Ards rahul
- 1. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Rahul Illaparambath
- 2. EPIDEMIOLOGY ? ARDS occurs in 1-4% of PICU admissions ? 10% of PICU patients who receive mechanical ventilation meet diagnostic criteria for ARDS ? Mortality varies between 20 ¨C 75%
- 3. ? Multicentered, prospective cohort study - Flori et al. -overall hospital mortality was 22% among children with a PaO2:FIO2 ratio <300 -ARDS (PaO2: FIO2 <200) had a mortality of 26% -MC diagnosis associated with ALI and ARDS among the entire study cohort pneumonia (35%)
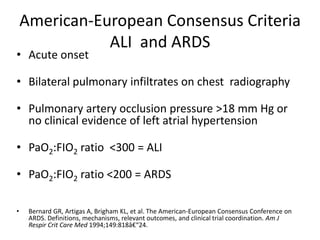
- 4. American-European Consensus Criteria ALI and ARDS ? Acute onset ? Bilateral pulmonary infiltrates on chest radiography ? Pulmonary artery occlusion pressure >18 mm Hg or no clinical evidence of left atrial hypertension ? PaO2:FIO2 ratio <300 = ALI ? PaO2:FIO2 ratio <200 = ARDS ? Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, et al. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994;149:818?€ˇ°24.
- 5. The Berlin Definition of ARDS ? Respiratory symptoms must have begun within one week of a known clinical insult, or the patient must have new or worsening symptoms during the past week ? Bilateral opacities consistent with pulmonary edema must be present on a chest radiograph or computed tomographic (CT) scan ? The patientˇŻs respiratory failure must not be fully explained by cardiac failure or fluid overload
- 6. ? A moderate to severe impairment of oxygenation must be present(PaO2/FiO2) -Mild ARDS ¨C The PaO2/FiO2 is >200 mmHg, but ˇÜ300 mmHg, -Moderate ARDS ¨C The PaO2/FiO2 is >100 mmHg, but ˇÜ200 mmHg -Severe ARDS ¨C The PaO2/FiO2 is ˇÜ100 all accompanied by ventilator setting that include PEEP ˇÝ5 cm H2O.
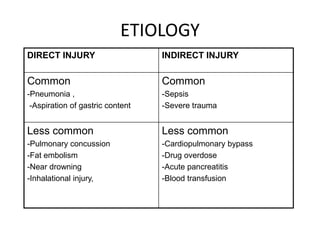
- 7. ETIOLOGY DIRECT INJURY INDIRECT INJURY Common Common -Pneumonia , -Sepsis -Aspiration of gastric content -Severe trauma Less common Less common -Pulmonary concussion -Cardiopulmonary bypass -Fat embolism -Drug overdose -Near drowning -Acute pancreatitis -Inhalational injury, -Blood transfusion
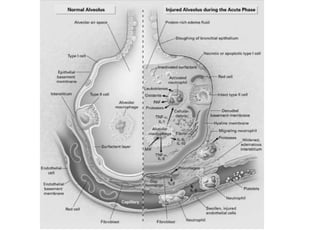
- 8. Mechanisms preventing alveolar edema ? Retained intravascular protein ? The interstitial lymphatics ? Tight junctions btw alveolar epithelial cells
- 9. Injury ? Injury causes release of pro-inflammatory cytokines ? Damage to the capillary endothelium and alveolar epithelium ? Functional surfactant is lost ? Ability to upregulate alveolar fluid clearance may also be lost
- 10. Consequences ? Impaired gas exchange - ventilation-perfusion mismatching -while increased physiologic dead space impairs carbon dioxide elimination ? Decreased lung compliance -stiffness of poorly or non-aerated lung ? Pulmonary hypertension -hypoxic vasoconstriction, -vascular compression by positive airway pressure, -parenchymal destruction, airway collapse,
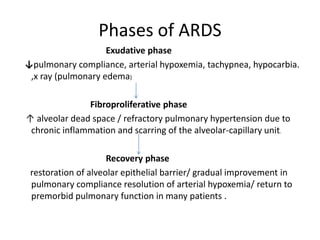
- 11. Phases of ARDS Exudative phase ˇýpulmonary compliance, arterial hypoxemia, tachypnea, hypocarbia. ,x ray (pulmonary edema) Fibroproliferative phase ˇü alveolar dead space / refractory pulmonary hypertension due to chronic inflammation and scarring of the alveolar-capillary unit. Recovery phase restoration of alveolar epithelial barrier/ gradual improvement in pulmonary compliance resolution of arterial hypoxemia/ return to premorbid pulmonary function in many patients .
