17- Thalamus Limbic System.ppt
Download as ppt, pdf0 likes44 views
The document provides an overview of the thalamus, its structure, and its functions, emphasizing its role as the gateway to the cerebral cortex, integrating sensory information, and connecting various brain regions. Additionally, it discusses the limbic system, detailing its components, such as the hippocampus and amygdala, and their involvement in emotions, memory, and behavioral responses. It highlights important connections and pathways within these brain structures and their implications for memory disorders.
1 of 30
Download to read offline






Ad
Recommended
17- Thalamus & Limbic System.pdffffffffffff
17- Thalamus & Limbic System.pdffffffffffffamalokwumarvelous9
╠²
The document outlines the anatomy, functions, and significance of the thalamus and limbic system. It provides details about the various thalamic nuclei, their connections, and the overarching role of the limbic system in emotional processing, memory, and behavior. Additionally, it highlights the impact of lesions in these brain regions and their relationship with various neurological conditions.17- Thalamus & Limbic System (3).ppt
17- Thalamus & Limbic System (3).pptRazzakurRahman1
╠²
This document provides an overview of the thalamus and limbic system. It begins by listing the learning objectives, which are to describe the anatomy and functions of the thalamus and its nuclei, as well as the main parts and functions of the limbic system. It then details the anatomy of the thalamus, including its surfaces, nuclei, and connections. Each thalamic nucleus is described in terms of its inputs and outputs. Finally, the main structures of the limbic system are defined as the limbic cortex, amygdala, hippocampus, and septal area. Their roles in emotion, memory, and other functions are summarized.L20-Thalamus & Limbic System.ppt
L20-Thalamus & Limbic System.pptAzmiNizar1
╠²
The limbic system is a set of brain structures located on top of the brainstem that are involved in emotions, motivations, and memory formation and storage. Key structures include the hippocampus, which forms and stores memories; the amygdala, which is involved in processing fear and emotions; and the septal nuclei, which is the pleasure center. Damage to limbic structures can result in disorders like amnesia, epilepsy, and schizophrenia.The brain
The brainAnasAlwadi
╠²
The hippocampus is located deep in the brain and plays an important role in memory formation and spatial navigation. It is involved in fear conditioning and damage to the hippocampus has been linked to anxiety disorders like PTSD. The hippocampus contains anxiety cells that respond to unfamiliar places, and suppressing these cells reduces anxiety in mice. CBD may help reduce activity in the amygdala and aid signaling in the endocannabinoid system involving the hippocampus to help treat anxiety symptoms.Limbic system brain
Limbic system brainDr Praveen kumar tripathi
╠²
The limbic system is a set of brain structures located on the edge of the brainstem that are involved in emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. It includes structures like the hippocampus, amygdala, septum, cingulate gyrus, and others. The hippocampus plays a key role in forming new declarative memories and is susceptible to epileptic activity due to its low seizure threshold. Damage to the hippocampus can cause anterograde amnesia by disrupting the transfer of memories from short-term to long-term storage. The cingulate cortex is connected to structures like the thalamus, striatum, and parahippocampal gyrus and isThalamus final
Thalamus finaldrsamianik
╠²
The thalamus is a large egg-shaped structure located in the brain that serves as a relay center for sensory and motor signals to and from the cerebral cortex. It has multiple nuclei that receive input from various sensory systems and project to different regions of the cortex. The thalamus plays an important role in sensory perception and motor control through its connections with the cortex, cerebellum, and basal ganglia.Cns bs2
Cns bs2Abay Alem
╠²
The document summarizes key aspects of the central nervous system. It describes the protective structures of the brain including the cranium, meninges and cerebrospinal fluid. It then outlines the four main regions of the brain - cerebrum, diencephalon, brainstem and cerebellum - and provides details about their structures and functions. The spinal cord is also briefly discussed.Cns bss
Cns bssAbay Alem
╠²
The document summarizes key aspects of the central nervous system. It describes the protective structures of the brain including the cranium, meninges and cerebrospinal fluid. It then outlines the major regions of the brain - cerebrum, diencephalon, brainstem and cerebellum - and provides details about their structure and function. It also discusses the spinal cord, its protective coverings, gray and white matter structure, and ascending and descending tracts.Nervous system gross (1)
Nervous system gross (1)BENZ BUNGGAY
╠²
The document summarizes the nervous system, which is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS contains the brain and spinal cord. The brain is divided into the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain includes the cerebrum and diencephalon. The cerebrum is made up of lobes that control functions like movement, speech, hearing, vision, and smell. The PNS includes cranial and spinal nerves. Spinal nerves emerge from the spinal cord and branch into dorsal and ventral roots.hippocampal formation
hippocampal formationMoitrayee Majumder
╠²
The hippocampus is located in the medial temporal lobe and resembles a seahorse in shape. It contains several layers of cells including the pyramidal cell layer and polymorphic layer. The hippocampus receives input from the entorhinal cortex and sends output primarily through the fornix to structures like the mammillary bodies and septal nuclei. It plays a key role in forming long term memories by converting short term memories through long term potentiation. Diseases like Alzheimer's can damage the hippocampus and impair memory.limbicsystem.pptThe limbic system is a group of interconnected brain structur...
