8f902 module 4b
- 1. Rational versus Emotional Motives • Rationality implies that consumers select goals based on totally objective criteria, such as size, weight, price, or miles per gallon • Emotional motives imply the selection of goals according to personal or subjective criteria Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Four şÝşÝߣ 1
- 2. The Dynamics of Motivation • Needs are never fully satisfied • New needs emerge as old needs are satisfied • People who achieve their goals set new and higher goals for themselves • Frustration – Failure to achieve a goal may result in frustration. – Some adapt; others adopt defense mechanisms to protect their ego. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Four şÝşÝߣ 2
- 3. Arousal of Motives • Physiological arousal • Emotional arousal • Cognitive arousal • Environmental arousal Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Four şÝşÝߣ 3
- 4. Philosophies Concerned with Arousal of Motives • Behaviorist School – Behavior is response to stimulus – Elements of conscious thoughts are to be ignored – Consumer does not act, but reacts • Cognitive School – Behavior is directed at goal achievement – Needs and past experiences are reasoned, categorized, and transformed into attitudes and beliefs Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Four şÝşÝߣ 4
- 5. Types and Systems of Needs • Henry Murray’s 28 psychogenic needs • Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs • A trio of needs Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Four şÝşÝߣ 5
- 6. Motivational Research • Term coined in the 1950s by Dr. Ernest Dichter • Based on premise that consumers are not always aware of their motivations • Identifies underlying feelings, attitudes, and emotions Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Four şÝşÝߣ 6
- 7. What Are Attitudes? • The attitude “object” • Attitudes are a learned predisposition • Attitudes have consistency • Attitudes occur within a situation Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 7
- 8. Structural Models of Attitudes • Tricomponent Attitude Model • Multiattribute Attitude Model • The Trying-to-Consume Model • Attitude-Toward-the-Ad Model Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 8
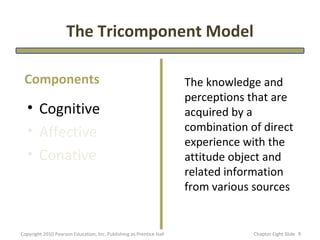
- 9. The Tricomponent Model Components The knowledge and perceptions that are • Cognitive acquired by a • Affective combination of direct experience with the • Conative attitude object and related information from various sources Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 9
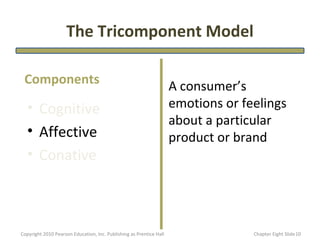
- 10. The Tricomponent Model Components A consumer’s • Cognitive emotions or feelings about a particular • Affective product or brand • Conative Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 10
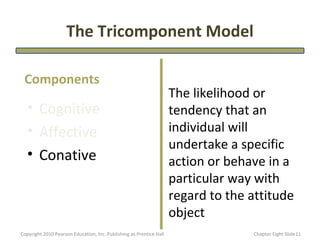
- 11. The Tricomponent Model Components The likelihood or • Cognitive tendency that an • Affective individual will undertake a specific • Conative action or behave in a particular way with regard to the attitude object Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 11
- 12. Attitude models that examine the Multiattribute composition of Attitude consumer attitudes Models in terms of selected product attributes or beliefs. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 12
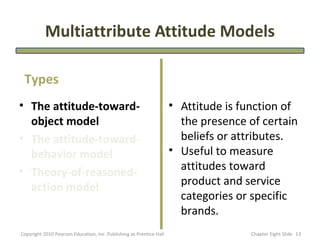
- 13. Multiattribute Attitude Models Types • The attitude-toward- • Attitude is function of object model the presence of certain • The attitude-toward- beliefs or attributes. behavior model • Useful to measure • Theory-of-reasoned- attitudes toward action model product and service categories or specific brands. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 13
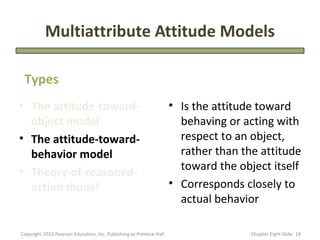
- 14. Multiattribute Attitude Models Types • The attitude-toward- • Is the attitude toward object model behaving or acting with • The attitude-toward- respect to an object, behavior model rather than the attitude • Theory-of-reasoned- toward the object itself action model • Corresponds closely to actual behavior Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 14
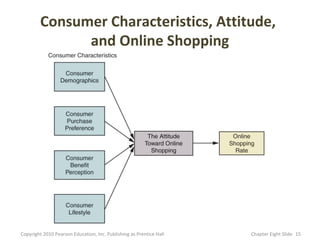
