1 of 16
Download to read offline




![HISTORY OF AI
’āś1941: First electronic computer [technology finally available]
’āś1956: Term Artificial Intelligence introduced
’āś1960s: Checkers-playing program that was able to play games
with opponents
’āś1980s: Quality Control Systems
’āś2000: First sophisticated walking robot](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artificialintelligencebisem-1-250321084620-bc24b102/85/artificial-intelligence-and-machine-learning-5-320.jpg)










Recommended
Artificial intelligence powerpoint presentation



Artificial intelligence powerpoint presentationmadhusrisanapathi2
╠²
The document discusses artificial intelligence, including its history from early computers in the 1940s to modern applications. It covers why AI is useful for tasks like quality control that humans struggle with, and how AI is applied in expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, and robotics. The document also briefly mentions some advantages of AI like reduced errors and improved efficiency, as well as disadvantages such as high costs and potential unemployment.Unit 1 of artificial intelligence and its introduction



Unit 1 of artificial intelligence and its introductionranjana dalwani
╠²
introduction of artificial intelligenceArtificial intelligence



Artificial intelligenceRahul Baghla
╠²
Artificial intelligence is a branch of science that aims to help machines solve complex problems like humans by applying human-like characteristics as algorithms. The document traces the history of AI from early electronic computers in 1941 to sophisticated robots today. It discusses how AI can help overcome limitations of human minds in tasks like object recognition. Applications of AI discussed include expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, and robotics. While AI may help in medicine, it also risks self-modification leading to unexpected results like new computer viruses. The future of AI allowing personal robot assistants but also risks of robot uprisings if anti-social elements gain control.Artificial intelligence



Artificial intelligenceIntekhab Alam Khan
╠²
This document presents an introduction to artificial intelligence. It begins with a definition of AI as using computer algorithms to solve complex problems like humans. The history of AI is then summarized, including early milestones from the 1940s to 2000s. Key reasons for AI are that computers can efficiently perform repetitive tasks that humans find monotonous. The document outlines applications of AI such as expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, and robotics. Both advantages like medical applications and disadvantages like self-modifying systems are presented. The future of AI allowing command of personal robots or potential robot revolts is discussed before concluding with continued challenges in fully understanding intelligence.Artificial intelligence



Artificial intelligenceIntekhab Alam Khan
╠²
This document provides an introduction to artificial intelligence (AI). It discusses the history of AI from its origins in 1941 to modern applications. Key topics covered include the limitations of human intelligence that AI aims to address, such as object recognition. The document outlines several applications of AI like expert systems, natural language processing, computer vision, robotics and more. Both advantages like medical diagnostic assistance and disadvantages like potential dangerous self-modifying code are mentioned. The future of AI is discussed as enabling convenient personal robots but also potential robot rebellion if anti-social cognition is achieved.ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE.PPT



ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE.PPTvandana gandhi
╠²
This document provides an introduction to artificial intelligence, including its history, applications, advantages, and future possibilities. It discusses how AI aims to help machines solve complex problems like humans by borrowing characteristics of human intelligence. The document outlines some key developments in AI's history from early computers in the 1940s to walking robots in 2000. It also describes common AI applications such as expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, and robotics. Both advantages of medical uses and potential disadvantages like self-modifying computer viruses are mentioned. The future of AI having personal robots or potentially turning against humans is speculated.artificial intelligence 



artificial intelligence Aamir Kiyani
╠²
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the intelligence demonstrated by machines, in contrast to the natural intelligence displayed by humans. This document provides an overview of AI, including its history beginning in 1943, main branches such as logical AI and pattern recognition, and applications like expert systems, speech recognition, computer vision, robotics. The advantages of AI are discussed, such as improving lives and doing dangerous jobs, but also potential disadvantages like unemployment and enhancing laziness in humans. The future of AI could include personal robots but also risks of robots being hacked or developing anti-social objectives.artificial intelligence



artificial intelligenceBikas Sadashiv
╠²
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), including its history, goals, applications, and future prospects. It discusses how AI works using artificial neural networks and logic. Some key applications mentioned are expert systems, natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, and robotics. Both advantages like fast response time and ability to process large data and disadvantages like lack of common sense and potential dangerous self-modification are outlined. The future of AI having both benefits of assistance and risks of robot rebellion if given full cognition is explored.Artificial intelligence



