3-use-casemodelling
- 1. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 1
- 2. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 2 For an in-depth understanding of use case issues, it is a good idea to refer to the book provided by the Founder of Use Cases, Jacobson. https://www.ivarjacobson.com/sites/default/files/field_iji_file/article/use-case_2_0_jan11.pdf
- 3. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 3
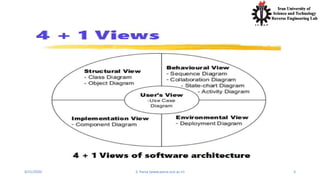
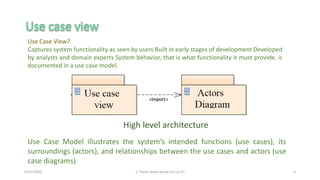
- 4. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 4 Use Case View? Captures system functionality as seen by users Built in early stages of development Developed by analysts and domain experts System behavior, that is what functionality it must provide, is documented in a use case model. Use Case Model illustrates the systemŌĆÖs intended functions (use cases), its surroundings (actors), and relationships between the use cases and actors (use case diagrams) High level architecture
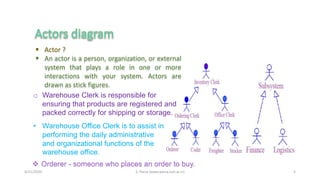
- 5. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 5 ’é¦ Actor ? ’é¦ An actor is a person, organization, or external system that plays a role in one or more interactions with your system. Actors are drawn as stick figures. ’üČ Orderer - someone who places an order to buy. ŌĆó Warehouse Office Clerk is to assist in performing the daily administrative and organizational functions of the warehouse office. o Warehouse Clerk is responsible for ensuring that products are registered and packed correctly for shipping or storage.
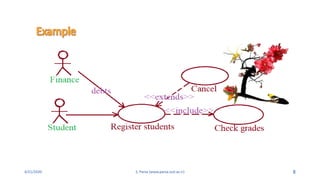
- 6. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 6 Use Case ? A use case is a list of actions or event steps typically defining the interactions between a role (known in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) as an actor) and a system to achieve a goal.
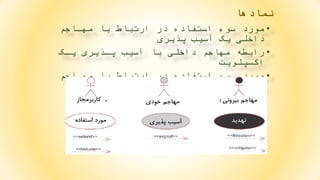
- 7. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 7 1. Association: ’é¦ A relationship that represents communication between an actor and a use case; can be navigable in both ways or in only one way. 2. Uses (includes) and extends are two types of relationships between use cases. ŌĆóAn extends relationship is used to show: - Optional behavior - Behavior that is only run under certain conditions, - Different flows which may be run based on actor selection ŌĆóA uses of includes relationship is used to show: - functionality shared by multiple use cases. - can be placed in a separate use case, related to these uses cases by a uses relationship
- 8. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 8
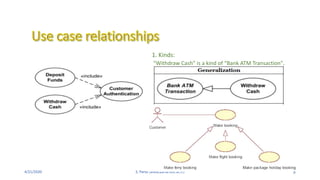
- 9. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 9 1. Kinds: ŌĆ£Withdraw CashŌĆØ is a kind of ŌĆ£Bank ATM TransactionŌĆØ.
- 10. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 10
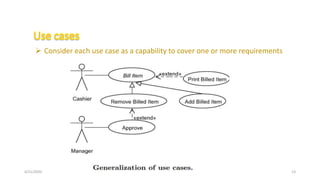
- 11. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 11 1. The application will record and maintain the product quantity in the stock in the central database. 2. The storekeeper can remove products from the database. 3. The storekeeper can add products into the database. 4. The storekeeper can change the product quantity in the database. 5. The cashier can bill the item by manually entering the bar code or with a bar code reader. 6. Only the products recorded in the database can be billed. 7. The billed items can be removed from the bill until it has been closed. ’é¦ The retail support application requirements.
- 12. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 12 8. The billed item removal must be approved by a store manager by entering his authentication data. 9. The billed items will be printed on the cash desk bill as they are entered. The bill will consist of the store name, billed items, information on removed billed items, the total amount of money to be paid, and date and time. 10. The product price can be entered or modified only by a properly authenticated store manager. ’é¦ The retail support application requirements. ’āś Consider each use case as a capability to cover one or more requirements
- 13. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 13 ’āś Consider each use case as a capability to cover one or more requirements
- 14. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 14 .ŌĆ½ž│žĘžŁŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž¦┘䞬ž▒┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž©┘Ŗž▒ž«ž¦┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»┘枦┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘Ŗž»┌»ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼
- 15. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 15 2.ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»┘枦┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘Ŗž»┌»ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ģž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼
- 16. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 163.ŌĆ½┘łž¦ž▒ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘垦┘ģ┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž▒┘ł┘Ŗž│┘枦┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž│ž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»┘枦┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘Ŗž»┌»ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼
- 17. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 17
- 18. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 18
- 19. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 19
- 20. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 20
- 21. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 21
- 22. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 22
- 23. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 23
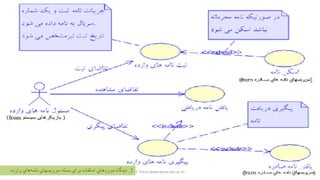
- 24. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 24 ŌĆó Each use case is documented with a flow of events, use-case scenario, which is a description of the events needed to accomplish the required behavior. ŌĆó The scenario is written in the language of the domain and describe what the system should do and not how the system does it. ŌĆó The flow of events should include: -When and how the use case starts and ends -What interaction the use case has with the actors -What data is needed by the use case -The normal sequence of events for the use case -The description of any alternate or exceptional flows
- 25. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 25 ’é¦ X Flow of Events for the Use Case ’é¦ X.1 Preconditions & Postconditions ’é¦ X.2 Main Flow ’é¦ X.3 Subflows (if applicable) ’é¦ X.4 Alternative Flows ’é¦ Where X is a number from 1 to the number of use cases
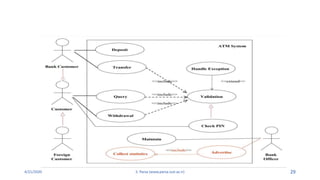
- 26. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 26 ŌĆó Main flow of events: (E1) The use case starts when the system prompts the User for a PIN number. The User can now enter a PIN number via the keypad. (E2) The User commits the entry by pressing the Enter button. (E3) The system then checks this PIN number to see if it is valid. If the PIN number is valid, the system acknowledges the entry, thus ending the use case. ŌĆó Subflows: S1: The system invokes Validate use case.
