1 tuberculosis
4 likes197 views
This document discusses tuberculosis (TB), including its causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. TB is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which most commonly affects the lungs. It can be transmitted through inhalation of airborne droplets from an infected person. Diagnosis involves tests like tuberculin skin tests, chest x-rays, and bacterial studies. Treatment consists of a combination of antibiotics taken for 6-9 months to prevent drug resistance. Nursing care focuses on improving breathing, preventing transmission, maintaining nutrition, and ensuring compliance with the medication regimen.
1 of 20


















Recommended
2 pnuemonia



2 pnuemoniaaaaj53
Ěý
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that causes inflammation in the air sacs, making it difficult to breathe. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. The document discusses the causes, types, symptoms, complications, treatment including antibiotics and respiratory support, and nursing management of pneumonia with a focus on improving breathing, rest, hydration, and nutrition.Pneumonia ppt



Pneumonia pptPriya Sharma
Ěý
Details about pneumonia, its demographics, classification, types, common symptoms, pathophysiology, brief introduction to different types of pneumoniaPneu



Pneumahamed adam
Ěý
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung caused by various microorganisms. It is classified as community-acquired, hospital-acquired, or in immunocompromised patients. Clinical features include fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Diagnosis involves a chest x-ray and cultures. Treatment consists of antibiotics based on culture results and supportive care like oxygen and hydration. Nursing focuses on improving airway clearance and promoting rest. Complications can include continuing symptoms, shock, respiratory failure, or fluid buildup in the lungs.PNEUMONIA



PNEUMONIAANILKUMAR BR
Ěý
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung parenchyma caused by various microorganisms, including bacteria, mycobacteria, fungi, and viruses.
Pneumonitis is a more general term that describes the inflammatory process in the lung tissue that may predispose and Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung parenchyma that is caused by a microbial agent.
place the patient at risk for microbial invasion.
Pneumonia is classified into four: community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP), pneumonia in the immunocompromised host, and aspiration pneumonia.
Pneumonia



Pneumoniaalexandrac27
Ěý
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs caused by bacterial or viral infection that fills the air sacs with fluid or pus. It can affect one or both lungs. Risk factors include impaired cough or mucociliary clearance from smoking, aging, or illness. Symptoms include cough, fever, chills, difficulty breathing, and chest pain. Diagnosis involves physical exam, chest x-ray, and tests of sputum or blood. Treatment focuses on antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia, supportive care like oxygen, clearing secretions, and preventing complications like respiratory failure. Vaccines can help prevent pneumococcal pneumonia.Pneumonia



PneumoniaEneutron
Ěý
This document discusses pneumonia, providing definitions, classifications, etiologies, clinical manifestations, diagnoses, and treatments. Pneumonia is an acute lung infection caused by various pathogens. It is classified based on pathogen (bacterial, viral, fungal, etc.), anatomy (lobar, lobular, interstitial), and environment acquired (community, hospital, nursing home). Clinical exams, imaging, and pathogen identification are used for diagnosis. Treatment involves antimicrobial therapy targeting the likely pathogens based on patient characteristics and environment. Complications can include sepsis, abscesses, and extrapulmonary infections if not properly treated.Pneumonia



PneumoniaMnazi Mmoja National Hospital Zanzibar/abdulla mzee hospital
Ěý
This presentation provides information about pneumonia, including its definition, classification, causes, signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, treatment, nursing management, preventive measures, prognosis, and complications. Pneumonia is an inflammatory process in the lungs caused most commonly by infection. It is classified based on its causes such as bacterial or viral, and the area of lung involvement. Common signs include fever, cough, and chest pain. Treatment involves antibiotics, oxygen therapy, and nursing interventions like chest physiotherapy. Preventive measures include vaccinations, smoking cessation, and reducing alcohol use. Most patients improve with treatment but elderly or very sick individuals may have longer recovery times.Gwen med surg pneumonia final



Gwen med surg pneumonia finalGwenneth Zoelie Nongkhlaw
Ěý
This document provides information on pneumonia and lung abscess from a seminar presentation. It begins with an introduction to pneumonia, defining it as an infection of the lungs. It then discusses the incidence of pneumonia globally and in various countries. Etiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, classification, signs and symptoms, complications, diagnosis, and management of pneumonia are explained. It also provides detail on lung abscess including definition, risk factors, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, complications, diagnosis, and management. Surgical interventions for complications like empyema are also mentioned.Pneumonia



PneumoniaHIRANGER
Ěý
Pneumonia,definition,types,pathology, microbiology, treatment, nursing plans, patient education, vaccinationPneumonia in children



Pneumonia in childrenFaisal Chowdhury
Ěý
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites that leads to inflammation of the alveoli or fluid in the alveoli. Common symptoms include cough, fever, fast breathing and chest pain. Treatment depends on the cause but often includes antibiotics, rest and fluids. Pneumonia can be prevented through vaccines for pneumococcal disease and healthy habits like hand washing, not smoking, and avoiding contact with others who have pneumonia.Pneumonia



PneumoniaDr Eva Velikoshi-Indongo
Ěý
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It affects millions of people annually and can sometimes be fatal. The document discusses the epidemiology, classification, risk factors, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, complications, and nursing care plan for pneumonia patients. Key points include the different types of pneumonia based on location (community-acquired vs. hospital-acquired), causative agents, and patient risk factors. Proper diagnosis involves tests of sputum or other samples, along with chest imaging. Treatment focuses on antibiotics, respiratory support, fluids, rest, and patient education.Pneumonia



