26.ppt
- 1. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western 26 Saving, Investment, and the Financial System
- 2. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western The Financial System ? The financial system consists of the group of institutions in the economy that help to match one personˇŻs saving with another personˇŻs investment. ? It moves the economyˇŻs scarce resources from savers to borrowers.
- 3. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS IN THE U.S. ECONOMY ? The financial system is made up of financial institutions that coordinate the actions of savers and borrowers. ? Financial institutions can be grouped into two different categories: financial markets and financial intermediaries.
- 4. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS IN THE U.S. ECONOMY ? Financial Markets ? Stock Market ? Bond Market ? Financial Intermediaries ? Banks ? Mutual Funds
- 5. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS IN THE U.S. ECONOMY ? Financial markets are the institutions through which savers can directly provide funds to borrowers. ? Financial intermediaries are financial institutions through which savers can indirectly provide funds to borrowers.
- 6. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Financial Markets ? The Bond Market ? A bond is a certificate of indebtedness that specifies obligations of the borrower to the holder of the bond. ? Characteristics of a Bond ? Term: The length of time until the bond matures. ? Credit Risk: The probability that the borrower will fail to pay some of the interest or principal. ? Tax Treatment: The way in which the tax laws treat the interest on the bond. ? Municipal bonds are federal tax exempt. IOU
- 7. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Financial Markets ? The Stock Market ? Stock represents a claim to partial ownership in a firm and is therefore, a claim to the profits that the firm makes. ? The sale of stock to raise money is called equity financing. ? Compared to bonds, stocks offer both higher risk and potentially higher returns. ? The most important stock exchanges in the United States are the New York Stock Exchange, the American Stock Exchange, and NASDAQ.
- 8. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Financial Markets ? The Stock Market ? Most newspaper stock tables provide the following information: ? Price (of a share) ? Volume (number of shares sold) ? Dividend (profits paid to stockholders) ? Price-earnings ratio
- 9. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Financial Intermediaries ? Financial intermediaries are financial institutions through which savers can indirectly provide funds to borrowers.
- 10. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Financial Intermediaries ? Banks ? take deposits from people who want to save and use the deposits to make loans to people who want to borrow. ? pay depositors interest on their deposits and charge borrowers slightly higher interest on their loans.
- 11. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Financial Intermediaries ? Banks ? Banks help create a medium of exchange by allowing people to write checks against their deposits. ? A medium of exchanges is an item that people can easily use to engage in transactions. ? This facilitates the purchases of goods and services.
- 12. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Financial Intermediaries ? Mutual Funds ? A mutual fund is an institution that sells shares to the public and uses the proceeds to buy a portfolio, of various types of stocks, bonds, or both. ? They allow people with small amounts of money to easily diversify.
- 13. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Financial Intermediaries ? Other Financial Institutions ? Credit unions ? Pension funds ? Insurance companies ? Loan sharks
- 14. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western SAVING AND INVESTMENT IN THE NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTS ? Recall that GDP is both total income in an economy and total expenditure on the economyˇŻs output of goods and services: Y = C + I + G + NX
- 15. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Some Important Identities ? Assume a closed economy ¨C one that does not engage in international trade: Y = C + I + G
- 16. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Some Important Identities ? Now, subtract C and G from both sides of the equation: Y ¨C C ¨C G =I ? The left side of the equation is the total income in the economy after paying for consumption and government purchases and is called national saving, or just saving (S).
- 17. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Some Important Identities ? Substituting S for Y - C - G, the equation can be written as: S = I
- 18. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Some Important Identities ? National saving, or saving, is equal to: S = I S = Y ¨C C ¨C G S = (Y ¨C T ¨C C) + (T ¨C G)
- 19. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western The Meaning of Saving and Investment ? National Saving ? National saving is the total income in the economy that remains after paying for consumption and government purchases. ? Private Saving ? Private saving is the amount of income that households have left after paying their taxes and paying for their consumption. Private saving = (Y ¨C T ¨C C)
- 20. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western The Meaning of Saving and Investment ? Public Saving ? Public saving is the amount of tax revenue that the government has left after paying for its spending. Public saving = (T ¨C G)
- 21. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western The Meaning of Saving and Investment ? Surplus and Deficit ? If T > G, the government runs a budget surplus because it receives more money than it spends. ? The surplus of T - G represents public saving. ? If G > T, the government runs a budget deficit because it spends more money than it receives in tax revenue.
