4._The_Ear_3 and all the anantomy of it.pdf
- 1. ANATOMY III 4. The Ear DR. MOHAMAD BAKER ABU-SNAINA GENERAL SURGEON
- 2. The Ear The ear consists of: ’ā╝ External ear. ’ā╝ Middle ear, or tympanic cavity. ’ā╝ Internal ear, or labyrinth, contains the organs of hearing & balance.
- 3. External Ear ŌĆó The external ear has: ’ā╝ Auricle ’ā╝ External auditory meatus. ’ü▒The auricle: ŌĆó Has a characteristic shape. ŌĆó Collects air vibrations. ŌĆó Consists of a thin plate of elastic cartilage covered by skin. ŌĆó It possesses extrinsic & intrinsic muscles, which are supplied by the facial nerve.
- 4. External Ear ’ü▒The external auditory meatus ŌĆó Is a curved tube that conducts sound waves from the auricle to the tympanic membrane. ŌĆó It outer 1/3 is elastic cartilage & the inner 2/3 is bone, formed by the tympanic plate. ŌĆó It is lined by skin & its outer 1/3 is provided with hairs & sebaceous & ceruminous glands (modified sweat glands) that secrete the wax. ŌĆó Sensory supply: auriculotemporal nerve & auricular branch of vagus.
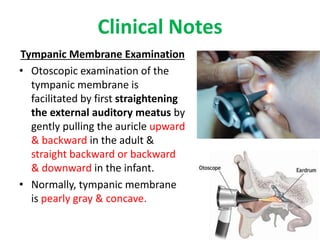
- 5. Clinical Notes Tympanic Membrane Examination ŌĆó Otoscopic examination of the tympanic membrane is facilitated by first straightening the external auditory meatus by gently pulling the auricle upward & backward in the adult & straight backward or backward & downward in the infant. ŌĆó Normally, tympanic membrane is pearly gray & concave.
- 6. Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) ŌĆó It is a small, oblique, biconvex cavity its long axis lies parallel to the plane of the tympanic membrane. ŌĆó It lies inside the petrous part of the temporal bone, lined by mucous m. ŌĆó It contains the auditory ossicles, that transmit the vibrations of the tympanic membrane to the perilymph of the internal ear. ŌĆó It has: roof, floor, 4 walls, ant., post, medial & lateral, it communicates: ’ā╝ In front with the nasopharynx through the auditory tube. ’ā╝ Behind with the mastoid antrum.
- 7. Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity)
- 8. ’ü▒Roof: a thin plate of bone, tegmen tympani, which separates the middle ear from the middle cranial fossa. ’ü▒Floor: a thin plate of bone which separates it from the superior bulb of the internal jugular vein. ’ü▒Lateral wall: mainly by the tympanic membrane. ’ü▒Medial wall: separates the middle ear from the inner ear, shows the following features: Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity)
- 9. ’ā╝ The promontory: is a rounded bulge produced by the 1st turn of the cochlea. ’ā╝ Oval window: above & behind the promontory, it leads to the vestibule of the inner ear. ’ā╝ Rounded window: below & behind the promontory, closed by the 2ry tympanic membrane. ’ā╝ Horizontal part of the fascial canal: arching above the promontory &oval window. Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity)
- 10. Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) ’ü▒Anterior wall: ’āś Upper part, 2 openings into 2 canals: ’ā╝ The upper for tensor tympani muscle. ’ā╝ The lower for the auditory tube. ’āś Lower part, a thin plate of bone, separates it from internal carotid artery ’ü▒Posterior wall: shows the following: ’ā╝ Aditus: is the inlet to mastoid antrum. ’ā╝ Pyramid a small projection, its apex transmits the tendon of stapedius muscle ’ā╝ Vertical part of the fascial canal: lies medial to the aditus.