PneumoniaOther Mother
Ěý
This document provides an overview of pneumonia, including its definition, classification, causes, transmission, risk factors, symptoms, diagnostic tests, treatment, nursing care, prevention, prognosis, and complications. Pneumonia is defined as an inflammatory condition of the lungs caused by infectious agents. It can be classified according to its causes such as bacterial, viral, fungal, or chemical, and the area of lung involvement. Common symptoms include fever, cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical exam, chest x-ray, and sputum/blood tests. Treatment consists of antibiotics, oxygen therapy, and chest physiotherapy. Nursing care focuses on airway maintenance, infection control, respiratory support,Lower respiratory tract infection Pneumonia



Lower respiratory tract infection PneumoniaFadzlina Zabri
Ěý
Pneumonia can be lobar, affecting an entire lung lobe, bronchopneumonia with multiple inflammatory foci around bronchioles, or interstitial affecting alveolar walls. Common causes are bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae, viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus, or atypical organisms. Symptoms vary from fever, cough, difficulty breathing to chest pain. Treatment involves antibiotics, oxygen, and addressing predisposing factors. Complications can include empyema, abscesses, or respiratory failure. Proper diagnosis and management are needed to prevent long-term pulmonary damage.PneumoniaCheck, the link between the diagnosis and treatment of pneumonia wit...



PneumoniaCheck, the link between the diagnosis and treatment of pneumonia wit...Steve Koontz
Ěý
This document discusses the need for an improved method of diagnosing pneumonia. Current methods often cannot identify the specific pathogen causing pneumonia, resulting in overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics and increased antibiotic resistance. It introduces PneumoniaCheck, a new device that uses fluid mechanics to separate upper airway particles from lower airway particles collected from a patient's cough, allowing identification of the pathogen. This more targeted approach can reduce unnecessary antibiotic use and complications by precisely diagnosing the type of pneumonia.Pneumonia



PneumoniaManiz Joshi
Ěý
Pneumonia is an inflammatory lung condition caused by bacteria or viruses that enter the lungs. When pathogens enter the alveoli, or air sacs, white blood cells rush to fight the infection, filling the sacs with fluid and pus. Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common bacterial cause. Risk factors include old age, smoking, lung diseases, and weakened immunity. Symptoms include fever, chills, cough with colored mucus, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Diagnosis involves physical exam, chest x-rays, and tests of sputum or blood. Antibiotics treat bacterial pneumonia while rest and fluids help viral cases. Vaccines can prevent pneumococcal pneumonia.Approach to a child with respiratry tract infection



Approach to a child with respiratry tract infectionTushar Jagzape
Ěý
This document discusses the approach to diagnosing and treating respiratory tract infections in children. It begins by listing the objectives and introducing that respiratory infections are common in children, with upper respiratory infections making up 40-50% of pediatric outpatient cases. It then describes the components of the respiratory tract, common symptoms, and appropriate examinations. The document emphasizes establishing if the infection is upper or lower respiratory, identifying causative organisms, and providing symptomatic relief with antibiotics reserved for specific bacterial infections.Alwesaibie pneumonia



Alwesaibie pneumoniaMedicine
Ěý
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It affects people of all ages. The document discusses pneumonia including its pathophysiology, types, risk factors, signs and symptoms, diagnosis through examination and investigations, treatment, management, prognosis and prevention. Pneumonia is usually diagnosed through a medical history, physical examination, and chest x-ray. Treatment involves antibiotics, oxygen therapy, and IV fluids. Prevention focuses on vaccination, smoking cessation, and a healthy lifestyle to reduce risks.Pneumonia



PneumoniaEko Priyanto
Ěý
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs caused by bacteria or viruses. It causes the air sacs in the lungs to fill with fluid or pus, making breathing difficult. There are several types of pneumonia defined by their causes, including bacterial, viral, aspiration, and hospital-acquired pneumonia. Symptoms include cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia is diagnosed through physical exam, chest x-ray, and sputum/blood tests and treated with antibiotics, oxygen, cough medication, and breathing exercises. Complications can include pleural effusion, abscesses, or spread of infection to the blood or brain.Pneumonia



PneumoniaPravin Prasad
Ěý
This document discusses pneumonia, including its classification, pathophysiology, presentation, investigation, treatment and severity assessment. It covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and hospital-acquired pneumonia (HCAP), comparing their predisposing factors, infecting agents, and management approaches. For CAP, it recommends empirical outpatient treatment regimens based on patient risk factors. In general, the document provides a comprehensive overview of pneumonia while emphasizing differences between CAP and HCAP.obstructive bronchitis



obstructive bronchitisDr. Hament Sharma
Ěý
The document discusses obstructive bronchitis in children. It defines bronchitis as an inflammation of the bronchial mucosa that can affect the upper respiratory tract. The main causes of obstructive bronchitis in children are viruses, bacteria, hypothermia, poor air quality, and contact with sick children. The symptoms of obstructive bronchitis include a heavy cough, cyanosis, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Treatment involves reducing bronchial obstruction through pulmonary medications, humidified oxygen, and bronchodilators.Chest Infections



Chest Infectionsshabeel pn
Ěý
This document discusses various types of chest infections including acute bronchitis, acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, and community acquired pneumonia. It outlines the typical bacteria that cause these infections and recommends antibiotics for treatment. For most cases of acute bronchitis and community acquired pneumonia in previously healthy individuals, amoxicillin is recommended. Erythromycin is suggested if an atypical infection like Mycoplasma pneumoniae is suspected. Antibiotic use should be limited to cases where symptoms meet specific criteria to reduce antibiotic resistance.8 Lower Respiratory Infections



