Carbon Sequestration: Potential of the Early Pennsylvanian Breathitt Group, Pocahontas Basin
- 1. CARBON SEQUESTRATION: RESERVOIR CHARACTERIZATION AND POTENTIAL OF EARLY PENNSYLVANIAN BREATHITT GROUP, CENTRAL APPALACHIAN BASIN Ryan Grimm Virginia Tech Dept. of Geosciences Committee members: Ken Eriksson, Chair Fred Read Bill Henika Steve Greb - University of Kentucky Early Pennsylvanian Breathitt Group - Raven and Kennedy coal zone roadcut, Grundy Virginia. USACOE Flood Protection Project.Ěý Vertical height ~100m
- 2. Carbon Capture and Geological Storage Opportunities in the Pocahontas Basin Objective – Investigate properties of geologic media for long term CO2 storage from a future point source in southwestern Virginia – think FUTUREGEN
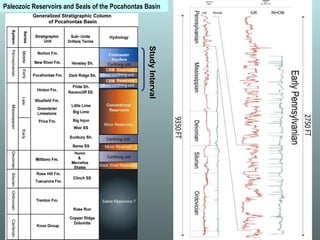
- 3. Paleozoic Reservoirs and Seals of the Pocahontas Basin Study Interval
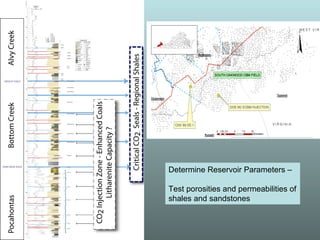
- 4. ECBM – ENHANCED COAL BED METHANE RECOVERY AND PRODUCTION USING CO2 FLOODS SECARB estimates 398 million tons of technically feasible ECBM - CO 2 storage capacity in the Pocahontas Basin Potential enhanced recovery of >2.5 TCF of CBM gas production Highlights need for increased understanding of surrounding lithologies Regional shale seals & Additional storage capacities / hazards of porous sandstones
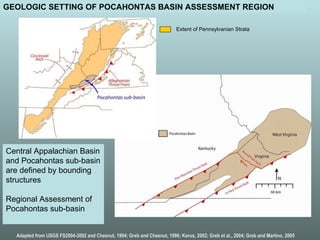
- 5. Central Appalachian Basin and Pocahontas sub-basin are defined by bounding structures Regional Assessment of Pocahontas sub-basin Adapted from USGS FS2004-3092 and Chesnut, 1994; Greb and Chesnut, 1996; Korus, 2002; Greb et al., 2004; Greb and Martino, 2005 GEOLOGIC SETTING OF POCAHONTAS BASIN ASSESSMENT REGION Extent of Pennsylvanian Strata
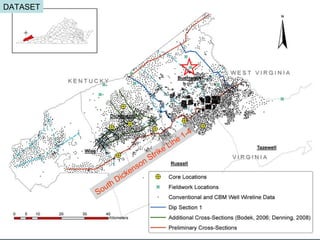
- 6. South Dickenson Strike Line 1-4 DATASET
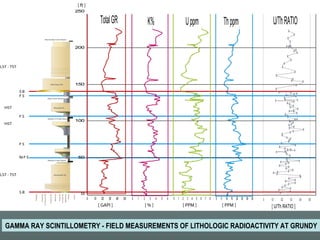
- 7. GAMMA RAY SCINTILLOMETRY - FIELD MEASUREMENTS OF LITHOLOGIC RADIOACTIVITY AT GRUNDY
- 8. Determine Reservoir Parameters – Test porosities and permeabilities of shales and sandstones
- 9. Ěý
- 10. STARVED RIPPLES SANDY RHTHYMITES ORGANIC PARTINGS
- 11. SB SB FS
- 12. Neonereites Scalarituba Trace Fossil Analysis
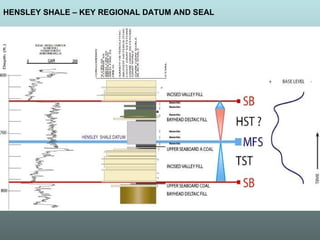
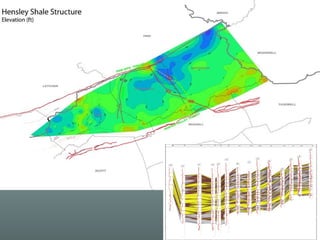
- 13. HENSLEY SHALE – KEY REGIONAL DATUM AND SEAL
- 14. Raw Data - South Dickenson Strike Line 1
- 15. Quartz Arenites - SDS 1
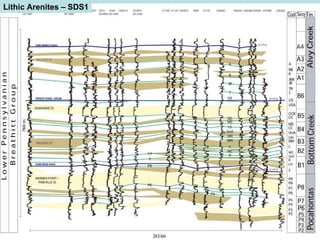
- 16. Lithic Arenites – SDS1
- 17. Minor Flooding Surfaces – SDS1
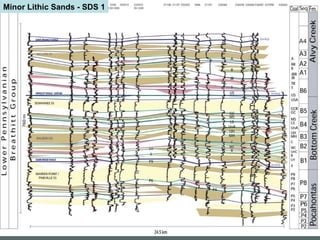
- 18. Minor Lithic Sands - SDS 1
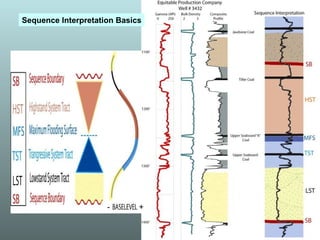
- 19. - + Sequence Interpretation Basics
- 20. Sequences – SDS 1
- 21. Ěý
- 22. Conclusions Sequence architecture of the Pocahontas basin exhibits broad, regional flooding surfaces and discontinuities in the subsurface Integration of core and outcrop measurements with geophysical well log data aids sequence model verification Sequence model identifies regional CO 2 storage and sealing lithologies for targeted sequestration opportunities Continued work will focus on the interplay of eustatic and tectonic controls on basin infilling
- 23. THANKS! Katie O’Donnell Bill Rouse Erik Haug Ben Roth David Greenwald Brad Kelley Nino Ripepi Ilija Miskovic