Accounting process
Download as PPTX, PDF1 like1,450 views
the accounting process is also called as accounting cycle it shows the process from the beginning to till the end of the financial year
1 of 11
Downloaded 11 times










Recommended
Introduction to accounting



Introduction to accountingAswin prakash i , Xantus Technologies
Ěý
Accounting is the technique of recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions and interpreting the results. It involves recording business transactions in journals and ledgers, grouping like transactions, and preparing financial statements like the trial balance, income statement, and balance sheet. The double-entry system records both aspects of each transaction to ensure accuracy and allow calculation of profit and financial position. Financial accounting focuses on external reporting while cost and management accounting support internal decision making.Ledger



LedgerSANGEETHASHAINU
Ěý
The ledger is the principal book of accounting that contains accounts where transactions are recorded. It collects all accounts from the journal and special journals. The ledger is useful for ascertaining the net result of transactions in an account on a given date. It organizes accounts by debit and credit sides, records journal folio references, and amounts. Ledger accounts are classified into five categories: assets, liabilities, capital, revenues/gains, and expenses/losses. Temporary accounts are closed at period end by transferring them to trading and profit and loss, while permanent accounts appear on the balance sheet.Trial balance



Trial balanceKULDEEP MATHUR
Ěý
The document discusses trial balance, which is a statement that lists the debit and credit balances of ledger accounts to test the arithmetical accuracy of accounting books. A trial balance has certain features, such as being prepared on a specific date and including all ledger accounts. It also discusses the purpose of a trial balance, which is to test accuracy, provide a summary of ledger account balances, and serve as the basis for preparing final financial statements. The document outlines different methods for preparing a trial balance and provides examples of common account adjustments that are made, such as for closing stock, depreciation, outstanding expenses, and prepaid expenses.Topic 8 trial balance



Topic 8 trial balanceSrinivas Methuku
Ěý
Know the Meaning, Objectives of Trial Balance.
Know the format of Trial Balance.
Preparation of Trial Balance.
Accounts and its functions



Accounts and its functionsHuma Ali
Ěý
Accounting records, classifies, and summarizes business transactions to provide financial information to both internal and external users. It aims to determine profits and financial position, facilitate management control, and assess tax liability. However, accounting has limitations as it uses monetary values and estimates, and may be manipulated. The main accounting systems are cash basis, accrual basis, and mixed basis. Stakeholders like shareholders, creditors, management, employees, and the government rely on accounting information for decision making.Final account ppt



Final account pptPratima57
Ěý
This PPT is for Students of 11th, 12th and BBA. This ppt includes basic information for Final Account.What Is Debit and Credit



What Is Debit and CreditTrendStatic Corporation
Ěý
Debit and Credit
Accounting is the systematic recording and organizing of all the financial information of a company. This refers to the bookkeeping function of Accounting; where bookkeepers record accounts in journals and transferring it to a ledger. Accounting also has the reporting function where all the gathered financial information is used to create financial statements to analyze and understand the financial health and performance of the business. It’s pretty straightforward, almost all people can understand this definition at first look, but what confuses everybody is the concept of Debit and Credit. Now to set things clear, let’s define first debit and credit.
We seriously do appreciate you examining this slide share. Just in case you want to study more about other important accounting theories, our company, TrendStatic Business Solutions delivers different Basic Accounting for Non-Accountants training programs. Educating regular individuals without Accounting qualifications all the stuff that they have to properly recognize to start out on accounting.
Accounting Basics



Accounting BasicsAccounts Arabia
Ěý
Basics of Accounting. Principles and concepts of Accounting
what is Double Entry System of Accounting?what Financial Statements?
Accounting is a process of identifying, recording, summarising and reporting economic information
to decision makers in the form of financial statements.ACCOUNTING BASICS &PRINCIPLES



ACCOUNTING BASICS &PRINCIPLESChristine Michael
Ěý
This document provides an overview of accounting basics and principles. It defines accounting as the process of identifying, recording, and communicating financial information. The objectives of accounting are to provide useful information to decision makers through relevance, reliability, and other qualitative characteristics. The document outlines key accounting principles like the business entity, accrual basis, and matching principles. It also describes the main financial statements - the balance sheet, income statement, statement of cash flows, and statement of owners' equity - and their purpose in communicating financial information to both internal and external users of accounting data.Basic Accounting Terms



Basic Accounting TermsDr. Bhavik Shah
Ěý
Business transactions involve the exchange of value, such as goods or services for money, between two or more entities. There are two main types of transactions: cash transactions involving an exchange of cash, and credit transactions where payment is promised at a future date. Capital refers to the value invested in a business by its owner, while drawings refer to amounts withdrawn by the owner. Assets are items owned by a business that have value, and liabilities are amounts owed to outside parties. Revenue is the income generated from sales or services, while expenses are costs incurred to generate that revenue.Accounting basics



