bacterial growth charactrstics.pptx Mbbs
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes28 views
Pathology,Physiology,slides for bacterial growth for students of mbbs and pharm d
1 of 31
Download to read offline





























Recommended
Biochemistry an overview



Biochemistry an overviewRamesh Gupta
╠²
1. Living organisms are composed of biomolecules like nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates and lipids made from carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.
2. Within cells, these biomolecules and inorganic elements confer the property of life and allow the cell to obtain materials, produce enzymes, and undergo chemical reactions to sustain itself.
3. Biochemistry studies the biomolecules, elements, and chemical reactions within living things to understand functions at the molecular level, from single-celled to multicellular organisms.Foundations of biochemistry



Foundations of biochemistryPharmacy Universe
╠²
ŌĆ£Foundations of BiochemistryŌĆØ is a processŌĆÉoriented guided inquiry learning (POGIL) style workbook for use in upper division Biochemistry courses. The book contains 36 exercises, which could be used for an almostŌĆÉexclusively POGIL one semester course or supplemented with lectures, case studies, or student presentations for a full year course. It is intended as a supplement to a textbook, and the very modest price makes it a very costŌĆÉeffective educational resource.Vocab review



Vocab reviewACKademic
╠²
The document contains definitions for various biology terms. It defines terms related to cells, genetics, evolution, ecosystems, anatomy and physiology. Some key terms defined include diffusion, DNA, protein, ecosystem, enzyme, and metabolism.The Cellular Level Of Organization



The Cellular Level Of OrganizationTammy Lacy
╠²
This document provides an overview of key concepts related to the cellular level of organization, including:
- The three main parts of a eukaryotic cell are the plasma membrane, organelles, and cytoplasm.
- Plasma membranes consist of phospholipids, proteins, and cholesterol.
- Organelles in eukaryotic cells include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, peroxisomes, and vacuoles.
- The document also discusses cellular transport mechanisms, DNA structure and replication, transcription and translation of DNA to synthesize proteins, and cellular respiration and photosynthesis.Le voc review



Le voc reviewLexume1
╠²
The document provides definitions for various biological terms:
1. It defines key terms related to cellular processes like diffusion, photosynthesis, protein synthesis, and sexual reproduction.
2. It also defines broader biological concepts including biodiversity, the circulatory system, nutrition, and pH.
3. The document acts as a reference for scientific terms across multiple levels of biological organization from cells and organelles to whole organisms and ecosystems.Medicinal Chemistry : Protein Structure



Medicinal Chemistry : Protein StructureRahul Patil PhD
╠²
- Proteins have primary, secondary, tertiary, and sometimes quaternary structures that are formed through interactions like hydrogen bonding, disulfide bonds, and Vander Waals forces. These interactions determine a protein's 3D shape.
- Common drug targets include transport proteins, which shuttle molecules across cell membranes, enzymes, which catalyze reactions, and receptors, which receive signals from outside cells. Tubulin is also targeted as it makes up microtubules essential for cell division.
- Protein-protein interactions mediate many cell processes and are potential drug targets. Proteomics studies novel proteins discovered through genomics.Microbial growth



Microbial growthmohammed zahid
╠²
MICROBIAL GROWTH
’üČ SYNOPSIS
’üČ INTRODUCTION
’üČ REQUIREMENT FOR MICROBIAL GROWTH
’āś PHYSICAL REQUIREMENT
’āś NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENT
’üČ BACTERIAL GROWTH CURVE
’üČ FACTORS AFFECTING BACTERIAL GROWTH
’üČ COUNTING OF BACTERIAL CELL
Factors that affecting-microbial-growth.pdf



