7 Habits Part 1 - Internal Victory
- 1. 7 Habits â Private Victories Miguel Aranda, MBA Site Director, Menifee Campus Adjunct Faculty, School of Business and Professional Studies Part 1 - Applying Key Principles
- 2. Agenda Inside Out ï§ Personality Vs. Character Ethic ï§ Paradigm Shifts and Maps ï§ Principles, Natural Laws and Reality Key Points ï§ Habits ï§ Maturity Continuum ï§ P/PC Be Proactive Begin With the End in Mind Put First Things First
- 3. Inside Out Personality vs. Character Ethic Personalityâ success as a function of personality, public image, attitude, behavior, skills and technique that lubricate the human interaction Characterâ Character qualities form the foundation of success â things like integrity, fidelity, humility, temperanceâĶ 3/4/2016
- 8. The Principle Centered Paradigm Principles Natural Laws Subjective Reality vs. Objective Reality Principles vs. Practices Personality vs. Principle Centered Ethic 3/4/2016
- 9. The Principle Centered Paradigm Change starts with me It is a process, not a quick fix Internal victory before external victory Independence leads to Interdependence 3/4/2016
- 10. Time To Exercise 3/4/2016 ïķ List key principles you live by? ïķ What are the exact opposites of those principles? ïķ Rank order your principles by importance
- 11. Habits âOur character, basically, is a composite of our habits.â
- 12. Habits About Habits: Can be learned and unlearned It is done over time It requires practice It involves a great deal of commitment Definition: âThe intersection of knowledge, skill and desire.â The Habit Loop: 1. The Trigger 2. Routine 3. Reward
- 13. Time To Exercise 3/4/2016 ïķ List some good and bad habits? ïķ Are there any habits you want to build? ïķ For your bad habits, rank them by how much you want to break them. ïķ Do you have the âhow toâ to break or build a new habit? Write a quick plan to change or build one.
- 14. The Maturity Continuum 1. Dependence 2. Independence 3. Interdependence
- 15. P/PC Balance P = Production of desired results PC = Production Capability, the ability or asset that produces 3/4/2016
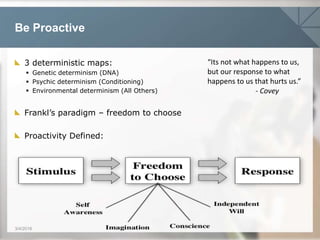
- 16. Be Proactive 3/4/2016 3 deterministic maps: ï§ Genetic determinism (DNA) ï§ Psychic determinism (Conditioning) ï§ Environmental determinism (All Others) Franklâs paradigm â freedom to choose Proactivity Defined: âIts not what happens to us, but our response to what happens to us that hurts us.â - Covey
- 18. Begin With the End in Mind All things are created twice: ï§ Mentally ï§ Physically âBy design or defaultâ â you decide! Busyness vs. Effectiveness Leadership vs. Management We begin with our destination as a clear image â How does your ideal end look? 3/4/2016
- 19. Put First Things First 3/4/2016 What one thing - that you are not doing now - that if you did it, would make a tremendous positive difference in your personal life?
- 20. Putting First Things First Discipline Principles First Self Management 3/4/2016
- 21. Putting First Things First 3/4/2016
- 22. Mastering the Habits Read 7 Habits Part 1 and 2 Review the exercises in this workshop Identify your key life principles Write or revise your mission statement Start rewriting your vision of the future by setting and acting on goals 3/4/2016
- 23. The Center 3/4/2016 1. What are my core principles? 2. What is it I am passionate about? 3. Who are the people I want to invest in, how am I doing at it, how am I doing it and how can I do better? 4. How can I make a unique contribution to The world? My Family? My Friends? My Community? My Career? 5. What goals do I have for my life? 6. What keeps me from achieving my goals? 7. What do I want people to say about me when Iâm gone?