8 Lower Respiratory InfectionsYaser Ammar
Ěý
Diagnosis and Management of community acquired pneumonia.
Diagnosis and Management of aspiration pneumoniaPneumonia overview and ncp



Pneumonia overview and ncpReynel Dan
Ěý
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi or other pathogens. It is classified based on location and cause. The main types are bronchopneumonia, lobular pneumonia, and lobar pneumonia. Pneumonia can also be primary, secondary, or due to aspiration. Clinical manifestations include fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Diagnosis involves chest x-rays, sputum tests, and blood tests. Treatment consists of antibiotics, oxygen therapy, and airway clearance techniques. Nursing care focuses on improving gas exchange, enhancing airway clearance, relieving pain, and monitoring for complications like pleural effusions or respiratory failure.Pneumonia



PneumoniaEdz Gapuz
Ěý
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs caused by infections that fill the air sacs with fluid or pus. There are two main types: primary pneumonia develops from direct inhalation of pathogens, while secondary pneumonia occurs due to another illness. Pneumonia has many causes including bacteria, viruses, and chemicals. It can range from mild to life-threatening, especially in young, old, or immune compromised patients. Treatment depends on the cause but often involves antibiotics, oxygen, fluids and rest. Vaccines can prevent some bacterial types of pneumonia.Pneumonia



PneumoniaPinky Rathee
Ěý
Pneumonia (pneumonitis) is an inflammatory process in lung parenchyma usually associated with a marked increased in interstitial and alveolar fluid.Pneumonia



PneumoniaFiroz Hakkim
Ěý
This document provides information about pneumonia, including:
- Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria or viruses. It is characterized by inflammation and consolidation of the lungs.
- The pathology of pneumonia involves an inflammatory response that leads to fluid build up in the lungs, visible on scans as infiltrates. This progresses from edema to red and gray hepatization as immune cells fight the infection.
- Community-acquired pneumonia has many potential causes and symptoms may include fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Treatment focuses on oxygen, intravenous fluids, and identifying the cause. Prevention involves vaccination, smoking cessation, and improving nutrition.Pneumonia seminar presentaation



Pneumonia seminar presentaationGAMANDEEP
Ěý
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lungs caused by microbial agents like bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It affects millions of people worldwide annually and is a common cause of death, especially in young children and older adults. Symptoms include cough, fever, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Diagnosis involves physical exam, chest x-ray, and tests of respiratory samples. Treatment focuses on antibiotics targeting the causative organism as well as oxygen therapy, breathing exercises, and ensuring adequate nutrition and hydration. Complications can include lung abscesses, empyema, and respiratory failure. With treatment, most cases stabilize within a week but full recovery may take several weeks.Respiratory infection in children



Respiratory infection in childrenVarsha Shah
Ěý
Respiratory disorders are the most common illnesses affecting children. They account for half of pediatric primary care visits and one-third of hospital admissions. The most frequent respiratory infections in children are caused by viruses like RSV. Bacterial pathogens like Streptococcus pneumoniae also commonly cause pneumonia. Conditions range from mild upper respiratory infections to serious illnesses like bronchiolitis and pneumonia that occasionally require hospitalization. Proper management depends on the specific pathogen, age of the child, and severity of symptoms.PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS health care setting nursing perspective.pptx



PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS health care setting nursing perspective.pptxAnanthakrishnan Ettumanoor
Ěý
TB is an infectious disease that is caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis which shows the manifestations like low grade fever, cough, night sweats, fatigue and weight loss
Air born transmission
Infected person releases droplet nuclei (generally particles 1-5 micrometers in diameter) through talking, coughing, sneezing, laughing or singing.
Immunocompromised status ( Eg : Those with HIV infection, cancer, transplanted organs, and prolonged high dose steroidal therapy ).
Substance abuse (IV injection drug users and alcoholics)Nosocomial infection



Nosocomial infectionMmedsc Hahm
Ěý
Hospital acquired infections, also known as nosocomial infections, are infections that patients acquire during the course of receiving treatment for other conditions within a healthcare setting. These infections can spread through direct contact or indirectly through hands, equipment, and the environment. Standard precautions like proper hand hygiene and the use of personal protective equipment are important for preventing the transmission of infections between patients and staff. Additional precautions tailored to specific infection types may also be implemented, such as isolating patients, wearing protective masks, and limiting movement. Regular surveillance and adherence to infection control guidelines and manuals are necessary to effectively reduce hospital acquired infections.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Pneumonia



PneumoniaHIRANGER
Ěý
Pneumonia,definition,types,pathology, microbiology, treatment, nursing plans, patient education, vaccinationPneumonia in children



Pneumonia in childrenFaisal Chowdhury
Ěý
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites that leads to inflammation of the alveoli or fluid in the alveoli. Common symptoms include cough, fever, fast breathing and chest pain. Treatment depends on the cause but often includes antibiotics, rest and fluids. Pneumonia can be prevented through vaccines for pneumococcal disease and healthy habits like hand washing, not smoking, and avoiding contact with others who have pneumonia.Pneumonia



PneumoniaDr Eva Velikoshi-Indongo
Ěý
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It affects millions of people annually and can sometimes be fatal. The document discusses the epidemiology, classification, risk factors, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, complications, and nursing care plan for pneumonia patients. Key points include the different types of pneumonia based on location (community-acquired vs. hospital-acquired), causative agents, and patient risk factors. Proper diagnosis involves tests of sputum or other samples, along with chest imaging. Treatment focuses on antibiotics, respiratory support, fluids, rest, and patient education.Pneumonia