Factors that affecting-microbial-growth.pdfdawitg2
╠²
Microbial growth requires both physical and nutritional requirements to be met. Bacteria will grow within a certain temperature, pH, oxygen, and osmotic pressure range. Nutritionally, bacteria require carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and trace elements which they obtain from organic and inorganic sources. Bacterial growth occurs in four phases - lag, log/exponential, stationary, and death - as seen in a bacterial growth curve. Factors like temperature, nutrients, water, oxygen levels, and pH can affect the bacterial growth rate. Bacteria are enumerated using methods like viable plate counts and direct microscopic cell counts.Enz┘łž▒ž▓ž▒┘åžż┘łž▒ž▓žĖž▒ž▓ž▒┘łž▒┘łž▒ž▓ž▒ž▓ž▒┘łž▒ž▓ž▒ž▓ž▒ž▓yme 1, 2 .pdf



Enz┘łž▒ž▓ž▒┘åžż┘łž▒ž▓žĖž▒ž▓ž▒┘łž▒┘łž▒ž▓ž▒ž▓ž▒┘łž▒ž▓ž▒ž▓ž▒ž▓yme 1, 2 .pdfadamusamaadam38
╠²
ž¦┘äž│┘Ŗž│┘Ŗ ž¦ž©┘ł┘Ŗž¦ Bohomolets Microbiology Lecture #2



Bohomolets Microbiology Lecture #2Dr. Rubz
╠²
The document discusses the chemical structure and metabolism of bacteria. It describes the principal elements that make up bacterial cells, including carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and others. It also discusses macromolecules that constitute bacterial cells, such as proteins, RNA, DNA, lipids, and carbohydrates. Additionally, it outlines various environmental factors that influence bacterial growth, such as temperature, oxygen, pH, and osmotic pressure.Nutritional Types of Bacteria - Classification of bacteria based on nutrition



Nutritional Types of Bacteria - Classification of bacteria based on nutritionSruthyPB3
╠²
Nutritional Types of Bacteria - Classification of bacteria based on nutritionBiochemistry Introduction.pptx



Biochemistry Introduction.pptxDr.Navaneethakrishnan S
╠²
Biochemistry serves as a fundamental discipline in the life sciences, exploring the chemical processes and biomolecules that underlie biological systems. It bridges the gap between biology and chemistry, investigating the molecular basis of life. Biochemistry delves into the study of macromolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids, as well as the intricate interactions and reactions that occur within cells. It encompasses vital topics such as metabolism, energy production, cellular respiration, and photosynthesis. The field examines DNA, RNA, and gene expression to unravel the genetic information and molecular mechanisms that govern living organisms. Additionally, biochemistry explores the molecular structures, chemical bonds, and synthesis of biomolecules, as well as the diverse biochemical pathways and cellular functions they regulate. It also encompasses aspects of molecular genetics, protein synthesis, enzyme kinetics, biochemical regulation, and cell signaling. Biochemistry finds applications in various areas including biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, genetic engineering, and the study of metabolic diseases. It plays a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of life at the molecular level and holds significant implications for numerous scientific and medical advancements.Sr chapter007



Sr chapter007Dana Acap
╠²
The document provides an overview of key topics in microbial physiology and genetics covered in Chapter 7, including:
- Microbial metabolism, including catabolic and anabolic reactions, and how ATP is used to store and transport energy.
- Aerobic respiration and fermentation pathways for breaking down glucose.
- Mutations and how bacteria can acquire new genetic material through transduction, transformation, conjugation and lysogenic conversion.
- Genetic engineering and how bacteria are used to produce compounds like insulin.RyanŌĆÖS Bio Final Project



RyanŌĆÖS Bio Final Projectguestf59844
╠²
The document provides an overview of topics covered in a biology course, including scientific method, nature of life, cells, biochemistry, genetics, evolution, ecology, and human impacts. It discusses key concepts such as the structures and functions of plant and animal cells, diffusion and osmosis, DNA replication, genetic disorders, natural selection, ecosystem interactions, and the greenhouse effect. Safety protocols for laboratories are also outlined.RyanŌĆÖS Bio Final Project



