1_Introduction.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes24 views
The document provides an introduction to algorithms, including definitions, characteristics, and the process of solving problems algorithmically. It discusses what algorithms are, how they are written, analyzed, and designed. Examples are given of algorithms to find the greatest common divisor of two numbers using different approaches like prime factorization, the Euclidean algorithm, and pseudocode. The significance of algorithms and various design approaches are also covered.
1 of 16
Download to read offline




![• English-like: Using some natural language to explain the steps
• Flowchart: Using diagrammatic representation of the steps
• Pseudocode: Using natural language, symbolic abbreviations
and mathematical notations to write a programming language
like structure but not exactly a program.
Algorithm Writing Formats
for i <- 1 to length(A)
x <- A[i]
j <- i
while j > 0 and A[j-1] > x
A[j] <- A[j-1]
j <- j - 1
A[j] <- x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1introduction-230113092204-ced3f6b8/85/1_Introduction-pptx-10-320.jpg)






Recommended
Analysis and Design of Algorithms



Analysis and Design of AlgorithmsBulbul Agrawal
Ěý
Design and Analysis of Algorithm help to design the algorithms for solving different types of problems in Computer Science. It also helps to design and analyze the logic of how the program will work before developing the actual code for a program.DAA 1 ppt.pptx



DAA 1 ppt.pptxRAJESH S
Ěý
Euclid's algorithm is an efficient method for computing the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. It works by repeatedly finding the remainder of dividing the larger number by the smaller number, and then setting the larger number equal to the smaller number and the smaller number equal to the remainder, until the smaller number is zero. The last non-zero remainder is the GCD. The time complexity of Euclid's algorithm is O(log n) where n is the smaller of the two input numbers. Algorithm analysis techniques such as worst-case, best-case, average-case analysis and asymptotic notations can be used to formally analyze the efficiency of algorithms.DAA ppt.pptx



DAA ppt.pptxRAJESH S
Ěý
Euclid's algorithm is an efficient method for computing the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. It works by repeatedly finding the remainder of dividing the larger number by the smaller number, and then setting the larger number equal to the smaller number and the smaller number equal to the remainder, until the smaller number is zero. The last non-zero remainder is the GCD. The time complexity of Euclid's algorithm is O(log n) where n is the smaller of the two input numbers. Algorithm analysis techniques such as worst-case, best-case, average-case analysis and asymptotic notations can be used to formally analyze the efficiency of algorithms.Design and Analysis of Algorithm for II year Computer science and Engineering...



Design and Analysis of Algorithm for II year Computer science and Engineering...Kalpana Devi M
Ěý
This PPT is useful to learn Design and Analysis of AlgorithmADA_Module 1_MN.pptx- Analysis and design of Algorithms



ADA_Module 1_MN.pptx- Analysis and design of Algorithmsmadhu614742
Ěý
Module 1 PPT of Analysis and Design of algorithms-BCS401Design Analysis of Alogorithm 1 ppt 2024.pptx



Design Analysis of Alogorithm 1 ppt 2024.pptxrajesshs31r
Ěý
This document discusses algorithms and their analysis. It begins by defining an algorithm as a sequence of unambiguous instructions to solve a problem in a finite amount of time. It then provides examples of Euclid's algorithm for computing the greatest common divisor. The document goes on to discuss the fundamentals of algorithmic problem solving, including understanding the problem, choosing exact or approximate solutions, and algorithm design techniques. It also covers analyzing algorithms by measuring time and space complexity using asymptotic notations.Analysis of Algorithm full version 2024.pptx



Analysis of Algorithm full version 2024.pptxrajesshs31r
Ěý
This document discusses algorithms and their analysis. It begins by defining an algorithm as a sequence of unambiguous instructions to solve a problem in a finite amount of time. Euclid's algorithm for computing the greatest common divisor is provided as an example. The document then covers fundamentals of algorithmic problem solving, including understanding the problem, choosing exact or approximate solutions, and algorithm design techniques. It also discusses analyzing algorithms based on time and space complexity, as well as worst-case, best-case, and average-case efficiencies. Common problem types like sorting, searching, and graph problems are briefly outlined.Chapter1.1 Introduction.ppt



