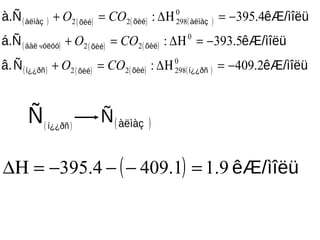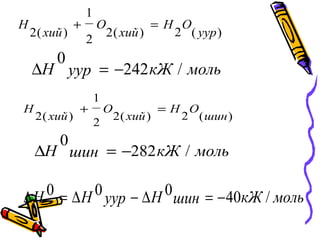101 9-termohimiin vndes
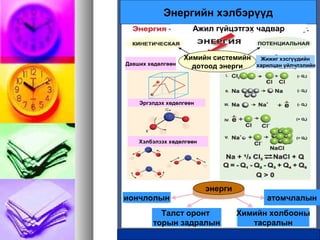
- 1. ąóąĄčĆą╝ąŠčģąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ 껹Įą┤čŹčüąóąĄčĆą╝ąŠčģąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ 껹Įą┤čŹčü ŌĆó ąÉą│čāčāą╗ą│ą░:菹Įą┤ąŠč鹥čĆą╝ ą▒ą░ 菹║ąĘąŠč鹥čĆą╝ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗, č鹥čĆą╝ąŠą┤ąĖąĮą░ą╝ąĖą║, ą┤ąŠč鹊ąŠą┤ 菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖ, ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮ, ą░ąČąĖą╗, ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ ąĖą╗čĆ菹╗
- 2. čģąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ č鹥čĆą╝ąŠą┤ąĖąĮą░ą╝ąĖą║čģąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ č鹥čĆą╝ąŠą┤ąĖąĮą░ą╝ąĖą║ ą│čŹąČ čÄčā ą▓菹│čŹąČ čÄčā ą▓čŹ?? ŌĆó ąźąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ ą┐čĆąŠčåąĄčüčüčŗąĮ čÅą▓čåą░ą┤ 菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖą╣ąĮ čģčāą▓ąĖčĆą░čģ čģčāčāą╗čī, ąĘ껹╣ č鹊ą│čéą╗čŗą│ č鹥čĆą╝ąŠą┤ąĖąĮą░ą╝ąĖą║ąĖą╣ąĮ čģčāčāą╗ąĖą╣ą│ ą░čłąĖą│ą╗ą░ąĮ čüčāą┤ą░ą╗ą┤ą░ą│ čāčģą░ą░ąĮ
- 3. ąŁąĮąĄčĆą│ąĖą╣ąĮ čģ菹╗ą▒čŹčĆę»ę»ą┤ ąÉąČąĖą╗ ą│껹╣čåčŹčéą│čŹčģ čćą░ą┤ą▓ą░čĆ ąźąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ ą┤ąŠč鹊ąŠą┤ 菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖąöą░ą▓čłąĖčģ čģė®ą┤ė®ą╗ą│ė®ė®ąĮ ąŁčĆą│菹╗ą┤čŹčģ čģė®ą┤ė®ą╗ą│ė®ė®ąĮ ąźčŹą╗ą▒菹╗ąĘčŹčģ čģė®ą┤ė®ą╗ą│ė®ė®ąĮ 菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖ ąĖąŠąĮčćą╗ąŠą╗čŗąĮ ąóą░ą╗čüčé ąŠčĆąŠąĮčé č鹊čĆčŗąĮ ąĘą░ą┤čĆą░ą╗čŗąĮ ąźąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ čģąŠą╗ą▒ąŠąŠąĮčŗ čéą░čüčĆą░ą╗čŗąĮ ą░č鹊ą╝čćą╗ą░ą╗čŗąĮ ą¢ąĖąČąĖą│ čģčŹčüą│ę»ę»ą┤ąĖą╣ąĮ čģą░čĆąĖą╗čåą░ąĮ 껹╣ą╗čćą╗菹╗ąĖą╣ąĮ
- 4. ąöąŠč鹊ąŠą┤ 菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖ-ąöąŠč鹊ąŠą┤ 菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖ-UU ’ü« čģąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮ čÅą▓čåą░ą┤ ą│ą░čĆą░čģčģąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮ čÅą▓čåą░ą┤ ą│ą░čĆą░čģ ą║ąĖąĮąĄčéąĖą║ ą▒ą░ ą┐ąŠč鹥ąĮčåąĖą░ą╗ą║ąĖąĮąĄčéąĖą║ ą▒ą░ ą┐ąŠč鹥ąĮčåąĖą░ą╗ 菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖą╣ąĮ ė®ė®čĆčćą╗ė®ą╗čéąĖą╣ą│菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖą╣ąĮ ė®ė®čĆčćą╗ė®ą╗čéąĖą╣ą│ č鹊ąŠčåąŠčģą│껹╣ą│čŹčŹčĆ čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ ąĮąĖą╣čéč鹊ąŠčåąŠčģą│껹╣ą│čŹčŹčĆ čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ ąĮąĖą╣čé 菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖą╣ąĮ ė®ė®čĆčćą╗ė®ą╗čéąĖą╣ą│ ą┤ąŠč鹊ąŠą┤菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖą╣ąĮ ė®ė®čĆčćą╗ė®ą╗čéąĖą╣ą│ ą┤ąŠč鹊ąŠą┤ 菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖą╣ąĮ ė®ė®čĆčćą╗ė®ą╗čéė®ė®čĆ č鹊ąŠčåąŠąČ菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖą╣ąĮ ė®ė®čĆčćą╗ė®ą╗čéė®ė®čĆ č鹊ąŠčåąŠąČ ą▒ąŠą╗ąĮąŠ.ą▒ąŠą╗ąĮąŠ. 12 UUU ŌłÆ=Ōłå
- 5. ąöčāą╗ą░ą░ąĮąöčāą╗ą░ą░ąĮ--QQ ’ü« ąØ菹│ čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ ąČąĖąČąĖą│ąØ菹│ čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ ąČąĖąČąĖą│ čģčŹčüą│ąĖą╣ąĮ ą┤ą░ą▓čłąĖčģ, čģ菹╗ą▒菹╗ąĘčŹčģ ą▒ą░čģčŹčüą│ąĖą╣ąĮ ą┤ą░ą▓čłąĖčģ, čģ菹╗ą▒菹╗ąĘčŹčģ ą▒ą░ čŹčĆą│菹╗ą┤čŹčģ čģė®ą┤ė®ą╗ą│ė®ė®ąĮė®ė®čĆčŹčĆą│菹╗ą┤čŹčģ čģė®ą┤ė®ą╗ą│ė®ė®ąĮė®ė®čĆ čéę»ę»ąĮčé菹╣ čģąĖą╗ą╗čŹąČ ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą░ą░ ė®ė®čĆčéę»ę»ąĮčé菹╣ čģąĖą╗ą╗čŹąČ ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą░ą░ ė®ė®čĆ ąĮ菹│ čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝ąĖą╣ąĮąĮ菹│ čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ ą┤ąŠč鹊ąŠą┤ 菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖą┤ąŠč鹊ąŠą┤ 菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖ ąĖčģčüčŹčģąĖčģčüčŹčģ 껹Ę菹│ą┤菹╗껹Ę菹│ą┤菹╗
- 6. ąźąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮ ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ čŹčäč乥ą║čé ąŻčĆą▓ą░ą╗ ąöčāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ ąĖą╗čĆ菹╗ą┤ ąĮė®ą╗ė®ė®ą╗ė®čģ čģę»čćąĖąĮ ąĘ껹╣ą╗čü ąæąŠą┤ąĖčüčŗąĮ ą╝ą░čüčü ąóąĄą╝ą┐ąĄčĆ -ą░čéčāčĆ ąÉą│čĆąĄą│ą░čé čéė®ą╗ė®ą▓ ąöę»čĆčü čģčāą▓ąĖčĆą░ą╗ ąæą░ą╣ą│ą░ą╗čīą┤ ąŠčĆčłąĖčģ ąŁą║ąĘąŠč鹥čĆą╝-čÅą╗ą│ą░čĆą░čģ ąŁąĮą┤ąŠč鹥čĆą╝-čłąĖąĮą│čŹčŹčģ ąĢčŹčģ ąĢą▒ę»čé ąŁčģ ą▒ąŠą┤ąĖčü ąśą┤菹▓čģąČčü菹Į čéė®ą╗ė®ą▓ ą▒ę»čéčŹčŹą│ą┤čŹčģę»ę»ąĮ ąŁčģ ą▒ąŠą┤ąĖčü ąæę»čéčŹčŹą│- -ą┤čŹčģę»ę»ąĮ ąśą┤菹▓čģąČčü菹Į čéė®ą╗ė®ą▓