Artificial intelligenceMohit Bishnoi
╠²
Hello beautiful people, i hope you all are doing great. Here I'm sharing a short PPT on Artificial Intelligence. if you found it helpful. say thanks it's appreciated.Artificial Intelligence



Artificial IntelligenceBikas Sadashiv
╠²
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI). It discusses the history of AI beginning in the mid-20th century. It describes how AI works using artificial neurons and neural networks that mimic the human brain. The document outlines several goals and applications of AI including expert systems, natural language processing, computer vision, robotics, and more. It also discusses both the advantages and disadvantages of AI as well as considerations for its future development and impact.PPT on Airtificial Intelligence.pptx



PPT on Airtificial Intelligence.pptxDRAGONGAMERZ1
╠²
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), including its history, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. It discusses how AI aims to help machines solve complex problems like humans by borrowing human characteristics. Some key applications mentioned include expert systems, natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, and robotics. The future of AI is discussed, with potential benefits in medicine but also risks if cognitive robots were to be controlled by anti-social people. The conclusion recognizes AI has increased understanding of intelligence while also revealing its complexity.Artificial intelligence



Artificial intelligenceJaveria Akram
╠²
Artificial intelligence is the study of how to create machines that can think and act like humans by learning and solving problems on their own. It is a branch of computer science that aims to help machines find solutions to complex problems like humans. While the idea of AI dates back to ancient Greece, significant work in the field began in the 20th century with pioneers like Turing developing the first computer programs and algorithms for problem solving. Major advances and achievements in AI have included programs that can play games, recognize speech and images, and perform human-like tasks through robotics.Artificial intelligence ppt



Artificial intelligence pptDikshaSharma391
╠²
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence, including:
- A brief history noting the term was coined in 1956.
- Comparisons between human and computer intelligence in terms of speed/memory versus understanding of intellectual mechanisms.
- Categories of AI including narrow/weak AI, general/strong AI, and super intelligence.
- Applications like expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, robotics, and automatic programming.
- Both positive and negative potential impacts are imagined, such as robots assisting with tasks but also potentially being programmed with antisocial intentions.a36ba6f5-0090-444b-9a2c-19b38b65d5f5-150215005736-conversion-gate02.pptx



a36ba6f5-0090-444b-9a2c-19b38b65d5f5-150215005736-conversion-gate02.pptxPoooi2
╠²
This document provides an introduction to artificial intelligence, including its history, applications, advantages, and limitations. It discusses how AI can help machines solve complex problems in a human-like way. Key applications of AI mentioned are expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, and robotics. The future of AI is promising, with the potential for intelligent robots to assist humans by performing tasks. However, challenges also exist, such as how to prevent dangerous self-modifying systems.Artificial intelligence



Artificial intelligenceVigneshwar Kumar
╠²
This document provides an introduction to artificial intelligence (AI) including its evolution, branches, applications, and conclusions. It discusses key concepts like the Turing test, definitions of AI, and intelligence. The history of AI is explored from early programs in the 1940s-50s to expert systems in the 1980s. Applications mentioned include expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, and robotics. Both positive and negative potential futures of AI and robotics are considered. In conclusion, AI has increased understanding of intelligence while also revealing its complexity, providing ongoing challenges and opportunities.Aritficial intelligence



Aritficial intelligenceMaqsood Awan
╠²
Artificial Intelligence an Amazing presentation By Group4.
Group4 is a unique group of Govt.postgraduate College sheikhupura affiliated with Punjab University of Punjab,Pakistan..
Contact details..
Shamimaqsoodulhassan@yahoo.com or Shamimaqsood@gmail.com
Phone Number: 03045128753ARRTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE [Autosaved].pptx![ARRTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE [Autosaved].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/arrtificialintelligenceautosaved-220414021238-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![ARRTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE [Autosaved].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/arrtificialintelligenceautosaved-220414021238-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![ARRTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE [Autosaved].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/arrtificialintelligenceautosaved-220414021238-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![ARRTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE [Autosaved].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/arrtificialintelligenceautosaved-220414021238-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
ARRTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE [Autosaved].pptxRoopsingh61
╠²
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), including its history, current applications, and future. It defines AI as machines that exhibit human-like intelligence through tasks like problem-solving and rational decision making. The document traces the history of AI from its origins in 1943 to major developments in the 1950s-1980s. It describes current AI applications like expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, robotics, and automatic programming. It also speculates that AI will continue advancing rapidly but that the future remains uncertain.More Related Content
Similar to artificial intelligence and machine learning (20)
Artificial intelligence



