2.4 analysing momentum
Download as PPT, PDF2 likes3,163 views
Momentum is defined as the product of an object's mass and velocity. The principle of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of a system remains constant if no external forces act on it. Applications include collisions between objects like cars and the jet propulsion of airplanes, where hot gases ejected from the back provide an equal and opposite momentum to push the plane forward.
1 of 18
Downloaded 104 times















Recommended
Forces & Changes in Motion



Forces & Changes in MotionStephen Taylor
Ã˝
The document compares the world record breaking skydives of Joe Kittinger in 1960 and Felix Baumgartner in 2012, noting that Baumgartner jumped from a higher altitude of 39,045m compared to Kittinger's 31,300m, allowing Baumgartner to reach a higher maximum speed of 1342.8 km/h over Kittinger's 988km/h. The document also explores the factors like air pressure and density that influence terminal velocity and made Baumgartner's higher jump necessary to break the speed of sound record.Unit 3: Motion and movement



Unit 3: Motion and movement≤—√≥≤‘æ±≥¶≤π
Ã˝
This document defines and describes concepts related to motion, including:
- Motion is defined as a change in an object's position over time. Characteristics of motion include position, trajectory, distance traveled, displacement, time, speed, and acceleration.
- Uniform linear motion occurs when an object's trajectory is a straight line and its speed is constant. Accelerated motion occurs when an object's speed changes.
- Acceleration is defined as the change in an object's speed over time. Forces are what can change an object's speed or deform it, causing accelerated motion.
- Several word problems are provided as examples to calculate distances, speeds, times, and positions given values in uniform and accelerated motionsMirror - Physics by: Rey San Andrew Rimando



Mirror - Physics by: Rey San Andrew RimandoRey Rimando
Ã˝
In this PowerPoint Presentation, you will find related topics with explanation like the Three Types of Mirror; it's characteristics and functions. Attached also is the video presentation used under the hyperlink(UNDERLINED WORDS). I'm hoping this will help a lot of students. Thanks! -Reylesson in projectile motion, grade 9.pptx



lesson in projectile motion, grade 9.pptxElisaEsteban9
Ã˝
The document discusses projectile motion, which refers to the motion of an object thrown or projected into the air at an angle, noting that the motion is determined by the object's initial velocity and gravity and follows a parabolic trajectory. It explores the independent horizontal and vertical components of a projectile's motion, with the horizontal motion at constant velocity and the vertical motion undergoing gravitational acceleration, and examines how changing the launch angle impacts the height, range, and time of the projectile's flight.Strategic intervention materials in Science



Strategic intervention materials in Sciencewelita evangelista
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of potential and kinetic energy. It defines potential energy as stored energy and kinetic energy as the energy of motion. Examples of objects possessing each type of energy are given. The formulas for calculating potential energy (PE=mgh) and kinetic energy (KE=1/2mv^2) are shown and explained. Sample problems demonstrating the use of each formula are worked out. The document also discusses classifying examples as potential or kinetic energy and assessing students' understanding through illustrations. Overall, the document aims to teach the key concepts and calculations of potential and kinetic energy.18. magnetic reversal



18. magnetic reversalHeart Break Institution
Ã˝
This document contains a detailed lesson plan for a Grade 10 Science class on magnetic reversals and seafloor spreading. The plan outlines the objectives, topics, materials, procedures, and evaluation for a 60 minute lesson. Students will analyze a magnetic polarity map, calculate seafloor spreading rates, and present their findings. They will learn that magnetic reversals are caused by changes in Earth's core and prove seafloor spreading by magnetic patterns in ocean floor rocks. The lesson aims to help students understand how new seafloor is created at mid-ocean ridges and how this relates to plate tectonics.Force and acceleration simplified



Force and acceleration simplifiedCombrink Lisa
Ã˝
Forces can push or pull on objects and change their motion. A force is measured in Newtons. The net force on an object determines its acceleration according to F=ma. Newton's three laws describe how forces interact: 1) objects in motion stay in motion unless a force acts, 2) F=ma, and 3) for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Centripetal force provides the inward force needed for circular motion. Levers, moments, and fulcrums can be used to make work easier by reducing the needed force. The location of an object's center of mass determines its stability.Inertia copy 2



Inertia copy 2Akhila G K Trivandrum
Ã˝
This document discusses the concept of inertia. It defines inertia as the property of matter that causes it to resist changes in its motion or state of rest. It explains that objects at rest will remain at rest, and objects in motion will remain in motion with constant speed and direction, unless acted on by an unbalanced force. The document provides examples of inertia in everyday life, such as a hammer head staying attached when the handle is struck, or passengers feeling pushed back when a bus starts moving. It also discusses how mass influences the effects of inertia, with more massive objects having greater inertia.Reflection of light (Physics)