- 7. ąÉąČąĖą╗ąÉąČąĖą╗-ąÉ-ąÉ ’ü« ąĪąĖčüč鹥ą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ ąČąĖąČąĖą│ čģčŹčüą│ę»ę»ą┤ąĪąĖčüč鹥ą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ ąČąĖąČąĖą│ čģčŹčüą│ę»ę»ą┤ čģčģę»čĆčŹčŹą╗菹Įę»čĆčŹčŹą╗菹Į ą▒ą░ą╣ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą│ą░ą░ ąŠčĆčćąĖąĮą┤ąŠąŠą░ą░ ąŠčĆčćąĖąĮą┤ąŠąŠ ą┤ą░ą▓čłąĖčģ čģė®ą┤ė®ą╗ą│ė®ė®ąĮąĖą╣ą│ą┤ą░ą▓čłąĖčģ čģė®ą┤ė®ą╗ą│ė®ė®ąĮąĖą╣ą│ ę»ę»čüą│菹Į čłąĖą╗ąČąĖčģ 껹Ąą┤ę»ę»čüą│菹Į čłąĖą╗ąČąĖčģ 껹Ąą┤ čÅą▓ą░ą│ą┤ą░čģčÅą▓ą░ą│ą┤ą░čģ ą┤ąŠč鹊ąŠą┤ 菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖą╣ąĮą┤ąŠč鹊ąŠą┤ 菹ĮąĄčĆą│ąĖą╣ąĮ ė®ė®čĆčćą╗ė®ą╗čéė®ė®čĆčćą╗ė®ą╗čé
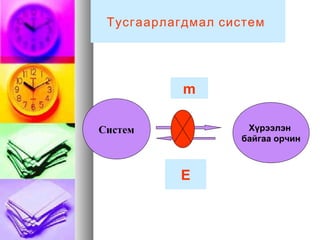
- 8. m CąĖčüč鹥ą╝ ąźę»čĆčŹčŹą╗菹Į ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą░ą░ ąŠčĆčćąĖąĮ E ąóčāčüą│ą░ą░čĆą╗ą░ą│ą┤ą╝ą░ą╗ čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝
- 9. ąźą░ą░ą╗čéčéą░ą╣ čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝ąźą░ą░ą╗čéčéą░ą╣ čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝ CCąĖčüč鹥ą╝ąĖčüč鹥ą╝ ąźę»čĆčŹčŹą╗菹Į ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą░ą░ ąŠčĆčćąĖąĮ m E
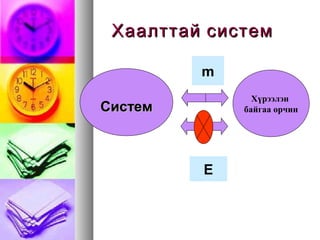
- 10. ąØčŹčŹą╗čéčé菹╣ čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝ąØčŹčŹą╗čéčé菹╣ čüąĖčüč鹥ą╝ CCąĖčüč鹥ąĖčüč鹥 ą╝ą╝ ąźę»čĆčŹčŹą╗菹Į ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą░ą░ ąŠčĆčćąĖąĮ m E
- 11. ąóąĄčĆą╝ąŠą┤ąĖąĮą░ą╝ąĖą║ąĖą╣ąĮ I- čģčāčāą╗čī AUQ +Ōłå= )()( )(, 1122 1212 2 1 pVUpVU pVpVUUQpdVA p V V +ŌłÆ+ =ŌłÆ+ŌłÆ== Ōł½
- 12. ąźąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ č鹥čĆą╝ąŠą┤ąĖąĮą░ą╝ąĖą║čéąźąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ č鹥čĆą╝ąŠą┤ąĖąĮą░ą╝ąĖą║čé U+pV=H (菹Įčéą░ą╗čīą┐ąĖ)U+pV=H (菹Įčéą░ą╗čīą┐ąĖ) ’ü« QQPP= U= U22-U-U11 ą▒čāčÄčāą▒čāčÄčā ’ü« QQVV== UŌłå
- 13. ąźąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮąźąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮ ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ ąĖą╗čĆ菹╗ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ ąĖą╗čĆ菹╗-H-H ąŁą║ąĘąŠč鹥čĆą╝ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮ čÅą▓čåą░ą┤ąŁą║ąĘąŠč鹥čĆą╝ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮ čÅą▓čåą░ą┤ čÅą╗ą│ą░čĆčüą░ąĮ ą▒čāčÄčā 菹Įą┤ąŠč鹥čĆą╝čÅą╗ą│ą░čĆčüą░ąĮ ą▒čāčÄčā 