- 27. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 27 ŌĆó Alternative flow of events: E1: The User can clear a PIN number any time before committing it and reenter a new PIN number. E2: The User can cancel a transaction at any time by pressing the Cancel button, thus restarting the use case. No changes are made to the UserŌĆÖs account. E3: If the User enters an invalid PIN number, the use case restarts. If this happens three times in a row, the system cancels the entire transaction, preventing the User from interacting with the ATM for 30 minutes.
- 28. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 28
- 29. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 29
- 30. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 30
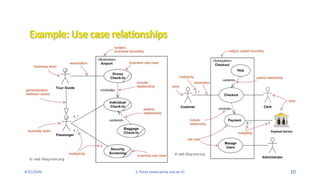
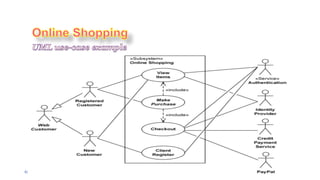
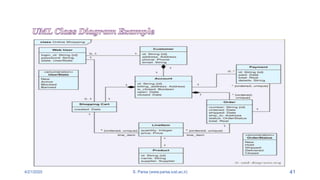
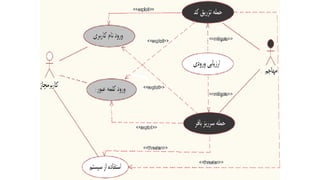
- 31. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 31 ’āśWeb Customer actor uses some web site to make purchases online. ’āśTop level use cases are View Items, Make Purchase and Client Register. ’āśView Items use case could be used by customer as top level use case if customer only wants to find and see some products. This use case could also be used as a part of Make Purchase use case. ’āśClient Register use case allows customer to register on the web site, for example to get some coupons or be invited to private sales. Note, that ’āśCheckout use case is included use case not available by itself - checkout is part of making purchase.
- 32. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 32
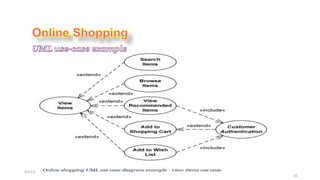
- 33. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 33 ŌĆó View Items use case is extended by several optional use cases - customer may search for items, browse catalog, view items recommended for him/her, add items to shopping cart or wish list. ŌĆó All these use cases are extending use cases because they provide some optional functions allowing customer to find item. ŌĆó Customer Authentication use case is included in view Recommended Items and Add to Wish List because both require the customer to be authenticated. ŌĆó At the same time, item could be added to the shopping cart without user authentication.
- 34. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 34
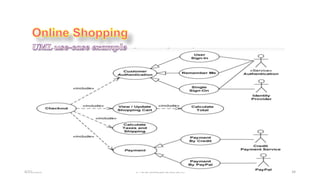
- 35. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 35 ŌĆó Checkout use case includes several required uses cases. ŌĆó Web customer should be authenticated. It could be done through user login page, user authentication cookie ("Remember me") or Single Sign-On (SSO). ŌĆó Web site authentication service is used in all these use cases, while SSO also requires participation of external identity provider. ŌĆó Checkout use case also includes Payment use case which could be done either by using credit card and external credit payment service or with PayPal.
- 36. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 36
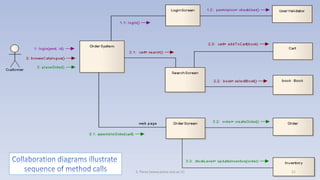
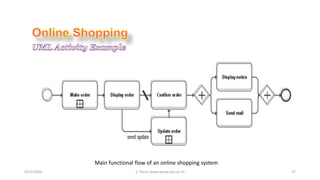
- 37. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 37 Main functional flow of an online shopping system
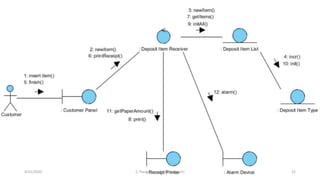
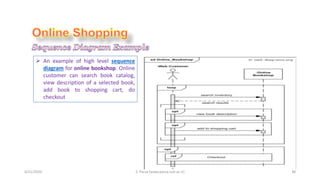
- 38. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 38 ’āś An example of high level sequence diagram for online bookshop. Online customer can search book catalog, view description of a selected book, add book to shopping cart, do checkout
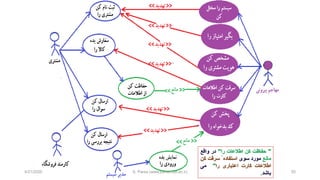
- 39. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 39 ’āśEach customer has unique id, linked to one account. ’āśAccount owns shopping cart and orders. ’āśCustomer could register as a web user to buy items online. ’āśCustomer could purchases by phone or by ordering from catalogues. ’āśWeb user has login name which also serves as unique id. ’āśWeb user could be in several states - new, active, temporary blocked, or banned, and be linked to a shopping cart. ’āśShopping cart belongs to account.
- 40. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 40 ’āśAccount owns customer orders. Customer may have no orders. ’āśEach order could refer to several payments, possibly none. ’āśEvery payment has unique id and is related to exactly one account. ’āśBoth order and shopping cart have line items linked to a specific product. ’āśEach line item is related to exactly one product. A product could be associated to many line items or no item at all.
- 41. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 41
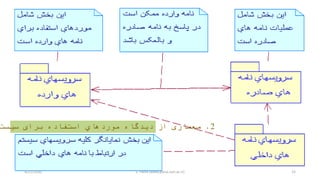
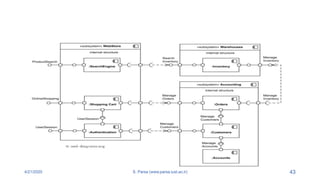
- 42. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 42 ŌĆó As shown in the next slide, the webStore subsystem contains three components: Search Engine, Shopping Cart, and Authentication. ŌĆó Search Engine component allows to search or browse items by exposing provided interface Product Search and uses required interface ŌĆó Search Inventory provided by Inventory component. ŌĆó Shopping Cart component uses Manage Orders interface provided by Orders component during checkout. ŌĆó Warehouses subsystem provides two interfaces Search Inventory and Manage Inventory used by other subsystems and wired through dependencies.