RyanŌĆÖS Bio Final Projectguestc32ebd
╠²
The document provides an overview of various topics in biology including cells, DNA, genetics, evolution, and ecology. It discusses key concepts such as the scientific method, cell structures, mitosis, biochemical reactions, DNA replication, genetic disorders, natural selection, photosynthesis, and human impact on the biosphere. Safety protocols for laboratories are also mentioned.Bm 2 review 2010



Bm 2 review 2010farrellw
╠²
The document provides information on organic and inorganic biomolecules, comparing carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. It also discusses prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structure, describing organelles such as mitochondria, DNA and ribosomes. Key cellular processes like photosynthesis, cellular respiration and homeostasis are summarized. Metric units for biological measurements including millimeters, meters and Celsius are defined.CELL.pptx



CELL.pptxKeval80
╠²
1. The document discusses the cellular level of organization, describing the main parts of the cell including the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus.
2. It explains the structure and functions of the plasma membrane, including its role in transport processes like diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport.
3. The cytoplasm and its organelles are described, such as the cytoskeleton, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and lysosomes, as well as their roles in cellular processes. FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOLOGY WEEK 3-4.pptx



FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOLOGY WEEK 3-4.pptxAnnamaeGrace
╠²
Recall the chemical basis of life, cell structure and
function, energy transfer in biological systems,
evolution, and biological classification.BIOMOLECULES.docx



BIOMOLECULES.docxMelissaGanituenBauti
╠²
The document discusses the four major types of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Carbohydrates include sugars and starches and store and provide energy. Lipids include fats and phospholipids and make up cell membranes and store energy. Nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA carry genetic information and drive protein synthesis. Proteins have many functions including structure, movement, defense, and catalysis. These biomolecules are essential building blocks of life and perform critical functions in cells and organisms.Basic metabolic



Basic metabolicMs. Pooja Bhandare
╠²
This document provides an overview of basic metabolic pathways in plants. It discusses primary and secondary metabolism, the role of enzymes and co-enzymes, and several key pathways such as the shikimic acid, acetate, and mevalonate pathways. Primary metabolites such as starch, cellulose, and chlorophyll are synthesized through basic metabolic pathways and are essential for plant growth and function. Secondary metabolites are derived from primary metabolites and have pharmacological activities. Enzymes help catalyze biochemical reactions in metabolic pathways, while co-enzymes assist enzymes and participate in reactions. Biosynthesis converts carbon dioxide into carbohydrates through photosynthesis.mEaKO2kgjdB4di7O800.pptx



mEaKO2kgjdB4di7O800.pptxNdayisengaJeanBercky
╠²
Primary metabolites are directly involved in normal growth, development and reproduction, and are essential for these processes. Examples include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. Secondary metabolites are not directly involved in these processes but have important ecological functions, such as antibiotics. Secondary metabolites include mycotoxins, antibiotics, alkaloids, amino acids, steroids and vitamins. They are produced late in the growth cycle and provide benefits to the producing organism or disadvantages to surrounding organisms.Bio final review game 10 2 (1)



Bio final review game 10 2 (1)Link976
╠²
The document provides a review of key biology concepts across several topics:
1) It begins with an outline of topics including cell biology, genetics, evolution, microscopy, and ecology.
2) It then presents vocabulary terms and their definitions related to these topics, such as organic compounds, ATP, osmosis, and active transport.
3) The document concludes by listing additional review concepts and questions to test understanding of the material.Non-Invasive ICP Monitoring for Neurosurgeons