Artificial intelligenceRahul Baghla
╠²
Artificial intelligence is a branch of science that aims to help machines solve complex problems like humans by applying human-like characteristics as algorithms. The document traces the history of AI from early electronic computers in 1941 to sophisticated robots today. It discusses how AI can help overcome limitations of human minds in tasks like object recognition. Applications of AI discussed include expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, and robotics. While AI may help in medicine, it also risks self-modification leading to unexpected results like new computer viruses. The future of AI allowing personal robot assistants but also risks of robot uprisings if anti-social elements gain control.Artificial intelligence



Artificial intelligenceIntekhab Alam Khan
╠²
This document presents an introduction to artificial intelligence. It begins with a definition of AI as using computer algorithms to solve complex problems like humans. The history of AI is then summarized, including early milestones from the 1940s to 2000s. Key reasons for AI are that computers can efficiently perform repetitive tasks that humans find monotonous. The document outlines applications of AI such as expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, and robotics. Both advantages like medical applications and disadvantages like self-modifying systems are presented. The future of AI allowing command of personal robots or potential robot revolts is discussed before concluding with continued challenges in fully understanding intelligence.Artificial intelligence



Artificial intelligenceIntekhab Alam Khan
╠²
This document provides an introduction to artificial intelligence (AI). It discusses the history of AI from its origins in 1941 to modern applications. Key topics covered include the limitations of human intelligence that AI aims to address, such as object recognition. The document outlines several applications of AI like expert systems, natural language processing, computer vision, robotics and more. Both advantages like medical diagnostic assistance and disadvantages like potential dangerous self-modifying code are mentioned. The future of AI is discussed as enabling convenient personal robots but also potential robot rebellion if anti-social cognition is achieved.ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE.PPT



ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE.PPTvandana gandhi
╠²
This document provides an introduction to artificial intelligence, including its history, applications, advantages, and future possibilities. It discusses how AI aims to help machines solve complex problems like humans by borrowing characteristics of human intelligence. The document outlines some key developments in AI's history from early computers in the 1940s to walking robots in 2000. It also describes common AI applications such as expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, and robotics. Both advantages of medical uses and potential disadvantages like self-modifying computer viruses are mentioned. The future of AI having personal robots or potentially turning against humans is speculated.artificial intelligence 



artificial intelligence Aamir Kiyani
╠²
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the intelligence demonstrated by machines, in contrast to the natural intelligence displayed by humans. This document provides an overview of AI, including its history beginning in 1943, main branches such as logical AI and pattern recognition, and applications like expert systems, speech recognition, computer vision, robotics. The advantages of AI are discussed, such as improving lives and doing dangerous jobs, but also potential disadvantages like unemployment and enhancing laziness in humans. The future of AI could include personal robots but also risks of robots being hacked or developing anti-social objectives.artificial intelligence



artificial intelligenceBikas Sadashiv
╠²
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), including its history, goals, applications, and future prospects. It discusses how AI works using artificial neural networks and logic. Some key applications mentioned are expert systems, natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, and robotics. Both advantages like fast response time and ability to process large data and disadvantages like lack of common sense and potential dangerous self-modification are outlined. The future of AI having both benefits of assistance and risks of robot rebellion if given full cognition is explored.Artificial intelligence



Artificial intelligenceMohit Bishnoi
╠²
Hello beautiful people, i hope you all are doing great. Here I'm sharing a short PPT on Artificial Intelligence. if you found it helpful. say thanks it's appreciated.Artificial Intelligence



Artificial IntelligenceBikas Sadashiv
╠²
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI). It discusses the history of AI beginning in the mid-20th century. It describes how AI works using artificial neurons and neural networks that mimic the human brain. The document outlines several goals and applications of AI including expert systems, natural language processing, computer vision, robotics, and more. It also discusses both the advantages and disadvantages of AI as well as considerations for its future development and impact.PPT on Airtificial Intelligence.pptx



PPT on Airtificial Intelligence.pptxDRAGONGAMERZ1
╠²
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), including its history, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. It discusses how AI aims to help machines solve complex problems like humans by borrowing human characteristics. Some key applications mentioned include expert systems, natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, and robotics. The future of AI is discussed, with potential benefits in medicine but also risks if cognitive robots were to be controlled by anti-social people. The conclusion recognizes AI has increased understanding of intelligence while also revealing its complexity.Artificial intelligence