Chapter1.1 Introduction.pptTekle12
Ěý
This document discusses the design and analysis of algorithms. It begins with defining what an algorithm is - a well-defined computational procedure that takes inputs and produces outputs. It describes analyzing algorithms to determine their efficiency and comparing different algorithms that solve the same problem. The document outlines steps for designing algorithms, including understanding the problem, deciding a solution approach, designing the algorithm, proving correctness, and analyzing and coding it. It discusses using mathematical techniques like asymptotic analysis and Big O notation to analyze algorithms independently of implementations or data. The importance of analyzing algorithms and techniques like divide-and-conquer are also covered.Chapter1.1 Introduction to design and analysis of algorithm.ppt



Chapter1.1 Introduction to design and analysis of algorithm.pptTekle12
Ěý
This document discusses the design and analysis of algorithms. It begins with defining what an algorithm is - a well-defined computational procedure that takes inputs and produces outputs. It describes analyzing algorithms to determine their efficiency and comparing different algorithms that solve the same problem. The document outlines steps for designing algorithms, including understanding the problem, deciding a solution approach, designing the algorithm, proving correctness, and analyzing and coding it. It discusses using mathematical techniques like asymptotic analysis and Big O notation to analyze algorithms independently of implementations or inputs. The importance of analysis is also covered.Algo_Lecture01.pptx



Algo_Lecture01.pptxShaistaRiaz4
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to the CS-701 Advanced Analysis of Algorithms course. It includes the course objectives, which are to design and analyze modern algorithms and evaluate their efficiency. The instructor and contact information are provided. The document outlines the course contents, including topics like sorting algorithms, graph algorithms, and complexity theory. It also discusses what algorithms are, how to represent them, and examples of algorithm applications. Common algorithm design techniques like greedy algorithms and heuristics are introduced.Introduction to Algorithms Complexity Analysis 



Introduction to Algorithms Complexity Analysis Dr. Pankaj Agarwal
Ěý
The document provides an overview of algorithms, including definitions, types, characteristics, and analysis. It begins with step-by-step algorithms to add two numbers and describes the difference between algorithms and pseudocode. It then covers algorithm design approaches, characteristics, classification based on implementation and logic, and analysis methods like a priori and posteriori. The document emphasizes that algorithm analysis estimates resource needs like time and space complexity based on input size.CS8461 - Design and Analysis of Algorithms



CS8461 - Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsKrishnan MuthuManickam
Ěý
Unit 1: Objectives, Introduction, Prime Factorization, Greatest Common Divisor , Fundamentals of Algorithm and Problem Solvingproblem solving and algorithm development



problem solving and algorithm developmentjessicajames100
Ěý
a PowerPoint presentation on object-oriented programming language using Java. it includes algorithm strategy, problem-solving using algorithms, how to develop an algorithm, flowcharts and pseudocode CH-1.1 Introduction (1).pptx



CH-1.1 Introduction (1).pptxsatvikkushwaha1
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to the analysis of algorithms. It discusses algorithm specification, performance analysis frameworks, and asymptotic notations used to analyze algorithms. Key aspects covered include time complexity, space complexity, worst-case analysis, and average-case analysis. Common algorithms like sorting and searching are also mentioned. The document outlines algorithm design techniques such as greedy methods, divide and conquer, and dynamic programming. It distinguishes between recursive and non-recursive algorithms and provides examples of complexity analysis for non-recursive algorithms.Design and Analysis of Algorithms.pptx



Design and Analysis of Algorithms.pptxSyed Zaid Irshad
Ěý
This document discusses algorithms and their analysis. It defines an algorithm as a finite sequence of unambiguous instructions that terminate in a finite amount of time. It discusses areas of study like algorithm design techniques, analysis of time and space complexity, testing and validation. Common algorithm complexities like constant, logarithmic, linear, quadratic and exponential are explained. Performance analysis techniques like asymptotic analysis and amortized analysis using aggregate analysis, accounting method and potential method are also summarized.Dynamic programming