Non-Invasive ICP Monitoring for NeurosurgeonsDhaval Shukla
╠²
This presentation delves into the latest advancements in non-invasive intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring techniques, specifically tailored for neurosurgeons. It covers the importance of ICP monitoring in clinical practice, explores various non-invasive methods, and discusses their accuracy, reliability, and clinical applications. Attendees will gain insights into the benefits of non-invasive approaches over traditional invasive methods, including reduced risk of complications and improved patient outcomes. This comprehensive overview is designed to enhance the knowledge and skills of neurosurgeons in managing patients with neurological conditions.
Invasive systems are commonly used for monitoring intracranial pressure (ICP) in traumatic brain injury (TBI) and are considered the gold standard. The availability of invasive ICP monitoring is heterogeneous, and in low- and middle-income settings, these systems are not routinely employed due to high cost or limited accessibility. The aim of this presentation is to develop recommendations to guide monitoring and ICP-driven therapies in TBI using non-invasive ICP (nICP) systems.
Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISM



Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISMShri Shivayogeeshwar Rural Ayurvedic Medical college, INCHAL,
╠²
Hingula(Cinnabar)
Synonyms - Churna Parada, Darada, Mleccha, Rasagarbha,Rasodbhava,
Shukatunda, Hamsapada, Lohagna
Mineralogical Identification
Chemical Formula- HgS
Chemical name- mercury sulfide
Nature ŌĆō Crystalline
Colour- Bright Red
Crystal- Trigonal.
Clevage- -
Diaphaneity- Transparent to Translucent
Fracture- Uneven
Tenacity- Brittle
Lustre- Vitreous
Streak- Red
Sp. Gravity- 8 to 8.1
Hardness- 2 to 2.5
Sources
- It is found near volcanic region and near mercury mines(extracted).
- It is associated with other minerals like Stibnite, pyrite, realgar, calcite etc.
- Almaden (Spain), California, Texas.
Types
1) Charmara
2) Shukhatunda
3) Hamsapada ( Ap 2/69)
1) Khanija
2) Kritrima (RT 9/4)
Grahya ad Agrahyata
Óż£Óż¬ÓżŠ ÓżĢÓźüÓżĖÓźüÓż« ÓżĄÓż░ÓźŹÓżŻÓżŠÓżŁ: Óż¬ÓźćÓżĘÓżŻ ÓżĖÓźüÓż«Óż©ÓźŗÓż╣Óż░: |
Óż«Óż╣ÓźŗÓż£ÓźŹÓżĄÓżŠÓż▓Óźŗ ÓżŁÓżŠÓż░Óż¬ÓźéÓż░ÓźŹÓżŻÓźŗ Óż╣Óż┐ÓżéÓżŚÓźüÓż▓: ÓżČÓźŹÓż░ÓźćÓżĘÓźŹÓżĀ ÓżēÓżÜÓźŹÓż»ÓżżÓźć || RT 9/3
Doshas
Andya( Blindness)
Kshinata
Klama
Bhrama
Moha
Prameha ( AP 2/73)
Shodhana
1) Grahya Hingula ChurnaŌĆöArdraka rasa bhavana(7)--Shuddhahingula (RT 9/12)
Marana
Other Processing Techniques
Satwa Patana
-Shuddha HingulaŌĆöAdhaha patana/Urdhwa patana -Satva (Parada) (RRS ŌĆō 3/144)
Yogas
Hinguleshwar rasa
Anandabhairava Rasa,
Mrutunjaya Rasa,
Tribhuvana keerti Rasa, etc.
Research Updates
A CONCEPTUAL REVIEW ON HINGULA (CINNABAR- HgS)
https://ijapr.in/index.php/ijapr/article/view/1237
EXTRACTION OF PARAD FROM HINGULA, A TRADITIONAL AYURVEDIC METHOD
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323601866_EXTRACTION_OF_PARAD_FROM_HINGULA_A_TRADITIONAL_AYURVEDIC_METHOD
DrMahantesh.B.Rudrapuri,
M.D.(Ayu) FAGE , PGDYT
HOD Department of Rasa Shastra&BhaishajyaKalpana
Shri Shivayogeeshwar Rural Ayurvedic Medical College,
INCHAL ŌĆō 591 102, Dist: Belgaum
Mob: 9972710790
More Related Content
Similar to bacterial growth charactrstics.pptx Mbbs (20)
Enz┘łž▒ž▓ž▒┘åžż┘łž▒ž▓žĖž▒ž▓ž▒┘łž▒┘łž▒ž▓ž▒ž▓ž▒┘łž▒ž▓ž▒ž▓ž▒ž▓yme 1, 2 .pdf