- 43. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 43
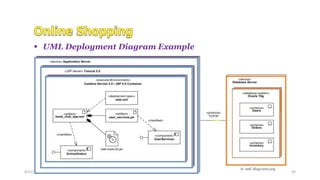
- 44. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 44 ’é¦ UML Deployment Diagram Example
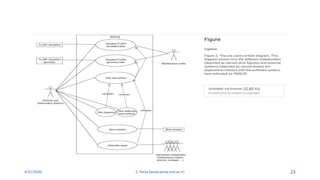
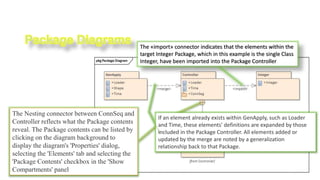
- 45. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 45 ŌĆó Package diagrams depict the organization of model elements into Packages and the dependencies amongst them, including Package imports and Package extensions. They also provide a visualization of the corresponding namespaces.
- 46. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 46 The Nesting connector between ConnSeq and Controller reflects what the Package contents reveal. The Package contents can be listed by clicking on the diagram background to display the diagram's 'Properties' dialog, selecting the 'Elements' tab and selecting the 'Package Contents' checkbox in the 'Show Compartments' panel The «import» connector indicates that the elements within the target Integer Package, which in this example is the single Class Integer, have been imported into the Package Controller If an element already exists within GenApply, such as Loader and Time, these elements' definitions are expanded by those included in the Package Controller. All elements added or updated by the merge are noted by a generalization relationship back to that Package.
- 47. iCloud S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 47 ŌĆ½ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žĄ┘åž╣ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦┘åž┤┌»ž¦┘ćž╣┘ä┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦┘ģ┘Š█ī┘łž¬ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ć┘åž»ž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦┘åž┤┌®ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łžČ┘łž╣ŌĆ¼: ŌĆ½ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘üŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘åž▒┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž│ž╣┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žŁ█īž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌åž▒ž«┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘ć┘åž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▒ž¦█ī┘ćŌĆ¼:ŌĆ½┘Šž¦ž▒ž│ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž╣█īž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘枦ž▒ŌĆ¼1395 4/21/2020
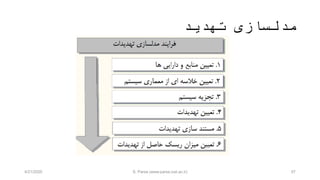
- 48. 1-1ŌĆ½┘ćž»┘üŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘å┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬žČ┘ģ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ 48 ŌĆ½ž¦┘ä┘üŌĆ¼-ŌĆ½┘ģžŁž▒┘ģž¦┘å┌»█īŌĆ¼ (Confidentiality):ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģžŁž»┘łž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž¼ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ģž¦┘åž╣ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž║┘Ŗž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž¼ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ŌĆ¼-ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┌®┘Šž¦ž▒┌å┌»█īŌĆ¼(Integrity): ŌĆ½┘鞦ž©┘ä┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦žĘ┘ģ┘Ŗ┘垦┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž╣ž»┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬ž║┘Ŗ┘Ŗž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘垦┘ģ┘垦ž│ž©ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž║┘Ŗž▒┘ģž¼ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘垦ž©ž╣ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦žĘž¦┘äž╣ž¦ž¬█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘łž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁ┘Ŗž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌åž▒ž«┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žĘ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┌»┘ł┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦┘üž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ćž»ž¦┘üŌĆ¼ 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 49. 494 9 1-2ŌĆ½┌åž▒ž«┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žŁ┘Ŗž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘ł┘ä┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åž▒┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘åŌĆ¼ 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 50. ŌĆ½ž¬┘ł┘ä█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁ█īž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌åž▒ž«┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘åž▒┘ģŌĆ¼ 50 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 51. ŌĆ½┘å┘Ŗž¦ž▓┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žóž║ž¦ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘Ŗž¦ž▓┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åž▒┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘ł┘ä┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘üž▒ž¦┘Ŗ┘åž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤┘łž»ŌĆ¼.ŌĆ½ž░┘Ŗž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘åž©ž╣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┘枦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘å┘Ŗž¬█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘Ŗž¦ž▓┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘ģ┘łž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ä█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁž¦┘䞬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼: 1-ŌĆ½┘å┘Ŗž¦ž▓┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘Ŗ┘ü█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘Ŗž¦ž▓┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘鞦┘äž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘å┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž╣┘ģ┘ä┘Ŗž¦ž¬█īŌĆ¼ 2-ŌĆ½ž╣┘ģ┘ä┘Ŗž¦ž¬█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘Ŗž¦ž▓┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘鞦┘äž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘å┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ 3-ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘łž¦┘Ŗž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ 4-ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘ł█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»┘枦█īŌĆ¼ 514/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 52. ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘ł█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘枦ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž¦ž│ž«ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž”┘łž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘āž¦ž¦ž▒┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łž¦┘éž╣┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘āž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┘āŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ā┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘ćž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘åž¼ž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼. ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¦ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž«ž¦┘ä┘üŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘łžĪŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¦ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘āž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘üž¬ž¦ž¦ž▒┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łžČ┘ŖžŁŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žó┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«┘łž¦┘ć┘垦ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘å┘ģ┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž¼┘łž»┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒┘üž¬ž¦ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤┘łž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘åž¼ž¦┘ģŌĆ¼.