limbicsystem.pptThe limbic system is a group of interconnected brain structur...christsanthoshkumar
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the limbic system, detailing its anatomy, physiological functions, historical context, and interconnections with various brain structures. It discusses the roles of components such as the amygdala and hippocampus in emotional regulation, memory processing, and behavior, while also exploring implications for mental health conditions like schizophrenia and AlzheimerŌĆÖs disease. Additionally, the text highlights the significance of neurotransmitter systems and the impact of limbic structure activity on emotional states and social behavior.Limbic system by dr ali
Limbic system by dr aliOSMAN ALI MD
╠²
The limbic system is a group of brain structures located on the edge of the brain involved in emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. It includes structures like the hippocampus, amygdala, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, and others. The limbic system is interconnected and influences functions like emotional responses, memory formation, instinctual behaviors, and the autonomic nervous system. It is also involved in regulating behaviors important for survival like fear, sex, and memory through connections with the hypothalamus and brainstem.Nervous system of the frog (1)
Nervous system of the frog (1)Timothy Uy
╠²
The document provides a detailed overview of the frog's nervous system, which is divided into the central, peripheral, and sympathetic systems. It highlights the structure and function of different parts, including the brain, spinal cord, and various cranial and spinal nerves. Additionally, it discusses the role of the nervous system in coordinating bodily functions and responding to stimuli.the brain and neurology all parts of brain
the brain and neurology all parts of brainsagy4459
╠²
This document provides information about the structures and functions of the brain and nervous system. It discusses the major parts of the brain including the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and ventricles. It describes the layers of meninges and cerebrospinal fluid. Key structures within the cerebrum like the basal ganglia, limbic system, and lobes are defined. The roles of various brain regions in sensory processing, motor control, emotion, learning, memory and higher cognitive functions are summarized. Common neurological disorders are also briefly explained.Thalamus
ThalamusSachin Adukia
╠²
The thalamus is a paired symmetrical structure located in the center of the brain that relays sensory and motor signals between the brainstem and cerebral cortex. It is divided into several nuclei that have distinct connections and functions. The document provides detailed information on the anatomy, physiology, functional organization and clinical syndromes associated with lesions of different thalamic nuclei. Key points include a description of the gross anatomy and location of the thalamus, its blood supply, the nuclei and their connections, and syndromes associated with infarcts in the posterolateral and medial thalamic territories.Neuropsychology.pptx
Neuropsychology.pptxAditiPandey48
╠²
The document summarizes key structures and functions of the forebrain and brainstem. It discusses the major components of the forebrain - the telencephalon including the cerebral hemispheres, limbic system, and basal ganglia. It also describes the diencephalon including the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus. The brainstem is formed of the medulla, pons, and midbrain. Key structures in the midbrain include the tectum, tegmentum, red nucleus, and substantia nigra. The document outlines functions of sensory processing, motor control, arousal, autonomic functions, and other roles of different brain regions.Limbic.system
Limbic.systemsai nath
╠²
The limbic system includes structures that border the hypothalamus and cerebral cortex. It is involved in emotional processing and behavior. The key structures are the hippocampus, amygdala, cingulate gyrus, and parahippocampal gyrus. These structures are interconnected and connected to the hypothalamus. Damage or abnormalities in limbic system structures have been implicated in conditions like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, anxiety, autism, and Alzheimer's disease. The limbic system plays an important role in emotions, memory, motivation, and other cognitive functions.Central Nervous system CNS
Central Nervous system CNSEduFlash
╠²
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is protected by three layers of tissue called meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. It contains four interconnected ventricles that produce cerebrospinal fluid. The brain is divided into the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain contains the cerebrum and limbic system. The cerebrum is made up of grey matter and white matter and is involved in voluntary movement and complex functions. The spinal cord carries signals between the brain and body and contains 31 pairs of spinal nerves.Limbic system
Limbic systemBharat Bhushan
╠²
This document provides an overview of the limbic system. It discusses the historical aspects of defining the limbic system. It then describes the key components of the limbic system including the amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and connections between these structures like the Papez circuit. Finally, it discusses some clinical implications of the limbic system, focusing on temporal lobe epilepsy which can arise from damage to limbic structures like the hippocampus and amygdala.Thalamus-Anatomy,Physiology,Applied aspects
Thalamus-Anatomy,Physiology,Applied aspectsRanadhi Das
╠²
The thalamus serves as a critical relay station in the brain, integrating general and special sensory impulses, and plays key roles in pain sensation, motor control, sleep, and wakefulness. It is anatomically structured into several nuclei that facilitate specific sensory and motor pathways, while also contributing to functions related to emotion, memory, and personality through connections with other brain regions. Thalamic disorders such as thalamic syndrome and korsakoffŌĆÖs syndrome can lead to significant sensory and memory impairments.Nervous System- Comparative account of Brain.pdf
Nervous System- Comparative account of Brain.pdfPRIMEPRIME4
╠²
The document discusses the comparative anatomy of brains across vertebrates. It notes that all vertebrate brains share a common underlying form and early development, with three initial swellings that become the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Across classes like fish, amphibians, and mammals, the relative sizes of these parts change. In mammals, the forebrain grows much larger and dominates. The functions of different brain regions are also described. The development of brain vesicles and flexures is outlined. Finally, features of the brain in different vertebrates like sharks, frogs, lizards, pigeons, and rabbits are compared.Control and coordination
Control and coordinationChetan Kute
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the human nervous system, detailing its structure, components, and functions. It describes key terms such as stimulus, impulse, neurons, and types of neurons, along with the central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems. Additionally, it outlines the brain's anatomy, the spinal cord's role, and the functions of different neural pathways in response to stimuli.AHD Sl Shahoumi Diencephalon.ppt final Feb 25.ppt
AHD Sl Shahoumi Diencephalon.ppt final Feb 25.pptssuserf131ab
╠²
The document outlines the structure and development of the diencephalon, which includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, ventral thalamus, and epithalamus, highlighting its role as a main processing center for information. It details the embryonic development of the diencephalon, the organization of its nuclei, and the associated functions, including regulation of various visceral activities and sensory processing. Additionally, it discusses various thalamic nuclei and their connections to the cerebral cortex, emphasizing the thalamus as a vital relay station for sensory and motor information.Anatomyofhypothalamusnlimbicsystem 100629082859-phpapp02
Anatomyofhypothalamusnlimbicsystem 100629082859-phpapp02mohammad ayaseh
╠²
The hypothalamus and limbic system help regulate basic physiological needs like blood pressure, body temperature, energy metabolism, reproduction, and stress responses. Specifically, the hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland to regulate these functions. It is connected to the limbic system, brainstem, and spinal cord. The limbic system includes structures like the hippocampus, amygdala, and fornix that are involved in emotion and memory.Anatomy of hypothalamus n limbic system
Anatomy of hypothalamus n limbic systemMBBS IMS MSU
╠²
The hypothalamus is a small region of the brain located below the thalamus. It regulates several important bodily functions through connections to the limbic system, autonomic nervous system, and endocrine system. The hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland and regulates processes like body temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep, and the stress response. The limbic system, including structures like the hippocampus, amygdala, and septum, is involved in emotion and memory processing. Together the hypothalamus and limbic system help regulate key physiological needs such as blood pressure, body temperature, energy metabolism, and reproduction.neural control and coordination chapter 19
neural control and coordination chapter 19lawliet7898
╠²
The document is a presentation on the neural control and coordination, detailing the structure and function of the human neural system, including the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). It explains the role of neurons as the fundamental units of the nervous system, how nerve impulses are generated and transmitted, and provides an overview of the brain's structure and functions. Key topics include the organization of the neural system across different organisms, the anatomy of neurons, and the processing capabilities of the brain.white fibres of cns modified
white fibres of cns modifiedMed Study
╠²
The document discusses the different types of white fibres in the brain, including association fibres, commissural fibres, and projection fibres. It describes key association fibre bundles like the cingulum and fornix. It also explains commissural fibres like the corpus callosum and anterior commissure. Projection fibres including the corticospinal tract are discussed, with details about fibre arrangement in the internal capsule and how lesions can cause motor or sensory deficits. Ascending and descending fibres passing through different parts of the internal capsule are identified.Nervous systems in vertebrates: T.Y.B.Sc. Sem VI Notes
Nervous systems in vertebrates: T.Y.B.Sc. Sem VI NotesDr. Sudesh D. Rathod, B N Bandodkar College of Science
╠²
The document discusses the development and differentiation of the brain in vertebrates. It begins by explaining how the neural tube develops and differentiates into three primary brain vesicles - the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. These later develop into five vesicles. It then describes the relationships between the early brain structures and the mature nervous system. The document also discusses the flexures of the brain, the evolution of the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum across different vertebrates, and provides a comparative overview of brain anatomy in key vertebrate groups.More Related Content
Similar to 17- Thalamus Limbic System.ppt (20)
Nervous system gross (1)
Nervous system gross (1)BENZ BUNGGAY
╠²
The document summarizes the nervous system, which is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS contains the brain and spinal cord. The brain is divided into the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain includes the cerebrum and diencephalon. The cerebrum is made up of lobes that control functions like movement, speech, hearing, vision, and smell. The PNS includes cranial and spinal nerves. Spinal nerves emerge from the spinal cord and branch into dorsal and ventral roots.hippocampal formation
hippocampal formationMoitrayee Majumder
╠²
The hippocampus is located in the medial temporal lobe and resembles a seahorse in shape. It contains several layers of cells including the pyramidal cell layer and polymorphic layer. The hippocampus receives input from the entorhinal cortex and sends output primarily through the fornix to structures like the mammillary bodies and septal nuclei. It plays a key role in forming long term memories by converting short term memories through long term potentiation. Diseases like Alzheimer's can damage the hippocampus and impair memory.limbicsystem.pptThe limbic system is a group of interconnected brain structur...