Reflection of light (Physics)Sheikh Amman
Ã˝
Light propagates in straight lines and can be reflected, refracted, and diffracted when interacting with matter. Reflection occurs when light hits a smooth surface and bounces back into the same medium at the same angle. Regular reflection occurs from plane mirrors where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Spherical mirrors can be concave or convex. Concave mirrors form real, inverted images, while convex mirrors form virtual, upright images. The mirror equation relates the focal length and distances of the object and image. concave mirror activity sheet



concave mirror activity sheetDARYL (MONKAYO NHS)
Ã˝
This document outlines an experiment to construct ray diagrams and describe images formed by a concave mirror as the object position is varied. The experiment involves placing an object at different positions (at C, at F, beyond C, between F and C, between F and V, and between F and C) and drawing the corresponding ray diagram to determine the image position, size, orientation, and type (real or virtual). The document then asks the student to analyze how the image changes as the object position varies and to discuss the importance of concave mirrors and examples of devices that use them.Concave mirrors



Concave mirrorsAbbinaya Helbig
Ã˝
Concave mirrors reflect light inwards like the inside of a bowl. Rays of light hitting any point on the curved mirror behave as if they are hitting a flat plane at that point. All the imaginary normal lines drawn from points on the curved surface meet at the center of curvature. Rays parallel to the principal axis, which runs through the vertex and center of curvature, meet at the focal point. The location and orientation of the mirror's image depends on where the object is placed relative to the focal point and center of curvature.Formation of image in a plane mirror



Formation of image in a plane mirrorNeena Haridas
Ã˝
The document discusses the formation of images in plane mirrors. It states that the position of an image formed in a plane mirror is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. The distance between the image and mirror is equal to the distance between the object and mirror. Additionally, the image has the same size as the object but is laterally inverted and virtual.Lesson 1 Forces.pptx



Lesson 1 Forces.pptxZeref77
Ã˝
Forces were investigated in relation to how they affect an object's motion. There are two types of forces - contact forces which require touching objects, like applied force, friction, normal force and tension, and non-contact forces which act over a distance without touching, like gravitational and magnetic forces. Balanced forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction and do not cause changes in motion, while unbalanced forces cause changes in motion and are not equal or opposite. The net or resultant force is the sum of all the individual forces acting on an object.Chapter 10 Optical Instruments-2.ppt slides



Chapter 10 Optical Instruments-2.ppt slidessomethingyouknow786
Ã˝
This document discusses various optical instruments and concepts related to fiber optics. It covers the basics of lenses, mirrors, the human eye and various optical devices like microscopes, telescopes and spectrometers. It explains key concepts such as magnification, resolving power, refraction, total internal reflection which enable the working of these instruments. The document also provides an introduction to fiber optics, the principles behind signal transmission using optical fibers and their advantages over traditional copper wiring.2.2 - Forces & Dynamics



2.2 - Forces & Dynamicssimonandisa
Ã˝
Forces can cause objects to deform, speed up, slow down, or change direction. A free-body diagram represents all the forces acting on an object with arrows pointing in the direction of each force. Newton's Second Law states that the acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force acting on it. Newton's Third Law states that for every force there is an equal and opposite reaction force.Science Learning Plan (Does the sun move)



Science Learning Plan (Does the sun move)Mavict Obar
Ã˝
1) The lesson plan is for a 2nd grade science class on whether the sun moves. Students will explore how the sun appears to move during the day through observation and modeling its rising and setting.
2) Through group work with compasses, students will demonstrate how the earth spins to make it seem the sun is moving from east to west. They will draw the sun's path and an arrow showing the earth's rotation.
3) Students will be assessed on their understanding that the sun's apparent motion is due to the earth's rotation, not the sun moving. They will observe and record the sun's position at different times of day.Physics Ppt



Physics Pptd8r7z
Ã˝
1. The document discusses projectile motion and provides an example problem of calculating the motion of a ball launched at a 30 degree angle from a table 1 meter high.
2. It explains that projectile motion can be used to study how objects move through the air or space, and gives some everyday examples.
3. Conservation of energy can also be used to solve projectile motion problems, since the only force acting is gravity, and the horizontal velocity does not change.Scalars And Vectors



Scalars And Vectorsyapshinn
Ã˝
Scalars and vectors are different types of quantities. Scalars only have magnitude and not direction, while vectors have both magnitude and direction. Common scalar quantities include speed, temperature, and time. Common vector quantities include displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, and electric field. Vectors can be represented using arrow diagrams with a specified scale and direction. The resultant of two or more vectors can be found geometrically by drawing them head to tail or mathematically using trigonometry, Pythagorean theorem, or graphical addition of vectors placed tail to head.Efect of force



Efect of forceakhil111121141171
Ã˝
The document presents the effects of force, including how force can:
1. Make an object move by pushing or pulling it in the direction of motion.
2. Stop a moving object by applying an opposite force.
3. Change the direction of a moving object by applying force at an angle.
4. Change the shape of an object by squeezing or compressing it with force.Rotational Motion & Equilibrium



Rotational Motion & EquilibriumTimothy Welsh
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of rotational motion concepts for an AP Physics tutorial. It defines angular analogs to linear motion concepts like displacement, velocity, acceleration, and introduces rotational concepts like torque and moment of inertia. Key formulas for angular kinematics and dynamics are presented along with examples of calculating angular acceleration, torque, and conceptual examples of moment of inertia. The tutorial aims to extend students' knowledge of linear motion to an understanding of rotational motion.force



forceRajni Mittal
Ã˝
force, pull, push, magnetic force, frictional force, direction, formula mass x acceleration, a vector quantity, magnitude, types of forces, muscular force, speed, shape, force, size, unit, newton, position, moving object, assignments1, assignment2Lateral inversion