- 53. ŌĆ½┘å┘ģž¦ž»┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆóŌĆ½┘ģ┘枦ž¦ž¼┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▒ž¬ž©ž¦žĘŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘łžĪŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž░┘Ŗž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žóž│┘Ŗž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž«┘ä█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆóŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž¦ž░┘Ŗž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žóž│┘Ŗž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž«┘ä█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘枦ž¼┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦ž©žĘ┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┌®ž│┘Š┘ä┘ł┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆóŌĆ½┘ģ┘枦ž¦ž¼┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▒ž¬ž©ž¦žĘŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘łžĪŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘Ŗž▒┘ł┘å█īŌĆ¼
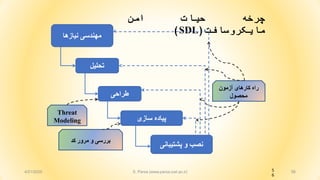
- 56. 565 6 ŌĆ½┌åž▒ž«┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žŁ┘Ŗž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž¦┘Ŗ┌®ž▒┘łž│ž¦┘üž¬ŌĆ¼(SDL) ŌĆ½┘å█īž¦ž▓┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ć┘åž»ž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž▓█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š█īž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬žŁ┘ä█ī┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žĘž▒ž¦žŁ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž┤ž¬█īž©ž¦┘å█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åžĄž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž▒┘łž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žóž▓┘ģ┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģžŁžĄ┘ł┘äŌĆ¼ Threat Modeling 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 57. ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž»┘äž│ž¦ž▓█īŌĆ¼ 574/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
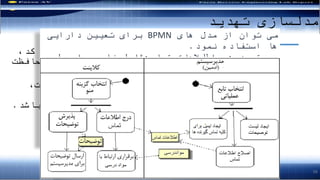
- 58. ŌĆ½ž©ž»ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘üž¬ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬žŁ┘ä┘Ŗ┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┌®ž¦┘å┘Ŗž▓┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž»┘äž│ž¦ž▓█īŌĆ¼ 58 1-ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž▒ž¦┘Ŗ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘垦ž©ž╣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ žīŌĆ½┌®ž»ŌĆ¼ žīŌĆ½ž¦žĘž¦┘äž╣ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ žīŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌»┘ł┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž¦┘ģ┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘垦ž©ž╣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģžŁž¦┘üžĖž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦┘Ŗž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┘Ŗž▓█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤┘ł┘åž»ŌĆ¼. žīŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘枦ž¼┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž╣ž¦┘ä┘é┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┘Ŗž▓█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žó┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž▒ž¦┘Ŗ█īŌĆ¼.ŌĆ½┘ä┘Ŗž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘ģ┘ł┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž▒ž¦┘Ŗ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¦┘åž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«┘łž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒┘ģ┘åž»┘枦ŌĆ¼. ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž»┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼BPMNŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž▒ž¦┘Ŗ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘ģ┘łž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼. ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¼┘ćŌĆ¼:ŌĆ½ž¬┘ģž¦ž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦žĘ┘䞦┘äž╣ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼:ŌĆ½ž¦┘Ŗ┘ģ┘Ŗ┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘垦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž¦┘ģ┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘ģž¦ž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¼ž▓┘Ŗ┘Ŗž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌»┘Ŗž▒┘åž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘ģž¦ž│ŌĆ¼.
- 59. 2-ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ģž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«ž¦┘䞥┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘Ŗž¼ž¦ž»ŌĆ¼ 59 -ŌĆ½ž»┘Ŗž»┌»ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ģž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘ł█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ -ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▓┘Ŗž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž¼┘łž▓┘枦█īŌĆ¼ 3-ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž¼ž▓┘Ŗ┘ćŌĆ¼ -ŌĆ½ž▓┘Ŗž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«ž▒┘łž¼█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łž▒┘łž»█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žó┘å┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘å┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ -ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž¼ž▓ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▓┘Ŗž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž¼ž▓┘Ŗ┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž¼ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘üž▒ž¦ž«┘łž¦┘å┘åž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž▒ž¼ž▓žĪŌĆ¼ -ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┘Ŗž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¼ž▒┘Ŗž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž¼ž▓ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤┘ł┘åž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž©ž¦ž»┘ä┘ćŌĆ¼ -ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘å┘Ŗž¬█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž▒┘ł┘üž¦┘Ŗ┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 60. 60 ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¦ž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▓┘ģž¦┘åž©┘åž»┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćž©┘łž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘āž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌»ž▒ž¦┘üŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▓┘ģž¦┘åž©┘åž»█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š█īž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž▓█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åžĖž▒█ī┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ 60 3-ŌĆ½ž¬ž¼ž▓┘Ŗ┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘å┘Ŗž¬█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž▒┘ł┘üž¦┘Ŗ┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼:ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žĘž▒ž¦žŁ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģžĘž▒žŁŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘łž¦ž¦┘䞬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģžĘ┘ģž”┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž▒žŁž»ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åž┤ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž»┘Ŗž▒┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łž▒┘łž»█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▒ž▓┘Ŗž¦ž©█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¼ž▒┘Ŗž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┘å┘枦┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘å┌»ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ć┘ł┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łž▒┘łž»█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘鞦žĘŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬┌®ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž¦ž▒ž¦┘ģž¬ž▒┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž¼┘łž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģž¬┘Ŗž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ł┘Ŗ┌ś┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž»┘Ŗž▒┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ž½┘垦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž»┘Ŗž▒┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬ž▒┌®┘Ŗž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž½ž©ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ģ┘Ŗž▓█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž©┘é┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁž│ž¦ž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģžĘž▒žŁŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘łž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘łž╣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©žĘ┘łž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ć┘ł┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žó┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▒ž│ž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž©┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤┘łž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ć┘ł┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž╣ž©┘łž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ä┘ģ┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘垦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žó┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¦┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žŁž»ž│ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▓ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘éž▒ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘ł┘Ŗ┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žó┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌»ž▒┘üž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ć┘ł┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤┘垦ž│ž¦┘Ŗ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¦ž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žó┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘åž»█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žĘž©┘é┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž¼┘łž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘Ŗž▓ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¦ž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žó┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘åž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘åž»█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žĘž©┘é┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģžŁž▒┘ģž¦┘å┌»█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┘Ŗž┤┘å┘枦ž»ŌĆ¼:ŌĆ½ž│┘łž¦ž¦┘䞬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¼┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ä┘Ŗž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģžĘž▒žŁŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘å┘Ŗž¬█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤┘łž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žĘž▒ž¦žŁ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘åŌĆ¼. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 62. 6262 ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┌®ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ģ┘łž¦┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ž┤ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ä█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬žŁž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž╣┘å┘łž¦┘åŌĆ¼STRIDEŌĆ½ž¬┘éž│┘Ŗ┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤┘ł┘åž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¬ž▒ž¬┘Ŗž©ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž╣ž©ž¦ž▒ž¬┘åž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼: 1.ŌĆ½ž¼ž╣┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ć┘ł┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼Spoofing identity ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┘āŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼ž╣┘äŌĆ¼žīŌĆ½┘ć┘ł┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž╣ž¦┘ģ┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«┘łž»ž┤ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┘āŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘āž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž┤ž▒┘łž╣ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▓┘åž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ŖŌĆ¼. 2.ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬┌®ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼Tampering with data ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┘āŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ćž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łž▒┘łž»┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘éž©┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž░ž«┘Ŗž▒┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Šž▒ž»ž¦ž▓ž┤ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žó┘åž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž╣ž¬ž©ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│┘åž¼┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ā┘åž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ŖŌĆ¼. ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ćž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒ž│ž¦┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž░ž«┘Ŗž▒┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž▓┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģžŁž¦┘üžĖž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤┘łž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ŖŌĆ¼. ŌĆ½ž╣ž¦┘ģ┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘åž©ž¦┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¬┘łž¦┘åž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 63. 63 4ŌĆ½ž¦┘üž┤ž¦┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦žĘž¦┘äž╣ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼-Information disclosure .1ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┘āŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ā┘垬ž▒┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘é┘ł┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼┘ä┘ł┌»┘Ŗž▒┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘üž┤ž¦┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦žĘž¦┘äž╣ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž┤ž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤ž»ŌĆ¼. 5.ŌĆ½ž¦┘å┌®ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│ž▒┘ł┘Ŗž│ŌĆ¼-DoS ŌĆ½žĘž▒ž¦žŁŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łžČ┘łž╣ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž«┘łž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ā┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ģ┘ā┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žŁ┘ģ┘ä┘ćŌĆ¼DoSŌĆ½┘éž▒ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌»┘Ŗž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žó┌»ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘éž»ž¦┘ģž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž¬┘鞦ž©┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž▓┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Š┘Ŗž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ā┘åž»ŌĆ¼. 6.ŌĆ½ž¦┘üž▓ž¦┘Ŗž┤ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žŁ┘éŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģž¬┘Ŗž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆōElevation of privilege ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┘āŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘å┘éž┤ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘āž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘å┘éž┤ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž»┘Ŗž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼ž»ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤ž»ŌĆ¼. -ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž╣ž»┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘āž¦┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘üž▓ž¦┘Ŗž┤ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž¼┘łž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘āž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģžĘ┘ģž”┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ž»ŌĆ¼. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 64. ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¼┘ćŌĆ¼: ŌĆ½ž¬ž¦┘Ŗ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž¼┘ģ┘łž╣┘ćŌĆ¼StrideŌĆ½žóž│┘Ŗž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ä┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘Ŗž¦┘å┌»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž│ž¬┘åž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž░┘Ŗž▒█īŌĆ¼. ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž»┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž░┘Ŗž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žóž│┘Ŗž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¼┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤┘łž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘Ŗž¼ž¦ž»ŌĆ¼. 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir) 64
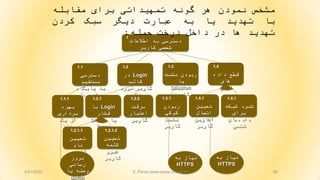
- 65. ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ž«ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘ģ┘ł┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ 65 ŌĆ½ž¦žĘž¦┘äž╣ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž«žĄ█īŌĆ¼ 1 ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž│ž¬┘é┘Ŗ┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž¦┘Ŗ┌»ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ 1.1 LoginŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘鞦┘äž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åžĖž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ 1.2 ŌĆ½ž▒ž©┘łž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åž┤ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ Session ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.3 ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘éžĘž╣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž«žĄ█īŌĆ¼ 1.4 ŌĆ½ž©┘ćž▒┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž»ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘å┘üž░ŌĆ¼ 1.1.1 Login ŌĆ½┘łžŁž┤┘Ŗž¦┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼brute- force 1.2.1 ŌĆ½ž▒ž©┘łž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ł┌®█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åž┤ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.3.1 ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž¬žĄž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žóž║ž¦ž▓┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.4.1 ŌĆ½ž│ž▒┘鞬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž╣ž¬ž©ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.2.2 ŌĆ½ž┤ž©┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤┘å┘łž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž«žĄ█īŌĆ¼ 1.4.1 ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ä┘ģ┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž╣ž©┘łž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.2.1.2 ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘垦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.2.1.1 and ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦žĄ┘ä█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž»┘üŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ž«ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘Ŗž┤┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žĘž▒┘Ŗ┘é█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž»ž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘Ŗž┤┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘üž▒ž▓┘åž»ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž»┘üŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž│┘Ŗž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž¬┘üž¦┘łž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ž«ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ü┘ł┘éŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žĄ┘łž▒ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž░┘Ŗ┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘å┘Ŗž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž┤ž«žĄŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łž»ŌĆ¼: .1ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦žĘž¦┘äž╣ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ž«žĄ█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ Or1.1ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž│ž¬┘é┘Ŗ┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Šž¦┘Ŗ┌»ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ 1.2loginŌĆ½ž»ž▒┘鞦┘äž©ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘åžĖž▒ŌĆ¼ or1.2.1loginŌĆ½┘łžŁž┤┘Ŗž¦┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼brute- force and1.2.1.1ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘垦┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼ user name 1.2.1.2ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ä┘ģ┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž╣ž©┘łž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.2.2ŌĆ½ž│ž▒┘鞬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž╣ž¬ž©ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.3ŌĆ½ž▒ž©┘łž»┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘åž┤ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼sessionŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.3.1ŌĆ½ž▒ž©┘łž»┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ł┌®█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘åž┤ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.4ŌĆ½┘éžĘž╣ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ž«žĄ█īŌĆ¼ or1.4.1ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž¬žĄž¦┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žóž║ž¦ž▓┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.4.2ŌĆ½ž┤┘å┘łž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ž©┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 66. 