- 15. Consumer Characteristics, Attitude, and Online Shopping Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 15
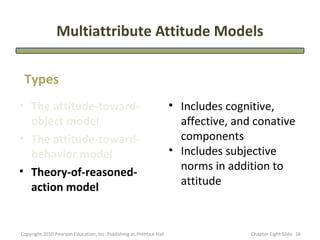
- 16. Multiattribute Attitude Models Types • The attitude-toward- • Includes cognitive, object model affective, and conative • The attitude-toward- components behavior model • Includes subjective • Theory-of-reasoned- norms in addition to action model attitude Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 16
- 17. An attitude theory designed to account for the many cases Theory of where the action or Trying to outcome is not certain Consume but instead reflects the consumer’s attempt to consume (or purchase). Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 17
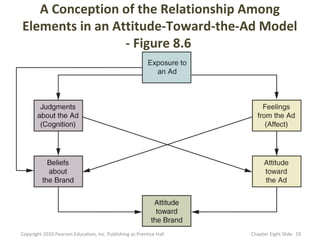
- 18. A model that proposes that a consumer forms various feelings (affects) and judgments Attitude- (cognitions) as the result of exposure to an Toward-the- advertisement, which, in Ad Model turn, affect the consumer’s attitude toward the ad and attitude toward the brand. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 18
- 19. A Conception of the Relationship Among Elements in an Attitude-Toward-the-Ad Model - Figure 8.6 Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 19
- 20. Issues in Attitude Formation • Sources of influence on attitude formation – Personal experience – Influence of family – Direct marketing and mass media • Personality factors Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 20
- 21. Strategies of Attitude Change Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 21
- 22. Changing the Basic Motivational Function Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 22
- 23. Attitude Change • Altering Components of the Multiattribute Model – Changing relative evaluation of attributes – Changing brand beliefs – Adding an attribute – Changing the overall brand rating • Changing Beliefs about Competitors’ Brands Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 23
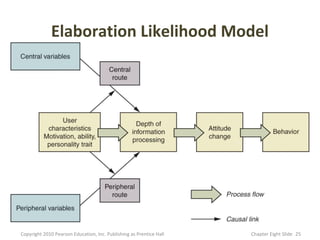
- 24. Customer attitudes are Elaboration changed by two Likelihood distinctly different Model routes to persuasion: (ELM) a central route or a peripheral route. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 24
- 25. Elaboration Likelihood Model Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 25
- 26. • The Elaboration Likelihood Model states that there are two routes through which persuasive messages are processed: – The central route, which provides complete information and is straightforward, and – The peripheral route: which uses means like catchy tunes, colors, and celebrity endorsements. 26
- 27. • The central route is what you could also call the 'thinking route': "The central route is characterized by considerable cognitive elaboration. • It occurs when individuals focus in depth on the central features of the issue, person, or message. When people process information centrally, they carefully evaluate message arguments, ponder implications of the communicator's ideas, and relate information to their own knowledge and values." (Perlof, 2003). 27
- 28. • "Rather than examining issue-relevant arguments, people examine the message quickly or focus on simple cues to help them decide whether to accept the position advocated in the message. Factors that are peripheral to message arguments carry the day. These can include a communicator's physical appeal, glib speaking style, or pleasant association between the message and music playing in the background. When processing peripherally, people invariably rely on simple decision-making rules or 'heuristics'. For example, an individual may invoke the heuristic that 'experts are to be believed', and for this reason (and this reason only) accept the speaker's recommendation." (Perlof, 2003). 28
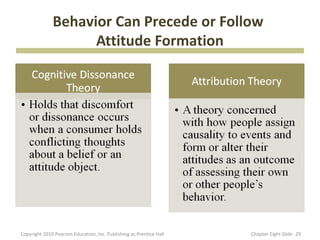
- 29. Behavior Can Precede or Follow Attitude Formation Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter Eight şÝşÝߣ 29
Editor's Notes
- #12: The conative component describes the likelihood that you will do something in regard to the object. One of the most important is your intention to buy a certain object.