菹Įą┤ąŠč鹥čĆą╝ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗ą░ą░čĆ čłąĖąĮą│čŹčŹčü菹ĮčāčĆą▓ą░ą╗ą░ą░čĆ čłąĖąĮą│čŹčŹčü菹Į ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ č鹊ąŠ čģ菹╝ąČčŹčŹą│ čāą│ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ č鹊ąŠ čģ菹╝ąČčŹčŹą│ čāą│ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮčāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮ ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ ąĖą╗čĆ菹╗ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ ąĖą╗čĆ菹╗
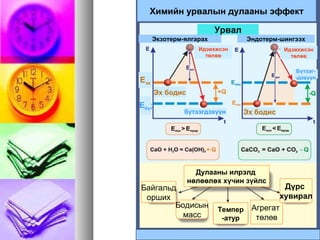
- 14. ąÉ. ąöčāą╗ą░ą░ąĮ čÅą╗ą│ą░čĆčāčāą╗ą░ąĮ čÅą▓ą░ą│ą┤ą┤ą┤ą░ą│ : ąŁą║ąĘąŠč鹥čĆą╝ ąæ. Q čłąĖąĮą│čŹčŹąČ čÅą▓ą░ą│ą┤ą┤ą░ą│: ąŁąĮą┤ąŠč鹥čĆą╝ ├¼├«├½├╝├¬ ├å/├Ą├©├®├Ą├©├ē├Ą├©├® 9.29622 +=+ SOOS ├¬├å/├¼├«├½├╝├Ą├©├®├Ą├Ā├▓├│├│├Ą├Ā├▓├│├│ 23434 0 ŌłÆ+’Ż¦ŌåÆ’Ż¦ SOZnOZnSO t
- 15. QQVV= ┬▒= ┬▒ QQąĀąĀ= ┬▒= ┬▒ ŌłåHŌłåH ąōąĄčüčüąĖą╣ąĮ čģčāčāą╗čīąōąĄčüčüąĖą╣ąĮ čģčāčāą╗čī :: ą×čĆąŠčüčŗąĮ čŹčĆą┤菹╝čé菹Įą×čĆąŠčüčŗąĮ čŹčĆą┤菹╝čé菹Į ąō.ąś. ąōąĄčüčü 1940 ąŠąĮą┤ąō.ąś. ąōąĄčüčü 1940 ąŠąĮą┤ č鹥čĆą╝ąŠčģąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ ą│ąŠą╗ čģčāčāą╗ąĖą╣ą│č鹥čĆą╝ąŠčģąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ ą│ąŠą╗ čģčāčāą╗ąĖą╣ą│ ą┤ą░čĆą░ą░čģ ą▒ą░ą╣ą┤ą╗ą░ą░čĆą┤ą░čĆą░ą░čģ ą▒ą░ą╣ą┤ą╗ą░ą░čĆ č鹊ą╝čŖčæąŠą╗ąČčŹčŹč鹊ą╝čŖčæąŠą╗ąČčŹčŹ.. UŌłå
- 16. ŌĆ£ŌĆ£ ąźąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮąźąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮ ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ ąĖą╗čĆ菹╗ ąĮčīą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ ąĖą╗čĆ菹╗ ąĮčī čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗą│ čÅą▓čāčāą╗ąČ ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą░ą░čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗą│ čÅą▓čāčāą╗ąČ ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą░ą░ ąĘą░ą╝ ą▒ą░ ą╝ąĄčģą░ąĮąĖąĘą╝ą░ą░čüąĘą░ą╝ ą▒ą░ ą╝ąĄčģą░ąĮąĖąĘą╝ą░ą░čü čģą░ą╝ą░ą░čĆą┤ą░ą│ą│껹╣ čģą░čĆąĖąĮčģą░ą╝ą░ą░čĆą┤ą░ą│ą│껹╣ čģą░čĆąĖąĮ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗ą┤ ąŠčĆąČ ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą░ą░čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗ą┤ ąŠčĆąČ ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą░ą░ ą▒ąŠą┤ąĖčüčŗąĮ čŹčģąĮąĖą╣ čéė®ą╗ė®ą▓ ą▒ą░ą▒ąŠą┤ąĖčüčŗąĮ čŹčģąĮąĖą╣ čéė®ą╗ė®ą▓ ą▒ą░ ą▒ę»čéčŹčŹą│ą┤čŹčģę»ę»ąĮ ą▒ąŠą┤ąĖčüčŗąĮą▒ę»čéčŹčŹą│ą┤čŹčģę»ę»ąĮ ą▒ąŠą┤ąĖčüčŗąĮ čŹčåčüąĖą╣ąĮ čéė®ą╗ė®ą▓ė®ė®čüčŹčåčüąĖą╣ąĮ čéė®ą╗ė®ą▓ė®ė®čü čģą░ą╝ą░ą░čĆąĮą░ŌĆØ.čģą░ą╝ą░ą░čĆąĮą░ŌĆØ.