Accounting basicsRITESH KUMAR SINGH
Ěý
Accounting is defined as the art of Recording, Classifying and Summarizing transactions in monetary terms (in Money terms) for preparation of Financial Statements
Book- keeping includes recording of journal, posting in ledgers and balancing of accounts. All the records before the preparation of trail balance is the whole subject matter of book- keeping.
Accounting, is an information system is the process of identifying, measuring and communicating the economic information of an organization to its users who need the information for decision making.Accounting process



Accounting processrohit kashyap
Ěý
The accounting process involves collecting documents, posting journal entries, transferring balances to ledger accounts, preparing a trial balance, making adjustments, creating an adjusted trial balance, preparing financial statements, making post-closing entries, and generating a post-closing trial balance. Source documents are collected and analyzed throughout the accounting period. Journal entries are posted using double entry accounting. Ledger accounts track debit and credit balances. An initial trial balance is prepared, then adjustment entries are made and an adjusted trial balance is created to develop financial statements showing the firm's profits, losses, and financial health. Finally, revenue and expense accounts are closed out and balances transferred in post-closing entries.Trial balance ppt



Trial balance pptharshika5
Ěý
A trial balance is a financial statement that lists the debit and credit balances of all accounts in the general ledger. It is prepared to check the arithmetic accuracy of the ledger accounts and help detect errors. The trial balance is not a conclusive proof of accuracy as certain errors may remain undetected even if the debit and credit totals match. Common errors include omissions, incorrect postings, or wrong account balances. If errors cannot be found, a suspense account is used to temporarily balance the trial balance.Journal Entries



Journal EntriesJosephin Remitha M
Ěý
Here are the journal entries for the transactions:
Jan 1: Capital 80,000
To Cash 80,000
(Commenced business with cash)
Jan 2: Bank 40,000
To Cash 40,000
(Deposited cash in bank)
Jan 3: Purchases 5,000
To Cash 5,000
(Purchased goods by paying cash)
Jan 4: Purchases 10,000
To Lipton & Co. 10,000
(Purchased goods from Lipton & Co. on credit)
Jan 5: Cash 11,000
To Sales 11,000
(Sold goods to Joy and received cash)
1 introduction to financial accounting



1 introduction to financial accountingItisha Sharma
Ěý
This presentation talks about Meaning, of accounting, distinction between book keeping and accounting, Branches of accounting, Objectives of accounting, Uses and users of accounting information, Advantages of Accounting, Is accounting a science or an art, double entry system of financial accounting, limitations of financial accounting, important terms, journal entry, accounting concepts and conventionsRectification of errors with accounting terms



Rectification of errors with accounting termsMuhammad Saqib Awan
Ěý
This document discusses various types of accounting errors and how to rectify them. It outlines two main types of errors: two-sided errors, which do not affect the trial balance, and one-sided errors, which do affect the trial balance. Two-sided errors include errors of omission, commission, original entry, principle, and compensating errors. One-sided errors require using a suspense account to rectify. The document provides examples for each type of error and explains how to make the correcting journal entries to rectify the errors.Double entry system



Double entry systemRaJesh Thakur
Ěý
It is the system in which both the aspects i.e. debit as well as credit are recorded in the books of accounts .It records transactions relating to all the accounts i.e. personal, real and nominal.accounting process



accounting processManish Tiwari
Ěý
The document provides an overview of the accounting process. It defines accounting and discusses its key principles and concepts. It describes the different branches and types of accounting. It then explains the accounting process which involves identifying transactions, preparing documents, recording transactions in a journal, posting to ledgers, preparing trial balances and final accounts such as profit and loss statements and balance sheets. It also discusses the different books of accounts used such as journals, ledgers and trial balances. Finally, it covers accounting systems and basics such as debits and credits, types of accounts and how to prepare and balance accounts.Account



AccountNiyati Mehta
Ěý
The document defines accounting as recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions and events to prepare financial statements. It discusses the basic accounting concepts like the accounting equation, assets, liabilities, equity, revenues and expenses. It also explains the key steps in accounting cycle which includes recording transactions, posting to ledger accounts, preparing an unadjusted trial balance, making adjusting entries, preparing an adjusted trial balance and financial statements, and closing temporary accounts. The accounting cycle aims to generate useful financial information for decision making in the form of income statement, balance sheet, and other financial reports.Trading Profit And Loss Account



Trading Profit And Loss AccountMarcus9000
Ěý
The document discusses the Trading Profit and Loss Account, which is prepared annually to show a business's trading activities and determine its profit over the year. It has two parts: the Trading Account, which summarizes information on goods bought, sold and returned; and the Profit and Loss Account, which shows costs incurred and calculates gross and net profit. The document provides examples of key items included in each account, such as purchases, sales, opening/closing stock, expenses, and gross/net profit.Final Accounts 