limbicsystem.pptThe limbic system is a group of interconnected brain structur...christsanthoshkumar
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the limbic system, detailing its anatomy, physiological functions, historical context, and interconnections with various brain structures. It discusses the roles of components such as the amygdala and hippocampus in emotional regulation, memory processing, and behavior, while also exploring implications for mental health conditions like schizophrenia and AlzheimerŌĆÖs disease. Additionally, the text highlights the significance of neurotransmitter systems and the impact of limbic structure activity on emotional states and social behavior.Limbic system by dr ali
Limbic system by dr aliOSMAN ALI MD
╠²
The limbic system is a group of brain structures located on the edge of the brain involved in emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. It includes structures like the hippocampus, amygdala, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, and others. The limbic system is interconnected and influences functions like emotional responses, memory formation, instinctual behaviors, and the autonomic nervous system. It is also involved in regulating behaviors important for survival like fear, sex, and memory through connections with the hypothalamus and brainstem.Nervous system of the frog (1)
Nervous system of the frog (1)Timothy Uy
╠²
The document provides a detailed overview of the frog's nervous system, which is divided into the central, peripheral, and sympathetic systems. It highlights the structure and function of different parts, including the brain, spinal cord, and various cranial and spinal nerves. Additionally, it discusses the role of the nervous system in coordinating bodily functions and responding to stimuli.the brain and neurology all parts of brain
the brain and neurology all parts of brainsagy4459
╠²
This document provides information about the structures and functions of the brain and nervous system. It discusses the major parts of the brain including the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and ventricles. It describes the layers of meninges and cerebrospinal fluid. Key structures within the cerebrum like the basal ganglia, limbic system, and lobes are defined. The roles of various brain regions in sensory processing, motor control, emotion, learning, memory and higher cognitive functions are summarized. Common neurological disorders are also briefly explained.Thalamus
ThalamusSachin Adukia
╠²
The thalamus is a paired symmetrical structure located in the center of the brain that relays sensory and motor signals between the brainstem and cerebral cortex. It is divided into several nuclei that have distinct connections and functions. The document provides detailed information on the anatomy, physiology, functional organization and clinical syndromes associated with lesions of different thalamic nuclei. Key points include a description of the gross anatomy and location of the thalamus, its blood supply, the nuclei and their connections, and syndromes associated with infarcts in the posterolateral and medial thalamic territories.Neuropsychology.pptx
Neuropsychology.pptxAditiPandey48
╠²
The document summarizes key structures and functions of the forebrain and brainstem. It discusses the major components of the forebrain - the telencephalon including the cerebral hemispheres, limbic system, and basal ganglia. It also describes the diencephalon including the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus. The brainstem is formed of the medulla, pons, and midbrain. Key structures in the midbrain include the tectum, tegmentum, red nucleus, and substantia nigra. The document outlines functions of sensory processing, motor control, arousal, autonomic functions, and other roles of different brain regions.Limbic.system
Limbic.systemsai nath
╠²
The limbic system includes structures that border the hypothalamus and cerebral cortex. It is involved in emotional processing and behavior. The key structures are the hippocampus, amygdala, cingulate gyrus, and parahippocampal gyrus. These structures are interconnected and connected to the hypothalamus. Damage or abnormalities in limbic system structures have been implicated in conditions like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, anxiety, autism, and Alzheimer's disease. The limbic system plays an important role in emotions, memory, motivation, and other cognitive functions.Central Nervous system CNS
Central Nervous system CNSEduFlash
╠²
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is protected by three layers of tissue called meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. It contains four interconnected ventricles that produce cerebrospinal fluid. The brain is divided into the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain contains the cerebrum and limbic system. The cerebrum is made up of grey matter and white matter and is involved in voluntary movement and complex functions. The spinal cord carries signals between the brain and body and contains 31 pairs of spinal nerves.Limbic system
Limbic systemBharat Bhushan
╠²
This document provides an overview of the limbic system. It discusses the historical aspects of defining the limbic system. It then describes the key components of the limbic system including the amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and connections between these structures like the Papez circuit. Finally, it discusses some clinical implications of the limbic system, focusing on temporal lobe epilepsy which can arise from damage to limbic structures like the hippocampus and amygdala.Thalamus-Anatomy,Physiology,Applied aspects
Thalamus-Anatomy,Physiology,Applied aspectsRanadhi Das
╠²
The thalamus serves as a critical relay station in the brain, integrating general and special sensory impulses, and plays key roles in pain sensation, motor control, sleep, and wakefulness. It is anatomically structured into several nuclei that facilitate specific sensory and motor pathways, while also contributing to functions related to emotion, memory, and personality through connections with other brain regions. Thalamic disorders such as thalamic syndrome and korsakoffŌĆÖs syndrome can lead to significant sensory and memory impairments.Nervous System- Comparative account of Brain.pdf
Nervous System- Comparative account of Brain.pdfPRIMEPRIME4
╠²