Artificial intelligenceJaveria Akram
╠²
Artificial intelligence is the study of how to create machines that can think and act like humans by learning and solving problems on their own. It is a branch of computer science that aims to help machines find solutions to complex problems like humans. While the idea of AI dates back to ancient Greece, significant work in the field began in the 20th century with pioneers like Turing developing the first computer programs and algorithms for problem solving. Major advances and achievements in AI have included programs that can play games, recognize speech and images, and perform human-like tasks through robotics.Artificial intelligence ppt



Artificial intelligence pptDikshaSharma391
╠²
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence, including:
- A brief history noting the term was coined in 1956.
- Comparisons between human and computer intelligence in terms of speed/memory versus understanding of intellectual mechanisms.
- Categories of AI including narrow/weak AI, general/strong AI, and super intelligence.
- Applications like expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, robotics, and automatic programming.
- Both positive and negative potential impacts are imagined, such as robots assisting with tasks but also potentially being programmed with antisocial intentions.a36ba6f5-0090-444b-9a2c-19b38b65d5f5-150215005736-conversion-gate02.pptx



a36ba6f5-0090-444b-9a2c-19b38b65d5f5-150215005736-conversion-gate02.pptxPoooi2
╠²
This document provides an introduction to artificial intelligence, including its history, applications, advantages, and limitations. It discusses how AI can help machines solve complex problems in a human-like way. Key applications of AI mentioned are expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, and robotics. The future of AI is promising, with the potential for intelligent robots to assist humans by performing tasks. However, challenges also exist, such as how to prevent dangerous self-modifying systems.Artificial intelligence



Artificial intelligenceVigneshwar Kumar
╠²
This document provides an introduction to artificial intelligence (AI) including its evolution, branches, applications, and conclusions. It discusses key concepts like the Turing test, definitions of AI, and intelligence. The history of AI is explored from early programs in the 1940s-50s to expert systems in the 1980s. Applications mentioned include expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, and robotics. Both positive and negative potential futures of AI and robotics are considered. In conclusion, AI has increased understanding of intelligence while also revealing its complexity, providing ongoing challenges and opportunities.Aritficial intelligence



Aritficial intelligenceMaqsood Awan
╠²
Artificial Intelligence an Amazing presentation By Group4.
Group4 is a unique group of Govt.postgraduate College sheikhupura affiliated with Punjab University of Punjab,Pakistan..
Contact details..
Shamimaqsoodulhassan@yahoo.com or Shamimaqsood@gmail.com
Phone Number: 03045128753ARRTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE [Autosaved].pptx![ARRTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE [Autosaved].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/arrtificialintelligenceautosaved-220414021238-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![ARRTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE [Autosaved].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/arrtificialintelligenceautosaved-220414021238-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![ARRTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE [Autosaved].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/arrtificialintelligenceautosaved-220414021238-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![ARRTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE [Autosaved].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/arrtificialintelligenceautosaved-220414021238-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
ARRTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE [Autosaved].pptxRoopsingh61
╠²
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), including its history, current applications, and future. It defines AI as machines that exhibit human-like intelligence through tasks like problem-solving and rational decision making. The document traces the history of AI from its origins in 1943 to major developments in the 1950s-1980s. It describes current AI applications like expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, robotics, and automatic programming. It also speculates that AI will continue advancing rapidly but that the future remains uncertain.Recently uploaded (20)
Hackathon-Problem-Statements-Technology-Track-with-Link.pptx



Hackathon-Problem-Statements-Technology-Track-with-Link.pptxdatahiverecruitment
╠²
Hackathon-Problem-Statements-Technology-Track-with-Link.pptxPROJECT REPORT ON PASTA MACHINE - KP AUTOMATIONS - PASTA MAKING MACHINE PROJE...