Dynamic programmingInternational Islamic University
Ěý
This document discusses greedy algorithms and dynamic programming. It explains that greedy algorithms find local optimal solutions at each step, while dynamic programming finds global optimal solutions by considering all possibilities. The document also provides examples of problems solved using each approach, such as Prim's algorithm and Dijkstra's algorithm for greedy, and knapsack problems for dynamic programming. It then discusses the matrix chain multiplication problem in detail to illustrate how a dynamic programming solution works by breaking the problem into overlapping subproblems.Algorithm and C code related to data structure



Algorithm and C code related to data structureSelf-Employed
Ěý
Everything lies inside an algorithm in the world of coding and algorithm formation which is the basis of data structure and manipulation of the algorithm in computer science and information technology which is ultimately used to find a particular problems solutionUnit 1, ADA.pptx



Unit 1, ADA.pptxjinkhatima
Ěý
This document provides an overview of algorithms and their analysis. It defines an algorithm as a finite sequence of unambiguous instructions that will terminate in a finite amount of time. Key aspects that algorithms must have are being input-defined, having output, being definite, finite, and effective. The document then discusses steps for designing algorithms like understanding the problem, selecting data structures, and verifying correctness. It also covers analyzing algorithms through evaluating their time complexity, which can be worst-case, best-case, or average-case, and space complexity. Common asymptotic notations like Big-O, Omega, and Theta notation are explained for describing an algorithm's efficiency. Finally, basic complexity classes and their properties are summarized.Part 1.ppt



Part 1.pptRAJESH S
Ěý
The document discusses the fundamentals of algorithmic problem solving. It describes the three main phases of the problem solving process: (1) analyzing the problem by designing an algorithm using pseudocode or flowcharts, (2) implementing the algorithm in a programming language, and (3) maintaining the program if requirements change. It also discusses choosing between exact and approximate algorithms, analyzing algorithms for time and space efficiency, and types of errors like syntax, runtime, and logic errors that can occur when implementing an algorithm.Lec1.ppt



Lec1.pptssuser8bddb2
Ěý
This course introduces students to analyzing and designing computer algorithms. The course objectives are to analyze asymptotic performance, demonstrate familiarity with major algorithms and data structures, apply algorithm design paradigms and analysis methods, and synthesize efficient algorithms for engineering problems. Topics covered include foundations of algorithms, accuracy, efficiency, comparing efficiencies, and understanding various algorithm variants and their design and analysis.Paper Study: Melding the data decision pipeline



Paper Study: Melding the data decision pipelineChenYiHuang5
Ěý
Melding the data decision pipeline: Decision-Focused Learning for Combinatorial Optimization from AAAI2019.
Derive the math equation from myself and match the same result as two mentioned CMU papers [Donti et. al. 2017, Amos et. al. 2017] while applying the same derivation procedure.2. Introduction to Algorithm.pptx



2. Introduction to Algorithm.pptxRahikAhmed1
Ěý
This document introduces algorithms and their basics. It defines an algorithm as a step-by-step procedure to solve a problem and get the desired output. Algorithms can be implemented in different programming languages. Common algorithm categories include search, sort, insert, update, and delete operations on data structures. An algorithm must be unambiguous, have well-defined inputs and outputs, terminate in a finite number of steps, and be feasible with available resources. The document also discusses how to write algorithms, analyze their complexity, and commonly used asymptotic notations like Big-O, Omega, and Theta.LECTURE 0.pptx



LECTURE 0.pptxASVKVinayak
Ěý
This document outlines the course details for EET 2211 Computer Organization and Architecture. It includes the evaluation scheme which consists of internal assessments like midterms and assignments worth 40 marks, and an external end-semester exam worth 60 marks. The topics to be covered are divided into 6 parts that include introduction to computer evolution and performance, computer system organization, arithmetic and logic, the central processing unit, parallel organization, and the control unit. The course will have 3 classes and 1 lab per week over 4 credits.questions.pptx



questions.pptxASVKVinayak
Ěý
The document contains two alphabetical series with missing terms. The first series is SCD, TEF, UGH, __, WKL where the missing term is VJI. The second series is A. CMN, B. UJI, C. VJI, D.IJT, where the missing term in the first series is filled in the second series. There are two alphabetical series presented with missing terms that are filled in by a second series.More Related Content
Similar to 1_Introduction.pptx (20)
Chapter1.1 Introduction.ppt