The document discusses the comparative anatomy of brains across vertebrates. It notes that all vertebrate brains share a common underlying form and early development, with three initial swellings that become the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Across classes like fish, amphibians, and mammals, the relative sizes of these parts change. In mammals, the forebrain grows much larger and dominates. The functions of different brain regions are also described. The development of brain vesicles and flexures is outlined. Finally, features of the brain in different vertebrates like sharks, frogs, lizards, pigeons, and rabbits are compared.Control and coordination
Control and coordinationChetan Kute
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the human nervous system, detailing its structure, components, and functions. It describes key terms such as stimulus, impulse, neurons, and types of neurons, along with the central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems. Additionally, it outlines the brain's anatomy, the spinal cord's role, and the functions of different neural pathways in response to stimuli.AHD Sl Shahoumi Diencephalon.ppt final Feb 25.ppt
AHD Sl Shahoumi Diencephalon.ppt final Feb 25.pptssuserf131ab
╠²
The document outlines the structure and development of the diencephalon, which includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, ventral thalamus, and epithalamus, highlighting its role as a main processing center for information. It details the embryonic development of the diencephalon, the organization of its nuclei, and the associated functions, including regulation of various visceral activities and sensory processing. Additionally, it discusses various thalamic nuclei and their connections to the cerebral cortex, emphasizing the thalamus as a vital relay station for sensory and motor information.Anatomyofhypothalamusnlimbicsystem 100629082859-phpapp02
Anatomyofhypothalamusnlimbicsystem 100629082859-phpapp02mohammad ayaseh
╠²
The hypothalamus and limbic system help regulate basic physiological needs like blood pressure, body temperature, energy metabolism, reproduction, and stress responses. Specifically, the hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland to regulate these functions. It is connected to the limbic system, brainstem, and spinal cord. The limbic system includes structures like the hippocampus, amygdala, and fornix that are involved in emotion and memory.Anatomy of hypothalamus n limbic system
Anatomy of hypothalamus n limbic systemMBBS IMS MSU
╠²
The hypothalamus is a small region of the brain located below the thalamus. It regulates several important bodily functions through connections to the limbic system, autonomic nervous system, and endocrine system. The hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland and regulates processes like body temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep, and the stress response. The limbic system, including structures like the hippocampus, amygdala, and septum, is involved in emotion and memory processing. Together the hypothalamus and limbic system help regulate key physiological needs such as blood pressure, body temperature, energy metabolism, and reproduction.neural control and coordination chapter 19
neural control and coordination chapter 19lawliet7898
╠²
The document is a presentation on the neural control and coordination, detailing the structure and function of the human neural system, including the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). It explains the role of neurons as the fundamental units of the nervous system, how nerve impulses are generated and transmitted, and provides an overview of the brain's structure and functions. Key topics include the organization of the neural system across different organisms, the anatomy of neurons, and the processing capabilities of the brain.white fibres of cns modified
white fibres of cns modifiedMed Study
╠²
The document discusses the different types of white fibres in the brain, including association fibres, commissural fibres, and projection fibres. It describes key association fibre bundles like the cingulum and fornix. It also explains commissural fibres like the corpus callosum and anterior commissure. Projection fibres including the corticospinal tract are discussed, with details about fibre arrangement in the internal capsule and how lesions can cause motor or sensory deficits. Ascending and descending fibres passing through different parts of the internal capsule are identified.Nervous systems in vertebrates: T.Y.B.Sc. Sem VI Notes
Nervous systems in vertebrates: T.Y.B.Sc. Sem VI NotesDr. Sudesh D. Rathod, B N Bandodkar College of Science
╠²
The document discusses the development and differentiation of the brain in vertebrates. It begins by explaining how the neural tube develops and differentiates into three primary brain vesicles - the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. These later develop into five vesicles. It then describes the relationships between the early brain structures and the mature nervous system. The document also discusses the flexures of the brain, the evolution of the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum across different vertebrates, and provides a comparative overview of brain anatomy in key vertebrate groups.limbicsystem.pptThe limbic system is a group of interconnected brain structur...
limbicsystem.pptThe limbic system is a group of interconnected brain structur...christsanthoshkumar
╠²
Nervous systems in vertebrates: T.Y.B.Sc. Sem VI Notes
Nervous systems in vertebrates: T.Y.B.Sc. Sem VI NotesDr. Sudesh D. Rathod, B N Bandodkar College of Science
╠²
More from M H (20)
Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.ppt
Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.pptM H
╠²
The document outlines various parasitic infections caused by worms, including Ascaris, Enterobius, Ancylostoma, and Trichuris, detailing their life cycles, clinical features, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options. Infections are primarily asymptomatic but can lead to significant health issues like respiratory problems, gastrointestinal symptoms, and anemia in heavy cases. Effective prevention strategies include improved sanitation, mass treatments, and proper health education.Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.ppt
Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.pptM H
╠²
The document provides a detailed overview of various intestinal parasites, their characteristics, modes of transmission, clinical features, laboratory diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. It discusses infections caused by Ascaris lumbricoides, Enterobius vermicularis, Ancylostoma duodenale, and Trichuris trichiura, highlighting symptoms associated with each, such as abdominal discomfort and respiratory issues. Treatment options generally include anthelmintic medications like mebendazole and albendazole, alongside recommendations for improved sanitation and hygiene.Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.ppt