- 12. The tympanic membrane ŌĆó It is a thin, fibrous membrane, pearly gray in color, circular, 1 cm diameter. ŌĆó It is obliquely placed, facing downward & laterally. ŌĆó It is concave laterally & contains small depression, the umbo, produced by the handle of the malleus. ŌĆó Its greater part is tense (pars tensa), but a small triangular part at its upper border is lax (pars flaccida). ŌĆó Extremely sensitive to pain innervated on its outer surface by auriculotemporal nerve & the auricular branch of vagus.
- 13. Auditory Ossicles ŌĆó There are 3 ossicles articulating together , from lateral to medial: the malleus, incus & stapes. ŌĆó The malleus is fixed to the tympanic membrane while the stapes is fixed at the fenestra vestibuli & the incus in between. ŌĆó The stapedius muscle in inserted to the neck of the stapes & is supplied by the fascial nerve. ŌĆó The tensor tempani muscle is inserted in the handle of the malleus.
- 14. Muscles of the Ossicles
- 15. Auditory (Eustachean) Tube ŌĆó It connects the anterior wall of the tympanic cavity to the nasal pharynx. ŌĆó Its posterior 1/3 is bony & its anterior 2/3 is cartilaginous, related superiorly to the skull, &inferiorly it passes over the superior constrictor muscle of the pharynx. ŌĆó It serves to equalize air pressures in the tympanic cavity & the nasal pharynx.
- 16. Complications of Otitis Media ŌĆó Pathogenic organisms can gain entrance to the middle ear by ascending through the auditory tube. ŌĆó Acute infection of the middle ear (otitis media) produces bulging & redness of the tympanic membrane. ŌĆó Spread of the infection into the mastoid antrum & the mastoid air cells (acute mastoiditis). ŌĆó Superior spread of the infection could produce meningitis & a cerebral abscess in the temporal lobe. ŌĆó Medial spread of the infection can cause a facial nerve palsy & labyrinthitis with vertigo. ŌĆó Posterior spread can cause sigmoid sinus thrombosis. ŌĆó These various complications emphasize the importance of knowing the anatomy of this region.
- 17. Facial Nerve ŌĆó Fiber Type: Sensory, motor, (special sensation, parasympathetic). ŌĆó Origin: Pons (Cerebellopontine angle) ŌĆó On reaching the bottom of the internal acoustic meatus the facial nerve enters the facial canal. ŌĆó The nerve runs laterally above the vestibule of the internal ear until it reaches the medial wall of the middle ear. Here, the nerve expands to form the sensory geniculate ganglion.
- 18. Facial Nerve ŌĆó The nerve then bends sharply backward above the promontory. ŌĆó On arriving at the posterior wall of the middle ear, it curves downward on the medial side of the aditus of the mastoid antrum. ŌĆó It descends in the posterior wall of the middle ear, behind the pyramid & finally emerges through the stylomastoid foramen into the neck.
- 19. Important Branches of the Intrapetrous Part of the Facial Nerve ŌĆó The greater petrosal nerve arises from the facial nerve at the geniculate ganglion It contains preganglionic parasympathetic fibers. ŌĆó The nerve to the stapedius arises from the facial nerve as it descends in the facial canal behind the pyramid ,It supplies the muscle within the pyramid. ŌĆó The chorda tympani arises from the facial nerve just above the stylomastoid foramen ŌĆó The chorda tympani contains: ’āś Taste fibers from the mucous membrane covering the anterior two thirds of the tongue & the floor of the mouth. ’āś Preganglionic parasympathetic secretomotor fibers that reach the submandibular ganglion & are there relayed to the submandibular & sublingual salivary glands. 19
- 20. Tympanic Nerve ŌĆó Arises from the glossopharyngeal nerve, just below the jugular foramen. ŌĆó It passes through the floor of the middle ear & onto the promontory. ŌĆó Here it splits into branches, which form the tympanic plexus. ŌĆó The tympanic plexus supplies the lining of the middle ear & gives off the lesser petrosal nerve, which sends secretomotor fibers to the parotid gland via the otic ganglion .