PROJECT REPORT ON PASTA MACHINE - KP AUTOMATIONS - PASTA MAKING MACHINE PROJE...yadavchandan322
╠²
All the materials and content contained in Project report is for educational purpose and reflect the views of the industry which are drawn from various research on pasta machine. PM FME- Detailed Project Report of Multigrain Pasta Making Unit. 3. 1. PROJECT ... A pasta extruder is a machine that makes pasta dough through dies to.The process is quite simple and requires not much skilled labour. The machine itself is high technology and provides the manufacturers to produce noodles with. In this article, you will be able to get all the detail about a pasta-making business unit in India and the financial status of this business as well.ENGINEERS INDIA RESEARCH INSTITUTE - Service Provider of Project Report on PASTA PRODUCTION PLANT (SHORT PASTA) [CODE NO. 1632] based in Delhi, India.
Macaroni Machines are used to produce pasta from the raw material. With ... The views expressed in this Project Report are advisory in nature. SAMADHAN.
Reinventando el CD_ Unificando Aplicaciones e Infraestructura con Crossplane-...



Reinventando el CD_ Unificando Aplicaciones e Infraestructura con Crossplane-...Alberto Lorenzo
╠²
En esta charla, exploraremos c├│mo Crossplane puede transformar la forma en que gestionamos despliegues, yendo m├Īs all├Ī de un simple IaC para convertirse en una potente herramienta de Continuous Deployment (CD).
Ō£ģ Aprenderemos que es Crossplane
Ō£ģ Como usar Crossplane como IaC pero sobretodo Deployment as Code de manera eficiente
Ō£ģ Unificar la gesti├│n de aplicaciones e infraestructura de forma nativa en KubernetesMachine Elements in Mechanical Design.pdf



Machine Elements in Mechanical Design.pdfSLatorreAndrs
╠²
Elementos importantes para el dise├▒o de elementos mec├ĪnicosLA11-Case study of motherboard and internal components of motheroard.docx



LA11-Case study of motherboard and internal components of motheroard.docxVidyaAshokNemade
╠²
Thisis case study of motherboardIntro of Airport Engg..pptx-Definition of airport engineering and airport pla...



Intro of Airport Engg..pptx-Definition of airport engineering and airport pla...Priyanka Dange
╠²
Definition of airport engineering and airport planning, Types of surveys required for airport site, Factors affecting the selection of site for AirportSupervised Learning Ensemble Techniques Machine Learning



Supervised Learning Ensemble Techniques Machine LearningShivarkarSandip
╠²
Supervised Learning Ensemble Techniques, Bagging-Random Forest trees, Voting types,Boosting -Ada boost, gradient boostinghe Wright brothers, Orville and Wilbur, invented and flew the first successfu...



he Wright brothers, Orville and Wilbur, invented and flew the first successfu...HardeepZinta2
╠²
The Wright brothers, Orville and Wilbur, invented and flew the first successful airplane in 1903. Their flight took place in Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. Explainability and Transparency in Artificial Intelligence: Ethical Imperativ...



Explainability and Transparency in Artificial Intelligence: Ethical Imperativ...AI Publications
╠²
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly embedded in high-stakes domains such as healthcare, finance, and law enforcement, where opaque decision-making raises significant ethical concerns. Among the core challenges in AI ethics are explainability and transparencyŌĆökey to fostering trust, accountability, and fairness in algorithmic systems. This review explores the ethical foundations of explainable AI (XAI), surveys leading technical approaches such as model-agnostic interpretability techniques and post-hoc explanation methods and examines their inherent limitations and trade-offs. A real-world case study from the healthcare sector highlights the critical consequences of deploying non-transparent AI models in clinical decision-making. The article also discusses emerging regulatory frameworks and underscores the need for interdisciplinary collaboration to address the evolving ethical landscape. The review concludes with recommendations for aligning technical innovation with ethical imperatives through responsible design and governance.Project Manager | Integrated Design Expert