Final Accounts PrachiSharma304
Ěý
The document discusses the preparation of final accounts, which includes three financial statements: (i) the trading account, which shows gross profit/loss; (ii) the profit and loss account, which shows net profit/loss; and (iii) the balance sheet, which shows the financial position. It provides details on what each statement shows and their importance. The trading account is the first stage and shows gross profit/loss. The profit and loss account indicates net profit/loss after deducting all expenses. The balance sheet presents the sources and uses of funds on a particular date. Final accounts are important to understand business results, financial position, and for tasks like getting loans.Accounting Cycle



Accounting CycleRavi Kapoor
Ěý
The accounting cycle is a series of 9 steps that are repeated each reporting period to record business transactions and prepare financial statements. The steps are: 1) analyze transactions, 2) journalize transactions, 3) post to ledger accounts, 4) prepare an unadjusted trial balance, 5) make adjustments, 6) prepare an adjusted trial balance, 7) make financial statements, 8) close temporary accounts, and 9) prepare a post-closing trial balance to verify the accounting records. The cycle ensures transactions are properly recorded and financial statements are prepared accurately.Accounting concept and convention



Accounting concept and conventionpoojanmantri
Ěý
This document discusses key accounting concepts and conventions. It defines 8 accounting concepts: business entity, money measurement, accounting period, accounting cost, going concern, dual aspect, realization, and matching. It also discusses 4 accounting conventions: consistency, materiality, conservatism, and full disclosure. The concepts and conventions establish standard principles and practices for preparing accurate financial statements and reports.Introduction to accounting



Introduction to accountingVishal Kukreja
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to the concepts of accounting. It defines accounting as a system that collects and processes financial information to allow informed decisions by users. It discusses the need for accounting to determine results of business transactions and the financial position. It outlines the key functions of accounting like identifying, recording, classifying, summarizing, analyzing, interpreting and communicating financial information. It also discusses the accounting cycle and different branches and users of accounting information. Finally, it provides definitions of some basic accounting terms.Ledger in financial accounting (11th commerce)



Ledger in financial accounting (11th commerce)Yamini Kahaliya
Ěý
This presentation is on ledger which is the topic of financial accounting. it contents details about following points. There are:-
1. Meaning of ledger
2. Need & Importance of ledger
3. Advantage of Ledger
4. Difference b/w Journal & ledger
5. Format of ledger
6. Rules of posting
7. Illustrations
8. Exercise
Double entry systme



Double entry systmeAsian Institute of Virtual Learning
Ěý
After reading this topic you should be able to understand
1-Double Entry System
2- Accounts and their classification
3- Rules of Debit and CreditLedger



LedgerJosephin Remitha M
Ěý
This document defines key concepts related to ledgers. It begins with defining a ledger as a summary of all transactions relating to an account over a period of time, showing the net effect. It then provides a flow chart and discusses the utilities of ledgers, including providing quick information on accounts, controlling transactions, preparing trial balances and financial statements. The document also covers the format of ledger accounts, the distinction between journals and ledgers, and the procedures for posting transactions to ledgers, including opening entries, compound entries, and balancing accounts.Recording Transactions



Recording TransactionsAlamgir Alwani
Ěý
This document discusses key concepts in accounting, including the double-entry system, T-accounts, journal entries, posting transactions, closing revenue and expense accounts, preparing trial balances, and correcting errors. It also covers how computers have transformed accounting data processing.Basics of Finance and Accounts



Basics of Finance and AccountsDr. Sushil Bansode
Ěý
This document provides an overview of key concepts in finance and accounting, including:
1. It defines financial accounting as the process of recording business transactions and preparing financial statements like the income statement and balance sheet.
2. Accounting principles and concepts are discussed, such as the business entity concept and matching principle. Conventions like conservatism are also covered.
3. Basic bookkeeping elements are introduced, including journals, ledgers, trial balances, and how final accounts like trading, profit and loss, and balance sheets are prepared.
4. The document distinguishes between financial and management accounting.
5. Cost accounting concepts are outlined, including different types of costs, cost statements, work-More Related Content
What's hot (20)
ACCOUNTING BASICS &PRINCIPLES



ACCOUNTING BASICS &PRINCIPLESChristine Michael
Ěý
This document provides an overview of accounting basics and principles. It defines accounting as the process of identifying, recording, and communicating financial information. The objectives of accounting are to provide useful information to decision makers through relevance, reliability, and other qualitative characteristics. The document outlines key accounting principles like the business entity, accrual basis, and matching principles. It also describes the main financial statements - the balance sheet, income statement, statement of cash flows, and statement of owners' equity - and their purpose in communicating financial information to both internal and external users of accounting data.Basic Accounting Terms



Basic Accounting TermsDr. Bhavik Shah
Ěý
Business transactions involve the exchange of value, such as goods or services for money, between two or more entities. There are two main types of transactions: cash transactions involving an exchange of cash, and credit transactions where payment is promised at a future date. Capital refers to the value invested in a business by its owner, while drawings refer to amounts withdrawn by the owner. Assets are items owned by a business that have value, and liabilities are amounts owed to outside parties. Revenue is the income generated from sales or services, while expenses are costs incurred to generate that revenue.Accounting basics