Chapter1.1 Introduction.pptTekle12
Ěý
This document discusses the design and analysis of algorithms. It begins with defining what an algorithm is - a well-defined computational procedure that takes inputs and produces outputs. It describes analyzing algorithms to determine their efficiency and comparing different algorithms that solve the same problem. The document outlines steps for designing algorithms, including understanding the problem, deciding a solution approach, designing the algorithm, proving correctness, and analyzing and coding it. It discusses using mathematical techniques like asymptotic analysis and Big O notation to analyze algorithms independently of implementations or data. The importance of analyzing algorithms and techniques like divide-and-conquer are also covered.Chapter1.1 Introduction to design and analysis of algorithm.ppt



Chapter1.1 Introduction to design and analysis of algorithm.pptTekle12
Ěý
This document discusses the design and analysis of algorithms. It begins with defining what an algorithm is - a well-defined computational procedure that takes inputs and produces outputs. It describes analyzing algorithms to determine their efficiency and comparing different algorithms that solve the same problem. The document outlines steps for designing algorithms, including understanding the problem, deciding a solution approach, designing the algorithm, proving correctness, and analyzing and coding it. It discusses using mathematical techniques like asymptotic analysis and Big O notation to analyze algorithms independently of implementations or inputs. The importance of analysis is also covered.Algo_Lecture01.pptx



Algo_Lecture01.pptxShaistaRiaz4
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to the CS-701 Advanced Analysis of Algorithms course. It includes the course objectives, which are to design and analyze modern algorithms and evaluate their efficiency. The instructor and contact information are provided. The document outlines the course contents, including topics like sorting algorithms, graph algorithms, and complexity theory. It also discusses what algorithms are, how to represent them, and examples of algorithm applications. Common algorithm design techniques like greedy algorithms and heuristics are introduced.Introduction to Algorithms Complexity Analysis 



Introduction to Algorithms Complexity Analysis Dr. Pankaj Agarwal
Ěý
The document provides an overview of algorithms, including definitions, types, characteristics, and analysis. It begins with step-by-step algorithms to add two numbers and describes the difference between algorithms and pseudocode. It then covers algorithm design approaches, characteristics, classification based on implementation and logic, and analysis methods like a priori and posteriori. The document emphasizes that algorithm analysis estimates resource needs like time and space complexity based on input size.CS8461 - Design and Analysis of Algorithms



CS8461 - Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsKrishnan MuthuManickam
Ěý
Unit 1: Objectives, Introduction, Prime Factorization, Greatest Common Divisor , Fundamentals of Algorithm and Problem Solvingproblem solving and algorithm development



problem solving and algorithm developmentjessicajames100
Ěý
a PowerPoint presentation on object-oriented programming language using Java. it includes algorithm strategy, problem-solving using algorithms, how to develop an algorithm, flowcharts and pseudocode CH-1.1 Introduction (1).pptx



CH-1.1 Introduction (1).pptxsatvikkushwaha1
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to the analysis of algorithms. It discusses algorithm specification, performance analysis frameworks, and asymptotic notations used to analyze algorithms. Key aspects covered include time complexity, space complexity, worst-case analysis, and average-case analysis. Common algorithms like sorting and searching are also mentioned. The document outlines algorithm design techniques such as greedy methods, divide and conquer, and dynamic programming. It distinguishes between recursive and non-recursive algorithms and provides examples of complexity analysis for non-recursive algorithms.Design and Analysis of Algorithms.pptx



Design and Analysis of Algorithms.pptxSyed Zaid Irshad
Ěý
This document discusses algorithms and their analysis. It defines an algorithm as a finite sequence of unambiguous instructions that terminate in a finite amount of time. It discusses areas of study like algorithm design techniques, analysis of time and space complexity, testing and validation. Common algorithm complexities like constant, logarithmic, linear, quadratic and exponential are explained. Performance analysis techniques like asymptotic analysis and amortized analysis using aggregate analysis, accounting method and potential method are also summarized.Dynamic programming