Project Manager | Integrated Design ExpertBARBARA BIANCO
╠²
Barbara Bianco
Project Manager and Project Architect, with extensive experience in managing and developing complex projects from concept to completion. Since September 2023, she has been working as a Project Manager at MAB Arquitectura, overseeing all project phases, from concept design to construction, with a strong focus on artistic direction and interdisciplinary coordination.
Previously, she worked at Progetto CMR for eight years (2015-2023), taking on roles of increasing responsibility: initially as a Project Architect, and later as Head of Research & Development and Competition Area (2020-2023).
She graduated in Architecture from the University of Genoa and obtained a Level II MasterŌĆÖs in Digital Architecture and Integrated Design from the INArch Institute in Rome, earning the MAD Award. In 2009, she won First Prize at Urban Promo Giovani with the project "From Urbanity to Humanity", a redevelopment plan for the Maddalena district of Genoa focused on the visual and perceptive rediscovery of the city.
Experience & Projects
Barbara has developed projects for major clients across various sectors (banking, insurance, real estate, corporate), overseeing both the technical and aesthetic aspects while coordinating multidisciplinary teams. Notable projects include:
The Sign Business District for Covivio, Milan
New L'Or├®al Headquarters in Milan, Romolo area
Redevelopment of Via C. Colombo in Rome for Prelios, now the PWC headquarters
Interior design for Spark One & Spark Two, two office buildings in the Santa Giulia district, Milan (Spark One: 53,000 m┬▓) for In.Town-Lendlease
She has also worked on international projects such as:
International Specialized Hospital of Uganda (ISHU) ŌĆō Kampala
Palazzo Milano, a residential building in Taiwan for Chonghong Construction
Chua Lang Street Building, a hotel in Hanoi
Manjiangwan Masterplan, a resort in China
Key Skills
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Integrated design: managing and developing projects from concept to completion
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Artistic direction: ensuring aesthetic quality and design consistency
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Project management: coordinating clients, designers, and multidisciplinary consultants
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Software proficiency: AutoCAD, Photoshop, InDesign, Office Suite
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Languages: Advanced English, Basic French
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Leadership & problem-solving: ability to lead teams and manage complex processes in dynamic environmentsBSS_1_E1.2_ElectromobilityElectromobility.pdf



BSS_1_E1.2_ElectromobilityElectromobility.pdfjungdan064
╠²
Electromobility, or e-mobility, refers to the use of electric powertrain technologies, in-vehicle information, and communication technologies, and connected infrastructure to enable electric vehicles (EVs) and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. As the world faces increasing environmental challenges such as climate change, air pollution, and the depletion of natural resources, electromobility has emerged as a promising solution for sustainable transportation.
At the heart of electromobility are electric vehicles, which include battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs). These vehicles use electricity either stored in batteries or generated through hydrogen fuel cells, drastically reducing or even eliminating tailpipe emissions. Compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, EVs have significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions over their lifecycle, especially when powered by renewable energy sources like wind or solar.
One of the primary drivers of the electromobility revolution is the urgent need to decarbonize transportation. The transport sector contributes nearly one-quarter of global COŌéé emissions, with road vehicles being the largest contributors. Transitioning to electric vehicles helps countries meet their climate goals under international agreements such as the Paris Accord. Furthermore, cities struggling with air pollution see electromobility as a way to improve public health by reducing harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides and particulate matter.
In addition to environmental benefits, electromobility offers economic advantages. EVs have lower operating and maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts and greater energy efficiency. Governments around the world have supported this shift by offering subsidies, tax incentives, and investing in charging infrastructure. The development of fast-charging networks and home-charging solutions has made EV ownership more convenient than ever before.
Technological advancements in battery chemistry, such as lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, are improving driving range and reducing charging time. At the same time, smart charging systems and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies are integrating EVs into the broader energy ecosystem. In V2G systems, EVs can feed electricity back into the grid during peak demand periods, creating a more resilient and balanced power network.
Electromobility extends beyond private passenger cars. It includes electric buses, trucks, bikes, scooters, and even ferries and airplanes. Public transportation authorities are increasingly adopting electric buses to reduce emissions and noise in urban areas. E-bikes and scooters provide convenient, zero-emission alternatives for short-distance travel, supporting the development of ŌĆ£last mileŌĆØ mobility solutions.
Production Planning & Control and Inventory Management.pptx



Production Planning & Control and Inventory Management.pptxVirajPasare
╠²
Production Planning and Control : Importance, Objectives and Functions . Inventory Management - Meaning, Types , Objectives, Selective Inventory Control : ABC AnalysisSelf-Compacting Concrete: Composition, Properties, and Applications in Modern...