- 24. The World You Want
Editor's Notes
- #4: Benjamin Franklin ascribed to this ethic There are basic principles to living effectively and you can only experience true success by learning and integrating these principles into your character What are some key characteristics that you feel are important? Is personality, public image, attitude, skills and technique important? What place does the personality ethic have in our lives? Is it a total waste of time? Who can you think of that applies personality or character ethic in our society? We will talk about this more in a minute â first lets talk about paradigmsâĶ
- #5: What is a paradigm? A model â a pattern What then is a paradigm shift? A new model or pattern that emerges that eclipses/replaces the old pattern or model Image 1: Can you see theĖýtwo faces in this picture,Ėýthen theĖývase Or maybe you see the vase first. It all depends on your point of view. This is a classic example of a visual paradigm shift that can occur. Image 2: A ladyâs face and a man thinking Image 3: A Native Chief or a man in a snowjacket
- #6: Image 1: Can you see theĖýtwo faces in this picture,Ėýthen theĖývase Or maybe you see the vase first. It all depends on your point of view. This is a classic example of a visual paradigm shift that can occur. Image 2: A ladyâs face and a man thinking Image 3: A Native Chief or a man in a snowjacket
- #7: Image 1: Can you see theĖýtwo faces in this picture,Ėýthen theĖývase Or maybe you see the vase first. It all depends on your point of view. This is a classic example of a visual paradigm shift that can occur. Image 2: A ladyâs face and a man thinking Image 3: A Native Chief or a man in a snowjacket
- #8: Image 1: Can you see theĖýtwo faces in this picture,Ėýthen theĖývase Or maybe you see the vase first. It all depends on your point of view. This is a classic example of a visual paradigm shift that can occur. Image 2: A ladyâs face and a man thinking Image 3: A Native Chief or a man in a snowjacket The point of a paradigm shift is that the way we see things, the maps we have of the world, affect how we see everything. It is the conditioning of how we were raised, what we learned, the influences in our lives, families, schools, churches, friends, work environment, associates etcâĶ and they have all made a direct impact shaping our frame of reference. These paradigms are the source of our attitudes and behaviors (beliefs â attitudes â behaviors). This brings out one of the main flaws of personality ethic â you can try to change your outward attitude and behavior, but it does little good if you fail to examine the paradigms that caused those attitudes and behaviors , the beliefs. We are not truly objective, we see the world how we are conditioned to see it, not as it really is. This is one of the major causes of communication issuesâĶ Ptolemyâs paradigm: Earth Centric Universe / Copernicusâ paradigm: Sun Centric Universe Governmental paradigm in 1700âs: Monarchs rule / Paradigm shift: Rule by the people (French and American revolutions) Story of the lighthouse and 2 battleships â page 40 (2 battleships were on patrol on a very foggy nightâĶ when the captain saw a light bearing starboard bow) What are some parading shifts you have experienced in life? (my shift â hurt people hurt people) So what is the paradigm shift Covey wants us to experience? From a Personality back to a Principle Centered Paradigm
- #9: There has been a paradigm change in our culture from a principle centered ethic to a personality ethicâĶ Principles: Fairness, Loyalty, Integrity, Human Dignity, Service, Quality, Excellence, Potential, Growth, Patience, Nurturance, Encouragement Principles vs. Values vs. Practices â Principles are Natural Laws â deep fundamental truths with universal application; Principles are guidelines for human conduct that are proven to have enduring, permanent value, they are fundamental, essentially unarguable because they are self evident. Values are like maps that describe the territory â Principles are the actual territoryâĶ Thieves can share values, but that does not make them principledâĶ Practices change based on circumstances; practices are things you can do to help you and can be based on principles, but are not eternal because they vary based on situations Objective vs. Subjective â goes back to natural law, not every thing is subjective â and those things that arenât, need to be looked at differently Personality ethic says we can change our personality or the way we do something and it will change us, but the reality is not true based on principle (Story of the farmer and the cramming student)
