Asynchronous Transfer Mode Introductory Presentation
- 2. 1.0 INTRODUCTION 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 2 Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a technology designed for the high-speed transfer of voice, video and data through public and private networks using cell relay technology ATM provides functionality that is both similar to Circuit switching and packet switching networks. ATM protocol was designed to support the transfer of data with guaranteed Q.o.S in mind. It divides the user data into small fixed-length packets called cells and it transport these cells over virtual connections. ATM is connection-oriented in a sense that before the two end devices communicates, resources have to be reserved in the intermediate switches similarly to telephone systems.
- 3. INTRODUCTION¡. 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 3 BASIC POINTS¡ The term transfer in this context means both transmission and switching And also the term asynchronous here means that cells belonging to same conversation can be multiplexed and appear in irregular pattern. ATM is the transfer mode for implementing Broadband Integrated services digital network BISDN ATM was driven by the integration of service and performance required of both telephony and data networking. Was therefore envisioned as the technology of providing B-ISDN
- 4. 2.1HOW ATM WORKS 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 4 This cell-based transmission is in contrast to typical local area network (LAN) variable-length packet mechanisms, which means that ATM connections are predictable and can be managed so that no single data type or connection can monopolize the transmission path. ATM technology originated in broadband ISDN (B-ISDN) technology and works primarily at layer 2 of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model. ATM connects devices over a WAN using virtual channels (VCs) and virtual paths (VPs). Virtual channels consist of one or more physical ATM links connected in a series for transmitting data between remote stations
- 5. 2.0 HOW ATM WORKS¡. 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 4 ATM uses fixed-size packets called ¡°cells.¡± Each 53-byte ATM cell contains 48 bytes of data payload and 5 bytes of control and routing information in the header. The header provides addressing information for switching the packet to its destination. The payload section carries the actual information, which can be data, voice, or video. The payload is properly called the user information field. An ATM network is made up of ATM switch and ATM endpoints. ATM switch is responsible for cell transit through an ATM network. ATM switch accepts the incoming cell from ATM endpoints or another ATM switch reads & update the cell header info and quickly switches the cell to an output interface toward its destination.
- 6. 3.0 BROADBAND ISDN 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 5 is a broadband communication network developed by International Telegraph And Telephone Consultative Committee(CCITT) that enables the transmission of design simulations and other multimedia transmission that include text, voice, video and graphics in one network This B-ISDN would be able to provide end users with increased transmission rate, up to 155.54Mbits/s on a switching basis. This is a great improvement as compared to the earlier rate of 64kbits/s employed in the ISDN which is not suitable for high definition moving pictures.
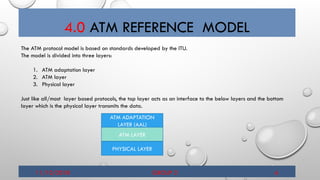
- 7. 4.0 ATM REFERENCE MODEL 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 6 The ATM protocol model is based on standards developed by the ITU. The model is divided into three layers: 1. ATM adaptation layer 2. ATM layer 3. Physical layer Just like all/most layer based protocols, the top layer acts as an interface to the below layers and the bottom layer which is the physical layer transmits the data. ATM ADAPTATION LAYER (AAL) ATM LAYER PHYSICAL LAYER
- 8. 4.1 PHYSICAL LAYER 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 7 The physical layer is divided into two sublayers: 1- The physical medium sub layer 2- The transmission convergence sub layer Physical Medium (PM) sub layer The physical medium sublayer performs medium-dependent functions. For example ? It provides bit transmission capabilities including bit alignment, line coding and electrical/optical conversion. ? Also responsible for bit timing, i.e., the insertion and extraction of bit timing information. ? The PM sublayer currently supports two types of interface: optical and electrical. Transmission Convergence (TC) sublayer Above the physical medium sublayer ? primarily responsible for framing of data transported over the physical medium.
- 9. 4.1 PHYSICAL LAYER.. 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 8 ? The TC sub layer is responsible for the following four functions: I. Cell Rate Decoupling : Cell rate decoupling is the insertion of idle cells at the sending side to adapt the ATM cell stream¡¯s rate to the rate of the transmission path II. Header Error Control : Header error control is the insertion of an 8-bit CRC value in the ATM cell header to protocol the contents of the ATM cell header III. Cell Delineation : Cell delineation is the detection of cell boundaries IV. Transmission Frame Adaptation : Transmission frame adaptation is the encapsulation of departing cells into an appropriate framing structure (either cell-based or SDH based).
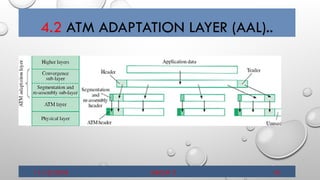
- 10. 4.2 ATM ADAPTATION LAYER (AAL) 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 9 The basic function of the ATM adaptation layer is to convert the user data supplied by higher layers into 48-byte blocks of data. The higher layer protocols accepts user data arrange it into packets and hand it over to the AAL The ATM adaptation layer is divided into two sub-layers 1. Convergence sub-layer 2. Segmentation and Re-assembly sub-layer. The convergence sub-layer : provides services to higher layers through a set of Protocols The segmentation and re-assembly : separates the messages from the convergence sub-layer into ATM cells. the two sub-layers above adds some protocol information, which is transported as the payload of 53 bytes ATM cells The below figure depicts this.
- 11. 4.2 ATM ADAPTATION LAYER (AAL).. 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 10
- 12. 4.3 ATM LAYER 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 11 We can say the primary function of ATM layer is associated with routing and switching of ATM cells But then the ATM layer changes functionality depending on current interface in use. There are two interfaces in ATM network 1-User-Network interface [between the ATM end point and ATM switch] 2-Network-Node interface [between ATM switches] The interfaces only differs in the cell header format. ATM FUNCTIONALITY ? VPI/VCI translation ? Multiplexes and de-multiplexes cells ? Cell Header creation and extraction before or after the cell is delivered to the AAL ? Maintains flow control using the GFC bits of the header
- 13. 5.0 ATM PLANE 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 12 In addition to the layers, the ATM reference model also has planes which are used to group functionality of the layers and for management purpose . The ATM reference model has three planes 1- User Plane : This plane is responsible for managing the transfer of data 2- Control Plane : This plane is responsible for generating and managing signaling requests 3- Management Plane : This plane contains two components: o Layer management : manages layer-specific functions, such as the detection of failures and protocol problems. o Plane management : manages and coordinates functions related to the complete system
- 14. 5.1 ATM LAYER 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 13
- 15. 5.2 ATM PLANE 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 14 NOTE: ? Within the user and control planes is a hierarchical set of layers. ? The user plane defines a set of functions for the transfer of user information between communication end- points. ? The control plane defines control functions such as call establishment, call maintenance, and call release. ? The management plane defines the operations necessary to control information flow between planes and layers, and maintain accurate and fault tolerant network operation. ? Also notice that the ATM functionality corresponds to the physical layer and part of the data link layer of the OSI reference model. ? As the ATM physical layer is analogous to physical layer of OSI model ? The ATM Layer combined with ATM Adaptation Layer is analogous to the data link layer of the Osi reference model.
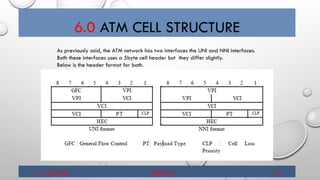
- 16. 6.0 ATM CELL STRUCTURE 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 15 As previously said, the ATM network has two interfaces the UNI and NNI interfaces. Both these interfaces uses a 5byte cell header but they differ slightly. Below is the header format for both.
- 17. 6.1 ATM CELL STRUCTURE 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 16 The VCI and VPI fields are identifier values for VC and VP respectively. [ A virtual channel connects two ATM communication end-points. A virtual path connects two ATM devices, which can be switches or end-points, and several virtual channels may be multiplexed onto the same virtual path.] The 2-bit PT field Identifiers whether the cell payload contains data or control information. The CLP bit Used by the user for explicit indication of cell loss priority. If the value of the CLP is 1, then the cell is subject to discarding in case of congestion. The HEC Field is an 8-bit CRC value that protects the contents of the cell header. The GFC field which appears only at the UNI, is used to assist the customer premises network in controlling the traffic flow for different qualities of service.
- 18. 6.2 ATM CELL STRUCTURE 11/10/2018 GROUP 2 17 A transmission path may comprise several virtual paths and each virtual path may carry several virtual channels