Accounting basicsRITESH KUMAR SINGH
Ěý
Accounting is defined as the art of Recording, Classifying and Summarizing transactions in monetary terms (in Money terms) for preparation of Financial Statements
Book- keeping includes recording of journal, posting in ledgers and balancing of accounts. All the records before the preparation of trail balance is the whole subject matter of book- keeping.
Accounting, is an information system is the process of identifying, measuring and communicating the economic information of an organization to its users who need the information for decision making.Accounting process



Accounting processrohit kashyap
Ěý
The accounting process involves collecting documents, posting journal entries, transferring balances to ledger accounts, preparing a trial balance, making adjustments, creating an adjusted trial balance, preparing financial statements, making post-closing entries, and generating a post-closing trial balance. Source documents are collected and analyzed throughout the accounting period. Journal entries are posted using double entry accounting. Ledger accounts track debit and credit balances. An initial trial balance is prepared, then adjustment entries are made and an adjusted trial balance is created to develop financial statements showing the firm's profits, losses, and financial health. Finally, revenue and expense accounts are closed out and balances transferred in post-closing entries.Trial balance ppt



Trial balance pptharshika5
Ěý
A trial balance is a financial statement that lists the debit and credit balances of all accounts in the general ledger. It is prepared to check the arithmetic accuracy of the ledger accounts and help detect errors. The trial balance is not a conclusive proof of accuracy as certain errors may remain undetected even if the debit and credit totals match. Common errors include omissions, incorrect postings, or wrong account balances. If errors cannot be found, a suspense account is used to temporarily balance the trial balance.Journal Entries



Journal EntriesJosephin Remitha M
Ěý
Here are the journal entries for the transactions:
Jan 1: Capital 80,000
To Cash 80,000
(Commenced business with cash)
Jan 2: Bank 40,000
To Cash 40,000
(Deposited cash in bank)
Jan 3: Purchases 5,000
To Cash 5,000
(Purchased goods by paying cash)
Jan 4: Purchases 10,000
To Lipton & Co. 10,000
(Purchased goods from Lipton & Co. on credit)
Jan 5: Cash 11,000
To Sales 11,000
(Sold goods to Joy and received cash)
1 introduction to financial accounting



1 introduction to financial accountingItisha Sharma
Ěý
This presentation talks about Meaning, of accounting, distinction between book keeping and accounting, Branches of accounting, Objectives of accounting, Uses and users of accounting information, Advantages of Accounting, Is accounting a science or an art, double entry system of financial accounting, limitations of financial accounting, important terms, journal entry, accounting concepts and conventionsRectification of errors with accounting terms



Rectification of errors with accounting termsMuhammad Saqib Awan
Ěý
This document discusses various types of accounting errors and how to rectify them. It outlines two main types of errors: two-sided errors, which do not affect the trial balance, and one-sided errors, which do affect the trial balance. Two-sided errors include errors of omission, commission, original entry, principle, and compensating errors. One-sided errors require using a suspense account to rectify. The document provides examples for each type of error and explains how to make the correcting journal entries to rectify the errors.Double entry system



Double entry systemRaJesh Thakur
Ěý
It is the system in which both the aspects i.e. debit as well as credit are recorded in the books of accounts .It records transactions relating to all the accounts i.e. personal, real and nominal.accounting process



accounting processManish Tiwari
Ěý
The document provides an overview of the accounting process. It defines accounting and discusses its key principles and concepts. It describes the different branches and types of accounting. It then explains the accounting process which involves identifying transactions, preparing documents, recording transactions in a journal, posting to ledgers, preparing trial balances and final accounts such as profit and loss statements and balance sheets. It also discusses the different books of accounts used such as journals, ledgers and trial balances. Finally, it covers accounting systems and basics such as debits and credits, types of accounts and how to prepare and balance accounts.Account



AccountNiyati Mehta
Ěý
The document defines accounting as recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions and events to prepare financial statements. It discusses the basic accounting concepts like the accounting equation, assets, liabilities, equity, revenues and expenses. It also explains the key steps in accounting cycle which includes recording transactions, posting to ledger accounts, preparing an unadjusted trial balance, making adjusting entries, preparing an adjusted trial balance and financial statements, and closing temporary accounts. The accounting cycle aims to generate useful financial information for decision making in the form of income statement, balance sheet, and other financial reports.Trading Profit And Loss Account



Trading Profit And Loss AccountMarcus9000
Ěý
The document discusses the Trading Profit and Loss Account, which is prepared annually to show a business's trading activities and determine its profit over the year. It has two parts: the Trading Account, which summarizes information on goods bought, sold and returned; and the Profit and Loss Account, which shows costs incurred and calculates gross and net profit. The document provides examples of key items included in each account, such as purchases, sales, opening/closing stock, expenses, and gross/net profit.Final Accounts 