Enz┘łž▒ž▓ž▒┘åžż┘łž▒ž▓žĖž▒ž▓ž▒┘łž▒┘łž▒ž▓ž▒ž▓ž▒┘łž▒ž▓ž▒ž▓ž▒ž▓yme 1, 2 .pdfadamusamaadam38
╠²
ž¦┘äž│┘Ŗž│┘Ŗ ž¦ž©┘ł┘Ŗž¦ Bohomolets Microbiology Lecture #2



Bohomolets Microbiology Lecture #2Dr. Rubz
╠²
The document discusses the chemical structure and metabolism of bacteria. It describes the principal elements that make up bacterial cells, including carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and others. It also discusses macromolecules that constitute bacterial cells, such as proteins, RNA, DNA, lipids, and carbohydrates. Additionally, it outlines various environmental factors that influence bacterial growth, such as temperature, oxygen, pH, and osmotic pressure.Nutritional Types of Bacteria - Classification of bacteria based on nutrition



Nutritional Types of Bacteria - Classification of bacteria based on nutritionSruthyPB3
╠²
Nutritional Types of Bacteria - Classification of bacteria based on nutritionBiochemistry Introduction.pptx



Biochemistry Introduction.pptxDr.Navaneethakrishnan S
╠²
Biochemistry serves as a fundamental discipline in the life sciences, exploring the chemical processes and biomolecules that underlie biological systems. It bridges the gap between biology and chemistry, investigating the molecular basis of life. Biochemistry delves into the study of macromolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids, as well as the intricate interactions and reactions that occur within cells. It encompasses vital topics such as metabolism, energy production, cellular respiration, and photosynthesis. The field examines DNA, RNA, and gene expression to unravel the genetic information and molecular mechanisms that govern living organisms. Additionally, biochemistry explores the molecular structures, chemical bonds, and synthesis of biomolecules, as well as the diverse biochemical pathways and cellular functions they regulate. It also encompasses aspects of molecular genetics, protein synthesis, enzyme kinetics, biochemical regulation, and cell signaling. Biochemistry finds applications in various areas including biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, genetic engineering, and the study of metabolic diseases. It plays a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of life at the molecular level and holds significant implications for numerous scientific and medical advancements.Sr chapter007



Sr chapter007Dana Acap
╠²
The document provides an overview of key topics in microbial physiology and genetics covered in Chapter 7, including:
- Microbial metabolism, including catabolic and anabolic reactions, and how ATP is used to store and transport energy.
- Aerobic respiration and fermentation pathways for breaking down glucose.
- Mutations and how bacteria can acquire new genetic material through transduction, transformation, conjugation and lysogenic conversion.
- Genetic engineering and how bacteria are used to produce compounds like insulin.RyanŌĆÖS Bio Final Project



RyanŌĆÖS Bio Final Projectguestf59844
╠²
The document provides an overview of topics covered in a biology course, including scientific method, nature of life, cells, biochemistry, genetics, evolution, ecology, and human impacts. It discusses key concepts such as the structures and functions of plant and animal cells, diffusion and osmosis, DNA replication, genetic disorders, natural selection, ecosystem interactions, and the greenhouse effect. Safety protocols for laboratories are also outlined.RyanŌĆÖS Bio Final Project



RyanŌĆÖS Bio Final Projectguestc32ebd
╠²
The document provides an overview of various topics in biology including cells, DNA, genetics, evolution, and ecology. It discusses key concepts such as the scientific method, cell structures, mitosis, biochemical reactions, DNA replication, genetic disorders, natural selection, photosynthesis, and human impact on the biosphere. Safety protocols for laboratories are also mentioned.Bm 2 review 2010



