Analgesics
- 1. Analgesics  Drugs which relive pain by acting on the central nervous system and reduce without loss of consciousness  They are of two types:  *Narcotic Analgesics  *Non-narcotic Analgesics.  Non-narcotic Analgesics: Don’t produce significant depression of the central nervous system. e.g.salicylates and related compounds  Narcotic Analgesics: Produce depression of the central nervous system.  Classified into  *Natural Analgesics e.g.morphine,codeine etc  *Synthetic Analgesics e.g. pethidine,methadone etc
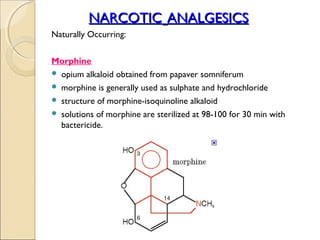
- 2. NARCOTIC ANALGESICS Naturally Occurring: Morphine ď‚— opium alkaloid obtained from papaver somniferum ď‚— morphine is generally used as sulphate and hydrochloride ď‚— structure of morphine-isoquinoline alkaloid ď‚— solutions of morphine are sterilized at 98-100 for 30 min with bactericide.
- 3. Analgesic action ď‚— powerful analgesic ď‚— relief from pain without altering the functions of the central nervous system. ď‚— does not lead to abnormal behavior. ď‚— large doses can relive all types of pain. ď‚— increases the threshold of the pain ď‚— does not remove pain completely but helps to tolerate the pain. ď‚— induces analgesia by acting on the receptors situated both in the higher centers and spinal cord. ď‚— produces depression of respiration and miosis. Uses ď‚— analgesic for reliving the pain ď‚— used to reduce pain in acute myocardial infraction, burns, fractures of bones, pleurisy etc. ď‚— administered intravenously ď‚— used to reduce post operative pain. ď‚— it shows sedative effect ď‚— used as a premedication for surgery.
- 4. . Disadvantage ď‚— invaluable in the treatment of pulmonary-edema ď‚— drug of addiction due to euphoriant effect ď‚— over dose causes poisoning ď‚— causes dryness of mouth, mental clouding, dysphoria, vomiting, headache, fatigue, constipation etc.
- 5. Codeine ď‚— White crystalline powder ď‚— sparingly soluble in water ď‚— bitter in taste ď‚— less potent analgesic than morphine ď‚— better absorbed when administered orally
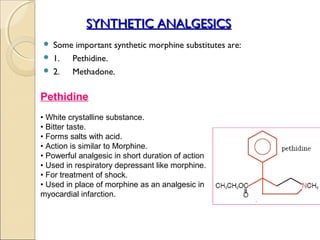
- 6. SYNTHETIC ANALGESICS  Some important synthetic morphine substitutes are:  1. Pethidine.  2. Methadone. Pethidine • White crystalline substance. • Bitter taste. • Forms salts with acid. • Action is similar to Morphine. • Powerful analgesic in short duration of action • Used in respiratory depressant like morphine. • For treatment of shock. • Used in place of morphine as an analgesic in myocardial infarction.
- 7. Methadone ď‚— Synthetic compound. ď‚— Slightly potent than morphine. ď‚— Available as Methadone Hydrochloride tablet doses 5 to 10mg. ď‚— Also available in ampoules in injection form. ď‚— Is a racemic mixture. ď‚— Used as a substitute for Morphine and Pethidine. ď‚— Gives relief from visceral pain. ď‚— As respiratory depressant.
- 8. Morphinan . ď‚— syntheticanalgesics ď‚— example of morphinan compound is levorphanol ď‚— potent than morphine ď‚— well absorbed when administered orally Benzomorphan ď‚— Potent than morphine ď‚— synthetic agent ď‚— used intramuscularly in the dose 2 to 3 mg
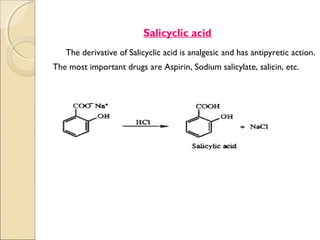
- 9. . Salicyclic acid The derivative of Salicyclic acid is analgesic and has antipyretic action. The most important drugs are Aspirin, Sodium salicylate, salicin, etc.