Final Accounts PrachiSharma304
Ěý
The document discusses the preparation of final accounts, which includes three financial statements: (i) the trading account, which shows gross profit/loss; (ii) the profit and loss account, which shows net profit/loss; and (iii) the balance sheet, which shows the financial position. It provides details on what each statement shows and their importance. The trading account is the first stage and shows gross profit/loss. The profit and loss account indicates net profit/loss after deducting all expenses. The balance sheet presents the sources and uses of funds on a particular date. Final accounts are important to understand business results, financial position, and for tasks like getting loans.Accounting Cycle



Accounting CycleRavi Kapoor
Ěý
The accounting cycle is a series of 9 steps that are repeated each reporting period to record business transactions and prepare financial statements. The steps are: 1) analyze transactions, 2) journalize transactions, 3) post to ledger accounts, 4) prepare an unadjusted trial balance, 5) make adjustments, 6) prepare an adjusted trial balance, 7) make financial statements, 8) close temporary accounts, and 9) prepare a post-closing trial balance to verify the accounting records. The cycle ensures transactions are properly recorded and financial statements are prepared accurately.Accounting concept and convention



Accounting concept and conventionpoojanmantri
Ěý
This document discusses key accounting concepts and conventions. It defines 8 accounting concepts: business entity, money measurement, accounting period, accounting cost, going concern, dual aspect, realization, and matching. It also discusses 4 accounting conventions: consistency, materiality, conservatism, and full disclosure. The concepts and conventions establish standard principles and practices for preparing accurate financial statements and reports.Introduction to accounting



Introduction to accountingVishal Kukreja
Ěý
This document provides an introduction to the concepts of accounting. It defines accounting as a system that collects and processes financial information to allow informed decisions by users. It discusses the need for accounting to determine results of business transactions and the financial position. It outlines the key functions of accounting like identifying, recording, classifying, summarizing, analyzing, interpreting and communicating financial information. It also discusses the accounting cycle and different branches and users of accounting information. Finally, it provides definitions of some basic accounting terms.Ledger in financial accounting (11th commerce)



Ledger in financial accounting (11th commerce)Yamini Kahaliya
Ěý
This presentation is on ledger which is the topic of financial accounting. it contents details about following points. There are:-
1. Meaning of ledger
2. Need & Importance of ledger
3. Advantage of Ledger
4. Difference b/w Journal & ledger
5. Format of ledger
6. Rules of posting
7. Illustrations
8. Exercise
Double entry systme



Double entry systmeAsian Institute of Virtual Learning
Ěý
After reading this topic you should be able to understand
1-Double Entry System
2- Accounts and their classification
3- Rules of Debit and CreditLedger



LedgerJosephin Remitha M
Ěý
This document defines key concepts related to ledgers. It begins with defining a ledger as a summary of all transactions relating to an account over a period of time, showing the net effect. It then provides a flow chart and discusses the utilities of ledgers, including providing quick information on accounts, controlling transactions, preparing trial balances and financial statements. The document also covers the format of ledger accounts, the distinction between journals and ledgers, and the procedures for posting transactions to ledgers, including opening entries, compound entries, and balancing accounts.Recording Transactions



Recording TransactionsAlamgir Alwani
Ěý
This document discusses key concepts in accounting, including the double-entry system, T-accounts, journal entries, posting transactions, closing revenue and expense accounts, preparing trial balances, and correcting errors. It also covers how computers have transformed accounting data processing.Similar to Accounting process (20)
Basics of Finance and Accounts



Basics of Finance and AccountsDr. Sushil Bansode
Ěý
This document provides an overview of key concepts in finance and accounting, including:
1. It defines financial accounting as the process of recording business transactions and preparing financial statements like the income statement and balance sheet.
2. Accounting principles and concepts are discussed, such as the business entity concept and matching principle. Conventions like conservatism are also covered.
3. Basic bookkeeping elements are introduced, including journals, ledgers, trial balances, and how final accounts like trading, profit and loss, and balance sheets are prepared.
4. The document distinguishes between financial and management accounting.
5. Cost accounting concepts are outlined, including different types of costs, cost statements, work-4. accounting cycle short mba



4. accounting cycle short mbaKaran Kukreja
Ěý
The accounting cycle refers to the complete sequence of accounting procedures that are repeated during each accounting period. It begins with recording transactions and ends with preparing financial statements. The key steps in the accounting cycle are: 1) analyzing transactions, 2) journalizing transactions, 3) posting to ledger accounts, 4) preparing a trial balance, and 5) preparing financial statements. BASIC ACCOUNTING



BASIC ACCOUNTINGNitish Kumar
Ěý
BASIC ACCOUNTING FOR ALL INCLUDING MANAGERS. ACCOUNTING, DOUBLE ENTRY SYSTEM, JOURNEL (defination,advantages/limitations, how to make,) TRAIL BALANCE(defination,limitations/advantages, steps}3.1. LEDGER & TRAIL BALANCE.pptx