Dynamic programmingInternational Islamic University
Ěý
This document discusses greedy algorithms and dynamic programming. It explains that greedy algorithms find local optimal solutions at each step, while dynamic programming finds global optimal solutions by considering all possibilities. The document also provides examples of problems solved using each approach, such as Prim's algorithm and Dijkstra's algorithm for greedy, and knapsack problems for dynamic programming. It then discusses the matrix chain multiplication problem in detail to illustrate how a dynamic programming solution works by breaking the problem into overlapping subproblems.Algorithm and C code related to data structure



Algorithm and C code related to data structureSelf-Employed
Ěý
Everything lies inside an algorithm in the world of coding and algorithm formation which is the basis of data structure and manipulation of the algorithm in computer science and information technology which is ultimately used to find a particular problems solutionUnit 1, ADA.pptx



Unit 1, ADA.pptxjinkhatima
Ěý
This document provides an overview of algorithms and their analysis. It defines an algorithm as a finite sequence of unambiguous instructions that will terminate in a finite amount of time. Key aspects that algorithms must have are being input-defined, having output, being definite, finite, and effective. The document then discusses steps for designing algorithms like understanding the problem, selecting data structures, and verifying correctness. It also covers analyzing algorithms through evaluating their time complexity, which can be worst-case, best-case, or average-case, and space complexity. Common asymptotic notations like Big-O, Omega, and Theta notation are explained for describing an algorithm's efficiency. Finally, basic complexity classes and their properties are summarized.Part 1.ppt



Part 1.pptRAJESH S
Ěý
The document discusses the fundamentals of algorithmic problem solving. It describes the three main phases of the problem solving process: (1) analyzing the problem by designing an algorithm using pseudocode or flowcharts, (2) implementing the algorithm in a programming language, and (3) maintaining the program if requirements change. It also discusses choosing between exact and approximate algorithms, analyzing algorithms for time and space efficiency, and types of errors like syntax, runtime, and logic errors that can occur when implementing an algorithm.Lec1.ppt



Lec1.pptssuser8bddb2
Ěý
This course introduces students to analyzing and designing computer algorithms. The course objectives are to analyze asymptotic performance, demonstrate familiarity with major algorithms and data structures, apply algorithm design paradigms and analysis methods, and synthesize efficient algorithms for engineering problems. Topics covered include foundations of algorithms, accuracy, efficiency, comparing efficiencies, and understanding various algorithm variants and their design and analysis.Paper Study: Melding the data decision pipeline



Paper Study: Melding the data decision pipelineChenYiHuang5
Ěý
Melding the data decision pipeline: Decision-Focused Learning for Combinatorial Optimization from AAAI2019.
Derive the math equation from myself and match the same result as two mentioned CMU papers [Donti et. al. 2017, Amos et. al. 2017] while applying the same derivation procedure.2. Introduction to Algorithm.pptx



2. Introduction to Algorithm.pptxRahikAhmed1
Ěý
This document introduces algorithms and their basics. It defines an algorithm as a step-by-step procedure to solve a problem and get the desired output. Algorithms can be implemented in different programming languages. Common algorithm categories include search, sort, insert, update, and delete operations on data structures. An algorithm must be unambiguous, have well-defined inputs and outputs, terminate in a finite number of steps, and be feasible with available resources. The document also discusses how to write algorithms, analyze their complexity, and commonly used asymptotic notations like Big-O, Omega, and Theta.More from ASVKVinayak (8)
LECTURE 0.pptx



LECTURE 0.pptxASVKVinayak
Ěý
This document outlines the course details for EET 2211 Computer Organization and Architecture. It includes the evaluation scheme which consists of internal assessments like midterms and assignments worth 40 marks, and an external end-semester exam worth 60 marks. The topics to be covered are divided into 6 parts that include introduction to computer evolution and performance, computer system organization, arithmetic and logic, the central processing unit, parallel organization, and the control unit. The course will have 3 classes and 1 lab per week over 4 credits.questions.pptx



questions.pptxASVKVinayak
Ěý
The document contains two alphabetical series with missing terms. The first series is SCD, TEF, UGH, __, WKL where the missing term is VJI. The second series is A. CMN, B. UJI, C. VJI, D.IJT, where the missing term in the first series is filled in the second series. There are two alphabetical series presented with missing terms that are filled in by a second series.12-greedy.ppt