Ascaris, Enterobius, Hookworm and Trichrous 6.pptM H
╠²
The document provides a detailed overview of various intestinal nematodes, including ascariasis caused by Ascaris lumbricoides, enterobiasis from Enterobius vermicularis, hookworm disease from Ancylostoma duodenale, and trichuriasis from Trichuris trichiura. It covers the geographical distribution, life cycle, pathogenicity, clinical features, laboratory diagnosis, and treatment options for these infections. Key treatments include mebendazole, albendazole, and preventive measures focusing on sanitation and hygiene.fluid an dd.ppt
fluid an dd.pptM H
╠²
The document covers fluid volume disturbances and electrolyte imbalances in the human body, highlighting causes, symptoms, diagnostic evaluations, and management strategies for conditions such as hypovolemia, hypervolemia, hyponatremia, hypernatremia, hypokalemia, and hyperkalemia. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining electrolyte homeostasis for cellular activities, offers detailed information on acid-base balance, and describes various intravenous solutions used for treatment. Additionally, it outlines the roles of body buffer systems in regulating pH levels.fluid a nd.ppt
fluid a nd.pptM H
╠²
The document provides an overview of fluid compartments, daily fluid intake and output, and the importance of electrolyte balance in the body. It details conditions such as fluid volume disturbances, electrolyte imbalances, and their clinical implications, along with diagnostic assessments and management strategies. Additionally, it discusses various IV solutions and buffer systems that regulate acid-base balance in the body.ž¦┘䞦┘ćž» ž¦┘ü ž¦┘äž│┘ä┘ł┘ā┘Ŗ┘ć.pptx
ž¦┘䞦┘ćž» ž¦┘ü ž¦┘äž│┘ä┘ł┘ā┘Ŗ┘ć.pptxM H
╠²
┘Ŗž¬┘垦┘ł┘ä ž¦┘ä┘łž½┘Ŗ┘éž® žŻ┘ć┘ģ┘Ŗž® ž¬žĄ┘å┘Ŗ┘ü ž©┘ä┘ł┘ģ ┘ü┘Ŗ ž¦┘䞬ž«žĘ┘ŖžĘ ž¦┘䞬ž╣┘ä┘Ŗ┘ģ┘Ŗ ┘łžŻ┘ćž»ž¦┘ü┘ć ž¦┘䞬ž▒ž©┘ł┘Ŗž®žī žŁ┘Ŗž½ ┘Ŗž©ž▒ž▓ ž»┘łž▒ ┘ćž░ž¦ ž¦┘䞬žĄ┘å┘Ŗ┘ü ┘ü┘Ŗ ž¬žŁž»┘Ŗž» ž¦┘䞯┘ćž»ž¦┘ü ž¦┘䞬ž╣┘ä┘Ŗ┘ģ┘Ŗž® ┘łž¬ž╣ž▓┘Ŗž▓ ž¦┘䞬ž╣┘ä┘ģ ┘ģ┘å ž«┘䞦┘ä ┘ģž│ž¬┘ł┘Ŗž¦ž¬ ┘ģž¬ž»ž▒ž¼ž® ┘ģ┘å ž¦┘䞥ž╣┘łž©ž®. ┘ā┘ģž¦ ┘Ŗ┘垦┘éž┤ ┘ā┘Ŗ┘ü┘Ŗž® žĄ┘Ŗž¦ž║ž® ž¦┘䞯┘ćž»ž¦┘ü ž¦┘䞬ž╣┘ä┘Ŗ┘ģ┘Ŗž® ž¦┘äž│┘ä┘ł┘ā┘Ŗž® ┘ł┘ü┘鞦┘ŗ ┘ä┘ģž╣ž¦┘Ŗ┘Ŗž▒ ┘ģžŁž»ž»ž® ž¬žČ┘ģ┘å ž¬žŁ┘é┘Ŗ┘é ž¦┘ä┘垬ž¦ž”ž¼ ž¦┘ä┘ģž▒ž¼┘łž®. ž¦┘ä┘łž½┘Ŗ┘éž® ž¬ž│┘äžĘ ž¦┘äžČ┘łžĪ ž╣┘ä┘ē ž¦┘ä┘üž▒┘ł┘é ž¦┘ä┘üž▒ž»┘Ŗž® ž©┘Ŗ┘å ž¦┘ä┘ģž¬ž╣┘ä┘ģ┘Ŗ┘å ┘łžČž▒┘łž▒ž® ž¬ž╣ž»┘Ŗ┘ä ž¦┘äžĘž▒┘é ž¦┘䞬ž╣┘ä┘Ŗ┘ģ┘Ŗž® ž©┘ģž¦ ┘Ŗž¬┘垦ž│ž© ┘ģž╣ ž¦žŁž¬┘Ŗž¦ž¼ž¦ž¬┘ć┘ģ.ž¦┘䞦┘ćž»ž¦ ┘ü ž¦┘äž│┘ä┘ł┘ā┘Ŗ┘ć.pptx
ž¦┘䞦┘ćž»ž¦ ┘ü ž¦┘äž│┘ä┘ł┘ā┘Ŗ┘ć.pptxM H
╠²
ž¬ž¬┘垦┘ł┘ä ž¦┘ä┘łž½┘Ŗ┘éž® žŻ┘ćž»ž¦┘ü ž¦┘äž╣┘ģ┘ä┘Ŗž® ž¦┘䞬ž╣┘ä┘Ŗ┘ģ┘Ŗž® ┘ł┘ā┘Ŗ┘ü┘Ŗž® ž¬┘åžĖ┘Ŗ┘ģ┘枦 ┘łž¬žŁ┘é┘Ŗ┘é┘枦 ┘ł┘ü┘é ┘ģž╣ž¦┘Ŗ┘Ŗž▒ ┘ģžŁž»ž»ž®. ž¬ž╣ž¬┘ģž» ┘ćž░┘ć ž¦┘䞯┘ćž»ž¦┘ü ž╣┘ä┘ē ž¬žĄ┘å┘Ŗ┘ü ž©┘ä┘ł┘ģ ž¦┘äž░┘Ŗ ┘Ŗž▒┘āž▓ ž╣┘ä┘ē ┘ģž│ž¬┘ł┘Ŗž¦ž¬ ž¦┘䞬┘ü┘ā┘Ŗž▒ ž¦┘ä┘ģž«ž¬┘ä┘üž® ┘ł┘Ŗž▒ž┤ž» ž¦┘ä┘ģž╣┘ä┘ģ┘Ŗ┘å ┘ü┘Ŗ ž¬žĄ┘ģ┘Ŗ┘ģ ž¦┘äž»ž▒┘łž│. ž¬ž│ž╣┘ē ž¦┘ä┘łž½┘Ŗ┘éž® ┘䞬žŁž»┘Ŗž» ┘ā┘Ŗ┘ü┘Ŗž® žĄ┘Ŗž¦ž║ž® ž¦┘䞯┘ćž»ž¦┘ü ž¦┘䞬ž╣┘ä┘Ŗ┘ģ┘Ŗž® ž©┘łžČ┘łžŁ ┘łž»┘éž® ┘äžČ┘ģž¦┘å ┘üž¦ž╣┘ä┘Ŗž® ž¦┘䞬ž╣┘ä┘ģ.Chain_of_Infe ction ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼.ppt
Chain_of_Infe ction ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼.pptM H
╠²
The document explains the route of transmission for pathogens, detailing methods by which they move from reservoirs to new hosts. Transmission can occur through direct contact, air, or insects. These modes highlight the various ways pathogens can spread.Chain_of_Infecti on ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼.ppt
Chain_of_Infecti on ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼.pptM H
╠²
The document outlines the stages of infectious disease transmission, starting with the infectious agent, which is a disease-causing microorganism. It details the reservoir host, where pathogens reside, and the portal of exit, which describes how pathogens leave the host. Finally, it explains the routes of transmission, including direct contact, air, and insects.Chain_of_In fection ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼.ppt
Chain_of_In fection ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼.pptM H
╠²
The document outlines the six links in the chain of infection, which include the infectious agent, reservoir host, portal of exit, and route of transmission. It explains that the infectious agent is any disease-causing microorganism, while the reservoir host is the organism that houses these microbes. Additionally, it details how pathogens can exit the reservoir and the various methods through which transmission can occur, such as direct contact and airborne spread.Chain_of_Infe ction ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼.ppt
Chain_of_Infe ction ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ŌĆ¼.pptM H
╠²
The document outlines the six links in the chain of infection, which include the infectious agent, reservoir host, portal of exit, and route of transmission. It explains that an infectious agent is a disease-causing microorganism, while the reservoir host is where microbes reside. Additionally, the document discusses how pathogens exit and transmit to new hosts through various means such as contact or air.fractu re.pptx
fractu re.pptxM H
╠²
A fracture is a disruption in bone continuity, classified as open or closed, with varying degrees of tissue damage. Common types include greenstick, transverse, oblique, and spiral fractures, each with distinct characteristics and causes. Treatment options range from conservative approaches like casts to surgical interventions such as internal and external fixation, with complications like infections and bone death being potential risks.fractur e.pptx
fractur e.pptxM H
╠²
The document discusses the functions and types of bones, as well as fracture classifications and their causes, including the specifics of open and closed fractures. It outlines various treatment methods, including internal and external fixation options, and the complications associated with fractures. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of prevention through nutrition, physical activity, and awareness of bone health, particularly in aging populations.Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Self-Awareness and Self-Care How Professionals Can Avoid Burnout
Self-Awareness and Self-Care How Professionals Can Avoid BurnoutOlaf Kraus de Camargo
╠²
Closing Keynote at the IV OG├ōLNOPOLSKA KONFERENCJA & WARSZTATY
KomunikAACja, Samoswiadomosc, Seksualnosc
June 13th ŌĆō 14th, 2025
An overview of the definition and presentation of burnout in healthcare workers, strategies to prevent it and to build resilience. The presentation also explores the barriers and enablers to introducing wellness strategies in organizations.From Preservation To Regeneration--The Stem Cell Era of Hair Restoration_DrAl...