Lateral inversionNeena Haridas
Ã˝
This document discusses four activities involving mirrors and lateral inversion. Activity 1 and 2 introduce mirrors, while Activity 3 has students observe the lateral inversion of letters' images in mirrors. Finally, Activity 4 generalizes that mirrors laterally invert objects, making the right side appear left and vice versa in reflections.Kinetic and Potential Energy



Kinetic and Potential EnergyLumen Learning
Ã˝
The document discusses the First Law of Thermodynamics regarding energy conservation. It defines kinetic energy as the energy of motion and potential energy as stored energy due to position. Examples are given of objects possessing kinetic or potential energy. The law states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted between forms. An example of a ball rolling down a ramp demonstrates the conversion between potential and kinetic energy, with total energy remaining constant.Torque



Torquerizalyndelacruz3
Ã˝
Torque is a rotational force that depends on three main factors: the distance from the axis of rotation (lever arm), the angle of the applied force, and the magnitude of the applied force. Torque causes an object to rotate and is measured in Newton-meters. Systems in rotational equilibrium have no net torque, meaning the sum of all torques acting on the object is zero. This allows seesaws and diving boards to remain balanced. Solving rotational equilibrium problems involves drawing free body diagrams and setting the sum of torques equal to zero.Frictional Force



Frictional ForceShadiya Basheer
Ã˝
Friction is the force that resists the motion of objects in contact with each other and is caused by irregularities in the surfaces in contact. The different types of friction include static, sliding, and rolling friction and are affected by factors like the type of surface and amount of force pressing the surfaces together. While friction provides advantages like allowing us to walk without slipping, it also has disadvantages as it slows movement and produces unwanted heat, requiring more energy to overcome. Methods like lubrication and using rollers can help reduce friction.Momentum and inertia



Momentum and inertiaamandayoung313
Ã˝
This document discusses momentum and inertia. It explains that momentum is calculated as mass times velocity, and was defined by Isaac Newton as the key factor for describing motion. The law of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of a system will remain constant if no outside forces act on it. When objects collide and one slows down, the other gains momentum and speeds up, keeping the total momentum the same. Examples of momentum transfers are described, such as billiard balls colliding in a rack.Force



Force2404isht
Ã˝
The document discusses force, pressure, and friction. It defines force as a push or pull and explains that forces can change the speed, direction, or shape of an object. It also distinguishes between elastic and inelastic objects based on whether they return to their original shape after a force is applied. Friction is described as a force that opposes motion.Light presentation



Light presentationpranali mankar
Ã˝
1) The document discusses key concepts of light including its properties, reflection, refraction, total internal reflection, and optical fibers.
2) It describes how light travels very fast in straight lines, and how we see objects because light reflects into our eyes from them. Shadows are formed when light is blocked.
3) Reflection and refraction of light follow specific laws, such as the law of reflection where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, and Snell's law relating the indices of refraction and angles of light passing through different mediums. Physics form 4 chapter 2



Physics form 4 chapter 2University Science Penang
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of forces and motion concepts taught in a physics chapter, including definitions of key terms like displacement, speed, velocity, acceleration, momentum, Newton's laws of motion, and different types of forces and energy. It defines important equations like those for speed, velocity, acceleration, work, kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, and power. It also summarizes the main objectives of understanding motion, momentum, and forces.4831603 physics-formula-list-form-4



4831603 physics-formula-list-form-4hongtee82
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of key physics equations and concepts related to forces and motion, including equations for relative deviation, prefixes, units of area and volume, average speed, velocity, acceleration, momentum, Newton's laws of motion, and impulse. Key variables and their units are defined for each equation. Examples of displacement-time and velocity-time graphs are also included to illustrate the relationships between displacement, velocity, time, and acceleration.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Reflection of light (Physics)



Reflection of light (Physics)Sheikh Amman
Ã˝
Light propagates in straight lines and can be reflected, refracted, and diffracted when interacting with matter. Reflection occurs when light hits a smooth surface and bounces back into the same medium at the same angle. Regular reflection occurs from plane mirrors where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Spherical mirrors can be concave or convex. Concave mirrors form real, inverted images, while convex mirrors form virtual, upright images. The mirror equation relates the focal length and distances of the object and image. concave mirror activity sheet



concave mirror activity sheetDARYL (MONKAYO NHS)
Ã˝
This document outlines an experiment to construct ray diagrams and describe images formed by a concave mirror as the object position is varied. The experiment involves placing an object at different positions (at C, at F, beyond C, between F and C, between F and V, and between F and C) and drawing the corresponding ray diagram to determine the image position, size, orientation, and type (real or virtual). The document then asks the student to analyze how the image changes as the object position varies and to discuss the importance of concave mirrors and examples of devices that use them.Concave mirrors



Concave mirrorsAbbinaya Helbig
Ã˝
Concave mirrors reflect light inwards like the inside of a bowl. Rays of light hitting any point on the curved mirror behave as if they are hitting a flat plane at that point. All the imaginary normal lines drawn from points on the curved surface meet at the center of curvature. Rays parallel to the principal axis, which runs through the vertex and center of curvature, meet at the focal point. The location and orientation of the mirror's image depends on where the object is placed relative to the focal point and center of curvature.Formation of image in a plane mirror