3.1. LEDGER & TRAIL BALANCE.pptxPoojaGautam89
Ěý
The document defines and explains key accounting concepts related to ledgers and trial balances. It begins by defining a ledger as the principal book of accounts where similar transactions are recorded under their appropriate accounts. It then discusses the features and purpose of ledgers, including that they contain various accounts, serve as the book of final entry, and help in preparing financial statements. The document also compares journals and ledgers, provides examples of ledger postings, and defines and explains the purpose and limitations of trial balances.Journal.pptx



Journal.pptxHiteshGarg79
Ěý
The document discusses journal entries, ledgers, and trial balances. Journal entries record transactions in accounts with debit and credit entries. Ledgers compile journal entries and associated debits and credits for each individual account. A trial balance is prepared after ledger accounts to check for accuracy by listing account balances on debit and credit sides.Principals of acounting



Principals of acountingAshraf DEV
Ěý
Accounting is the process of recording, analyzing, and summarizing financial transactions. It originated in the 16th century with Luca Pacioli, who developed the modern bookkeeping system. The primary purpose of accounting is to provide financial information to management for efficient business operations. This includes recording transactions, keeping financial records, performing audits, reporting financial data, and providing tax advice. The accounting cycle involves recording transactions in journals, posting to ledgers, preparing a trial balance, making adjustments, and producing a balance sheet.LEDGER.pptx



LEDGER.pptxHARSHITGARG688173
Ěý
A ledger is a book containing accounts that records all business transactions. It allows the transfer of transactions from journals into separate accounts. The document discusses key aspects of ledgers including components like date, amount, particulars; examples of common ledger accounts; the T-format used; and the process of posting journal entries to ledger accounts. It also covers the meaning of debit and credit balances, preparation of trial balances to check the accuracy of accounts, and common types of accounting errors.Accounting cycle



Accounting cyclehydeumb
Ěý
The document discusses the accounting cycle, which is a series of steps that involve recording business transactions from source documents through journal entries, posting to ledgers, preparing a trial balance, and ultimately producing financial statements. It describes each step in detail, including source documents, journal entries, posting to ledgers, trial balances, and financial statements such as the income statement and balance sheet. The accounting cycle is an important process for small businesses to understand their financial status and performance over a period of time.THEORY BASE OF ACCOUNTING.pptx



THEORY BASE OF ACCOUNTING.pptxHARSHITGARG688173
Ěý
Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions and interpreting the results. It involves maintaining systematic records, ascertaining profits and losses, determining financial position, providing information to users, and assisting management. The accounting cycle includes recording transactions in source documents and journals, posting to ledger accounts, preparing a trial balance, and ultimately financial statements. Accounting provides quantitative and qualitative information to internal and external users for decision making.Accounting steps of accounting cycle



Accounting steps of accounting cyclesehrish shahid
Ěý
The accounting cycle refers to the series of steps involved in recording business transactions and producing financial statements. The key steps are: 1) identifying transactions and preparing source documents, 2) recording transactions in journals using double-entry bookkeeping, and 3) posting transaction details from journals to individual accounts in the ledger to accumulate balances over time. This process allows a business to track the financial effects of transactions and produce accurate financial statements.Accounting steps of accounting cycle



Accounting steps of accounting cyclesehrish shahid
Ěý
The accounting cycle refers to the series of steps involved in recording business transactions from occurrence through inclusion in financial statements. The key steps are: 1) identifying transactions and preparing source documents, 2) recording transactions in journals using double-entry bookkeeping, and 3) posting transaction details from journals to individual accounts in the ledger to update account balances. This process allows determination of updated account balances to prepare financial statements.Accounting cycle- a bird eye view b



Accounting cycle- a bird eye view bmounika ramachandruni
Ěý
The accounting cycle summarizes the process of recording accounting transactions from occurrence through to financial statements. It begins with journal entries to record transactions, followed by posting to ledger accounts. An adjusted trial balance is prepared after adjusting entries. Financial statements are then prepared, followed by closing entries and a post-closing trial balance. The accounting cycle ensures all transactions are recorded, summarized and reported accurately.Accounting!!!!!!!



Accounting!!!!!!!stefanie
Ěý
The double-entry system of accounting requires every transaction to have equal debits and credits so that the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity) remains balanced. The accounting cycle involves identifying, recording, posting, adjusting, and summarizing transactions into financial statements over an accounting period. Key steps include journalizing, posting to ledgers, preparing a trial balance to check that total debits equal total credits, and generating financial reports.J.pptx



J.pptxMarcelVelasco1
Ěý
The document discusses accounting periods, the accounting cycle, journalizing transactions, debit and credit rules, and the journal entry process. It defines accounting periods as segments of time used to prepare financial statements and shows the typical steps in an accounting cycle. It also explains that journalizing records transactions in journals using debit and credit rules, and that a journal entry displays all effects of a transaction through debits and credits with an explanation.Accounting and its process.pptx.ita about accounting and it's process and dif...