PneumoniaOther Mother
Ěý
This document provides an overview of pneumonia, including its definition, classification, causes, transmission, risk factors, symptoms, diagnostic tests, treatment, nursing care, prevention, prognosis, and complications. Pneumonia is defined as an inflammatory condition of the lungs caused by infectious agents. It can be classified according to its causes such as bacterial, viral, fungal, or chemical, and the area of lung involvement. Common symptoms include fever, cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical exam, chest x-ray, and sputum/blood tests. Treatment consists of antibiotics, oxygen therapy, and chest physiotherapy. Nursing care focuses on airway maintenance, infection control, respiratory support,Lower respiratory tract infection Pneumonia



Lower respiratory tract infection PneumoniaFadzlina Zabri
Ěý
Pneumonia can be lobar, affecting an entire lung lobe, bronchopneumonia with multiple inflammatory foci around bronchioles, or interstitial affecting alveolar walls. Common causes are bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae, viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus, or atypical organisms. Symptoms vary from fever, cough, difficulty breathing to chest pain. Treatment involves antibiotics, oxygen, and addressing predisposing factors. Complications can include empyema, abscesses, or respiratory failure. Proper diagnosis and management are needed to prevent long-term pulmonary damage.PneumoniaCheck, the link between the diagnosis and treatment of pneumonia wit...



PneumoniaCheck, the link between the diagnosis and treatment of pneumonia wit...Steve Koontz
Ěý
This document discusses the need for an improved method of diagnosing pneumonia. Current methods often cannot identify the specific pathogen causing pneumonia, resulting in overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics and increased antibiotic resistance. It introduces PneumoniaCheck, a new device that uses fluid mechanics to separate upper airway particles from lower airway particles collected from a patient's cough, allowing identification of the pathogen. This more targeted approach can reduce unnecessary antibiotic use and complications by precisely diagnosing the type of pneumonia.Pneumonia



PneumoniaManiz Joshi
Ěý
Pneumonia is an inflammatory lung condition caused by bacteria or viruses that enter the lungs. When pathogens enter the alveoli, or air sacs, white blood cells rush to fight the infection, filling the sacs with fluid and pus. Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common bacterial cause. Risk factors include old age, smoking, lung diseases, and weakened immunity. Symptoms include fever, chills, cough with colored mucus, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Diagnosis involves physical exam, chest x-rays, and tests of sputum or blood. Antibiotics treat bacterial pneumonia while rest and fluids help viral cases. Vaccines can prevent pneumococcal pneumonia.Approach to a child with respiratry tract infection



Approach to a child with respiratry tract infectionTushar Jagzape
Ěý
This document discusses the approach to diagnosing and treating respiratory tract infections in children. It begins by listing the objectives and introducing that respiratory infections are common in children, with upper respiratory infections making up 40-50% of pediatric outpatient cases. It then describes the components of the respiratory tract, common symptoms, and appropriate examinations. The document emphasizes establishing if the infection is upper or lower respiratory, identifying causative organisms, and providing symptomatic relief with antibiotics reserved for specific bacterial infections.Alwesaibie pneumonia



Alwesaibie pneumoniaMedicine
Ěý
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It affects people of all ages. The document discusses pneumonia including its pathophysiology, types, risk factors, signs and symptoms, diagnosis through examination and investigations, treatment, management, prognosis and prevention. Pneumonia is usually diagnosed through a medical history, physical examination, and chest x-ray. Treatment involves antibiotics, oxygen therapy, and IV fluids. Prevention focuses on vaccination, smoking cessation, and a healthy lifestyle to reduce risks.Pneumonia



PneumoniaEko Priyanto
Ěý
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs caused by bacteria or viruses. It causes the air sacs in the lungs to fill with fluid or pus, making breathing difficult. There are several types of pneumonia defined by their causes, including bacterial, viral, aspiration, and hospital-acquired pneumonia. Symptoms include cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia is diagnosed through physical exam, chest x-ray, and sputum/blood tests and treated with antibiotics, oxygen, cough medication, and breathing exercises. Complications can include pleural effusion, abscesses, or spread of infection to the blood or brain.Pneumonia



PneumoniaPravin Prasad
Ěý
This document discusses pneumonia, including its classification, pathophysiology, presentation, investigation, treatment and severity assessment. It covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and hospital-acquired pneumonia (HCAP), comparing their predisposing factors, infecting agents, and management approaches. For CAP, it recommends empirical outpatient treatment regimens based on patient risk factors. In general, the document provides a comprehensive overview of pneumonia while emphasizing differences between CAP and HCAP.obstructive bronchitis



obstructive bronchitisDr. Hament Sharma
Ěý
The document discusses obstructive bronchitis in children. It defines bronchitis as an inflammation of the bronchial mucosa that can affect the upper respiratory tract. The main causes of obstructive bronchitis in children are viruses, bacteria, hypothermia, poor air quality, and contact with sick children. The symptoms of obstructive bronchitis include a heavy cough, cyanosis, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Treatment involves reducing bronchial obstruction through pulmonary medications, humidified oxygen, and bronchodilators.Chest Infections



Chest Infectionsshabeel pn
Ěý
This document discusses various types of chest infections including acute bronchitis, acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, and community acquired pneumonia. It outlines the typical bacteria that cause these infections and recommends antibiotics for treatment. For most cases of acute bronchitis and community acquired pneumonia in previously healthy individuals, amoxicillin is recommended. Erythromycin is suggested if an atypical infection like Mycoplasma pneumoniae is suspected. Antibiotic use should be limited to cases where symptoms meet specific criteria to reduce antibiotic resistance.8 Lower Respiratory Infections



