anatomy of nose¶nasal sinuses.pdf
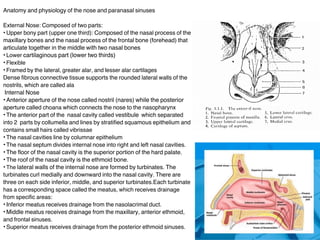
- 1. Anatomy and physiology of the nose and paranasal sinuses External Nose: Composed of two parts: ŌĆóUpper bony part (upper one third): Composed of the nasal process of the maxillary bones and the nasal process of the frontal bone (forehead) that articulate together in the middle with two nasal bones ŌĆóLower cartilaginous part (lower two thirds) ŌĆóFlexible ŌĆóFramed by the lateral, greater alar, and lesser alar cartilages Dense fibrous connective tissue supports the rounded lateral walls of the nostrils, which are called ala Internal Nose ŌĆóAnterior aperture of the nose called nostril (nares) while the posterior aperture called choana which connects the nose to the nasopharynx ŌĆóThe anterior part of the nasal cavity called vestibule which separated into 2 parts by collumella and lines by stratified squamous epithelium and contains small hairs called vibrissae ŌĆóThe nasal cavities line by columnar epithelium ŌĆóThe nasal septum divides internal nose into right and left nasal cavities. ŌĆóThe floor of the nasal cavity is the superior portion of the hard palate. ŌĆóThe roof of the nasal cavity is the ethmoid bone. ŌĆóThe lateral walls of the internal nose are formed by turbinates. The turbinates curl medially and downward into the nasal cavity. There are three on each side inferior, middle, and superior turbinates.Each turbinate has a corresponding space called the meatus, which receives drainage from specific areas: ŌĆóInferior meatus receives drainage from the nasolacrimal duct. ŌĆóMiddle meatus receives drainage from the maxillary, anterior ethmoid, and frontal sinuses. ŌĆóSuperior meatus receives drainage from the posterior ethmoid sinuses.
- 2. Nasal Septum: ŌĆóComposed of quadrangular septal cartilage anteriorly, perpendicular plate of ethmoid posterosuperiorly and vomer bone posteroinferiorly. ŌĆóNasal septum Separates the nose into 2 nasal cavities. Internal Nose Blood Supply ŌĆóTwo vascular trunks of the common carotid artery: ŌĆóExternal carotid artery, which has the following branches: ŌĆóSphenopalatine artery ŌĆóGreater palatine artery ŌĆóSuperior labial artery ŌĆóAngular artery ŌĆóInternal carotid artery, which has the following branches: ŌĆóAnterior ethmoid artery from the ophthalmic artery ŌĆóPosterior ethmoid artery from the ophthalmic artery KiesselbachŌĆÖs plexus (LittleŌĆÖs area): ŌĆóMost common site for anterior epistaxis ŌĆóFour arteries anastomose to form this area: ŌĆóAnterior ethmoidal artery (from the ophthalmic artery) ŌĆóSphenopalatine artery (terminal branch of the maxillary artery) ŌĆóGreater palatine artery (from the maxillary artery) ŌĆóSeptal branch of the superior labial artery (from the facial artery) WoodruffŌĆÖs plexus: ŌĆóMost common site for posterior epistaxis ŌĆóTwo arteries anastomose to form this area: 1. the sphenopalatine artery 2. Posterior ethmoid artery
- 3. Internal Nose Lymphatic Drainage ŌĆóAnterior 1/3 of the nose drains in to the submental and submandibular nodes ŌĆóPosterior two thirds of the nose and sinuses drain in to the retropharyngeal nodes and superior deep cervical nodes Nerve supply of the nose: by 3 cranial nerves ŌĆóCN I (olfactory nerve) ŌĆóPasses through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone into the olfactory bulb lying in the anterior cranial fossa ŌĆóCarries the sense of smell from the olfactory mucosa in the roof of the nose ŌĆóCN V (trigeminal nerve) ŌĆóThrough ethmoidal branches of the ophthalmic division of CN V:Responsible for sensory innervation to: ŌĆóThe lining of the anterior part of the nasal cavity ŌĆóTo the surrounding olfactory mucosa in the roof of the nose ŌĆóTo the lining of the frontal sinus ŌĆóThrough Maxillary division of CN V:Responsible for sensory innervation to: ŌĆóThe lateral wall of the nose ŌĆóThe nasal septum ŌĆóThe maxillary sinus ŌĆóCN VII (facial nerve|: Responsible for movement of external nose. Venous Drainage ŌĆóVenous system is valveless. ŌĆóSphenopalatine vein drains via sphenopalatine foramen into pterygoid plexus. ŌĆóEthmoidal veins drain into superior ophthalmic vein ŌĆóAnterior facial vein drains through common facial vein to internal jugular vein; also communicates with cavernous sinus via ophthalmic veins, infra orbital and deep facial veins, and the pterygoid plexus. ŌĆóAngular vein drains external nose via ophthalmic vein to cavernous sinus. Lymphatic Drainage ŌĆóAnterior portion of nose drains toward external nose in the subcutaneous tissue to the facial vein and submandibular nodes. ŌĆóOthers pass posterior to tonsillar region and drain into upper deep cervical nodes. Most drain into pharyngeal plexus and then to the retropharyngeal nodes
