An introduction to PHP : PHP and Using PHP, Variables Program control and Built-in functions.pptx
- 1. UNIT 4- PHP & XML CS8651 - INTERNET PROGRAMMING
- 2. âĒ An introduction to PHP: PHP- Using PHP- Variables- Program control- Built-in functions- Form Validation- Regular Expressions - File handling â Cookies - Connecting to Database. âĒ XML: Basic XML- Document Type Definition- XML Schema DOM and Presenting XML, XML âĒ Parsers and Validation, XSL and XSLT Transformation, News Feed (RSS and ATOM). UNIT IV: SYLLABUS
- 3. AN INTRODUCTION TO PHP
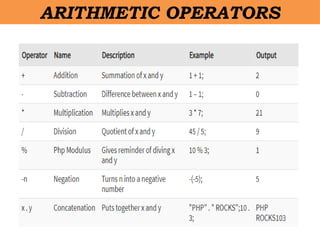
- 4. âĒ PHP is an open-source, interpreted, and object-oriented scripting language that can be executed at the server-side. âĒ PHP is well suited for web development. âĒ PHP stands for Hypertext Pre-processor. âĒ PHP is an interpreted language, i.e., there is no need for compilation. âĒ PHP is faster than other scripting languages, for example, ASP and JSP. PHP
- 5. âĒ PHP is a server-side scripting language, which is used to manage the dynamic content of the website. âĒ PHP can be embedded into HTML. âĒ PHP is an object-oriented language. âĒ PHP is an open-source scripting language. âĒ PHP is simple and easy to learn language. PHP
- 6. âĒ PHP is a server-side scripting language, which is used to design the dynamic web applications with MySQL database. â It handles dynamic content, database as well as session tracking for the website. â You can create sessions in PHP. â It can access cookies variable and also set cookies. â It helps to encrypt the data and apply validation. â PHP supports several protocols such as HTTP, POP3, SNMP, LDAP, IMAP, and many more. WHY USE PHP?
- 7. â Using PHP language, you can control the user to access some pages of your website. â As PHP is easy to install and set up, this is the main reason why PHP is the best language to learn. â PHP can handle the forms, such as - collect the data from users using forms, save it into the database, and return useful information to the user. For example - Registration form. WHY USE PHP?
- 8. PHP FEATURES
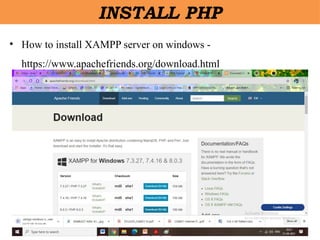
- 9. âĒ How to install XAMPP server on windows - https://www.apachefriends.org/download.html INSTALL PHP
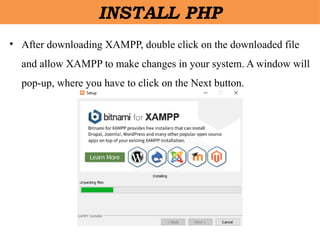
- 10. âĒ After downloading XAMPP, double click on the downloaded file and allow XAMPP to make changes in your system. A window will pop-up, where you have to click on the Next button. INSTALL PHP
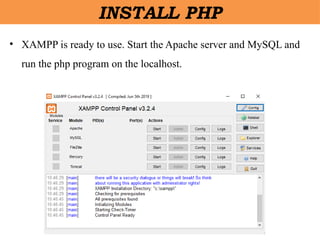
- 11. âĒ XAMPP is ready to use. Start the Apache server and MySQL and run the php program on the localhost. INSTALL PHP
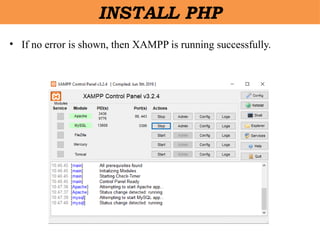
- 12. âĒ If no error is shown, then XAMPP is running successfully. INSTALL PHP
- 13. âĒ PHP programs can be written on any editor, such as - Notepad, Notepad++, Dreamweaver, etc. âĒ These programs save with .php extension, i.e., filename.php inside the htdocs folder. âĒ Step 1: Create a simple PHP program like hello world. <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>PHP</h1> <?php echo "Hello World"; ?> </body></html> RUN PHP CODE IN XAMPP
- 14. âĒ Step 2: Save the file with hello.php name in the htdocs folder, which resides inside the xampp folder. âĒ Step 3: Run the XAMPP server and start the Apache and MySQL. âĒ Step 4: Now, open the web browser and type localhost â http://localhost/hello.php on your browser window. RUN PHP CODE IN XAMPP