8 Lower Respiratory InfectionsYaser Ammar
Ěý
Diagnosis and Management of community acquired pneumonia.
Diagnosis and Management of aspiration pneumoniaPneumonia overview and ncp



Pneumonia overview and ncpReynel Dan
Ěý
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi or other pathogens. It is classified based on location and cause. The main types are bronchopneumonia, lobular pneumonia, and lobar pneumonia. Pneumonia can also be primary, secondary, or due to aspiration. Clinical manifestations include fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Diagnosis involves chest x-rays, sputum tests, and blood tests. Treatment consists of antibiotics, oxygen therapy, and airway clearance techniques. Nursing care focuses on improving gas exchange, enhancing airway clearance, relieving pain, and monitoring for complications like pleural effusions or respiratory failure.Pneumonia



PneumoniaEdz Gapuz
Ěý
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lungs caused by infections that fill the air sacs with fluid or pus. There are two main types: primary pneumonia develops from direct inhalation of pathogens, while secondary pneumonia occurs due to another illness. Pneumonia has many causes including bacteria, viruses, and chemicals. It can range from mild to life-threatening, especially in young, old, or immune compromised patients. Treatment depends on the cause but often involves antibiotics, oxygen, fluids and rest. Vaccines can prevent some bacterial types of pneumonia.Pneumonia



PneumoniaPinky Rathee
Ěý
Pneumonia (pneumonitis) is an inflammatory process in lung parenchyma usually associated with a marked increased in interstitial and alveolar fluid.Pneumonia



PneumoniaFiroz Hakkim
Ěý
This document provides information about pneumonia, including:
- Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria or viruses. It is characterized by inflammation and consolidation of the lungs.
- The pathology of pneumonia involves an inflammatory response that leads to fluid build up in the lungs, visible on scans as infiltrates. This progresses from edema to red and gray hepatization as immune cells fight the infection.
- Community-acquired pneumonia has many potential causes and symptoms may include fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Treatment focuses on oxygen, intravenous fluids, and identifying the cause. Prevention involves vaccination, smoking cessation, and improving nutrition.Pneumonia seminar presentaation



Pneumonia seminar presentaationGAMANDEEP
Ěý
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lungs caused by microbial agents like bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It affects millions of people worldwide annually and is a common cause of death, especially in young children and older adults. Symptoms include cough, fever, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Diagnosis involves physical exam, chest x-ray, and tests of respiratory samples. Treatment focuses on antibiotics targeting the causative organism as well as oxygen therapy, breathing exercises, and ensuring adequate nutrition and hydration. Complications can include lung abscesses, empyema, and respiratory failure. With treatment, most cases stabilize within a week but full recovery may take several weeks.Respiratory infection in children



Respiratory infection in childrenVarsha Shah
Ěý
Respiratory disorders are the most common illnesses affecting children. They account for half of pediatric primary care visits and one-third of hospital admissions. The most frequent respiratory infections in children are caused by viruses like RSV. Bacterial pathogens like Streptococcus pneumoniae also commonly cause pneumonia. Conditions range from mild upper respiratory infections to serious illnesses like bronchiolitis and pneumonia that occasionally require hospitalization. Proper management depends on the specific pathogen, age of the child, and severity of symptoms.Similar to 1 tuberculosis (20)
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS health care setting nursing perspective.pptx



PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS health care setting nursing perspective.pptxAnanthakrishnan Ettumanoor
Ěý
TB is an infectious disease that is caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis which shows the manifestations like low grade fever, cough, night sweats, fatigue and weight loss
Air born transmission
Infected person releases droplet nuclei (generally particles 1-5 micrometers in diameter) through talking, coughing, sneezing, laughing or singing.
Immunocompromised status ( Eg : Those with HIV infection, cancer, transplanted organs, and prolonged high dose steroidal therapy ).
Substance abuse (IV injection drug users and alcoholics)Nosocomial infection



Nosocomial infectionMmedsc Hahm
Ěý
Hospital acquired infections, also known as nosocomial infections, are infections that patients acquire during the course of receiving treatment for other conditions within a healthcare setting. These infections can spread through direct contact or indirectly through hands, equipment, and the environment. Standard precautions like proper hand hygiene and the use of personal protective equipment are important for preventing the transmission of infections between patients and staff. Additional precautions tailored to specific infection types may also be implemented, such as isolating patients, wearing protective masks, and limiting movement. Regular surveillance and adherence to infection control guidelines and manuals are necessary to effectively reduce hospital acquired infections.Pulmonary Tuberculosis.pptx



Pulmonary Tuberculosis.pptxTifani Nazreth
Ěý
This document provides an overview of pulmonary tuberculosis (TB). It defines TB as an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which primarily affects the lungs. TB is spread through airborne droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The document discusses the pathogenesis, stages, risk factors, signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, medical management including drug therapy, and nursing care of patients with pulmonary TB. It also covers complications, education on respiratory hygiene and home care considerations for patients.Tb -copy