- 4. Paranasal Sinuses ŌĆóThe paranasal sinuses are air-filled spaces located within the bones of the skull and face and they are centered on the nasal cavity ŌĆóIncludes 4 pairs one on each side: sphenoid, frontal, ethmoid, and maxillary ŌĆóAll sinuses are lined with respiratory epithelium capable of producing mucus. ŌĆóThe cilia in the sinus cavities help to empty secretions into the nasal cavities. ŌĆóMaxillary Sinus ŌĆóPresent at birth ŌĆóLargest of the paranasal sinuses (15 ml its volume) ŌĆóLateral wall of the nose separates the sinus from the nose ŌĆóRoof of the sinus is also the floor of the orbit ŌĆóDrains into the middle meatus of the nasal cavity ŌĆóRoots of the posterior molar teeth may extend into the floor of the sinus ŌĆóThe anterior maxillary sinus wall houses the infraorbital nerve, which runs along the roof of the sinus and supplies sensory innervation to the lower eyelid, the side of the nose, and the upper lip. Ethmoidal sinus ŌĆóPaired bony scaffolds, connected by cribriformplate ŌĆóBoundaries: ŌĆóLamina papyracea of orbit ŌĆóOrbital process of the frontal bone ŌĆóMiddle and superior turbinates medially ŌĆóLateral cribriform plate lamella (also medially) ŌĆóSphenoid sinus posterioriy ŌĆóNerve supply: anterior and posterior ethmoidal nerves ŌĆóBlood supply: anterior and posterior ethmoidal arteries from the ophthalmic A. ŌĆóAnt. cells: drain into middle meatus, the Post. cells drain into superior meatus.
- 5. Frontal sinus:- . abscent at birth ŌĆóOccupy the frontal bone, 2 in number ŌĆóRelations: The floor of the frontal sinus corresponds to the roof of the orbit. The frontal sinus is defined anteriorly by the thicker anterior table of the frontal bone and the thinner posterior table which separates the frontal sinus from the anterior horns of the frontal lobes of the brain. ŌĆóThe pneumatization patterns of the frontal sinus widely vary. An intersinus septation generally divides the sinus, albeit asymmetrically. ŌĆó5-15% of adults, the frontal sinus is completely aplastic. ŌĆóThe frontal sinus ostium opens inferiorly into middle meatus Sphenoid Sinus ŌĆóOccupies sphenoid bone, 2 in number separated by Intersinus septum (not usually midline) ŌĆóPost-ethmoid A and N give vascular and sensory supplies, respectively ŌĆóOstium ~1 cm above choana, and drains into sphenoethmoidal recess Relations: 1. Pituitary fossa and middle cranial fossa superiorly 2. Cavernous sinus and ICA laterally 3. Pons and posterior cranial fossa posteriorly 4. Optic nerve lies next to or even within the sinus 5. Pterygoid canal with nerve inferiorly. Sphenoid sinus forms the roof of nasopharynx. Ostiomeatal Complex (OMC) ŌĆóArea that drains the frontal, anterior ethmoid, and maxillary sinuses. The OMC drains into the middle meatus and then into the nasopharynx Functions of the Nose ŌĆóAirway: conduit for air ŌĆóFiltration: trap and remove airborne particulate matter ŌĆóHumidification: increases relative humidity ŌĆóHeating: provides radiant heat of inspired air ŌĆóNasal reflex: causes periodic nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, or sneezing A. Postural reflex: increased congestion with supine position; congestion on the side of dependence upon lying on the side B. Hot or cold temperature reflex: sneezing upon sudden exposure of skin to dramatic temperature extremes ŌĆóChemosensation: detects irritants and temperature changes Olfaction
- 6. Functions of paranasal sinuses The following are the possible functions of paranasal sinuses: ŌĆóImparting resonance to the voice. ŌĆóHumidification and warming of inspired air. ŌĆóIncreasing the olfactory area of nose. ŌĆóProviding thermal insulation to vital parts of head. ŌĆóShock absorber function. ŌĆóAiding facial growth: frontal and maxillary sinuses were designed to assist forward and downward growth of the face. ŌĆóLightening the skull bones to maintain head position. ŌĆóSecreting mucous to moisten the nasal cavity. ŌĆóAiding nasal cavity immune defense and production of nitric oxide. CONGENITAL ANOMALIES CHOANAL ATRESIA Choanal atresia (CA) is a rare congenital disorder where the back of the nasal passage (choana) is blocked, usually by abnormal bony or soft tissue. Although it is rare, it is the most common cause of nasal obstruction in neonates and young infants. It can be unilateral or bilateral. When it is bilateral, it can cause immediate respiratory compromise in the newborn and is considered a medical emergency. The diagnosis can be made on physical examination by trying to pass a small catheter through the patientŌĆÖs nose. Surgery is the treatment of choice. Congenital Midline masses include 1. Dermoid cyst 2. Glioma 3. Encephalocele: Congenital herniation of central nervous system (CNS) tissue through skull base