Accounting and its process.pptx.ita about accounting and it's process and dif...vetnotes1610
Ěý
Accounting involves tracking all financial transactions within a business, such as money coming in and going out. It is important for both legal and tax purposes.
The accounting process begins with collecting source documents of transactions. Journal entries are made to record transactions using double-entry bookkeeping. The entries are then posted to ledger accounts. A trial balance is prepared to check that debits equal credits. Adjustment entries are made and an adjusted trial balance is prepared. Financial statements like the income statement and balance sheet are then prepared from the trial balance. Finally, closing entries are made to clear revenue and expense accounts, and transfer the net income or loss to the capital account.1 Tally erp 9 tutorial with shortcut keys



1 Tally erp 9 tutorial with shortcut keysMD. Monzurul Karim Shanchay
Ěý
1. Accounting is the process of identifying, recording, and reporting economic information to help decision makers. It provides financial statements to various stakeholders like suppliers, customers, banks, and owners.
2. There are three types of accounts: real accounts for assets, personal accounts for persons, and nominal accounts for income and expenses. The double entry system records each transaction with a debit and credit entry.
3. Financial statements like the trading account, profit and loss statement, and balance sheet are prepared at the end of an accounting period to show the profitability and financial position of the organization.Tally erp9.0



Tally erp9.0PULIPATISIVAKUMAR
Ěý
Tally.ERP 9 is a comprehensive, flexible and easy-to-use accounting software that provides real-time processing and instant reports. It allows users to set up and manage multiple companies with integrated inventory and accounting features. Tally.ERP 9's key advantages include no accounting codes, speed, power, flexibility, multi-lingual capability and versatility for organizations of all sizes.Accountancy,Business and Management (ABM)



Accountancy,Business and Management (ABM)Caszel Suello
Ěý
The Accountancy, Business and Management (ABM) strand focuses on financial management, business management, corporate operations, and accounting. It can lead to careers in management and accounting such as sales manager, human resources, marketing director, project officer, bookkeeper, accounting clerk, internal auditor, and more.
The accounting cycle has 9 steps: 1) Identifying transactions, 2) Recording in journals, 3) Posting to ledgers, 4) Preparing an unadjusted trial balance, 5) Making adjusting entries, 6) Preparing an adjusted trial balance, 7) Creating financial statements, 8) Making closing entries, and 9) Preparing a post-closing trial balance to test the equality of debits andRecently uploaded (20)
TLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...



TLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...RizaBedayo
Ěý
Hand Tools, Power Tools, and Equipment in Industrial ArtsUseful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣs



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣsCeline George
Ěý
In this slide we’ll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18



How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18Celine George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to modify existing web pages in Odoo 18. Web pages in Odoo 18 can also gather user data through user-friendly forms, encourage interaction through engaging features. The Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir Dotan



The Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir DotanHistory of Stoke Newington
Ěý
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptx



Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ěý
This ppt has been made for the students pursuing PG in social science and humanities like M.Ed., M.A. (Education), Ph.D. Scholars. It will be also beneficial for the teachers and other faculty members interested in research and teaching research concepts.Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Finals of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
Ěý
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...



Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...Ajaz Hussain
Ěý
This presentation delves into the systemic blind spots within pharmaceutical science and regulatory systems, emphasizing the significance of "inactive ingredients" and their influence on therapeutic equivalence. These blind spots, indicative of normalized systemic failures, go beyond mere chance occurrences and are ingrained deeply enough to compromise decision-making processes and erode trust.
Historical instances like the 1938 FD&C Act and the Generic Drug Scandals underscore how crisis-triggered reforms often fail to address the fundamental issues, perpetuating inefficiencies and hazards.
The narrative advocates a shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, adaptable systems prioritizing continuous enhancement. Key hurdles involve challenging outdated assumptions regarding bioavailability, inadequately funded research ventures, and the impact of vague language in regulatory frameworks.
The rise of large language models (LLMs) presents promising solutions, albeit with accompanying risks necessitating thorough validation and seamless integration.
Tackling these blind spots demands a holistic approach, embracing adaptive learning and a steadfast commitment to self-improvement. By nurturing curiosity, refining regulatory terminology, and judiciously harnessing new technologies, the pharmaceutical sector can progress towards better public health service delivery and ensure the safety, efficacy, and real-world impact of drug products.Computer Network Unit IV - Lecture Notes - Network Layer