Tb -copymahamed adam
Ěý
Tuberculosis is caused by mycobacterium species, mainly M. tuberculosis, which is transmitted via airborne droplets. It most commonly affects the lungs, causing symptoms like cough and sputum production. Diagnosis involves chest x-ray, sputum smear and culture. Treatment involves a multi-drug regimen over 6-12 months to prevent resistance. Complications include pleural effusion, pneumonia or other organ involvement. Prevention focuses on treatment of active cases, BCG vaccination, and improving socioeconomic conditions.infection_control;_covid_19,_herpes_virus_&_hpv[1][1BN].pptx![infection_control;_covid_19,_herpes_virus_&_hpv[1][1BN].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/infectioncontrolcovid19herpesvirushpv11bn-240301081908-385864cd-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![infection_control;_covid_19,_herpes_virus_&_hpv[1][1BN].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/infectioncontrolcovid19herpesvirushpv11bn-240301081908-385864cd-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![infection_control;_covid_19,_herpes_virus_&_hpv[1][1BN].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/infectioncontrolcovid19herpesvirushpv11bn-240301081908-385864cd-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![infection_control;_covid_19,_herpes_virus_&_hpv[1][1BN].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/infectioncontrolcovid19herpesvirushpv11bn-240301081908-385864cd-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
infection_control;_covid_19,_herpes_virus_&_hpv[1][1BN].pptxboaznabiswa
Ěý
This document provides information about NabiswaBoaz infection control. It discusses COVID-19, including its symptoms, transmission, who is most at risk, screening and testing methods, treatments, and prevention strategies. Some key points covered include how COVID-19 is transmitted via droplets, its most common symptoms, those at highest risk like the elderly and immunocompromised, the use of RT-PCR testing for diagnosis, supportive treatments and isolating patients. Prevention strategies discussed social distancing, hand washing, use of PPE, and vaccinations.Isolation precautions



Isolation precautionsMEEQAT HOSPITAL
Ěý
This document discusses isolation precautions in hospitals. It outlines the rationale for isolation precautions, noting that infection transmission requires a microorganism, source, susceptible host, and means of transmission. Various sources of infection and host factors are described. The main routes of transmission - contact, droplet, airborne, and vector-borne - are explained. Guidelines for isolation precautions from the CDC in 1983, 1990, and 1996 are summarized. These include category-specific and disease-specific isolation as well as standard and transmission-based precautions. Specific precautions for airborne, droplet, and contact transmission are provided. Fundamental aspects of isolation precautions like hand washing, gloves, patient placement, and transport are also coveredInfection control sandra



Infection control sandraSandraJohnAbraham
Ěý
The document discusses infection control in a healthcare setting. It defines infection control as preventing healthcare-associated infections and outlines its objectives like protecting patients and staff from infection. It describes strategies for infection control like screening, barriers, aseptic technique, and proper disposal. The importance of infection control is to prevent infections, provide safe services, and control costs. Key components of an infection control program are outlined like surveillance, education, and standard precautions.Prevention of mycobateria tuberculosis in healthcare settings



Prevention of mycobateria tuberculosis in healthcare settingsMoustapha Ramadan
Ěý
This document discusses the prevention of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) in healthcare settings. It begins with an introduction to mycobacteria and the diseases they cause like tuberculosis, leprosy, and atypical mycobacterial infections. It then provides facts about MTB globally and its symptoms. The remainder of the document outlines administrative, environmental, and respiratory precautions that can be taken to prevent MTB transmission in healthcare settings, including proper patient management, cleaning/disinfection, staff training/surveillance, and use of airborne isolation rooms and respiratory protection equipment.Epcm l15 control of nosocomial (Hospital-Acquired) infection



Epcm l15 control of nosocomial (Hospital-Acquired) infectionDr Ghaiath Hussein
Ěý
This lecture was given as a part of the Introduction to Epidemiology & Community Medicine Course given for third-year medical students.Understanding Infection



Understanding Infectionwindleh
Ěý
The document discusses infection and the infectious process. It defines key terms like pathogens, virulence, and susceptibility. It describes the chain of infection and factors that influence susceptibility. It also discusses infection control methods like hand hygiene, immunizations, and multidrug-resistant infections. Nursing responsibilities in managing infections include assessing patients, administering antibiotics, providing treatments and education.Communicable diseases



Communicable diseasesGian Carlo Almario
Ěý
Tuberculosis is caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis and usually affects the lungs. It spreads through the air when infected people cough or sneeze. Symptoms include coughing for 3+ weeks, weight loss, coughing up blood or mucus, and night sweats. Treatment involves isolating infected patients and starting antibiotic therapy. Leprosy is caused by mycobacterium leprae and affects the skin and nerves, causing disfigurement. It spreads through prolonged contact with infected individuals and has a long incubation period. Malaria is transmitted through the bites of infected anopheles mosquitoes and causes cycles of chills, fever and sweating. Control methods for these diseases include treatment, isolation, vector control04 infection prevention and control



04 infection prevention and controlREKHA DEHARIYA
Ěý
The document discusses infection prevention and control in healthcare settings. It states that hospital-acquired infections affect over 2 million patients annually in the US, leading to 90,000 deaths. Standard precautions like hand hygiene and personal protective equipment are the most basic methods for preventing transmission. Additional precautions may be needed depending on the type of infection, such as contact, droplet, or airborne precautions. Healthcare workers must be trained on infection control practices to minimize the spread of infections.PREVENTION OF FUNGAL INFECTIONS 



PREVENTION OF FUNGAL INFECTIONS icsp
Ěý
Lecture on Prevention of Fungal Infections by Dr. Gamini Kumarasinghe during the 6th International Infection Control Conference 200613.Tuberculosis... management