- 15. âĒ In PHP, keyword (e.g., echo, if, else, while), functions, user- defined functions, classes are not case-sensitive. âĒ However, all variable names are case-sensitive. PHP - CASE SENSITIVE
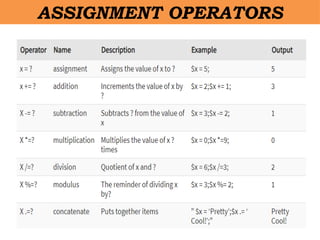
- 16. âĒ A variable is a name given to a memory location that stores data at runtime. âĒ The scope of a variable determines its visibility. âĒ The rules followed when creating variables in PHP â All variable names must start with the dollar sign. â Variable names are case sensitive; â All variables names must start with a letter follow other characters â Variable names must not contain any spaces PHP - VARIABLE
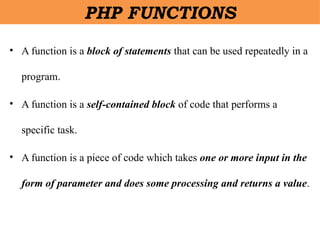
- 21. âĒ A function is a block of statements that can be used repeatedly in a program. âĒ A function is a self-contained block of code that performs a specific task. âĒ A function is a piece of code which takes one or more input in the form of parameter and does some processing and returns a value. PHP FUNCTIONS
- 22. âĒ Better code organization â PHP functions allow us to group blocks of related code that perform a specific task together. âĒ Reusability â Once defined, a function can be called by a number of scripts in our PHP files. This saves us time of reinventing the wheel when we want to perform some routine tasks such as connecting to the database âĒ Easy maintenance â Updates to the system only need to be made in one place. WHY USE PHP FUNCTIONS?
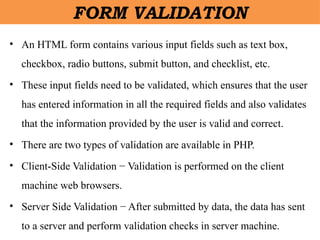
- 23. âĒ An HTML form contains various input fields such as text box, checkbox, radio buttons, submit button, and checklist, etc. âĒ These input fields need to be validated, which ensures that the user has entered information in all the required fields and also validates that the information provided by the user is valid and correct. âĒ There are two types of validation are available in PHP. âĒ Client-Side Validation â Validation is performed on the client machine web browsers. âĒ Server Side Validation â After submitted by data, the data has sent to a server and perform validation checks in server machine. FORM VALIDATION
- 24. âĒ The things need to be validate are as follows: â Empty String â Validate String â Validate Numbers â Validate Email â Validate URL â Input length FORM VALIDATION
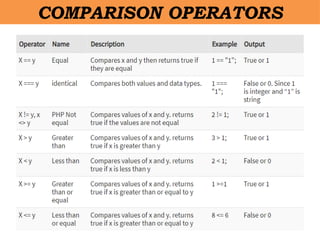
- 25. âĒ A regular expression is a sequence of characters that forms a search pattern. âĒ When you search for data in a text, you can use this search pattern to describe what you are searching for. âĒ A regular expression can be a single character, or a more complicated pattern. âĒ Regular expressions can be used to perform all types of text search and text replace operations. REGULAR EXPRESSION
- 26. âĒ In PHP, regular expressions are strings composed of delimiters, a pattern and optional modifiers. âĒ In the example above, / is the delimiter, w3schools is the pattern that is being searched for, and i is a modifier that makes the search case-insensitive. REGULAR EXPRESSION - SYNTAX
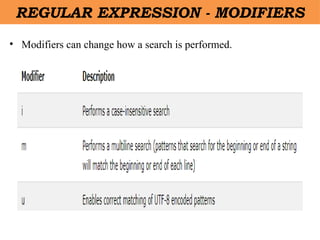
- 27. âĒ Modifiers can change how a search is performed. REGULAR EXPRESSION - MODIFIERS