12-greedy.pptASVKVinayak
Ěý
The document discusses greedy algorithms for optimization problems. It provides examples of greedy algorithms for counting money, interval scheduling, and minimizing lateness. For interval scheduling, the greedy algorithm of scheduling jobs in order of earliest finish time is proven to be optimal. For minimizing lateness, the greedy algorithm of scheduling jobs in order of earliest deadline is shown to produce a schedule with no idle time and no inversions.Digital Logic-Lecture19.pptx



Digital Logic-Lecture19.pptxASVKVinayak
Ěý
This document discusses code conversion between different digital systems. It provides an example of converting between binary coded decimal (BCD) code and excess-3 code using a combinational logic circuit. The circuit is designed using a truth table to map the input and output bits. Logic gates are then used to implement the mapping and produce the output bit combinations specified by the target code. Another example provided is the design of a circuit to convert a 4-bit binary number to a 4-bit Gray code.26.ppt



26.pptASVKVinayak
Ěý
This document discusses financial institutions and markets that coordinate saving and investment. It describes how savers provide funds to borrowers through both direct financial markets like the stock and bond markets, as well as indirect financial intermediaries like banks and mutual funds. The financial system matches savings with investments and determines interest rates through the market for loanable funds, where the supply of saved funds meets demand from borrowers. Government policies around taxes, spending, and deficits can impact incentives for saving and investment and shift supply and demand in this market.interdependence.ppt



interdependence.pptASVKVinayak
Ěý
The document discusses the concept of comparative advantage and how specialization and trade according to comparative advantage benefits individuals and societies. It explains that while one party may have an absolute advantage in producing both goods, comparative advantage looks at opportunity cost and determines that parties are better off specializing in the good where they have a lower opportunity cost. This allows for gains from trade as parties produce according to their comparative advantage and trade with one another.LOGIC DESIGN-Lecture24.pptx



LOGIC DESIGN-Lecture24.pptxASVKVinayak
Ěý
This document discusses combinational logic and multiplexers. It provides details on multiplexers, including that they are combinational circuits that select an input line based on selection lines. A 2n-to-1 multiplexer has 2n input lines and n selection lines. The document then gives examples of HDL code for 2-to-1 and 4-to-1 multiplexers. It also explains that Boolean functions can be implemented using multiplexers, and provides an example of HDL code to do so for a 4-input function.Recently uploaded (20)
cPanel Dedicated Server Hosting at Top-Tier Data Center comes with a Premier ...



cPanel Dedicated Server Hosting at Top-Tier Data Center comes with a Premier ...soniaseo850
Ěý
cPanel Dedicated Server Hosting at Top-Tier Data Center comes with a Premier Metal License. Enjoy powerful performance, full control & enhanced security.BSEO - The Ultimate GA4 Audit - Anna Lewis - Polka Dot Data



BSEO - The Ultimate GA4 Audit - Anna Lewis - Polka Dot DataAnna Lewis
Ěý
Discover Anna Lewis şÝşÝߣs on what to include when auditing your GA4 and the key points people usually miss!LITERATURE-MODEL.pptxddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddd



LITERATURE-MODEL.pptxdddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddMaimai708843
Ěý
Ăą»ĺłó´ÚłÜ´Ç˛őłó˛µ´ÇłÜłó˛µ´Çłó˛őľ±´Ç˛µ˛őHadoop-and-R-Programming-Powering-Big-Data-Analytics.pptx



Hadoop-and-R-Programming-Powering-Big-Data-Analytics.pptxMdTahammulNoor
Ěý
Hadoop and its uses in data analyticsIntroduction to Microsoft Power BI is a business analytics service



Introduction to Microsoft Power BI is a business analytics serviceKongu Engineering College, Perundurai, Erode
Ěý
Microsoft Power BI is a business analytics service that allows users to visualize data and share insights across an organization, or embed them in apps or websites, offering a consolidated view of data from both on-premises and cloud sourcesVisionaize for Visionaize AI Powered Solution For Thermal Power Plant.pptx