Self-Compacting Concrete: Composition, Properties, and Applications in Modern...NIT SILCHAR
╠²
Self-Compacting Concrete (SCC) is a high-performance material that flows under its own weight, eliminating the need for vibration. It offers superior workability, durability, and structural efficiency, making it ideal for complex designs, congested reinforcement, and sustainable construction practices.Mix Design of M40 Concrete & Application of NDT.pptx



Mix Design of M40 Concrete & Application of NDT.pptxnarayan311979
╠²
This presentation briefs the audience about how to carry out design mix of M40 concrete, what are the cares one need to take while doing trials. Second part of presentation deals with various NDT test and its applications in evaluating quality of concrete of existing structures. 22PCOAM16_ML_Unit 1 notes & Question Bank with answers.pdf



22PCOAM16_ML_Unit 1 notes & Question Bank with answers.pdfGuru Nanak Technical Institutions
╠²
22 PCOAM16 _ML_ Unit 2 Full unit notes.pdfVirtual Power plants-Cleantech-Revolution



Virtual Power plants-Cleantech-RevolutionAshoka Saket
╠²
VPPs are virtual aggregations of distributed energy resources, such as energy storage, solar panels, and wind turbines, that can be controlled and optimized in real-time to provide grid services.artificial intelligence and machine learning
- 1. Chaudhary Charan Singh University UTTAR PRADESH, MEERUT ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE Presented By : Sakshi Gupta M.Sc. 1st Semester
- 3. CONTENTS ’āśIntroduction ’āśHistory of Artificial Intelligence ’āśWhy AI ’āśLimitations of Human Mind ’āśApplications ’āśAdvantages ’āśDisadvantages
- 4. INTRODUCTION Artificial Intelligence is a branch of science which deals with helping machines finds solutions to complex problems in a more human-like fashion. This generally involves borrowing characteristics rom human intelligence, and applying them as algorithms in a computer friendly way.
- 5. HISTORY OF AI ’āś1941: First electronic computer [technology finally available] ’āś1956: Term Artificial Intelligence introduced ’āś1960s: Checkers-playing program that was able to play games with opponents ’āś1980s: Quality Control Systems ’āś2000: First sophisticated walking robot
- 6. WHY AI ? Computers are fundamentally well suited to perform mechanical computations, using fixed programmed rules. This allows artificial machines to perform simple monotonous tasks efficiently and reliably, which humans are ill-suited to.
- 7. LIMITATIONS OF HUMAN MIND ’āśObject recognition. People cannot properly explain how they recognize objects. ’āśFace recognition. Cannot be passed on to another person by explanation. ’āśNaming of colours. Based on learning, not on absolute standards.
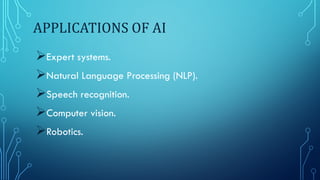
- 8. APPLICATIONS OF AI ’āśExpert systems. ’āśNatural Language Processing (NLP). ’āśSpeech recognition. ’āśComputer vision. ’āśRobotics.
- 9. EXPERT SYSTEMS ’āśAn Expert System is a computer program designed to act as an expert in a particular domain (area of expertise). Phases in Expert System ’āśExpert Systems currently are designed to assist experts, not to replace them, they have been used in medical diagnosis, chemical analysis, geological explorations etc.
- 10. NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING The goal of NLP is to enable people and computers to communicate in a natural (humanly) language (such as, English) rather than in a computer language. The field of NLP is divided in 2 categories: ŌĆó Natural Language understanding. ŌĆó Natural Laguage generation.
- 11. SPEECH RECOGNITION ’āśThe primary interactive method of communication used by humans is not reading and writing, it is speech. ’āśThe goal of speech recognition research is to allow computers to understand human speech. So that they can hear our voices and recognize the words we are speaking. ’āśIt simplifies the process of interactive communication between people and computers, thus it advances the goal of NLP.
- 12. COMPUTER VISION ’āśPeople generally use vision as their primary means of sensing their environment, we generally see more than we hear, fell or smell or taste. ’āśThe goal of computer vision research is to give computers this same powerful facility for understanding their surrounding. Here A.I helps computer to understand what they see through attached cameras.
- 13. ROBOTICS ’āśA Robot is a electro-mechanical device that can by programmed to perform manual tasks or a reprogrammable multi functional manipulator designed to move materials, parts, tools, or specialized devices through variable programmed motions for performance of variety of tasks. ’āśAn ŌĆśintelligentŌĆÖ robot includes some kind of sensory apparatus that allows it to respond to change in itŌĆÖs environment.
- 14. ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES ’āśLess room for errors. ’āśImproved efficiency. ’āśTakes risk instead of humans. ’āśAlways available. ’āśDigital assistance. ’āśFaster decision. ’āśHigh development cost. ’āśUnemployment. ’āśMakes humans dependent. ’āśLack of out box thinking. ’āśCould dominate humans.
- 16. THANK YOU