From Preservation To Regeneration--The Stem Cell Era of Hair Restoration_DrAl...Alan Bauman
╠²
How can the latest in Regenerative Medicine help those suffering from hair loss? Cell Surgical Conference 2025 featured Dr Alan Bauman as a faculty member once again to discuss all things related to hair loss, hair transplantation and the use of regenerative stem cell therapies for hair restoration. Tuberculosis Nepal 2025 National Plan.pptx
Tuberculosis Nepal 2025 National Plan.pptxDr. Anu Marhatta
╠²
The presentation contains preventive therapy, the DOTS program, and the national program of Nepal. This material is intended for educational purposes only.Mastering the Review Article: Structure, Strategy & Success
Mastering the Review Article: Structure, Strategy & SuccessRajendra Dev Bhatt
╠²
A scoping search identified various types of review articles. For this training, most common types were selected, highlighting their key features, strengths, weaknesses, and uses.INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS.pptx
INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS.pptxEliLawluvi
╠²
THE DOCUMENT SUMMARIZES THE KEY COMPONENTS OF INTERPRETING FULL BLOOD CUNTBias, Cofounding Bias, Matching , Blinding
Bias, Cofounding Bias, Matching , BlindingDr. Anu Marhatta
╠²
The slide contains small sippets about the bias, confounding bias, and the ways by which we can remove them. Like by using the methods such as matching and blinding. This slide can be useful as a reference for students in MBBS. JUNE 2025 ONCOLOGY CARTOONS BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRO
JUNE 2025 ONCOLOGY CARTOONS BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATROKanhu Charan
╠²
JUNE 2025 ONCOLOGY CARTOONS BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRORCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient Care
RCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient CarePVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair, Sumanta Kumar Pal, MD, FASCO, David F. McDermott, MD, and Tian Zhang, MD, MHS, prepared useful Practice Aids pertaining to renal cell carcinoma for this CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£RCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient Care.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/4brGF4h. CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until June 30, 2026.Coarse Dispersion, Physical Pharmaceutics
Coarse Dispersion, Physical Pharmaceuticsnishiprakashj
╠²
Its a compilation of unit 3 as per PCI syllabus of B.Pharm IV sem, Subject Physical Pharmaceutics.Clinical Signs Overview: PICCKLE Mnemonic
Clinical Signs Overview: PICCKLE MnemonicDr Aman Suresh Tharayil
╠²
This presentation provides a concise yet comprehensive review of common clinical signs and their diagnostic significance, summarized under the acronym PICCKLE ŌĆō Pallor, Icterus, Clubbing, Cyanosis, Koilonychia, Lymphadenopathy, and Edema. Each condition is defined, followed by key causes, pathophysiology, diagnostic techniques, and clinical relevance. The content is tailored for undergraduate and postgraduate students in medicine and pharmacy, as well as early-career clinicians seeking to reinforce their clinical examination skillsHEALTH CARE PLANNING AND ORGANIZATION OF HEALTH CARE
HEALTH CARE PLANNING AND ORGANIZATION OF HEALTH CAREnawaabaquib
╠²
This PowerPoint presentation covers Unit II: Health Care Planning and Organization of Health Care at Various Levels in a simple and easy-to-understand format. It explains importance of health planning in India. The PPT also includes the structure of the health care system at central, state, and local levels. It is useful for GNM ,BSc And Msc Nursing students. This presentation is also helpful for exam preparation .AlzheimerŌĆÖs Disease Neuroradiology Case Conference: Mastering the New Frontie...
AlzheimerŌĆÖs Disease Neuroradiology Case Conference: Mastering the New Frontie...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Co-Chairs, Gloria Chiang, MD, and Ana M. Franceschi, MD, PhD, discuss AlzheimerŌĆÖs disease in this CME/AAPA activity titled ŌĆ£AlzheimerŌĆÖs Disease Neuroradiology Case Conference: Mastering the New Frontier in Diagnosis and Treatment.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/AAPA information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/43CE1XA. CME/AAPA credit will be available until July 3, 2026.Navigating the Open Enrollment Period for Medicare Supplement Insurance in Sa...
Navigating the Open Enrollment Period for Medicare Supplement Insurance in Sa...dfwdirectinsurance
╠²
Understanding Medicare options can feel like navigating a maze, especially during the open enrollment period. For residents of Sarasota approaching age 65 or already enrolled in Medicare, this window offers a vital opportunity to secure additional health coverage that helps reduce out-of-pocket costs. If you're planning to enhance your Medicare plan, it's essential to understand the rules, deadlines, and options that apply to Medicare supplement insurance in Sarasota.Patient-Centric Frameworks in Desmoid Tumors: Integrating Emerging Science on...
Patient-Centric Frameworks in Desmoid Tumors: Integrating Emerging Science on...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Co-Chairs, Prof. Dr. Patrick Sch├Čffski, MPH, and Breelyn A. Wilky, MD, discuss desmoid tumors in this CME activity titled ŌĆ£Patient-Centric Frameworks in Desmoid Tumors: Integrating Emerging Science on Gamma Secretase Inhibitors for Progressive Disease.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/4iDPUQY. CME credit will be available until June 29, 2026.RCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient Care
RCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient CarePVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
AlzheimerŌĆÖs Disease Neuroradiology Case Conference: Mastering the New Frontie...
AlzheimerŌĆÖs Disease Neuroradiology Case Conference: Mastering the New Frontie...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Navigating the Open Enrollment Period for Medicare Supplement Insurance in Sa...
Navigating the Open Enrollment Period for Medicare Supplement Insurance in Sa...dfwdirectinsurance
╠²
Patient-Centric Frameworks in Desmoid Tumors: Integrating Emerging Science on...