Visionaize for Visionaize AI Powered Solution For Thermal Power Plant.pptxSumantaBasu12
Ěý
Visionaize AI Powered Solution For Thermal Power PlantData-Ethics-and-Privacy-What-Every-Analyst-Should-Know



Data-Ethics-and-Privacy-What-Every-Analyst-Should-KnowOzias Rondon
Ěý
In the era of big data and AI, ethical data handling is no longer optional—it's essential. This presentation explores the core principles of data ethics, data privacy regulations (like GDPR), consent, bias, and the responsibilities analysts must uphold. Learn how to protect users and build trust through responsible data practices.Information Security Management-Planning 1.pptx



Information Security Management-Planning 1.pptxFrancisFayiah
Ěý
nformation Security Management Planning refers to the process of designing and implementing a structured approach to protect an organization’s information assets against threats, vulnerabilities, and risks. It is an essential part of overall corporate governance and risk management. Here's a comprehensive overview:The rise of AI Agents - Beyond Automation_ The Rise of AI Agents in Service ...



The rise of AI Agents - Beyond Automation_ The Rise of AI Agents in Service ...Yasen Lilov
Ěý
Deep dive into how agency service-based business can leverage AI and AI Agents for automation and scale. Case Study example with platforms used outlined in the slides.brightonSEO - Metehan Yesilyurt - Generative AI & GEO: the new SEO race and h...



brightonSEO - Metehan Yesilyurt - Generative AI & GEO: the new SEO race and h...Metehan YeĹźilyurt
Ěý
This talk is for SEO experts, consultants, leads, managers, founders and growth marketers
SEO has evolved significantly over the years; when the user first entered the field, tactics like meta keywords and backlink packages were commonplace. With the rapid advancements in AI, their approach to SEO has transformed, necessitating constant adaptation and refinement of techniques.
As tools like Perplexity, SearchGPT emerge, the landscape will shift further with new algorithms, rankings, and optimization strategies, pushing the boundaries of SEO expertise even further.
Metehan is a seasoned Growth Lead with extensive experience in SEO, recognized for driving impactful growth through AI-driven solutions. Known for his unique expertise, he consistently delivers data-backed, effective organic growth strategies.Introduction to Microsoft Power BI is a business analytics service



Introduction to Microsoft Power BI is a business analytics serviceKongu Engineering College, Perundurai, Erode
Ěý
brightonSEO - Metehan Yesilyurt - Generative AI & GEO: the new SEO race and h...