66 ŌĆ½ž¦žĘž¦┘äž╣ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž«žĄ█īŌĆ¼ 1 ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž│ž¬┘é┘Ŗ┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž¦┘Ŗ┌»ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ 1.1 LoginŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘鞦┘äž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åžĖž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.2 ŌĆ½┘åž┤ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž©┘łž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼ Session ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.3 ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘éžĘž╣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž«žĄ█īŌĆ¼ 1.4 ŌĆ½ž©┘ćž▒┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž»ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘å┘üž░ŌĆ¼ 1.1.1 LoginŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘üž┤ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼brute- force 1.2.1 ŌĆ½ž▒ž©┘łž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ł┌®█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘åž┤ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.3.1 ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž¬žĄž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žóž║ž¦ž▓┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.4.1 ŌĆ½ž│ž▒┘鞬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž╣ž¬ž©ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.2.2 ŌĆ½ž┤ž©┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤┘å┘łž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤ž«žĄ█īŌĆ¼ 1.4.1 ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ä┘ģ┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž╣ž©┘łž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.2.1.2 ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘垦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦ž▒ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ 1.2.1.1 ŌĆ½ž©ž▒┘łž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž│ž¦┘å█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łžĄ┘ä┘ćŌĆ¼ patch ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘Ŗž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ HTTPS ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘Ŗž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ HTTPS and and ŌĆ½┘ģž┤ž«žĄŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘å┘ģ┘łž»┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ćž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌»┘ł┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘ģ┘ć┘Ŗž»ž¦ž¬█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘鞦ž©┘ä┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž╣ž©ž¦ž▒ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»┘Ŗ┌»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│ž©┌®ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž▒ž»┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž«┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ž«ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žŁ┘ģ┘ä┘ćŌĆ¼: 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 69. ŌĆ½ž│┘łž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┌»┘ł┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž▒ž»ž¤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘枦ž▒ŌĆ¼1395
- 70. Second Page
- 71. ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘ł┘Ŗž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒┘垦┘ģ┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦žĄ┘ł┘äŌĆ¼ 714/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 72. ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘ł┘Ŗž│█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒┘垦┘ģ┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦žĄ┘ł┘äŌĆ¼ 72 1-ŌĆ½žŁ┘ģ┘ä┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│žĘžŁŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁž»ž¦┘é┘äŌĆ¼ 2-ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦┘Ŗž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘Ŗ┘ģ┘å┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž╣ž»┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘üž▒žČŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ 3-ŌĆ½ž«žĘž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž░┘Ŗž▒┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬žŁ┘ģ┘äŌĆ¼ 4-ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┌®ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁž»ž¦┘é┘äŌĆ¼ 5-ŌĆ½┌®ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž»ž║ž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┌®ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž╣ž»┘ģŌĆ¼ 6-ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž│ž”┘ł┘ä┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘垦ž│ž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž▓┘Ŗž╣ŌĆ¼ 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 73. 73 1-ŌĆ½žŁ┘ģ┘ä┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│žĘžŁŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁž»ž¦┘é┘äŌĆ¼ 2-ŌĆ½ž¦┘Ŗ┘ģ┘å┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž╣ž»┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘üž▒žČŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦┘Ŗž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ 3-ŌĆ½ž«žĘž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž░┘Ŗž▒┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬žŁ┘ģ┘äŌĆ¼ 4-ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┌®ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁž»ž¦┘é┘äŌĆ¼ 5-ŌĆ½ž¦ž»ž║ž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┌®ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž╣ž»┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ 6-ŌĆ½ž¦┘ä┘Ŗ┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┘åž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘üž¦ž╣ŌĆ¼ ’é¦ŌĆ½žŁ┘ģž¦┘䞬┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž½┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬ž▓ž▒┘Ŗ┘éŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘łž¦ž│žĘ┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž»ž║ž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│┌®ž▒┘Ŗ┘Šž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žóž»ž▒ž│ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ž«┘łž¦ž│ž¬┘枦┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┌®ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Šž░┘Ŗž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼.ŌĆ½ž¦ž»ž║ž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│┌®ž▒┘Ŗ┘Šž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ä┌®ž¬ž▒┘ł┘å┘Ŗ┌®ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘å┘Ŗž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┌®ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žŁ┘ģ┘ä┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žĘž▒┘Ŗ┘éŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘łž¼┘łž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žó┘łž▒ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼. ’é¦ŌĆ½┌å┘åž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘å┘ģ┘ł┘å┘ćŌĆ¼: 1-ŌĆ½žŁ┘ģž¦┘䞬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬ž▓ž▒┘Ŗ┘éŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬ž▓ž▒┘Ŗ┘éŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│┌®┘Ŗ┘łž¦┘äŌĆ¼ 2-ŌĆ½ž¦ž▒ž│ž¦┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│┌®ž▒┘Ŗ┘Šž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žĘž▒┘Ŗ┘éŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Šž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ä┌®ž¬ž▒┘ł┘å┘Ŗ┌®ŌĆ¼ 3-ŌĆ½ž¦ž»ž║ž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│┌®ž▒┘Ŗ┘Šž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬žĄž¦┘ł┘Ŗž▒ŌĆ¼ 4-ŌĆ½┘ģ┌®ž▒┘ł┘枦█īŌĆ¼WORD -ŌĆ½┘ģ┘üž│ž▒┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘鞦ž©┘äž©ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬ž©ž»┘Ŗ┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž¼ž▒ž¦┘Ŗ█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▓┘ģž¦┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž¼ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž▒┘åž»ŌĆ¼. -ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘鞦ž©┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž¼ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ŖŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¦┘åž»ŌĆ¼ 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 74. 74 ’é¦ŌĆ½ž╣┘ģž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćž»┘Ŗž»ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘å┘Ŗž¬█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘łž¦ž│žĘ┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žóž│┘Ŗž©ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Šž░┘Ŗž▒█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▓ž©ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž▒┘垦┘ģ┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž▓█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼. ’é¦ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»┘Ŗž»┌»ž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘å┘Ŗž¬█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦┘Ŗž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▓ž©ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž▒┘垦┘ģ┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│ž¦ž▓█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘垬ž«ž¦ž©ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼: -ŌĆ½┘åž©ž¦ž┤ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¼┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ -ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ž┤ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž┤ž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž░┘Ŗž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žóž│┘Ŗž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁž»ž¦┘é┘äŌĆ¼. ’é¦ŌĆ½ž│┘łž¦┘äŌĆ¼:ŌĆ½ž¤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┘Ŗž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž«žĘž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž░┘Ŗž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žóž│┘Ŗž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘üž¦┘łž¬ŌĆ¼ 4/21/2020 S. Parsa (www.parsa.iust.ac.ir)
