҘј м ңмӢңн•Ё мқҳлҜё мһҲлҠ” м •ліҙмқҳ м ҖмһҘ н•ҷмҠөмқ„ м•ҲлӮҙн•Ё мһ¬мғқкіј л°ҳмқ‘ н•ҷм—…мҲҳн–үмқ„ кІ©л Өн•Ё к°•нҷ” мҲҳн–үкІ°кіјм—җ лҢҖн•ҙ н”јл“ңл°ұмқ„ м ңкіөн•Ё н•ҷмҠөмқҳ мһ¬мғқкіј м „мқҙ мһ¬мғқ мҲҳн–үмқ„ нҸүк°Җн•Ё мқјл°ҳнҷ” кё°м–өкіј м „мқҙлҘј кІ©л Өн•Ё
- 16. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ лӢӨмқҢ мғҒнҷ©м—җм„ң мқём§ҖмЈјмқҳм Ғ көҗмңЎ м „лһөмқ„ м–ҙл–»кІҢ м Ғмҡ©н•ҳл©ҙ мўӢмқ„к№Ң? мқём§ҖмЈјмқҳмһҗлЎң көҗмңЎн•ҳкё° мҳҒнқ¬лҠ” мҶҢмң„ вҖҳлІ”мғқвҖҷмқҙлӢӨ. лҠҳ 30분 м •лҸ„ мқјм°Қ л“ұкөҗн•ҳкі мҲҳм—… мӨ‘м—җлҠ” л°”лҘё мһҗ м„ёлЎң мҲҳм—…м—җ 집мӨ‘н•ҳкі л…ёнҠё м •лҰ¬лҸ„ м—ҙмӢ¬нһҲ н•ңлӢӨ. мҳҒнқ¬лҠ” лӘЁл“ мҲҳм—…м—җм„ң лӘЁ лІ”м Ғмқё нғңлҸ„лҘј к°Җм§Җкі мһҲм§Җл§Ң, мӢңн—ҳмқ„ ліҙл©ҙ лҠҳ нҸүк· мқҙн•ҳм—җ лЁёл¬јлҹ¬мһҲлӢӨ. мөң көҗмӮ¬лҠ” мҳҒнқ¬мқҳ н•ҷл Ҙмқҙ н–ҘмғҒлҗҳм§Җ м•ҠлҠ” мӣҗмқёмқ„ 분м„қн–ҲлӢӨ. мҳҒнқ¬лҠ” мҲҳм—… мӨ‘ көҗмӮ¬к°Җ м ңкіөн•ҳлҠ” м •ліҙлӮҳ м§ҖмӢқмқ„ лӘЁл‘җ м •лҰ¬н•ҳкё° мң„н•ҙ в‘ н•„кё°лҘј н•ҳм§Җл§Ң, н•„ кё° лӮҙмҡ©мқ„ лҢҖл¶Җ분 кё°м–өн•ҳм§Җ лӘ»н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. мұ…мқ„ мқҪмқ„ л•Ңм—җлҠ” в‘ЎлӮҙмҡ©мқ„ мһҳ нҢҢм•… н•ҳм§Җ лӘ»н•ҳмҳҖмңјл©°, мһҗмӢ мқҳ кё°мЎҙ м§ҖмӢқкіј м Ғм Ҳн•ҳкІҢ кҙҖл Ё 짓м§Җ лӘ»н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. лҳҗн•ң в‘ўн•ҷмҠөмқ„ нҡЁмңЁм ҒмңјлЎң 진н–үн•ҳм§Җ лӘ»н•ҳлҠ” кІҪн–Ҙмқҙ мһҲм—ҲлӢӨ.
- 17. көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ Q. м•өл¬ҙмғҲмІҳлҹј мҷёмҡ°кІҢ н• н•„мҡ”к°Җ мһҲмқ„к№Ң? вҖў көҗмңЎм—җм„ң мЈҪмқҖ мӮ¬мӢӨмқҳ нҳ•нғңлЎң 축м ҒлҗҳлҠ” л¬ҙм§Җмқҳ м–‘л§ҢнҒј лҶҖлқјмҡҙ кІғмқҖ м—ҶлӢӨ (мһ‘к°Җ м• лҚӨмҠӨ) вҖў мғҒмғҒл Ҙмқҙ м§ҖмӢқліҙлӢӨ мӨ‘мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ (л¬јлҰ¬н•ҷмһҗ м•„мқёмҠҲнғҖмқё) вҖў мҡ°лҰ¬к°Җ н•ҷкөҗ көҗмӢӨм—җ к°ҮнҳҖ 10-15л…„мқ„ ліҙлӮҙлӢӨ кІ°көӯ л§җл§Ң л§Һкі м ңлҢҖлЎң м•„лҠ” кІғ н•ҳлӮҳ м—ҶлҠ” мғҒнғңлЎң лӮҳмҳЁлӢӨ (мӢңмқё м—җлЁёмҠЁ) вҖў мөңкі мқҳ м§Җм§Ҳн•ҷмһҗлҠ” лҸҢмқ„ м ңмқј л§Һмқҙ ліё мӮ¬лһҢмқҙлӢӨ (м§Җм§Ҳн•ҷмһҗ, лҰ¬л“ң) вҖў мӮ¬мӢӨм Ғ м§ҖмӢқмқҖ лҸ…н•ҙмқҳ н•„мҲҳ мҡ”мҶҢмқҙл©°, кіјн•ҷм Ғ мӮ¬кі /л¬ём ңн•ҙкІ° лҠҘл Ҙ/비нҢҗм Ғ мӮ¬кі л“ұ кі м°Ём Ғ мӮ¬кі нҷңлҸҷмқҖ лҢҖк°ң м Ғм Ҳн•ң л°°кІҪм§ҖмӢқмқҙ м—Ҷмңјл©ҙ л¬ҙмҡ©м§Җл¬јмқҙлӢӨ.



