Formation of image in a plane mirrorNeena Haridas
Ã˝
The document discusses the formation of images in plane mirrors. It states that the position of an image formed in a plane mirror is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. The distance between the image and mirror is equal to the distance between the object and mirror. Additionally, the image has the same size as the object but is laterally inverted and virtual.Lesson 1 Forces.pptx



Lesson 1 Forces.pptxZeref77
Ã˝
Forces were investigated in relation to how they affect an object's motion. There are two types of forces - contact forces which require touching objects, like applied force, friction, normal force and tension, and non-contact forces which act over a distance without touching, like gravitational and magnetic forces. Balanced forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction and do not cause changes in motion, while unbalanced forces cause changes in motion and are not equal or opposite. The net or resultant force is the sum of all the individual forces acting on an object.Chapter 10 Optical Instruments-2.ppt slides



Chapter 10 Optical Instruments-2.ppt slidessomethingyouknow786
Ã˝
This document discusses various optical instruments and concepts related to fiber optics. It covers the basics of lenses, mirrors, the human eye and various optical devices like microscopes, telescopes and spectrometers. It explains key concepts such as magnification, resolving power, refraction, total internal reflection which enable the working of these instruments. The document also provides an introduction to fiber optics, the principles behind signal transmission using optical fibers and their advantages over traditional copper wiring.2.2 - Forces & Dynamics



2.2 - Forces & Dynamicssimonandisa
Ã˝
Forces can cause objects to deform, speed up, slow down, or change direction. A free-body diagram represents all the forces acting on an object with arrows pointing in the direction of each force. Newton's Second Law states that the acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force acting on it. Newton's Third Law states that for every force there is an equal and opposite reaction force.Science Learning Plan (Does the sun move)



Science Learning Plan (Does the sun move)Mavict Obar
Ã˝
1) The lesson plan is for a 2nd grade science class on whether the sun moves. Students will explore how the sun appears to move during the day through observation and modeling its rising and setting.
2) Through group work with compasses, students will demonstrate how the earth spins to make it seem the sun is moving from east to west. They will draw the sun's path and an arrow showing the earth's rotation.
3) Students will be assessed on their understanding that the sun's apparent motion is due to the earth's rotation, not the sun moving. They will observe and record the sun's position at different times of day.Physics Ppt



Physics Pptd8r7z
Ã˝
1. The document discusses projectile motion and provides an example problem of calculating the motion of a ball launched at a 30 degree angle from a table 1 meter high.
2. It explains that projectile motion can be used to study how objects move through the air or space, and gives some everyday examples.
3. Conservation of energy can also be used to solve projectile motion problems, since the only force acting is gravity, and the horizontal velocity does not change.Scalars And Vectors



Scalars And Vectorsyapshinn
Ã˝
Scalars and vectors are different types of quantities. Scalars only have magnitude and not direction, while vectors have both magnitude and direction. Common scalar quantities include speed, temperature, and time. Common vector quantities include displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, and electric field. Vectors can be represented using arrow diagrams with a specified scale and direction. The resultant of two or more vectors can be found geometrically by drawing them head to tail or mathematically using trigonometry, Pythagorean theorem, or graphical addition of vectors placed tail to head.Efect of force



Efect of forceakhil111121141171
Ã˝
The document presents the effects of force, including how force can:
1. Make an object move by pushing or pulling it in the direction of motion.
2. Stop a moving object by applying an opposite force.
3. Change the direction of a moving object by applying force at an angle.
4. Change the shape of an object by squeezing or compressing it with force.Rotational Motion & Equilibrium



Rotational Motion & EquilibriumTimothy Welsh
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of rotational motion concepts for an AP Physics tutorial. It defines angular analogs to linear motion concepts like displacement, velocity, acceleration, and introduces rotational concepts like torque and moment of inertia. Key formulas for angular kinematics and dynamics are presented along with examples of calculating angular acceleration, torque, and conceptual examples of moment of inertia. The tutorial aims to extend students' knowledge of linear motion to an understanding of rotational motion.force



forceRajni Mittal
Ã˝
force, pull, push, magnetic force, frictional force, direction, formula mass x acceleration, a vector quantity, magnitude, types of forces, muscular force, speed, shape, force, size, unit, newton, position, moving object, assignments1, assignment2Lateral inversion



Lateral inversionNeena Haridas
Ã˝
This document discusses four activities involving mirrors and lateral inversion. Activity 1 and 2 introduce mirrors, while Activity 3 has students observe the lateral inversion of letters' images in mirrors. Finally, Activity 4 generalizes that mirrors laterally invert objects, making the right side appear left and vice versa in reflections.Kinetic and Potential Energy



Kinetic and Potential EnergyLumen Learning
Ã˝
The document discusses the First Law of Thermodynamics regarding energy conservation. It defines kinetic energy as the energy of motion and potential energy as stored energy due to position. Examples are given of objects possessing kinetic or potential energy. The law states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted between forms. An example of a ball rolling down a ramp demonstrates the conversion between potential and kinetic energy, with total energy remaining constant.Torque