- 22. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western The Meaning of Saving and Investment ? For the economy as a whole, saving must be equal to investment. S = I
- 23. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western THE MARKET FOR LOANABLE FUNDS ? Financial markets coordinate the economyˇŻs saving and investment in the market for loanable funds.
- 24. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western THE MARKET FOR LOANABLE FUNDS ? The market for loanable funds is the market in which those who want to save supply funds and those who want to borrow to invest demand funds.
- 25. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western THE MARKET FOR LOANABLE FUNDS ? Loanable funds refers to all income that people have chosen to save and lend out, rather than use for their own consumption.
- 26. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Supply and Demand for Loanable Funds ? The supply of loanable funds comes from people who have extra income they want to save and lend out. ? The demand for loanable funds comes from households and firms that wish to borrow to make investments.
- 27. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Supply and Demand for Loanable Funds ? The interest rate is the price of the loan. ? It represents the amount that borrowers pay for loans and the amount that lenders receive on their saving. ? The interest rate in the market for loanable funds is the real interest rate.
- 28. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Supply and Demand for Loanable Funds ? Financial markets work much like other markets in the economy. ? The equilibrium of the supply and demand for loanable funds determines the real interest rate.
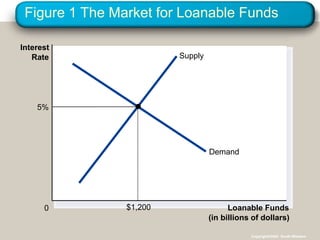
- 29. Figure 1 The Market for Loanable Funds Loanable Funds (in billions of dollars) 0 Interest Rate Supply Demand 5% $1,200 Copyright?2004 South-Western
- 30. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Supply and Demand for Loanable Funds ? Government Policies That Affect Saving and Investment ? Taxes and saving ? Taxes and investment ? Government budget deficits
- 31. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Policy 1: Saving Incentives ? Taxes on interest income substantially reduce the future payoff from current saving and, as a result, reduce the incentive to save.
- 32. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Policy 1: Saving Incentives ? A tax decrease increases the incentive for households to save at any given interest rate. ? The supply of loanable funds curve shifts to the right. ? The equilibrium interest rate decreases. ? The quantity demanded for loanable funds increases.
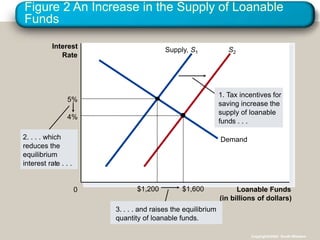
- 33. Figure 2 An Increase in the Supply of Loanable Funds Loanable Funds (in billions of dollars) 0 Interest Rate Supply, S1 S2 2. . . . which reduces the equilibrium interest rate . . . 3. . . . and raises the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds. Demand 1. Tax incentives for saving increase the supply of loanable funds . . . 5% $1,200 4% $1,600 Copyright?2004 South-Western
- 34. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Policy 1: Saving Incentives ? If a change in tax law encourages greater saving, the result will be lower interest rates and greater investment.
- 35. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Policy 2: Investment Incentives ? An investment tax credit increases the incentive to borrow. ? Increases the demand for loanable funds. ? Shifts the demand curve to the right. ? Results in a higher interest rate and a greater quantity saved.
- 36. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Policy 2: Investment Incentives ? If a change in tax laws encourages greater investment, the result will be higher interest rates and greater saving.