- 28. âĒ PHP supports file handling which is used to read, write and append data to the file. âĒ Basic file handling steps â Opening a file fopen() â Reading a file fclose() â Writing a file fread() â Closing a file fwrite() â Delete File unlink() FILE HANDLING
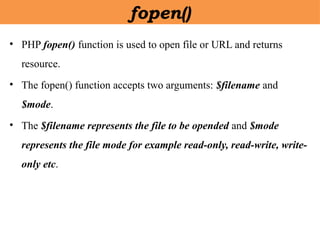
- 29. âĒ PHP fopen() function is used to open file or URL and returns resource. âĒ The fopen() function accepts two arguments: $filename and $mode. âĒ The $filename represents the file to be opended and $mode represents the file mode for example read-only, read-write, write- only etc. fopen()
- 30. Modes Description r Open a file for read only. File pointer starts at the beginning of the file w Open a file for write only. Erases the contents of the file or creates a new file if it doesn't exist. File pointer starts at the beginning of the file a Open a file for write only. The existing data in file is preserved. File pointer starts at the end of the file. Creates a new file if the file doesn't exist x Creates a new file for write only. Returns FALSE and an error if file already exists r+ Open a file for read/write. File pointer starts at the beginning of the file w+ Open a file for read/write. Erases the contents of the file or creates a new file if it doesn't exist. File pointer starts at the beginning of the file a+ Open a file for read/write. The existing data in file is preserved. File pointer starts at the end of the file. Creates a new file if the file doesn't exist x+ Creates a new file for read/write. Returns FALSE and an error if file already exists fopen()
- 31. FILE OPERATIONS âĒ The fread() function reads from an open file. âĒ The fclose() function is used to close an open file. âĒ The fgets() function is used to read a single line from a file. âĒ The feof() function checks if the "end-of-file" (EOF) has been reached. âĒ The fgetc() function is used to read a single character from a file. âĒ The fwrite() function is used to write to a file.
- 32. COOKIES âĒ A cookie is a small file with the maximum size of 4KB that the web server stores on the client computer. âĒ They are typically used to keeping track of information such as a username that the site can retrieve to personalize the page when the user visits the website next time. âĒ A cookie can only be read from the domain that it has been issued from.
- 33. Create Cookies With PHP âĒ A cookie is created with the setcookie() function. âĒ The value of the cookie can be retrieved using the global variable $_COOKIE. âĒ isset() function is used to find out if the cookie is set. âĒ The setcookie() function must appear before the <html> tag. âĒ To delete a cookie, use the setcookie() function with an expiration date in the past. âĒ Check whether cookies enabled or not!!!!
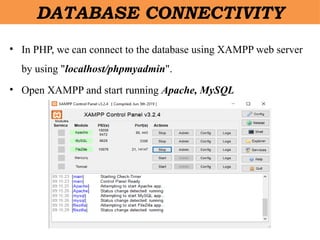
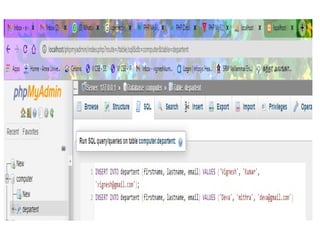
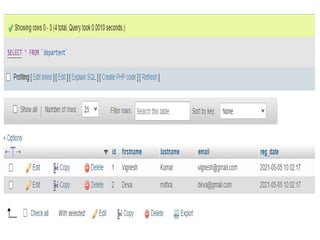
- 34. DATABASE CONNECTIVITY âĒ In PHP, we can connect to the database using XAMPP web server by using "localhost/phpmyadmin". âĒ Open XAMPP and start running Apache, MySQL
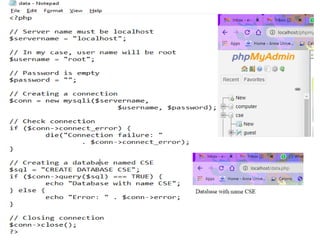
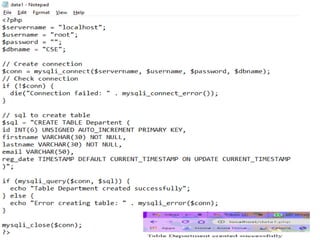
- 35. DATABASE CONNECTIVITY âĒ Now open PHP file and write PHP code to create database and a table in your database. âĒ Save the file as âdata.phpâ in htdocs folder under XAMPP folder. âĒ Then open web browser and type localhost/data.php. Finally the database is created and connected to PHP.