Torquerizalyndelacruz3
Ã˝
Torque is a rotational force that depends on three main factors: the distance from the axis of rotation (lever arm), the angle of the applied force, and the magnitude of the applied force. Torque causes an object to rotate and is measured in Newton-meters. Systems in rotational equilibrium have no net torque, meaning the sum of all torques acting on the object is zero. This allows seesaws and diving boards to remain balanced. Solving rotational equilibrium problems involves drawing free body diagrams and setting the sum of torques equal to zero.Frictional Force



Frictional ForceShadiya Basheer
Ã˝
Friction is the force that resists the motion of objects in contact with each other and is caused by irregularities in the surfaces in contact. The different types of friction include static, sliding, and rolling friction and are affected by factors like the type of surface and amount of force pressing the surfaces together. While friction provides advantages like allowing us to walk without slipping, it also has disadvantages as it slows movement and produces unwanted heat, requiring more energy to overcome. Methods like lubrication and using rollers can help reduce friction.Momentum and inertia



Momentum and inertiaamandayoung313
Ã˝
This document discusses momentum and inertia. It explains that momentum is calculated as mass times velocity, and was defined by Isaac Newton as the key factor for describing motion. The law of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of a system will remain constant if no outside forces act on it. When objects collide and one slows down, the other gains momentum and speeds up, keeping the total momentum the same. Examples of momentum transfers are described, such as billiard balls colliding in a rack.Force



Force2404isht
Ã˝
The document discusses force, pressure, and friction. It defines force as a push or pull and explains that forces can change the speed, direction, or shape of an object. It also distinguishes between elastic and inelastic objects based on whether they return to their original shape after a force is applied. Friction is described as a force that opposes motion.Light presentation



Light presentationpranali mankar
Ã˝
1) The document discusses key concepts of light including its properties, reflection, refraction, total internal reflection, and optical fibers.
2) It describes how light travels very fast in straight lines, and how we see objects because light reflects into our eyes from them. Shadows are formed when light is blocked.
3) Reflection and refraction of light follow specific laws, such as the law of reflection where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, and Snell's law relating the indices of refraction and angles of light passing through different mediums. Viewers also liked (13)
Physics form 4 chapter 2



Physics form 4 chapter 2University Science Penang
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of forces and motion concepts taught in a physics chapter, including definitions of key terms like displacement, speed, velocity, acceleration, momentum, Newton's laws of motion, and different types of forces and energy. It defines important equations like those for speed, velocity, acceleration, work, kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, and power. It also summarizes the main objectives of understanding motion, momentum, and forces.4831603 physics-formula-list-form-4



4831603 physics-formula-list-form-4hongtee82
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of key physics equations and concepts related to forces and motion, including equations for relative deviation, prefixes, units of area and volume, average speed, velocity, acceleration, momentum, Newton's laws of motion, and impulse. Key variables and their units are defined for each equation. Examples of displacement-time and velocity-time graphs are also included to illustrate the relationships between displacement, velocity, time, and acceleration.Physics f4 chapter2



Physics f4 chapter2marjerin
Ã˝
The document discusses key concepts in linear motion including distance, displacement, speed, velocity, average speed, average velocity, uniform and non-uniform motion, acceleration, deceleration, and zero acceleration. It provides definitions, equations, examples, and comparisons between related concepts. Formulas are given for calculating velocity, acceleration from ticker tape experiments measuring displacement and time intervals.FORCE & MOTION (Inertia) FORM 4



FORCE & MOTION (Inertia) FORM 4Fatimah1986
Ã˝
This document discusses the concept of inertia. It defines inertia as an object's tendency to remain at rest or in motion unless acted upon by an external force. It explains that inertia is influenced by mass, with more massive objects having greater inertia. Examples are given of how inertia causes objects and passengers in moving vehicles to continue moving when motion stops suddenly without external forces like seatbelts intervening. Safety measures in vehicles are described that counteract the negative effects of inertia during sudden stops.Inertia



InertiaIdrul Nafiz
Ã˝
Students will be able to explain inertia, relate it to mass, and provide examples involving inertia. Inertia is an object's tendency to resist changes in its motion - objects at rest will stay at rest and objects in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced outside force. An object's inertia is directly proportional to its mass - the more mass an object has, the greater its inertia. Examples of inertia include a coin on cardboard pulled quickly, a ladder on a stopping truck, and other situations involving objects in motion experiencing changes.Conservation of momentum - Physics 



Conservation of momentum - Physics Idrus Aizat
Ã˝
Newton's Cradle demonstrates the law of conservation of momentum through a series of balls. When one ball is pulled back and released, it strikes the next ball, transferring its momentum down the line and causing the last ball to move. This process repeats as the balls continue to exchange momentum. Rockets and jet engines also demonstrate conservation of momentum, as the high velocity exhaust ejected from the engines provides momentum that propels the engine in the opposite direction, allowing for flight. Collisions between objects also conserve total momentum, such as when squids eject water for propulsion or when players collide during a game.Law of inertia



Law of inertiaAiza Mae Bernabe
Ã˝
The document discusses inertia and how it relates to motion. It defines inertia as the property of an object that resists changes to its motion. It explains that according to Newton's first law, an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Real-world examples are provided to illustrate inertia, such as why seatbelts are important in vehicles.Laporan Amali Fizik: Prinsip Keabadian Momentum