- 75. ŌĆ½ž©ž»ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘üž¬ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬žŁ┘ä┘Ŗ┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┌®ž¦┘å┘Ŗž▓┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å█īž▒┘ł┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž┤ž»ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž│┘䞣ŌĆ¼ By Kaspersky Lab on October 30, 2013. 2:44 am 1-ŌĆ½ž▓┘ģž¦┘å█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦┘łž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žĘž▒ž¦žŁ█īŌĆ¼žīŌĆ½ž┤ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ž╣┘ģ┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žŁ┘ģž¦┘䞬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žĘž▒┘Ŗ┘éŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘ł█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žóž│┘Ŗž©ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Šž░┘Ŗž▒█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łž¼┘łž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘åž»ž¦ž┤ž¬ŌĆ¼. 2-ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘Ŗž┤ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žŁž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦┘łž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž¼ž©ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¼┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘Ŗž┤ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žŁž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘枦ž¼┘ģ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ć┌®ž▒┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▓ž©ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼.ŌĆ½ž©┘垦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦žĖ┘枦ž▒ž¦ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▓ž©ž¦┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦┘łž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘Ŗž┤ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘Ŗ┘ä┘Ŗ┘ł┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž©ž▓ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│ž▒ž¦ž│ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼┘枦┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘łž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼. 3-ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬┘üž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▓┘Ŗž¦ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦┘łž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»┘ä┘Ŗ┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žóž┤┌®ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ž»┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žóž│┘Ŗž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘垬ž¦┘ŖžŁŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž▒ž│█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘åž¼ž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž▒┌®ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬žŁ┘é┘Ŗ┘鞦ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž│┘Šž▒ž¦ž│┌®█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž»ž¬ŌĆ¼12ŌĆ½┘ģž¦┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦┘äŌĆ¼2012ŌĆ½ž¬ž¦ŌĆ¼2013ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Šž¦ž│ž«ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│┘łž¦┘äŌĆ¼:ŌĆ½┌åž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žóž│┘Ŗž©ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž░┘Ŗž▒█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦┘łž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬ž╣ž»ž¦ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▓┘Ŗž¦ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ćž│ž¬┘åž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¤ŌĆ¼
- 76. ŌĆ½ž©ž»ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘üž¬ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬žŁ┘ä┘Ŗ┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┌®ž¦┘å┘Ŗž▓┘ģŌĆ¼ The U.S. Department of Homeland Security warned that a security update of Oracle Corp's Java software for Web browsers does not do enough to protect computers from attack, sticking to its previous advice that the program be disabled. Technology | Mon Jan 14, 2013 4:16pm ESTRelated: TECH U.S. says Java still risky, even after security update BY JIM FINKLE Java was responsible for 50 percent of all cyber attacks last year in which hackers broke into computers by exploiting software bugs, according to Kaspersky Lab (2012). ŌĆ½┘ģž▒┌®ž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘å┘Ŗž¬█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ć┘ł┘ģ┘ä┘åž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žó┘ģž▒┘Ŗ┌®ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ćž┤ž»ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒┘łž▓ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž▒ž│ž¦┘å█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬žĄžŁ┘ŖžŁŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦┘łž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž│žĘŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ž▒┌®ž¬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž▒ž¦┌®┘äŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ž¦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž▒┘łž▒┌»ž▒┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łž©ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘垬┘Ŗž¼┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž«ž┤ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘åž©┘łž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘å┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¬┘łž¦┘åž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž¦┘åž╣ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žŁ┘ģž¦┘䞬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦┘ģ┘Š┘Ŗ┘łž¬ž▒█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤┘łž»ŌĆ¼. ŌĆ½┘ģž¬ž«žĄžĄ┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģ┘å┘Ŗž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ćž┤ž»ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ž»┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘åž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦┘ģ┘Š┘Ŗ┘łž¬ž▒┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ž«žĄ█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž▒┘łž▒┌»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž«┘łž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦┘łž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž¼ž▒ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žó┘łž▒┘åž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘ģ┌®┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┘łž▒ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘枦ž¼┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģž¼ž▒┘ģ┘Ŗ┘åŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘éž▒ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌»┘Ŗž▒┘åž»ŌĆ¼. ŌĆ½ž©┘垦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©┘Ŗž¦┘å┘Ŗ┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┌®ž│┘Šž▒ž¦ž│┌®█īŌĆ¼50%ŌĆ½┌®┘ä┘Ŗ┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žŁ┘ģž¦┘䞬ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦┘Ŗž©ž▒█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž»ž▒ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž│ž¦┘äŌĆ¼žīŌĆ½┌»ž░ž┤ž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž©ž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘łž▒┘łž»ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ć┌®ž▒┘枦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦ž▓ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½žĘž▒┘Ŗ┘éŌĆ¼ŌĆ½žóž│┘Ŗž©ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘Šž░┘Ŗž▒█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¼ž¦┘łž¦ŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž¦┘åž¼ž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ŌĆ½ž┤ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž│┘䞣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å█īž▒┘ł┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž┤ž»ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼
- 77. ŌĆ½ž©ž»ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒┘üž¬ž¦ž▒█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬žŁ┘ä┘Ŗ┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘枦█īŌĆ¼ŌĆ½┘ģ┌®ž¦┘å┘Ŗž▓┘ģŌĆ¼ The Web Just Became More Secure: Google Drops Support for Java Written by Matthew HughesSeptember 11, 2015 Ads by Google ItŌĆÖs safe to say that Java ŌĆō particularly in the browser ŌĆō has lost its shine. A large part of this is due to security concerns. The next version of Google Chrome (version 45, scheduled for December) has removed support for it entirely. ŌĆ½┘ģž│┘䞣ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å█īž▒┘ł┘枦█īŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž┤ž»ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼
- 78. Second Page
Editor's Notes
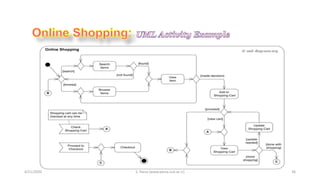
- #37: n example of╠²activity diagram╠²for╠²online shopping. Online customer can browse or search items, view specific item, add it to shopping cart, view and update shopping cart, checkout. User can view shopping cart at any time. Checkout is assumed to include user registration and login. This example does not use partitions, most of the actions are assumed to be fulfilled by online customer.
- #38: n example of╠²activity diagram╠²for╠²online shopping. Online customer can browse or search items, view specific item, add it to shopping cart, view and update shopping cart, checkout. User can view shopping cart at any time. Checkout is assumed to include user registration and login. This example does not use partitions, most of the actions are assumed to be fulfilled by online customer.
- #45: An example of╠²web application╠²UML╠²deployment diagram. Book club web application╠²artifact book_club_app.war╠²is deployed on Catalina Servlet 2.4 / JSP 2.0 Container which is part of Apache Tomcat 5.5╠²web server. The╠²book_club_app.war╠²artifact╠²manifests╠²(embodies) OnlineOrders╠²component. The artifact contains three other artifacts, one of which╠²manifests╠²UserServices╠²component. The Application Server╠²┬½device┬╗╠²(computer server) has╠²communication path╠²to Database Server ┬½device┬╗ (another server).