Computer Network Unit IV - Lecture Notes - Network LayerMurugan146644
Ěý
Title:
Lecture Notes - Unit IV - The Network Layer
Description:
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on Computer Network concepts, tailored for final year B.Sc. Computer Science students affiliated with Alagappa University. This document covers fundamental principles and advanced topics in Computer Network. PDF content is prepared from the text book Computer Network by Andrew S. Tenanbaum
Key Topics Covered:
Main Topic : The Network Layer
Sub-Topic : Network Layer Design Issues (Store and forward packet switching , service provided to the transport layer, implementation of connection less service, implementation of connection oriented service, Comparision of virtual circuit and datagram subnet), Routing algorithms (Shortest path routing, Flooding , Distance Vector routing algorithm, Link state routing algorithm , hierarchical routing algorithm, broadcast routing, multicast routing algorithm)
Other Link :
1.Introduction to computer network - /slideshow/lecture-notes-introduction-to-computer-network/274183454
2. Physical Layer - /slideshow/lecture-notes-unit-ii-the-physical-layer/274747125
3. Data Link Layer Part 1 : /slideshow/lecture-notes-unit-iii-the-datalink-layer/275288798
Target Audience:
Final year B.Sc. Computer Science students at Alagappa University seeking a solid foundation in Computer Network principles for academic.
About the Author:
Dr. S. Murugan is Associate Professor at Alagappa Government Arts College, Karaikudi. With 23 years of teaching experience in the field of Computer Science, Dr. S. Murugan has a passion for simplifying complex concepts in Computer Network
Disclaimer:
This document is intended for educational purposes only. The content presented here reflects the author’s understanding in the field of Computer NetworkN.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity Briefing



N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity BriefingMebane Rash
Ěý
The number of languages spoken in NC public schools.APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ěý
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a Master’s degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APM’s People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the Move



QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the MoveTechSoup
Ěý
If you use QuickBooks Desktop and are stressing about moving to QuickBooks Online, in this webinar, get your questions answered and learn tips and tricks to make the process easier for you.
Key Questions:
* When is the best time to make the shift to QuickBooks Online?
* Will my current version of QuickBooks Desktop stop working?
* I have a really old version of QuickBooks. What should I do?
* I run my payroll in QuickBooks Desktop now. How is that affected?
*Does it bring over all my historical data? Are there things that don't come over?
* What are the main differences between QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online?
* And moreA PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
Ěý
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardKaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
Ěý
APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ěý
Accounting process
- 1. Dr. RACHAKONDA SRIKANTH Assistant Professor of Commerce
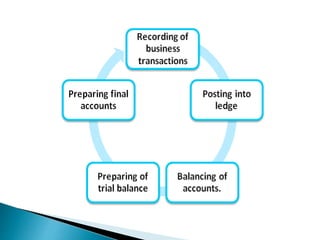
- 2. ACCOUNTING PROCESS Accounting process also called as Accounting cycle Accounting cycle is a process of a complete sequence of accounting procedures in appropriate order during each accounting period. Accounting process is a combination of a series of activities that begin when a transaction takes place and ends with its inclusion in the financial statements at the end of the accounting period.
- 4. 1. Identifying and Analyzing Business Transactions The accounting process starts with identifying and analyzing business transactions. Only those that pertain to the business entity are included in the process.
- 5. 2. Recording in the Journals A journal is a book in which transactions are recorded at first. Hence, it is called book of prime entry or original entry.  Business transactions are recorded in the form of journal entries by using the double-entry bookkeeping system. Each entry has at least two accounts (one debited and one credited). The process of recording transaction in the book journal is called as “Journalising”. Transactions are recorded in “chronological order” and as they occur.
- 6. 3. Posting into Ledger It is also known as the principal book of accounts as well as the book of final entry. It is a book in which all ledger accounts and related monetary transactions are posted and maintained in a summarized and classified form. It is a permanent record of all transactions. it helps in the creation of trial balance. The process of transforming journal entries to Ledger is called as “Posting”
- 7. 4. Balance of Accounts •At the end of every accounting year all the accounts which are operated in the ledger book are closed, totalled and balanced. • Balancing of ledgers means finding the difference between the total of debit side and total of credit side of a particular account • total difference should be recorded on the lesser side of an account.
- 8. 5. Preparation of Trial Balance •Trial Balance is a statement in which the balances of all ledger accounts are assembled into debit and credit columns • T.B. is a base for the preparation of financial statements • the objective is to preparation of T.B. is to check the arithmetical accuracy of the ledger accounts. •If there is any difference between the totals of debit columns and credit column , should be transferred temporarily “ Suspense account” •It helps to rectify the mistakes or errors.
- 9. 6. Preparation of Financial statements •It is the last stage in the accounting cycle • It includes trading, profit and loss account, and balance sheet. • Trading account: It helps in determining the gross profit or gross loss of a business concern, made strictly out of trading activities means buying and selling activities. It considers only direct expenses.
- 10. •Profit and Loss account: •It is opened by recording the gross profit on the credit side or gross loss on the debit side. • It records only indirect expenses and indirect incomes •It finds Net Profit or Net Loss of a business enterprise •Both trading and profit and loss accounts shows operational performance of business •Balance Sheet: •It is a statement and shows the financial position of a business •It shows business's net worth at the end • Assets = Liabilities + Equity