Laporan Amali Fizik: Prinsip Keabadian MomentumAtifah Ruzana Abd Wahab
Ã˝
SCE1024
Prinsip Keabadian Momentum bagi perlanggaran kenyal, perlanggaran tak kenyal dan letupan
By: Atifah Ruzana binti Abd Wahab, PPISMP Sains Ambilan Jun 2014, IPG Kampus Kent Tuaran SabahNota Fizik 



Nota Fizik Smk Gelam
Ã˝
The document describes key concepts related to forces and motion, including:
- Acceleration is a change in an object's velocity, which can be a change in speed or direction. Deceleration is negative acceleration as an object slows down.
- Speed is calculated by dividing the distance an object travels by the time it takes, while velocity also includes the object's direction of motion.
- Balanced forces do not cause a change in an object's motion, while unbalanced forces will change its motion or speed.Senarai formula fizik F4



Senarai formula fizik F4Ramli Rem
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of the topics covered in a Form 4 physics textbook. Chapter 1 introduces fundamental physics concepts like measurements, scalar and vector quantities, and the five base physical quantities. Chapter 2 discusses forces and motion, including linear motion, momentum, impulse, and Newton's laws of motion. Chapter 3 covers forces and pressure, including Pascal's principle, Archimedes' principle, and Bernoulli's principle. Chapter 4 examines heat, including specific heat capacity, latent heat, and the gas laws. Chapter 5 looks at light, including reflection, refraction, total internal reflection, and lenses. Formulas and concepts are presented for each chapter.BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 6 - NUTRITION PART 2



BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 6 - NUTRITION PART 2Nirmala Josephine
Ã˝
1. The document discusses digestion in humans from the mouth to the small intestine. It describes the organs and glands involved in digestion and their functions, including the mouth, salivary glands, stomach, pancreas, liver, and intestines.
2. Key points covered include the roles of enzymes like amylase, pepsin and lipase in breaking down carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The importance of conditions like acidity for proper enzyme function is also explained.
3. Adaptations of the small intestine for absorption are summarized, including villi and microvilli that increase surface area for nutrients to pass into the bloodstream.AP Physics - Chapter 2 Powerpoint



AP Physics - Chapter 2 PowerpointMrreynon
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of key concepts in kinematics including:
1) Kinematics deals with concepts of motion without considering forces, while dynamics considers the effects of forces on motion.
2) Displacement, speed, velocity, acceleration, and equations of motion for constant acceleration are introduced.
3) Applications include analyzing the motion of falling bodies and interpreting position-time and velocity-time graphs.Similar to 2.4 analysing momentum (20)
C:\fakepath\momentum



C:\fakepath\momentumFatimah Saipuddin
Ã˝
The document discusses momentum, conservation of momentum, collisions, impulse, and friction. It defines momentum as mass times velocity and states that the total momentum before and after a collision remains the same if no external forces act, according to the conservation of momentum principle. It also distinguishes between elastic, inelastic, and completely inelastic collisions, and defines impulse as the change in momentum caused by a force over time. Static and kinetic friction are defined, with kinetic friction less than static friction. Examples and exercises demonstrate applications of these concepts.Momentum



MomentumFatimah Saipuddin
Ã˝
The document discusses momentum, conservation of momentum, collisions, impulse, and friction. It defines momentum as mass times velocity and states that the total momentum before and after a collision remains the same if no external forces act, according to the conservation of momentum principle. It also distinguishes between elastic, inelastic, and completely inelastic collisions, and defines impulse as the change in momentum caused by a force over time. Static and kinetic friction are defined, with kinetic friction less than static friction. Examples and exercises demonstrate applications of these concepts.2.4 analysing momentum



2.4 analysing momentumShahadah Rahim
Ã˝
The document discusses linear momentum, the principle of conservation of momentum, and its applications. It defines momentum as the product of mass and velocity (p=mv) and explains that momentum is a vector quantity. The principle of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant. Elastic collisions result in bodies separating after collision while maintaining the total momentum, inelastic collisions result in bodies sticking together, and explosions involve contact before and separation after. Examples demonstrate applying the principle to calculate velocities and momentum in collisions and explosions.211461260-Igcse-14-Momentum_2.ppt



211461260-Igcse-14-Momentum_2.pptssuser5087b61
Ã˝
The document provides information on momentum including:
- The equation for momentum (p = mv) and its units (kg m/s)
- The relationship between force, momentum change and time (F = Δp/Δt)
- How conservation of momentum can be used to calculate velocities after collisions
- How car safety features like crumple zones increase the time for a momentum change to reduce force and injury
- Newton's third law of motion which states that every action has an equal and opposite reactionMomentum and Impulse.pptx



Momentum and Impulse.pptxJhunLerryTayan3
Ã˝
1) Momentum is the product of an object's mass and velocity. Impulse is the product of force acting on an object and the time during which it acts, and is also equal to the change in an object's momentum.
2) The document provides examples of calculating momentum, impulse, and changes in momentum for various scenarios involving objects with different masses and velocities.
3) The law of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant, meaning the total momentum before an event involving only internal forces equals the total momentum after the event.2_Force&Motion_T.pptx