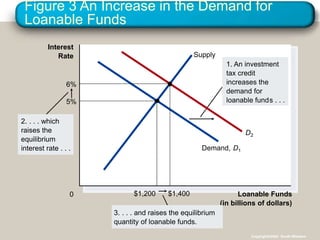
- 37. Figure 3 An Increase in the Demand for Loanable Funds Loanable Funds (in billions of dollars) 0 Interest Rate 1. An investment tax credit increases the demand for loanable funds . . . 2. . . . which raises the equilibrium interest rate . . . 3. . . . and raises the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds. Supply Demand, D1 D2 5% $1,200 6% $1,400 Copyright?2004 South-Western
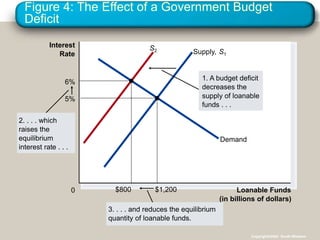
- 38. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Policy 3: Government Budget Deficits and Surpluses ? When the government spends more than it receives in tax revenues, the short fall is called the budget deficit. ? The accumulation of past budget deficits is called the government debt.
- 39. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Policy 3: Government Budget Deficits and Surpluses ? Government borrowing to finance its budget deficit reduces the supply of loanable funds available to finance investment by households and firms. ? This fall in investment is referred to as crowding out. ? The deficit borrowing crowds out private borrowers who are trying to finance investments.
- 40. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Policy 3: Government Budget Deficits and Surpluses ? A budget deficit decreases the supply of loanable funds. ? Shifts the supply curve to the left. ? Increases the equilibrium interest rate. ? Reduces the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds.
- 41. Figure 4: The Effect of a Government Budget Deficit Loanable Funds (in billions of dollars) 0 Interest Rate 3. . . . and reduces the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds. S2 2. . . . which raises the equilibrium interest rate . . . Supply, S1 Demand $1,200 5% $800 6% 1. A budget deficit decreases the supply of loanable funds . . . Copyright?2004 South-Western
- 42. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Policy 3: Government Budget Deficits and Surpluses ? When government reduces national saving by running a deficit, the interest rate rises and investment falls.
- 43. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Policy 3: Government Budget Deficits and Surpluses ? A budget surplus increases the supply of loanable funds, reduces the interest rate, and stimulates investment.
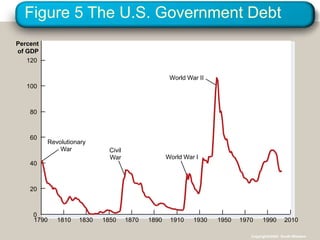
- 44. Figure 5 The U.S. Government Debt Percent of GDP 1790 1810 1830 1850 1870 1890 1910 1930 1950 1970 1990 Revolutionary War 2010 Civil War World War I World War II 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 Copyright?2004 South-Western
- 45. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Summary ? The U.S. financial system is made up of financial institutions such as the bond market, the stock market, banks, and mutual funds. ? All these institutions act to direct the resources of households who want to save some of their income into the hands of households and firms who want to borrow.
- 46. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Summary ? National income accounting identities reveal some important relationships among macroeconomic variables. ? In particular, in a closed economy, national saving must equal investment. ? Financial institutions attempt to match one personˇŻs saving with another personˇŻs investment.
- 47. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Summary ? The interest rate is determined by the supply and demand for loanable funds. ? The supply of loanable funds comes from households who want to save some of their income. ? The demand for loanable funds comes from households and firms who want to borrow for investment.
- 48. Copyright ? 2004 South-Western Summary ? National saving equals private saving plus public saving. ? A government budget deficit represents negative public saving and, therefore, reduces national saving and the supply of loanable funds. ? When a government budget deficit crowds out investment, it reduces the growth of productivity and GDP.



























































































![Letasoft Sound Booster 1.12.0.538 Crack + Product Key [Latest] 2025](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/wtqproposal2023-250310234537-35b42dc4-250311173648-10477ef4-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)