brightonSEO - Metehan Yesilyurt - Generative AI & GEO: the new SEO race and h...Metehan YeĹźilyurt
Ěý
1_Introduction.pptx
- 1. Introduction to Algorithm Design Rangaballav Pradhan Asst. Professor, Dept. of CSE, ITER, SOA Deemed to be University
- 2. Introducing Algorithms •What is an Algorithm? • Computer • Computing/ Data Processing • Complex Operations • Programming Language • A program • A Problem • An Algorithm • A solution
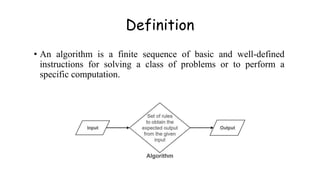
- 3. Definition • An algorithm is a finite sequence of basic and well-defined instructions for solving a class of problems or to perform a specific computation.
- 4. Characteristics of algorithms •Input ≥ 0 •Output ≥ 1 •Finiteness •Definiteness •Effectiveness •Correctness •Efficiency
- 5. Process of problem solving • Define the problem (specifications, input and constraints) • Develop a model using problem specifications and constraints • Define the specification of an algorithm • Design an algorithm using a suitable design approach • Verify the correctness of the algorithm • Analysis of the algorithm • Implement the algorithm • Program testing • Documentation or publish the algorithm
- 6. Significance of algorithms • To find the solutions for complex computational problems • To improve the efficiency of a computer program • Proper utilization of computing resources • To handle the processing of larger problem instances efficiently
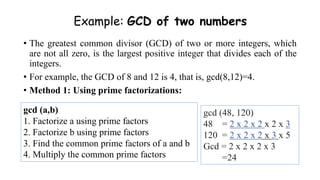
- 7. Example: GCD of two numbers • The greatest common divisor (GCD) of two or more integers, which are not all zero, is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers. • For example, the GCD of 8 and 12 is 4, that is, gcd(8,12)=4. • Method 1: Using prime factorizations: gcd (48, 120) 48 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 120 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 5 Gcd = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 =24 gcd (a,b) 1. Factorize a using prime factors 2. Factorize b using prime factors 3. Find the common prime factors of a and b 4. Multiply the common prime factors
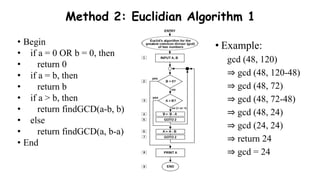
- 8. • Begin • if a = 0 OR b = 0, then • return 0 • if a = b, then • return b • if a > b, then • return findGCD(a-b, b) • else • return findGCD(a, b-a) • End Method 2: Euclidian Algorithm 1 • Example: gcd (48, 120) ⇒ gcd (48, 120-48) ⇒ gcd (48, 72) ⇒ gcd (48, 72-48) ⇒ gcd (48, 24) ⇒ gcd (24, 24) ⇒ return 24 ⇒ gcd = 24
- 9. • If A = 0 then • GCD(a, b) = b • If b = 0 then • GCD(a, b) = a • GCD(a, b) = GCD(b, a % b) Method 3: Euclidian Algorithm 2 • Example: gcd (48, 120) ⇒ gcd (120, 48) ⇒ gcd (48, 24) ⇒ gcd (24, 0) ⇒ gcd = 24
- 10. • English-like: Using some natural language to explain the steps • Flowchart: Using diagrammatic representation of the steps • Pseudocode: Using natural language, symbolic abbreviations and mathematical notations to write a programming language like structure but not exactly a program. Algorithm Writing Formats for i <- 1 to length(A) x <- A[i] j <- i while j > 0 and A[j-1] > x A[j] <- A[j-1] j <- j - 1 A[j] <- x
- 12. • The problem definition that is to be solved by the algorithm. • The constraints of the problem that must be considered while solving the problem. • The input to be taken to solve the problem instance. • The output to be expected when the problem is solved. • The design approach to be followed. Algorithm Design: Pre-requisites
- 13. • Various design approaches exist: 1. Brute force 2. Divide and conquer 3. Greedy algorithm 4. Dynamic programming 5. Backtracking algorithm 6. Branch and Bound Algorithm Design: Formulation/Definition
- 14. • Recursive vs Iterative: A recursive algorithm calls itself again and again until a base condition is met whereas iterative algorithms use loops to solve any problem. • Exact vs Approximate: Algorithms that are capable of finding an exact optimal solution for a problem are known as the exact algorithm. For some problems, it is not possible to find the most optimized solution. In such cases an approximation algorithm is used that finds an approximate solution to a problem which may not be optimal but is near optimal. • Serial vs Parallel vs Distributed: In serial algorithms, one instruction is executed at a time while parallel algorithms divide the problem into subproblems and execute them on different processors. If parallel algorithms are distributed on different machines over a network, then they are known as distributed algorithms. Algorithm Design: Testing/Implementation
- 15. • Analysis refers to the computation of complexity of a given algorithm • Analysis gives a measure of efficiency of the algorithm in terms of resource consumption • Mainly two parameters are considered for analysis of algorithms: the amount of running time and the memory space. • The running time of an algorithm is expressed as a function of the input size and is known as time complexity and the volume of memory space consumed is known as space complexity. Analysis of Algorithm
- 16. • Priori Analysis: A priori analysis means checking the algorithm before its implementation. In this, the algorithm is checked when it is written in the form of theoretical steps. This Efficiency of an algorithm is measured by assuming that all other factors, for example, processor speed, are constant and have no effect on the implementation. It is in this method, that the Algorithm Complexity is determined. • Posterior Analysis: A posterior analysis means checking the algorithm after its implementation. In this, the algorithm is checked by implementing it in any programming language and executing it. This analysis helps to get the actual and real analysis report about correctness, space required, time consumed etc. Analysis of Algorithm
