Patient-Centric Frameworks in Desmoid Tumors: Integrating Emerging Science on...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Ad
17- Thalamus Limbic System.ppt
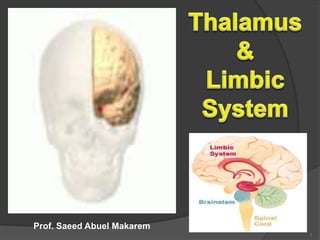
- 1. 1 Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem
- 2. 2 THALAMUS ’āśIt is the largest nuclear mass of the whole body. ’āśIt is the largest part of the diencephalon ’āśIt is formed of two oval masses of grey matter. ’āśIt is the gateway to the cortex. ’āśResemble a small hen. ’āśTogether with the hypothalamus they form the lateral wall of the 3rd ventricle. PONS Thalamus Corpus callosum Midbrain
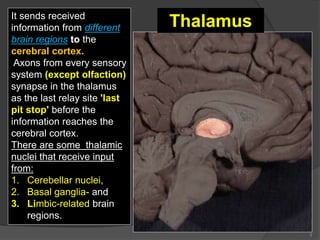
- 3. 3 It sends received information from different brain regions to the cerebral cortex. Axons from every sensory system (except olfaction) synapse in the thalamus as the last relay site 'last pit stop' before the information reaches the cerebral cortex. There are some thalamic nuclei that receive input from: 1. Cerebellar nuclei, 2. Basal ganglia- and 3. Limbic-related brain regions. Thalamus
- 4. It has 4 surfaces & 2 ends. Surfaces Lateral:(L) Posterior limb of the internal capsule Medial: (3) The 3rd ventricle In some people it is connected to the thalamus of the opposite side by the interthalamic connexus, (adhesion) or Massa intermedia. Superior: (s) Lateral ventricle and fornix. Inferior: Hypothalamus, anteriorly & Subthalamus posteriorly. 4 Relations I S L 3 T T
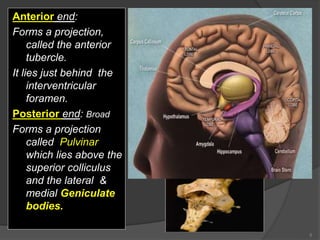
- 5. Anterior end: Forms a projection, called the anterior tubercle. It lies just behind the interventricular foramen. Posterior end: Broad Forms a projection called Pulvinar which lies above the superior colliculus and the lateral & medial Geniculate bodies. 5
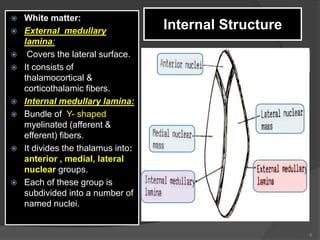
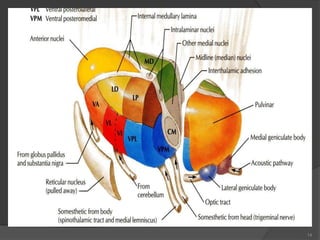
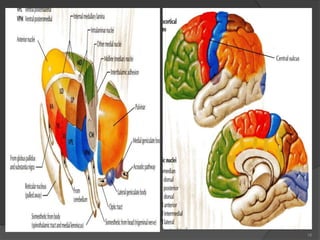
- 6. Internal Structure ’é× White matter: ’é× External medullary lamina: ’é× Covers the lateral surface. ’é× It consists of thalamocortical & corticothalamic fibers. ’é× Internal medullary lamina: ’é× Bundle of Y- shaped myelinated (afferent & efferent) fibers. ’é× It divides the thalamus into: anterior , medial, lateral nuclear groups. ’é× Each of these group is subdivided into a number of named nuclei. 6
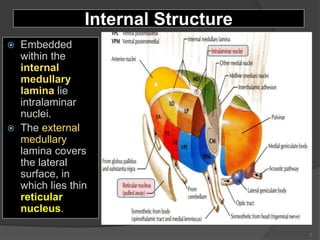
- 7. Internal Structure ’é× Embedded within the internal medullary lamina lie intralaminar nuclei. ’é× The external medullary lamina covers the lateral surface, in which lies thin reticular nucleus. 7
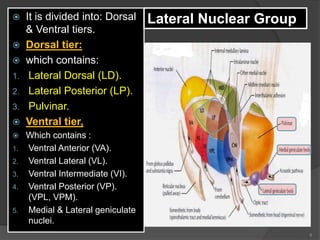
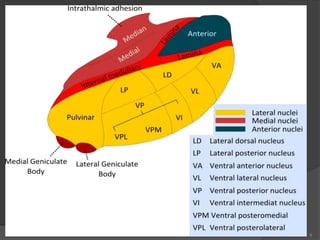
- 8. 8 ’é× It is divided into: Dorsal & Ventral tiers. ’é× Dorsal tier: ’é× which contains: 1. Lateral Dorsal (LD). 2. Lateral Posterior (LP). 3. Pulvinar. ’é× Ventral tier, ’é× Which contains : 1. Ventral Anterior (VA). 2. Ventral Lateral (VL). 3. Ventral Intermediate (VI). 4. Ventral Posterior (VP). (VPL, VPM). 5. Medial & Lateral geniculate nuclei. Lateral Nuclear Group
- 9. 9
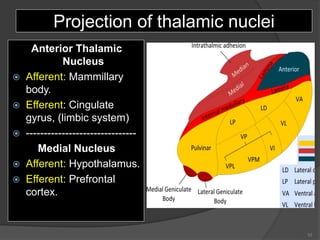
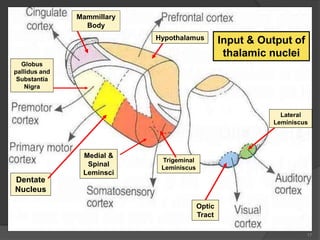
- 10. Projection of thalamic nuclei Anterior Thalamic Nucleus ’é× Afferent: Mammillary body. ’é× Efferent: Cingulate gyrus, (limbic system) ’é× ------------------------------- Medial Nucleus ’é× Afferent: Hypothalamus. ’é× Efferent: Prefrontal cortex. 10
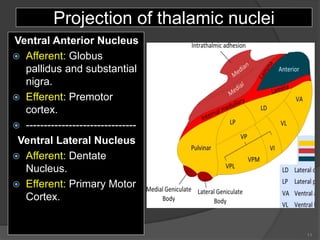
- 11. Projection of thalamic nuclei Ventral Anterior Nucleus ’é× Afferent: Globus pallidus and substantial nigra. ’é× Efferent: Premotor cortex. ’é× ------------------------------- Ventral Lateral Nucleus ’é× Afferent: Dentate Nucleus. ’é× Efferent: Primary Motor Cortex. 11
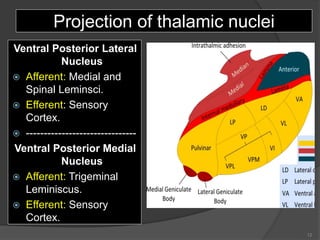
- 12. Projection of thalamic nuclei Ventral Posterior Lateral Nucleus ’é× Afferent: Medial and Spinal Leminsci. ’é× Efferent: Sensory Cortex. ’é× ------------------------------- Ventral Posterior Medial Nucleus ’é× Afferent: Trigeminal Leminiscus. ’é× Efferent: Sensory Cortex. 12
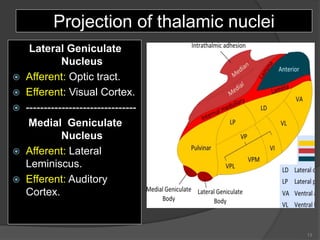
- 13. Projection of thalamic nuclei Lateral Geniculate Nucleus ’é× Afferent: Optic tract. ’é× Efferent: Visual Cortex. ’é× ------------------------------- Medial Geniculate Nucleus ’é× Afferent: Lateral Leminiscus. ’é× Efferent: Auditory Cortex. 13
- 14. 14
- 15. 15