2_Force&Motion_T.pptxssusera6add7
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of chapter 2 on forces and motion from the Form 4 Physics textbook. It includes 12 learning objectives covering topics like linear motion, motion graphs, inertia, momentum, forces, impulse, and applications. The chapter also analyzes past year exam questions and provides a concept map relating different concepts in forces and motion. Examples and exercises are given to illustrate key concepts.032316 momentum week2



032316 momentum week2Subas Nandy
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of key concepts in chapter 12 on momentum. It discusses linear momentum and how it is calculated as mass times velocity (p=mv). It also discusses angular momentum and how it is calculated as moment of inertia times angular velocity (L=Iω). The chapter covers conservation of linear and angular momentum, elastic and inelastic collisions, impulse, forces as a change in momentum, and applications like rockets and gyroscopes.6.-linear-momewwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwntum.pdf



6.-linear-momewwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwntum.pdfJadidahSaripada
Ã˝
wwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwwEvery Equation



Every EquationDaniel McClelland
Ã˝
The document discusses key physics concepts related to motion, forces, energy, and electricity. It defines terms like speed, velocity, acceleration, force, work, power, kinetic energy, potential energy, current, voltage, and resistance. Formulas are provided for calculating these values along with example problems and explanations of physics principles.2.4 momentum & energy 2017



2.4 momentum & energy 2017Paula Mills
Ã˝
This document discusses momentum and impulse in mechanics. It defines momentum as the product of mass and velocity, and impulse as the product of force and time. Impulse causes changes in momentum according to the equation Ft = Δp. Collisions can be elastic, inelastic, or perfectly inelastic, with elastic collisions conserving both momentum and kinetic energy. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating momentum, velocity, and kinetic energy before and after collisions.Force and laws of motion 2



Force and laws of motion 2Swetha Ravichandran
Ã˝
1. The document discusses Newton's laws of motion and related concepts like momentum, force, and collisions.
2. Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. It is expressed as F=ma.
3. Newton's third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Examples given are the recoil of a gun and the forward force exerted on a rocket during takeoff.Hp 06 win



Hp 06 winJeffinner
Ã˝
This presentation provides instructions on how to view and navigate through a slideshow on momentum and collisions. It contains sections on momentum and impulse, conservation of momentum, and elastic and inelastic collisions. Sample problems are included with step-by-step worked solutions showing calculations and applying concepts like conservation of momentum and kinetic energy.Hp 06 Win



Hp 06 Winjosoborned
Ã˝
This presentation provides instructions on how to view and navigate through a slideshow on momentum and collisions. It contains sections on momentum and impulse, conservation of momentum, and elastic and inelastic collisions. Sample problems are included with step-by-step worked solutions showing calculations and applying concepts like conservation of momentum and kinetic energy.work energy theorem and kinetic energy



work energy theorem and kinetic energyKharen Adelan
Ã˝
Karen Adelan presented on the topic of classical mechanics and energy. Some key points:
- Energy is a conserved quantity that can change forms but is never created or destroyed. It is useful for describing motion when Newton's laws are difficult to apply.
- Kinetic energy is the energy of motion and depends on an object's mass and speed. The work-kinetic energy theorem states that the net work done on an object equals the change in its kinetic energy.
- Potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position or state. The work done by a constant force equals the product of force, displacement, and the cosine of the angle between them.Linear Momentum and Collisions



Linear Momentum and Collisionsmjurkiewicz
Ã˝
This document discusses linear momentum and collisions, including definitions of momentum, impulse, and conservation of momentum. It provides examples of elastic and inelastic collisions, and practice problems calculating momentum, impulse, and velocities before and after collisions using conservation of momentum. Formulas and concepts are explained for momentum, impulse, completely inelastic and elastic collisions.1.5 form 4 e_momentum



1.5 form 4 e_momentumchris lembalemba
Ã˝
1. Momentum is defined as the product of an object's mass and velocity. It is a vector quantity measured in kg*m/s. When objects collide, momentum is transferred from the moving object to the stationary one.
2. There are two types of collisions - elastic and inelastic. The law of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum before a collision equals the total momentum after.
3. Impulse is the product of force applied over time. It results in a change in an object's momentum. Impulse is equal to the change in momentum, and can be used to calculate the force applied if the time of application is known.Academic Physics Chapter 6 Powerpoint



Academic Physics Chapter 6 PowerpointMrreynon
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of momentum and collisions. It discusses linear momentum, impulse, the impulse-momentum theorem, conservation of momentum, and elastic and inelastic collisions. Key points include:
- Momentum is defined as mass times velocity.
- Impulse is the product of force and time. According to the impulse-momentum theorem, impulse causes a change in momentum.
- The total momentum of interacting objects before a collision equals the total momentum after (law of conservation of momentum).
- Collisions can be perfectly inelastic (objects stick together), elastic (momentum and kinetic energy conserved), or inelastic (kinetic energy not conserved).11 momentum



11 momentumIZZUDIN IBRAHIM
Ã˝
1. Momentum is defined as the product of an object's mass and velocity. It is a conserved quantity such that the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant.
2. During collisions, conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of colliding objects before the collision equals the total momentum after. If no external forces are applied, momentum is conserved.
3. Collisions can be elastic, where both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved, or inelastic where kinetic energy is not conserved but momentum still is. The analysis of collisions uses conservation laws to solve for unknown velocities.Ap review total