- 40. XML âĒ Xml (eXtensible Markup Language) is a mark up language. âĒ XML is designed to store and transport data. âĒ XML is not a replacement for HTML. âĒ XML is designed to be self-descriptive. âĒ XML is designed to carry data, not to display data. âĒ XML tags are not predefined. You must define your own tags. âĒ XML is platform independent and language independent.
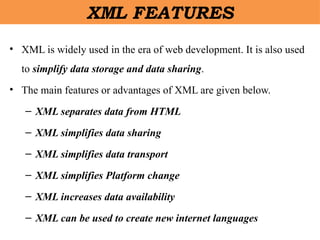
- 41. XML FEATURES âĒ XML is widely used in the era of web development. It is also used to simplify data storage and data sharing. âĒ The main features or advantages of XML are given below. â XML separates data from HTML â XML simplifies data sharing â XML simplifies data transport â XML simplifies Platform change â XML increases data availability â XML can be used to create new internet languages
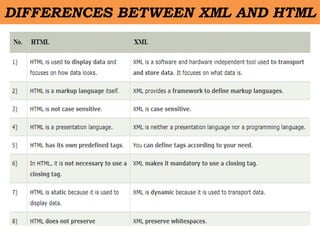
- 42. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN XML AND HTML âĒ .
- 43. EXAMPLE
- 44. DTD âĒ DTD stands for Document Type Definition. âĒ It defines the legal building blocks of an XML document. âĒ It is used to define document structure with a list of legal elements and attributes. âĒ Its main purpose is to define the structure of an XML document. âĒ It contains a list of legal elements and define the structure with the help of them. âĒ Before proceeding with XML DTD, you must check the validation. An XML document is called "well-formed" if it contains the correct syntax.
- 45. AN INTERNAL DTD DECLARATION âĒ If the DTD is declared inside the XML file, it must be wrapped inside the <!DOCTYPE> definition:
- 46. AN EXTERNAL DTD DECLARATION âĒ If the DTD is declared in an external file, the <!DOCTYPE> definition must contain a reference to the DTD file:
- 47. DTD - XML BUILDING BLOCKS âĒ All XML documents are made up by the following building blocks: â Elements : main building blocks of both XML and HTML documents â Attributes : provide extra information about elements â Entities : expanded when a document is parsed by an XML parser â PCDATA : parsed character data â CDATA : character data
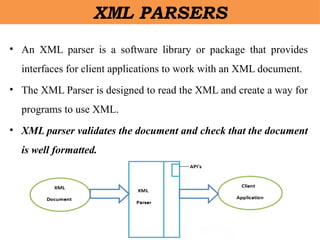
- 48. XML PARSERS âĒ An XML parser is a software library or package that provides interfaces for client applications to work with an XML document. âĒ The XML Parser is designed to read the XML and create a way for programs to use XML. âĒ XML parser validates the document and check that the document is well formatted.
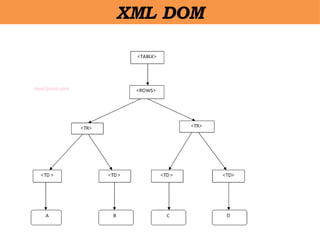
- 49. XML DOM âĒ DOM is an acronym stands for Document Object Model. âĒ It defines a standard way to access and manipulate documents. âĒ Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming API for HTML and XML documents. âĒ It defines the logical structure of documents and the way a document is accessed and manipulated. âĒ XML DOM defines a standard way to access and manipulate XML documents.
- 50. XML DOM
- 51. XML DOM