![4.3 ATM LAYER
11/10/2018 GROUP 2 11
We can say the primary function of ATM layer is associated with routing and switching of ATM cells
But then the ATM layer changes functionality depending on current interface in use.
There are two interfaces in ATM network
1-User-Network interface [between the ATM end point and ATM switch]
2-Network-Node interface [between ATM switches]
The interfaces only differs in the cell header format.
ATM FUNCTIONALITY
? VPI/VCI translation
? Multiplexes and de-multiplexes cells
? Cell Header creation and extraction before or after the cell is delivered to the AAL
? Maintains flow control using the GFC bits of the header](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atm1-240804044844-448f7413/85/Asynchronous-Transfer-Mode-Introductory-Presentation-12-320.jpg)



![6.1 ATM CELL STRUCTURE
11/10/2018 GROUP 2 16
The VCI and VPI fields are identifier values for VC and VP respectively.
[ A virtual channel connects two ATM communication end-points.
A virtual path connects two ATM devices, which can be switches or end-points, and several
virtual channels may be multiplexed onto the same virtual path.]
The 2-bit PT field
Identifiers whether the cell payload contains data or control information.
The CLP bit
Used by the user for explicit indication of cell loss priority. If the value
of the CLP is 1, then the cell is subject to discarding in case of congestion.
The HEC
Field is an 8-bit CRC value that protects the contents of the cell
header.
The GFC field
which appears only at the UNI, is used to assist the
customer premises network in controlling the traffic flow for different qualities of
service.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atm1-240804044844-448f7413/85/Asynchronous-Transfer-Mode-Introductory-Presentation-17-320.jpg)













































![[Webinar] Scaling Made Simple: Getting Started with No-Code Web Apps](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/webinarscalingmadesimplegettingstartedwithno-codewebapps-mar52025-250305183437-f03c78a3-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)