- 17. 1.1. ąźąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ ąĮ菹│ą┤ą╗ąĖą╣ąĮ ę»ę»čüčŹčģąĖą╣ąĮąźąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ ąĮ菹│ą┤ą╗ąĖą╣ąĮ ę»ę»čüčŹčģąĖą╣ąĮ ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮ:ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮ: P=Const 껹Ąą┤ čģą░čĆą│ą░ą╗ąĘą░čģ ą┤ą░ąĮP=Const 껹Ąą┤ čģą░čĆą│ą░ą╗ąĘą░čģ ą┤ą░ąĮ ą▒ąŠą┤ąĖčüąŠąŠčü ąĮčī 1 ą╝ąŠą╗čī ąĮ菹│ą┤菹╗ą▒ąŠą┤ąĖčüąŠąŠčü ąĮčī 1 ą╝ąŠą╗čī ąĮ菹│ą┤菹╗ ę»ę»čüčŹčģ菹┤ ąĖą╗čŹčĆčć ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą░ą░ę»ę»čüčŹčģ菹┤ ąĖą╗čŹčĆčć ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą░ą░ ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ čģ菹╝ąČčŹčŹą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ čģ菹╝ąČčŹčŹ 54321 Ōłå╬Ś+Ōłå╬Ś=Ōłå╬Ś+Ōłå╬Ś=Ōłå╬Ś
- 18. 1-čĆ ą╝ė®čĆą┤ą╗ė®ą│ė®ė®: ę«ę»čüčŹčģąĖą╣ąĮ ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮ : ŌłåąØčģ 0 = 2-čĆ ą╝ė®čĆą┤ą╗ė®ą│ė®ė®: ŌłåąØčģ 0 = ( ) ( )ŌłæŌłæ Ōłå╬ŚŌłÆŌłå╬Ś ├Ī├«├ż├©├▒├Į├Ą ┬┐┬┐├▒ ├Ī┬┐├▓ ┬┐┬┐├▒ ,0,0 nn ( ) ( )ŌłæŌłæ Ōłå╬ŚŌłÆŌłå╬Ś ┬┐├Ł├Ī┬┐├▓├Į├Į├Ż├ż├Į├Ą┬┐ ├Ė├Ā├▓ ├Į├Ą.├Ī├«├ż├©├▒ ├Ė├Ā├▓ ,0,0 nn
- 19. 3-čĆ ą╝ė®čĆą┤ą╗ė®ą│ė®ė®: ŌĆó ąŚą░ą┤čĆą░ą╗čŗąĮ ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮ: ŌłåąØčģ ąĘą░ą┤ = - ŌłåąØčģ ę»ę»čü
- 20. 4-čĆ ą╝ė®čĆą┤ą╗ė®ą│ė®ė®: ŌĆó ąŻčĆą▓ą░ą╗ą┤ ąŠčĆąČ ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą░ą░ ą▒ąŠą┤ąĖčüčāčāą┤čŗąĮ ąŠčĆčłąĖčģ čéė®ą╗ė®ą▓ čÅą╗ą│ą░ą░čéą░ą╣ ą▒ąŠą╗ąŠą▓čć ą▒ę»čéčŹčŹą│ą┤čŹčģę»ę»ąĮ ą▒ąŠą┤ąĖčüčāčāą┤ ąĮčī ąĮ菹│菹Į ąĖąČąĖą╗ čéė®ą╗ė®ą▓ ę»ę»čüą│čŹąČ ą▒ą░ą╣ą│ą░ą░ čģąĖą╝ąĖą╣ąĮ 2 čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮ ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ ąĖą╗čĆ菹╗ąĖą╣ąĮ čÅą╗ą│ą░ą▓ą░čĆ ąĮčī čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮ čŹčģ菹Įą┤ ą▒ą░ą╣čüą░ąĮ ą▒ąŠą┤ąĖčü 1 čéė®ą╗ą▓ė®ė®čü ąĮė®ą│ė®ė® čéė®ą╗ė®ą▓čé čłąĖą╗ąČąĖčģąĖą╣ąĮ ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ ąĖą╗čĆ菹╗čé菹╣ čé菹Įčåę»ę» ą▒ą░ą╣ąĮą░.