13.Tuberculosis... managementPapiyonEmpireEthiost
Ěý
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It typically affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body. There are several drug regimens used to treat TB, with the primary first-line drugs being isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol, and streptomycin. Treatment must continue for a sufficient time, such as 6-9 months, to fully cure the infection and prevent relapse or development of drug resistance. Second-line drugs are used for cases of drug-resistant TB or in cases where patients cannot tolerate first-line drugs. The goals of TB treatment are to cure the patient, prevent death, prevent relapseTuberculosis 



Tuberculosis Ruth Nwokoma
Ěý
Tuberculosis is a global disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It infects around a third of the world's population and causes millions of deaths each year. Common symptoms include cough, weight loss, and fever. Diagnosis involves sputum smear microscopy, chest x-ray, and culture. Treatment requires prolonged multi-drug chemotherapy over 6-24 months to prevent drug resistance. Directly observed therapy is recommended to ensure treatment adherence and cure.Ventilator associated infections VAP 



Ventilator associated infections VAP Thair Abuaqeel
Ěý
This document discusses ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP), including its definition, causes, risk factors, prevention, and treatment. Some key points:
- VAP is pneumonia that develops in intubated patients and accounts for most ICU infections. It occurs in 10-20% of mechanically ventilated patients and has a high mortality rate.
- Risk factors include underlying illnesses, suppression of immune system, and prolonged ventilation. Common causes are oropharyngeal/GI bacteria and viruses that enter the lungs through the endotracheal tube or around the cuff.
- Prevention strategies include following bundles like elevating the head, oral care with chlorhexidine, and stopping unnecessary devices; as wellPneumonia.epidemiology person, place, time graph



Pneumonia.epidemiology person, place, time graphABHISHEK
Ěý
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be classified as community-acquired, hospital-acquired, ventilator-associated, or healthcare-associated based on where infection was contracted. It progresses through stages including congestion, red and gray hepatization, and resolution. Diagnosis involves chest x-rays, sputum culture, urine antigen tests, and biomarkers. Risk factors are addressed through primary prevention like immunization, secondary prevention like screening high risk groups, and tertiary prevention like case management of recurrent cases. Treatment is based on CURB-65 severity score and may include outpatient therapy or ICU care.Tuberculosis TB



Tuberculosis TBANILKUMAR BR
Ěý
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) that most often affect the lungs. Tuberculosis is curable and preventable.
TB is spread from person to person through the air. When people with lung TB cough, sneeze or spit, they propel the TB germs into the air. A person needs to inhale only a few of these germs to become infected.
The causative agent is Mycobacterium tuberculosis (also known as the tubercle bacillus).
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease that primarily affects the lung parenchyma. The primary infection usually involves the middle or lower lung area.
It is also may be transmitted to other parts of the body, including the Meninges, kidneys, bone, joints, pericardium, GI tract and lymph nodes And this condition known as Extra pulmonary TB.
The disease also can affects animals such as cattle, this is known as “bovine tuberculosis” which may sometimes be transmitted to man.The primary infectious agent, “ M.Tuberculosis”, is an acid – fast aerobic (AFB) rod that grows slowly and is sensitive to heat and ultraviolet light.
KAWALAN INFEKSI HOSPITAL



KAWALAN INFEKSI HOSPITALunittbjknphg
Ěý
This document discusses cough etiquette and respiratory hygiene to prevent the spread of respiratory infections in healthcare settings. It recommends that individuals with respiratory symptoms cover their mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and dispose of tissues properly. Healthcare facilities should promote these practices and make resources like masks and hand hygiene supplies available. Proper patient placement, respiratory protection for healthcare workers, and other infection control measures are needed to manage patients with infectious respiratory illnesses like tuberculosis.Recently uploaded (20)
Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok Sonawala



Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok SonawalaAssociation for Project Management
Ěý
APM event hosted by the South Wales and West of England Network (SWWE Network)
Speaker: Aalok Sonawala
The SWWE Regional Network were very pleased to welcome Aalok Sonawala, Head of PMO, National Programmes, Rider Levett Bucknall on 26 February, to BAWA for our first face to face event of 2025. Aalok is a member of APM’s Thames Valley Regional Network and also speaks to members of APM’s PMO Interest Network, which aims to facilitate collaboration and learning, offer unbiased advice and guidance.
Tonight, Aalok planned to discuss the importance of a PMO within project-based organisations, the different types of PMO and their key elements, PMO governance and centres of excellence.
PMO’s within an organisation can be centralised, hub and spoke with a central PMO with satellite PMOs globally, or embedded within projects. The appropriate structure will be determined by the specific business needs of the organisation. The PMO sits above PM delivery and the supply chain delivery teams.
For further information about the event please click here.Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ěý
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxKaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Finals of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby Basnet



Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby BasnetBoby Basnet
Ěý
Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding Full Note
|| Assistant Professor Boby Basnet ||IAAS || AFU || PU || FUDatabase population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slides



Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slidesCeline George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss the database population in Odoo 18. In Odoo, performance analysis of the source code is more important. Database population is one of the methods used to analyze the performance of our code. Information Technology for class X CBSE skill Subject



Information Technology for class X CBSE skill SubjectVEENAKSHI PATHAK
Ěý
These questions are based on cbse booklet for 10th class information technology subject code 402. these questions are sufficient for exam for first lesion. This subject give benefit to students and good marks. if any student weak in one main subject it can replace with these marks.Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ěý
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...



Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...Ajaz Hussain
Ěý
This presentation delves into the systemic blind spots within pharmaceutical science and regulatory systems, emphasizing the significance of "inactive ingredients" and their influence on therapeutic equivalence. These blind spots, indicative of normalized systemic failures, go beyond mere chance occurrences and are ingrained deeply enough to compromise decision-making processes and erode trust.
Historical instances like the 1938 FD&C Act and the Generic Drug Scandals underscore how crisis-triggered reforms often fail to address the fundamental issues, perpetuating inefficiencies and hazards.
The narrative advocates a shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, adaptable systems prioritizing continuous enhancement. Key hurdles involve challenging outdated assumptions regarding bioavailability, inadequately funded research ventures, and the impact of vague language in regulatory frameworks.
The rise of large language models (LLMs) presents promising solutions, albeit with accompanying risks necessitating thorough validation and seamless integration.
Tackling these blind spots demands a holistic approach, embracing adaptive learning and a steadfast commitment to self-improvement. By nurturing curiosity, refining regulatory terminology, and judiciously harnessing new technologies, the pharmaceutical sector can progress towards better public health service delivery and ensure the safety, efficacy, and real-world impact of drug products.A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
Ěý
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardSOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...



SOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...DrNidhiAgarwal
Ěý
This PPT is showing the effect of social changes in human life and it is very understandable to the students with easy language.in this contents are Itroduction, definition,Factors affecting social changes ,Main technological factors, Social change and stress , what is eustress and how social changes give impact of the human's life.EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdf



EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfLiz Walsh-Trevino
Ěý
EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfMate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
Ěý
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18



How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18Celine George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to modify existing web pages in Odoo 18. Web pages in Odoo 18 can also gather user data through user-friendly forms, encourage interaction through engaging features. Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
1 tuberculosis
- 1. CLINICAL SPECIALITY – II CARDIOVASCULAR & THORACIC NURSING UNIT V CARDIAC DISORDERS AND NURSING MANAGEMENT TUBERCULOSIS
- 2. General objective: ď‚— At the end of this class students will be acquainted with Tuberculosis. Specific objective: ď‚— Define Tuberculosis. ď‚— Mention the causes of Tuberculosis ď‚— Discuss the types of Tuberculosis ď‚— Describe clinical manifestation of Tuberculosis ď‚— Discuss management of Tuberculosis.
- 4. ď‚— Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs, but it also occurs in the larynx, kidneys , bones, adrenal glands, lymph nodes and meninges and can be disseminated throughout the body. TUBERCULOSIS
- 6. ď‚— Close contact with TB patient. ď‚— Inhalation of airborne nuclei from an infected person. ď‚— Immunocompromised status ( HIV, Cancer, prolonged high-dose corticosteroid therapy) ď‚— Substance abuse. ď‚— Pre-existing medical condition. ď‚— Living in overcrowded , substandard living. RISK FACTORS
- 8. Exposure to source Aerosolization of droplet nuclei Inhalation of bacteria Bacteria reach lungs enter macrophages Bacteria multiply in macrophages Granulomatous lesions begins to form ( caseous necrosis) Lesion liqifies & spread to blood , organs Death
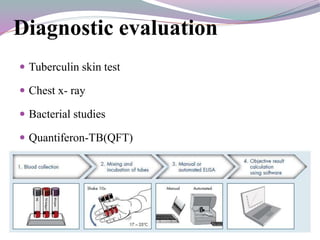
- 10. ď‚— Tuberculin skin test ď‚— Chest x- ray ď‚— Bacterial studies ď‚— Quantiferon-TB(QFT) Diagnostic evaluation
- 12. First line drugs “PERIS”  Pyrazinamide.  Ethambutol.  Rifampicin.  Isoniazid.  Streptomycin.
- 13. Second Line drugs: ď‚— Fluroquinolones. ď‚— Aminoglycosides (Kanamycin, amikacin, capreomycin) ď‚— Ethionamide ď‚— P-Amino salicylic acid ď‚— Cylcoserine.
- 15. Improving Breathing Pattern ď‚— Administer and teach self-administration of medications as ordered ď‚— Encourage rest and avoidance of exertion ď‚— Monitor breath sounds, respiratory rate, sputum production, and dyspnea ď‚— Provide supplemental oxygen as ordered. NURSING MANAGEMENT
- 16. Preventing Transmission of Infection ď‚— Be aware that TB is transmitted by respiratory droplets or secretions. ď‚— Provide care for hospitalized patient in a negative-pressure room to prevent respiratory droplets from escaped when door is opened. ď‚— Enforce rule that all staff and visitors use well-fitted standard dust/mist/fume masks for contact with patient.
- 17.  Use high-efficiency particulate masks, such as high- efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter masks, for high- r_M procedures, including suctioning, bronchoscopy, or pentamidine treatments.  Use standard precautions for additional protection— gowns and gloves for direct contact with patient, linens :: articles in room, meticulous hand washing.
- 18. Improving Nutritional Status ď‚— Explain the importance of eating a nutritious diet to promote healing and improve defense against infection. ď‚— Provide small, frequent meals and liquid supplements during symptomatic period. ď‚— Monitor weight. ď‚— Administer vitamin supplements, as ordered, particularly pyridoxine (vitamin B(.) to prevent peripheral neuropathy in patients taking isoniazid.
- 19. Improving Compliance ď‚— Educate the patient about the etiology, transmission, and effects of TB. Stress the importance of continuing to take medicine for the prescribed time because bacilli multiply slowly and thus can only be eradicated over a long period ď‚— Review adverse effects of the drug therapy. Question the patient specifically about common toxicities of drugs being used, and emphasize immediate reporting should these occur.
- 20. ď‚— Participate in observation of medication taking, weekly pill counts, or other programs designed to increase compliance with treatment for TB.