- 16. 16
- 17. 17 Input & Output of thalamic nuclei Mammillary Body Optic Tract Lateral Leminiscus Medial & Spinal Leminsci Trigeminal Leminiscus Globus pallidus and Substantia Nigra Dentate Nucleus Hypothalamus
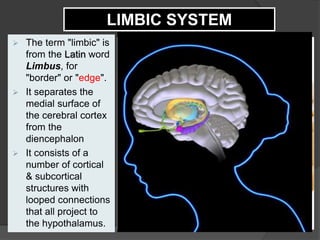
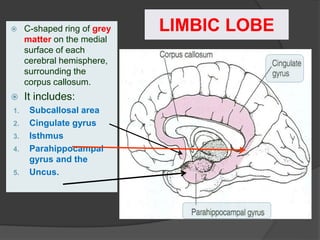
- 18. ’āś The term "limbic" is from the Latin word Limbus, for "border" or "edge". ’āś It separates the medial surface of the cerebral cortex from the diencephalon ’āś It consists of a number of cortical & subcortical structures with looped connections that all project to the hypothalamus. LIMBIC SYSTEM
- 19. It control a variety of functions including: ’üČ Emotions, ’üČ Emotional responses ’üČ Behaviour & Mood (happy, cry, laugh, sad, afraid, aggression, depression) ’üČ Motivation. ’üČ Memory. ’üČ Visceral & Motor responses involved in (sex, pleasure, hunger, and reproduction). ’üČ Olfaction. WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF THE LIMBIC SYSTEM? MEMORY OLFACTION Pleasure sensation
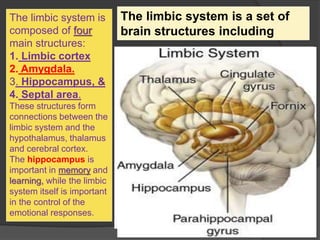
- 20. The limbic system is composed of four main structures: 1. Limbic cortex 2. Amygdala. 3. Hippocampus, & 4. Septal area. These structures form connections between the limbic system and the hypothalamus, thalamus and cerebral cortex. The hippocampus is important in memory and learning, while the limbic system itself is important in the control of the emotional responses. The limbic system is a set of brain structures including
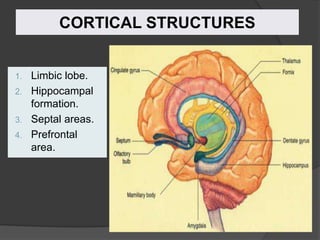
- 21. CORTICAL STRUCTURES 1. Limbic lobe. 2. Hippocampal formation. 3. Septal areas. 4. Prefrontal area.
- 22. LIMBIC LOBE ’é× C-shaped ring of grey matter on the medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere, surrounding the corpus callosum. ’é× It includes: 1. Subcallosal area 2. Cingulate gyrus 3. Isthmus 4. Parahippocampal gyrus and the 5. Uncus.
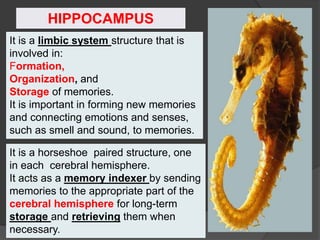
- 23. It is a limbic system structure that is involved in: Formation, Organization, and Storage of memories. It is important in forming new memories and connecting emotions and senses, such as smell and sound, to memories. It is a horseshoe paired structure, one in each cerebral hemisphere. It acts as a memory indexer by sending memories to the appropriate part of the cerebral hemisphere for long-term storage and retrieving them when necessary. HIPPOCAMPUS
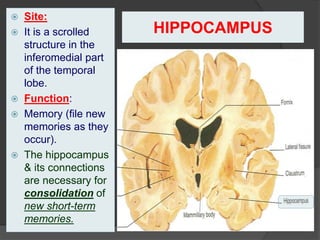
- 24. HIPPOCAMPUS ’é× Site: ’é× It is a scrolled structure in the inferomedial part of the temporal lobe. ’é× Function: ’é× Memory (file new memories as they occur). ’é× The hippocampus & its connections are necessary for consolidation of new short-term memories.
- 25. HIPPOCAMPUS ’é× Its principal efferent pathway is called the: FORNIX: It is C-shaped group of fibers connecting the hippocampus with mammillary body. it consists of: 2 Fimbria, 2 Crus, 1 Body & 2 Column. ’é× The Fornix is an important component of PAPEZ CIRCUIT
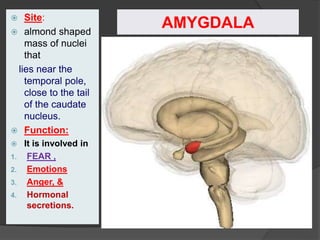
- 26. AMYGDALA ’é× Site: ’é× almond shaped mass of nuclei that lies near the temporal pole, close to the tail of the caudate nucleus. ’é× Function: ’é× It is involved in 1. FEAR , 2. Emotions 3. Anger, & 4. Hormonal secretions.
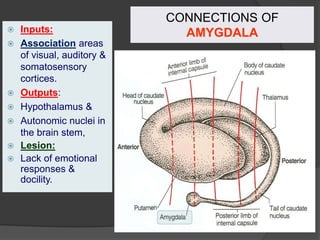
- 27. CONNECTIONS OF AMYGDALA ’é× Inputs: ’é× Association areas of visual, auditory & somatosensory cortices. ’é× Outputs: ’é× Hypothalamus & ’é× Autonomic nuclei in the brain stem, ’é× Lesion: ’é× Lack of emotional responses & docility.
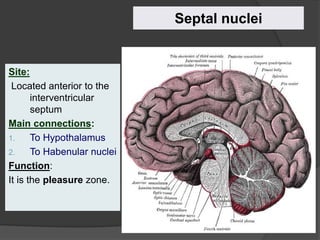
- 28. Site: Located anterior to the interventricular septum Main connections: 1. To Hypothalamus 2. To Habenular nuclei Function: It is the pleasure zone. Septal nuclei
- 29. ’é× KorsakoffŌĆÖs psychosis (Retrograde = loss of new memories at the time of lesion with retained old memories & anterograde amnesia= inability to gain new memories) ’é× Temporal lobe epilepsy ’é× The hippocampus is a common focus site in epilepsy, and can be damaged through chronic seizures. ’é× It is sometimes damaged in diseases such as herpes encephalitis, ’é× AlzheimerŌĆÖs disease: The hippocampus is one of the first brain areas to show damage in Alzheimer's disease ’é× Schizophrenia. Lesions associated with limbic lobe disorders