- #11: They key is to align our maps / frame of reference, to principles that are indisputable. That will help us to see the world more clearly. Principles are the fundamental scientific, logical, or moral/ethical âtruths,â arising from experience, knowledge, and (often) values, on which we base our actions and thinking Fairness, Loyalty, Integrity, Human Dignity, Service, Quality, Excellence, Potential, Growth, Patience, Nurturance, Encouragement, forgiveness, gratitude, harmony, humility, Love, Wisdom, Peace, Compassion, Joy, Contentment, Persistence,
- #12: âHabits are consistent, unconscious patterns that express our character and produce our effectiveness or ineffectiveness.â âSow a thought, reap an action; sow an action, reap a habit; sow a habit, reap a character; sow a character, reap a destiny.â
- #13: Knowledge: the what to do and why Skill: the how to do Desire âthe want to do (motivation) Why does AA work? Its not science, itâs a new habit, and the people in your life to help you overcome your weakness when it happens (because it will), its process and retraining the automatic processes in your brain. How Habits Form It turns out that every habit starts with a psychological pattern called a "habit loop," which is a three-part process. First, there's a cue, or trigger, that tells your brain to go into automatic mode and let a behavior unfold. "Then there's the routine, which is the behavior itself," Duhigg tellsĖýFresh Air's Terry Gross. "That's what we think about when we think about habits.â The third step, he says, is the reward: something that your brain likes that helps it remember the "habit loop" in the future. The Power of Habit Why We Do What We Do in Life and Business byĖýCharles Duhigg Hardcover, 371 pages
- #15: We begin life as dependent We grow to be independent We grow to achieve interdependence physically, mentally, emotionally, financialy etcâĶ All of nature is interdependentâĶ Dependence is the paradigm of you â you take care of me Independence is the paradigm of I â I can do it myself Interdependence is the paradigm of we â we can do it when we combine talents, abilities, etc âĶ As a city â you are in an interdependent relationship with your constituency â can you think of some situations where this is particularly true? (resources, accomplishing meeting needs, etcâĶ)
- #16: Since 7 habits is about effectiveness, we have to look at production and production capabilityâĶ the goose (PC) and the golden egg (P) 3 types of assets: Physical Financial Human Each of these has a production and capability that must be managed. Misusing them will decrease effectiveness. You must maintain balance. Work Life Balance comes from a proper understanding of P/PC Balance What are some of the assets you manage in your daily activities? Are you paying attention to the balance?
- #17: Proactivity: taking responsibility for our own lives (78) Behavior is a function of decisions We can subordinate feelings to values and principles We can choose our response Story of Job â things can hurt us, but our response is what defines our character. Eleanor Roosevelt: no one can hurt you without your consent Ghandi â they cannot take away our self respect if we do not give it to them Exercise Question: Think of an area in your life where you have allowed yourself to blame someone or something? Or you could take a more proactive response?
- #18: Circle of concern, influence, control Our control over problems: Direct Indirect No control Want to practice proactivity? Make the effort to be a positive influence. How can you be a positive influence in the lives of the people around you? (me: positive communication, build people up)
- #19: Leadership vs. Management â Coveyâs view Leadership deals with what I want to accomplish Management deals with how to best accomplish them Leaders direct people to the right paradigm, managing helps them work within it To get to your end â you have to start to envision it now and address the important issues you will face as you become self aware.
- #20: Habit 1 is based on the four human endowments of 1) imagination, 2) conscience, 3) independent will and 4) self-awareness and emposers you to say âthat is an unhealthy program I am on and I can changeâ Habit 2 is based on imagination and allows us to create or envision our own potential. Habit 3 is the phsycial fulfillment of habits 1 and 2 â the exercise of our independent will to make our vision happen. You cant have an effective habit 3 without 1 and 2 Computer analogy: Habit 1: You are the programmer Habit 2: Write the program Habit 3: Run the program
- #21: Discipline â disciple to a philosophy, your philosophy If you are to be good at it, you must use your self discipline and subordinate your activities, feelings, impulses, moods to your principles.
- #22: A simple tool for personal effectiveness
- #24: Now that we are