- #50: ž¦┘ģ┘å█īž¬ ┘åž▒┘ģ ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ ž©┘ć ┘ģ┘ü┘ć┘ł┘ģ ┘ģ┘ć┘åž»ž│█ī ┌®ž▒ž»┘å ┘åž▒┘ģ ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ ž©┘ć žĄ┘łž▒ž¬█ī ž¦ž│ž¬ ┌®┘ć ┘åž▒┘ģ ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒┘枦█ī ┘ģ┘łž▒ž» ┘å█īž¦ž▓ ┘ć žĄ┘łž▒ž¬ ž©█ī ┘ł┘é┘ü┘ć ž╣┘ģ┘ä ┘å┘ģ┘łž»┘ć ┘鞦ž»ž▒ █ī┘ć ┌®┘垬ž▒┘ä ž¬┘ćž»█īž»ž¦ž¬ ž¦┘ģ┘å█īž¬█ī ž»ž▒ ┘ć┘å┌»ž¦┘ģ žŁ┘ģ┘䞦ž¬ ž©ž»ž«┘łž¦┘枦█ī ž©ž¦ž┤ž». ž▒┘łž┤ žĄžŁ█īžŁ ┘ģ┘ć┘åž»ž│█ī ┘åž▒┘ģ ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ ž¦█ī┘å ž¦ž│ž¬ ┌®┘ć ž»ž▒ ┘ģ┘łž▒ž» ž¦┘ģ┘å█īž¬ ┘ć┘ģ ž¦ž▓ žóž║ž¦ž▓ ┌åž▒ž«┘ć žŁ█īž¦ž¬žī ž¦┘éž»ž¦┘ģ ž┤┘łž». ž©ž▒ žĘž©┘é ž¬ž╣ž▒█ī┘ü ž¦žĘ┘ģ█ī┘垦┘å ž¦ž▓ ┘åž▒┘ģ ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ █īž¦ ž│ž¦┘üž¬┘ł█īž▒ ž¦ž┤┘łž▒┘åž│ ┘ģ█īž▓ž¦┘å ž¦žĘ┘ģ█ī┘垦┘å ž¦ž▓ ž╣ž»┘ģ žóž│█īž© ┘Šž░█īž▒█ī ┘åž▒┘ģ ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ ┘ģ█ī ž©ž¦ž┤ž». ž»ž▒ ž┤┌®┘ä ┘ü┘ł┘é ž¼ž▒ž«┘ć žŁ█īž¦ž¬ ž¬┘ł┘ä█īž» ┘åž▒┘ģ ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒ ž¦┘ģ┘å ┘ģž┤ž«žĄ ž┤ž»┘ć ž¦ž│ž¬. ž¦█ī┘å ┌åž▒ž«┘ć žŁ█īž¦ž¬ ž░ž¦ž¬ž¦┘ŗ ž¬┌®ž▒ž¦ž▒█ī ž¦ž│ž¬. ž¦┌»ž▒ ┌®┘ģž©┘łž»█ī ž©ž╣ž»ž¦┘ŗ ž©ž▒ž¦█ī ┘ģž▒žŁ┘ä┘ć ž¦█ī ┘ģž┤ž¦┘ćž»┘ć ž┤┘łž»žī ž©ž¦█īž» ž©┘ć žó┘å ┘ģž▒žŁ┘ä┘ć ž©ž▒┌»ž┤ž¬ ┘ł ┌®┘ģž©ž» ž▒ž¦ ž¼ž©ž▒ž¦┘å ┌»ž▒ž». ž©ž▒ž¦█ī ┘å┘ģ┘ł┘å┘ć ž¦┌»ž▒ █ī┌® ž│█īž│ž¬┘ģ ┘Š┘å┘枦┘å ┘å┌»ž¦ž▒█ī ž▒ž¦ ž¦█īž¼ž¦ž» ┘ģ█ī ┌®┘å█īž» ┘ł ž©ž╣ž»ž¦┘ŗ ┘ģž┤ž¦┘ćž»┘ć ┌®┘å█īž» ┌®┘ć ┘å█īž¦ž▓┘枦█ī█ī ┘垦ž»█īž»┘ć ┌»ž▒┘üž¬┘ć ž┤ž»┘ć ž©ž¦█īž» ž©┘ć ┘ģž▒žŁ┘ä┘ć ž¬ž╣█ī█ī┘å ┘å█īž¦ž▓ ž©ž¦ž▓┌»ž┤ž¬ ┘å┘ģ┘łž» ┘ł žó┘å ┘å█īž¦ž▓┘枦 ž▒ž¦ ž©ž▒┘łž▓ž▒ž│ž¦┘å█ī ┌®ž▒ž».
- #52: Before defining security requirements, security engineers need to identify those parts of the software system that requires security. These parts of the software system are called Target of Evaluation (TOE). Once TOE is identified then finding security functional requirements (SFR) for those parts becomes simple. [8] lists different set of classes depending on the nature of application. Different set of SFRs can be chosen for the required TOE. Once required SFRs are chosen, then table can be designed to monitor its implementation in required software application. SFRs are chosen to counter threats in TOE of software system. For example; if we are trying to gather SFR of a web application; Table 1 lists related SFRŌĆÖs and their activity. There can be different TOE in a single software application; therefore different set of SFRs are collected for each TOE. Once the uncertain requirements are refined by SFR module, then we are ready to start designing our software. Design phase is important and requires more consideration in terms of security. Based on the information provided by analysis phase (Security Requirements by user stories and SFR) a threat model is developed. If security engineer feels some of the information is missing or some other security threats are possible then it goes back to analysis for the refinement of the security requirements. If security expert finds no problems, then a mitigation plan is designed to cater all those threats listed in threat model. Requirements engineering is the main building block for any software development. Security engineers try to elicit security requirements by different methods, e.g. user stories, abuse cases, etc. Most of the occasion requirements gathered from user stories and other sources are not well defined. These requirements can be refined by security functional requirements (SFR) module (Details are given in section ŌĆśIV-AŌĆÖ).
- #60: ž¬ž╣█ī█ī┘å ž▓█īž▒ž│█īž│ž¬┘ģ ┘枦 ┘ł ┘ģž¼┘łž▓┘枦█ī ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│█ī ž©┘ć ┘ćž▒ ž▓█īž▒ ž│█īž│ž¬┘ģ ŌĆō ž©ž▒ž¦█ī ┘å┘ģ┘ł┘å┘ć ž»ž│ž¬ž▒ž│█ī ž©┘ć ž▓█īž▒ ž│█īž│ž¬┘ģ ┘ģž¦┘ä█ī ŌĆō ž¬ž╣█ī█ī┘å ┘åž▒┘ģ ž¦┘üž▓ž¦ž▒┘枦 ž©ž▒ ž¦ž│ž¦ž│ ┘ģ█īž▓ž¦┘å ž¦žČžĘž▒ž¦ž▒
- #61: Privileged Code When you design and build secure assemblies, be able to identify privileged code. This has important implications for code access security. Privileged code is managed code that accesses secured resources or performs other security sensitive operations such as calling unmanaged code, using serialization, or using reflection. It is referred to as privileged code because it must be granted permission by code access security policy to be able to function. Non-privileged code only requires the permission to execute. Auditing is the practice of inspecting logs for the purpose of verifying that the system is in a desirable state In software engineering, software configuration management (SCM) is the task of tracking and controlling changes in the software
- #63: ž©ž¦█īž» ž©ž¦ ž¬┘łž¼┘ć ž©┘ć ž┤ž┤ ž»ž│ž¬┘ć ž¬┘ćž»█īž»ž¦ž¬ ┘ģž»┘ä ž¬┘ćž»█īž» ž▒ž¦ ┘ģž┤ž«žĄ ┘å┘ģ┘łž».