- 10. . Asprin It’s also known as Acetyl salicyclic acid. • Obtained by acetylation of Salicyclic acid. • White crystalline, odorless powder. • Sparingly soluble in water. • Slight acid taste. • In the presence of moisture, it gets hydrolyzed to acetic acid & salicyclic acid. • Stored in airtight containers. • Stable in dry conditions. • Used as analgesic in case of mild pain. • Has antipyretic action. • Used in headaches, cold, arthritis, toothache, etc. • Used as anti-inflammatory agent. • Reduces edema, tissue swelling, etc. • Used as antirheumatic drug. • Reliefs from signs and symptoms of inflammation. • Has shown beneficial effect in radiation diarrhea.
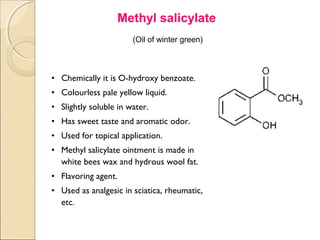
- 11. Methyl salicylate . (Oil of winter green) • Chemically it is O-hydroxy benzoate. • Colourless pale yellow liquid. • Slightly soluble in water. • Has sweet taste and aromatic odor. • Used for topical application. • Methyl salicylate ointment is made in white bees wax and hydrous wool fat. • Flavoring agent. • Used as analgesic in sciatica, rheumatic, etc.
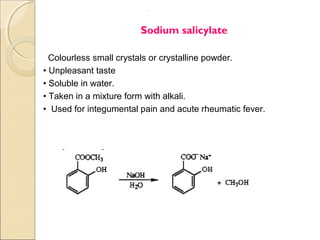
- 12. . Sodium salicylate Colourless small crystals or crystalline powder. • Unpleasant taste • Soluble in water. • Taken in a mixture form with alkali. • Used for integumental pain and acute rheumatic fever.
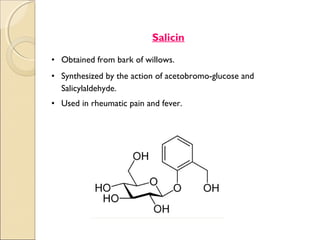
- 13. Salicin • Obtained from bark of willows. • Synthesized by the action of acetobromo-glucose and Salicylaldehyde. • Used in rheumatic pain and fever.
- 14. . Diethylamine Salicylate • It is a diethyl amine salt of salicylic acid. • White crystalline substance. • Topically used. • Available as creams. • Used in rheumatic and muscular pain.
- 15. . The Para-aminophenol derivatives  Analgesic and antipyretic effects.  Not useful anti-inflammatory drugs.  Commonly used drugs are Phenacetin and para-acetamol. Para acetamol • Chemically it is 4-hydroxy Actanilide. • White crystalline powder. • Is odourless ans highly soluble in water. • Daily dosage should not exceed 2.5% in adults. • More potent antipyretic than Phenacetin. • Used for relief of pain and fever. • Shows adverse effect are sweating, nausea, vomiting, etc.
- 16. . Phenacetin • White odourless, crystalline powder. • Sparingly bitter in taste. • Prepared from p-nitrophenol. • Used with aspirin for relief of integumental pain. • Phenacetin is hydrolyzed to paracetamol and this is the cause for antipyretic-analgesic action.
- 17. . Indolyl and aryl acetic acid derivatives Important drugs are Indomethacin and Sulindae Indomethacin • Chemically it is named as 1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3 indolylacetic acid. • It is an indole acetic acid derivative. • Brownish yellow crystalline powder. • Insoluble in water. • Soluble in organic solvents. • Available as 25 mg capsules. • Has an inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic action. • Effective in rheumatic disorders. • Useful in treatment of gout. • Some adverse effects are nausea, vomiting, skin rashes, diarrhea, etc.
- 18. Sulindae • Chemically it is named as [5-fluoro-2 methyl-1 (4-methyl sulphinyl-benzylidene) inden-3 yl] acetic acid. • It is a fluorinated derivative of indomethacin. • Yellow crystalline powder. • Insoluble in water. • Has longer duration of action than indomethacin. • Used in the treatment of rheumatic and musculo-skeletal disorders.











![Sulindae
• Chemically it is named as [5-fluoro-2 methyl-1 (4-methyl
sulphinyl-benzylidene) inden-3 yl] acetic acid.
• It is a fluorinated derivative of indomethacin.
• Yellow crystalline powder.
• Insoluble in water.
• Has longer duration of action than indomethacin.
• Used in the treatment of rheumatic and musculo-skeletal
disorders.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analgesics-130221090430-phpapp01/85/Analgesics-18-320.jpg)