- 21. ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ├¬├å/├¼├«├½├╝├æ├ó. ├¬├å/├¼├«├½├╝├Ī.├æ ├¬├å/├¼├«├½├╝├Ā.├æ ├Ł┬┐┬┐├░├▒├Ą├©├®├Ą├©├®├Ł┬┐┬┐├░├▒ ├Ą├©├®├Ą├©├®├│├½├│├│├Ī├Ā├½ ├Ā├½├¼├Ā├¦├Ą├©├®├Ą├©├®├Ā├½├¼├Ā├¦ 2.409: 5.393: 4.395: 0 29822 0 22 0 29822 ŌłÆ=Ōłå╬Ś=+ ŌłÆ=Ōłå╬Ś=+ ŌłÆ=Ōłå╬Ś=+ COO COO COO čć ( )├Ł┬┐┬┐├░├▒ ├æ ( )├Ā├½├¼├Ā├¦├æ ( ) ├¼├«├½├╝├¬├å/9.11.4094.395 =ŌłÆŌłÆŌłÆ=Ōłå╬Ś
- 22. 5-čĆ ą╝ė®čĆą┤ą╗ė®ą│ė®ė®: ąÉąĮčģąĮčŗ čéė®ą╗ė®ą▓ ąĮčī ąĖąČąĖą╗ ą▒ąŠą┤ąĖčüčāčāą┤ą░ą░čü ę»ę»čüčü菹Į ąĮ菹│ą┤ą╗ąĖą╣ąĮ čŹčåčüąĖą╣ąĮ čéė®ą╗ė®ą▓ ąĮčī ė®ė®čĆ ė®ė®čĆ ą▒ą░ą╣čģ čāčĆą▓ą░ą╗čŗąĮ ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ ąĖą╗čĆ菹╗ ąĮčī ą▒ę»čéčŹčŹą│ą┤čŹčģę»ę»ąĮ ą▒ąŠą┤ąĖčüčŗąĮ čéė®ą│čüą│ė®ą╗ąĖą╣ąĮ 1čéė®ą╗ą▓ė®ė®čü ąĮė®ą│ė®ė®ą┤ čłąĖą╗ąČąĖčģ ą┐čĆąŠčåąĄčüčüčŗąĮ ą┤čāą╗ą░ą░ąĮčŗ ąĖą╗čĆ菹╗čé菹╣ čé菹Įčåę»ę».
- 23. )(2)(2 2 1 )(2 čāčāčĆ OH čģąĖą╣ O čģąĖą╣ H =+ ą╝ąŠą╗čīą║ą¢čāčāčĆH /242 0 ŌłÆ=Ōłå )(2)(2 2 1 )(2 čłąĖąĮ OH čģąĖą╣ O čģąĖą╣ H =+ ą╝ąŠą╗čīą║ą¢čłąĖąĮH /282 0 ŌłÆ=Ōłå ą╝ąŠą╗čīą║ą¢čłąĖąĮąØčāčāčĆąØH /40000 ŌłÆ=ŌłåŌłÆŌłå=Ōłå