- 21. The Internal Ear, or Labyrinth ŌĆó Situated in the petrous part of the temporal bone, medial to the middle ear. ŌĆó It consists of: ’ü▒Bony labyrinth a series of cavities within the bone. ’ü▒Membranous labyrinth a series of membranous sacs & ducts contained within the bony labyrinth.
- 22. Bony Labyrinth ŌĆó Consists of three parts: ’ā╝ The vestibule. ’ā╝ The semicircular canals. ’ā╝ The cochlea. ŌĆó These are cavities situated in the substance of dense bone. ŌĆó They are lined by endosteum & contain clear fluid, the perilymph in which is suspended the membranous labyrinth.
- 23. The Vestibule ŌĆó The central part of the bony labyrinth, lies posterior to the cochlea & anterior to the semicircular canals. ŌĆó In its lateral wall are the fenestra vestibuli, which is closed by the base of the stapes & its anular ligament, & the fenestra cochleae. ŌĆó Lodged within the vestibule are the saccule & utricle of the membranous labyrinth.
- 24. Semicircular Canals ŌĆó These are 3 canals, each 2/3 of a circle, each canal has a swelling at one end called the ampulla. ŌĆó They open into vestibule by 5 orifices ’ā╝ The superior canal is vertical & placed at right angles to long axis of petrous bone. ’ā╝ The posterior canal is also vertical but is placed parallel with the long axis of the petrous bone. ’ā╝ The lateral canal is set in a horizontal position & lies in the medial wall of the aditus to the mastoid antrum, above the facial nerve canal.
- 25. The Cochlea ŌĆó It resembles a snail shell. ŌĆó It opens into the anterior part of the vestibule. ŌĆó It consists of a central pillar, the modiolus, around which a hollow bony tube makes 2.5 spiral turns. ŌĆó Each successive turn is of decreasing radius so that the whole structure is conical. ŌĆó The apex faces anterolaterally & the base faces posteromedially.
- 26. Membranous Labyrinth ŌĆó Situated within the bony labyrinth ŌĆó It is filled with endolymph & surrounded by perilymph. ŌĆó It consists of: ’ā╝ The utricle & saccule which placed in the bony vestibule. ’ā╝ The 3 semicircular ducts, which lie within the bony semicircular canals. ’ā╝ The duct of the cochlea, which lies within the bony cochlea. ŌĆó All these structures freely communicate with one another.
- 27. ŌĆó Specialized sensory receptors are located on the walls of the utricle & saccule which are sensitive to the orientation of the head to gravity. ŌĆó When the head begins or stop to move, or accelerates or decelerates, the endolymph in the semicircular ducts changes its speed relative to that of the walls of semicircular ducts. ŌĆó This change is detected in the sensory receptors in the ampullae of the semicircular ducts. ŌĆó The highly specialized epithelium that lies on the basilar membrane forms the spiral Organ of Corti & contains the sensory receptors for hearing. Membranous Labyrinth
- 28. Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) ŌĆó It is a sensory nerve(Special sensory) vestibular & cochlear. ’ā╝ The vestibular fibers originate from the vestibule & the semicircular canals & ’ā╝ The cochlear fibers originate in the organ of Corti. ŌĆó The 2 types of fibers pass the internal acoustic meatus as one nerve to reach the anterior surface of the brain between pons & medulla oblongata.
- 29. Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) ŌĆó The vestibular nerve expanded to form vestibular ganglion ŌĆó Its branches pierce the lateral end of the internal acoustic meatus & gain entrance to membranous labyrinth, where they supply the utricle, the saccule, & the ampullae of the semicircular ducts. ŌĆó Therefore, they are concerned with the sense of position & with movement of the head. ŌĆó Cochlear Fibers: are the central processes of the nerve cells of the spiral ganglion of the cochlea. ŌĆó Originate in the spiral organ of Corti & are therefore concerned with hearing. ŌĆó The peripheral branches of this nerve pass from the ganglion to the spiral organ of Corti. 29