![[көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ] 2мЈјм°Ё көҗмңЎнҳҒмӢ мӣҢнҒ¬мҲҚ](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/02-160913044201-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)

![[көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ] 3мЈјм°Ё көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷмқҳ м •мқҳмҷҖ м—ӯмӮ¬](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/03-160920013911-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[진лЎңм„Өкі„мҷҖ мһҗкё°кі„л°ң] 4мЈјм°Ё MBTI м„ұкІ©мқҙн•ҙ_мҷёкөӯмқёл¶„л°ҳ](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/201602pt4mbti-160921233658-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)





![[көҗмңЎл°©лІ• л°Ҹ көҗмңЎкіөн•ҷ] 1мЈјм°Ё мҳӨлҰ¬м—”н…Ңмқҙм…ҳ](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/01-160906011702-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)

![[OpenCollege] мқём§ҖмӢ¬лҰ¬н•ҷ 101](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/random-140209020213-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[진лЎңм„Өкі„мҷҖ мһҗкё°кі„л°ң] 3мЈјм°Ё л©ҳнҶ мқён„°л·°](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/2016023-160919014809-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)



![[진лЎңм„Өкі„мҷҖ мһҗкё°кі„л°ң] 3мЈјм°Ё MBTI м„ұкІ©мқҙн•ҙ](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/201602pt4mbti-160918094430-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)














![[лҢҖн‘ңлӢҳнҠ№к°•]м•„лҸҷмқҳ л‘җлҮҢкіјн•ҷм Ғ мқҙн•ҙмҷҖ н•ҷмҠө л°Ҹ мғқнҷңм§ҖлҸ„ мӣҗлҰ¬](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/random-150714015502-lva1-app6892-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)







![[진лЎңм„Өкі„мҷҖ мһҗкё°кі„л°ң] 2мЈјм°Ё лІ„нӮ·лҰ¬мҠӨнҠё](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/201602pt2-160912011355-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[진лЎңм„Өкі„мҷҖ мһҗкё°кі„л°ң] 2мЈјм°Ё лІ„нӮ·лҰ¬мҠӨнҠё(мҷёкөӯмқёл¶„л°ҳ)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/201602pt2-160907135611-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[진лЎңм„Өкі„мҷҖ мһҗкё°кі„л°ң] 1мЈјм°Ё мҳӨлҰ¬м—”н…Ңмқҙм…ҳ](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/2016pt1-160903134146-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[진лЎңм„Өкі„мҷҖ мһҗкё°кі„л°ң] 1мЈјм°Ё мҳӨлҰ¬м—”н…Ңмқҙм…ҳ(мҷёкөӯмқёл¶„л°ҳ)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/pt1-160831143953-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)