- 13. Clinical features ? Fluid accumulation ? Lung compliance declines and tachypnea ensues ? Regional atelectasis and small-airways closure ? Hypoxia / breathing labored ? Hypocarbia followed by hypercarbia ? Rales over areas of atelectasis or alveolar congestion and decreased air entry over areas that are largely consolidated. Occasionally rhonchi
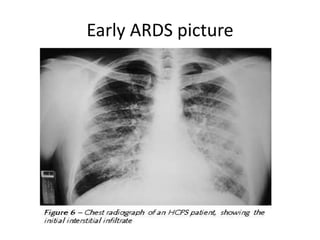
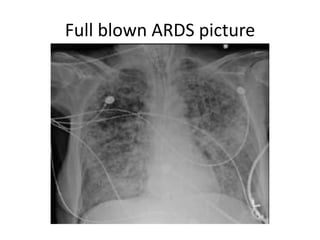
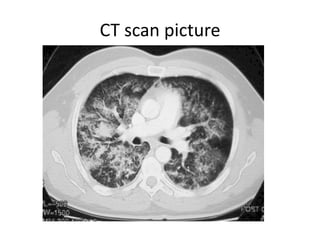
- 14. Investigations Chest Xray ? Small volume lungs ? Diffuse infiltrates ? Airbronchograms , atelectasis ? Fibrosis with reticular opacities CT scan ? Heterogenous opacification in dependent regions
- 16. Full blown ARDS picture
- 17. CT scan picture
- 18. Differentialsˇ. ? Cardiogenic pulmonary edema ? An acute exacerbation of IPF - previous chest radiographs - subpleural reticulocytic changes -surgical lung biopsy ? Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage ? Idiopathic acute eosinophilic pneumonia(IAEP) ? Malignancy ? Acute interstitial pneumonia (Hamman-Rich syndrome)
- 19. Management ? MECHANICAL VENTILATION ? FLUID MANAGEMENT ? SEDATION AND ANALGESIA ? POSITIONING ? HFOV ? DRUGS
- 20. Ventilation-Goals ? Maintain adequate gas exchange ? Minimal VILI -Keep FiO2 less than 60% -Avoid volutrauma and barotrauma -Avoid repetitive disconnection
- 21. ? Controlled oxygen exposure -Direct cellular injury -Absorption atelectasis -Accept saturation of 86-90% ? Low tidal volume ventilation -To limit harmful airway pressures -TV of 6 ml/kg
- 22. ? PEEP -augment anatomical dead space by distending large airways -cardiovascular compromise in high PEEP ? Optimal PEEP -Improves oxygenation -Displacement of fluid from alveoli -Recruitment and opening up of collapsed alveoli -Improved FRC ? Permissive hypercapnia -Accept high CO2 till pH 7.2
- 23. ? Most children have concomitant shock ? Aggressive fluid resuscitation till stable ? Excess lung water will decrease saturation ? Adequate sedation and analgesia ? Antibiotic therapy for primary cause ? Early enteral nutrition
- 24. Prone positioning ? Prone position improves V/Q mismatch ? Recruitment of dependent portions ? Decreases chest wall compliance (transmitting airway pressure to the alveoli more efficiently and stabilizing alveolar volume over a larger portion of previously nonaerated lung units) ? If no deterioration with prone position, continue for 18-20 hours
- 25. Adjuvant Therapies in ARDS ? HFOV ? NITRIC OXIDE ¨C pulmonary vasodilatation ? STEROIDS ? SURFACTANT ? ECMO ? Inhaled &systemic beta agonists
- 26. Predictors of outcome ? Disease-related -Oxygenation-PaO2/FiO2( mild, moderate, and severe ARDS had mortality rates of 27, 32, and 45 percent, respectively) -Pulmonary vascular dysfunction(elevated transpulmonary gradient (ie, ˇÝ12 mmHg) -Underlying cause of the ARDS ? Patient related
- 27. ? Treatment related -Fluid balance-positive fluid balance may be associated with higher mortality (1) -Treatment with glucocorticoids -Packed red blood cell transfusion-increased likelihood of death (odds ratio 1.10 per unit transfused, 95% CI 1.04-1.17) (2) 1.Rosenberg AL, Dechert RE, Park PK, et al. Review of a large clinical series: association of cumulative fluid balance on outcome in acute lung injury: a retrospective review of the ARDSnet tidal volume study cohort. J Intensive Care Med 2009; 24:35. 2.Gong MN, Thompson BT, Williams P, et al. Clinical predictors of and mortality in acute respiratory distress syndrome: potential role of red cell transfusion. Crit Care Med 2005; 33:1191.