Ap review totaljsawyer3434
Ã˝
This document covers concepts in one-dimensional and three-dimensional kinematics, dynamics, work, energy, momentum, rotational motion, and more. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to apply equations for instantaneous and average velocity/acceleration, projectile motion, Newton's laws, work-energy theorem, impulse-momentum, center of mass, moment of inertia, and torque. Problem-solving strategies are outlined for analyzing forces, energy, momentum, and rotational equilibrium.2.4 analysing momentum
- 2. Learning Outcome : ÔÉí Define the momentum of an object ÔÉí Define momentum (p) as the product of mass ( m) and velocity (v), e. p=mv ÔÉí State the principle of conversation of momentum ÔÉí Describe applications of conservation of momentum.
- 3. ÔÉí Momentum is a commonly used term in sports ÔÉí A team that has the
- 4. ÔÉí The momentum of an object is the product of the mass and the velocity of the object
- 5. ÔÉí Situation 1 ÔÉí Car A and car B have the same mass but they move with different velocities. ÔÉí Which car possess more momentum?
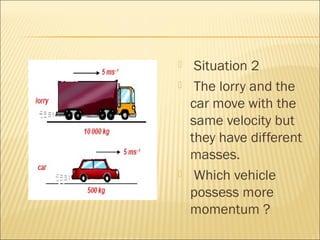
- 6. ÔÉí Situation 2 ÔÉí The lorry and the car move with the same velocity but they have different masses. ÔÉí Which vehicle possess more momentum ?
- 7. The principle of conservation of momentum states that in a system make out of objects that react (collide or explode), the total momentum is constant if no external force is acted upon the system. Sum of Momentum Before Reaction = Sum of Momentum After Reaction
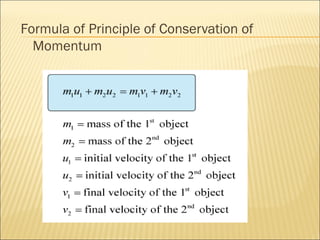
- 8. Formula of Principle of Conservation of Momentum
- 9. Example : Both objects are same direction before collision A Car A of mass 600 kg moving at 40 ms-1 collides with a car B of mass 800 kg moving at 20 ms-1 in the same direction. If car B moves forwards at 30 ms-1 by the impact, what is the velocity, v, of the car A immediately after the crash? m1 = 600kg m2 = 800kg u1 = 40 ms-1 u2 = 20 ms-1 v1 = ? v2 = 30 ms -1
- 10. Answer : According to the principle of conservation of momentum, m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2 (600)(40) + (800)(20) = (600)v1 + (800)(30) 40000 = 600v1 + 24000 600v1 = 16000 v1 = 26.67 ms-1
- 11. Example 2 : Both objects are in opposite direction before collision A 0.50kg ball traveling at 6.0 ms-1 collides head-on with a 1.0 kg ball moving in the opposite direction at a speed of 12.0 ms-1. The 0.50kg ball moves backward at 14.0 ms-1 after the collision. Find the velocity of the second ball after collision. m1 = 0.5 kg m2 = 1.0 kg u1 = 6.0 ms-1 u2 = -12.0 ms-1 v1 = -14.0 ms-1 v2 = ? (IMPORTANT: velocity is negative when the object move in opposite siredtion)
- 12. Answer : According to the principle of conservation of momentum, m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2 (0.5)(6) + (1.0)(-12) = (0.5)(-14) + (1.0)v 2 -9 = - 7 + 1v 2 v2 = -2 ms-1
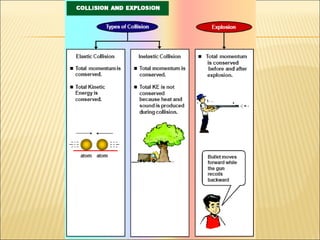
- 14. Elastic collision is the collision where the kinetic energy is conserved after the collision. Total Kinetic Energy before Collision = Total Kinetic Energy after Collision Additional notes: -In an elastic collision, the 2 objects separated right after the collision, and -the momentum is conserved after the collision.
- 15. Inelastic collision is the collision where the kinetic energy is not conserved after the collision. Additional notes: -In a perfectly elastic collision, the 2 objects attach together after the collision, and -the momentum is also conserved after the collision.
- 16. ÔÉí Example 3 : Perfectly Inelastic Collision A lorry of mass 8000kg is moving with a velocity of 30 ms-1. The lorry is then accidentally collides with a car of mass 1500kg moving in the same direction with a velocity of 20 ms-1. After the collision, both the vehicles attach together and move with a speed of velocity v. Find the value of v.
- 17. According to the principle of conservation of momentum, m1u1 + m2u2 =( m1+ m2) v (8,000) (30) + (1,500)(20) = (8,000)v+ (1,500)v 270,000 = 9500v v = 28.42 ms-1 Answer: (IMPORTANT: When 2 object attach together, they move with same speed.)
- 18. Application of Conservation of Momentum : Jet Engine •The hot gas is forced through the engine to turn the turbine blade, which turn the compressor. • High-speed hot gases are ejected from the back with •Air is taken in from the front and is high momentum. This compressed by the compressor. produces an equal and •Fuel is injected and burnt with the opposite momentum to push compressed air in the combustion the jet plane forward. chamber.