Bm 2 review 2010farrellw
╠²
The document provides information on organic and inorganic biomolecules, comparing carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. It also discusses prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structure, describing organelles such as mitochondria, DNA and ribosomes. Key cellular processes like photosynthesis, cellular respiration and homeostasis are summarized. Metric units for biological measurements including millimeters, meters and Celsius are defined.CELL.pptx



CELL.pptxKeval80
╠²
1. The document discusses the cellular level of organization, describing the main parts of the cell including the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus.
2. It explains the structure and functions of the plasma membrane, including its role in transport processes like diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport.
3. The cytoplasm and its organelles are described, such as the cytoskeleton, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and lysosomes, as well as their roles in cellular processes. FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOLOGY WEEK 3-4.pptx



FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOLOGY WEEK 3-4.pptxAnnamaeGrace
╠²
Recall the chemical basis of life, cell structure and
function, energy transfer in biological systems,
evolution, and biological classification.BIOMOLECULES.docx



BIOMOLECULES.docxMelissaGanituenBauti
╠²
The document discusses the four major types of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Carbohydrates include sugars and starches and store and provide energy. Lipids include fats and phospholipids and make up cell membranes and store energy. Nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA carry genetic information and drive protein synthesis. Proteins have many functions including structure, movement, defense, and catalysis. These biomolecules are essential building blocks of life and perform critical functions in cells and organisms.Basic metabolic



Basic metabolicMs. Pooja Bhandare
╠²
This document provides an overview of basic metabolic pathways in plants. It discusses primary and secondary metabolism, the role of enzymes and co-enzymes, and several key pathways such as the shikimic acid, acetate, and mevalonate pathways. Primary metabolites such as starch, cellulose, and chlorophyll are synthesized through basic metabolic pathways and are essential for plant growth and function. Secondary metabolites are derived from primary metabolites and have pharmacological activities. Enzymes help catalyze biochemical reactions in metabolic pathways, while co-enzymes assist enzymes and participate in reactions. Biosynthesis converts carbon dioxide into carbohydrates through photosynthesis.mEaKO2kgjdB4di7O800.pptx



mEaKO2kgjdB4di7O800.pptxNdayisengaJeanBercky
╠²
Primary metabolites are directly involved in normal growth, development and reproduction, and are essential for these processes. Examples include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. Secondary metabolites are not directly involved in these processes but have important ecological functions, such as antibiotics. Secondary metabolites include mycotoxins, antibiotics, alkaloids, amino acids, steroids and vitamins. They are produced late in the growth cycle and provide benefits to the producing organism or disadvantages to surrounding organisms.Bio final review game 10 2 (1)



Bio final review game 10 2 (1)Link976
╠²
The document provides a review of key biology concepts across several topics:
1) It begins with an outline of topics including cell biology, genetics, evolution, microscopy, and ecology.
2) It then presents vocabulary terms and their definitions related to these topics, such as organic compounds, ATP, osmosis, and active transport.
3) The document concludes by listing additional review concepts and questions to test understanding of the material.Recently uploaded (20)
Non-Invasive ICP Monitoring for Neurosurgeons



Non-Invasive ICP Monitoring for NeurosurgeonsDhaval Shukla
╠²
This presentation delves into the latest advancements in non-invasive intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring techniques, specifically tailored for neurosurgeons. It covers the importance of ICP monitoring in clinical practice, explores various non-invasive methods, and discusses their accuracy, reliability, and clinical applications. Attendees will gain insights into the benefits of non-invasive approaches over traditional invasive methods, including reduced risk of complications and improved patient outcomes. This comprehensive overview is designed to enhance the knowledge and skills of neurosurgeons in managing patients with neurological conditions.
Invasive systems are commonly used for monitoring intracranial pressure (ICP) in traumatic brain injury (TBI) and are considered the gold standard. The availability of invasive ICP monitoring is heterogeneous, and in low- and middle-income settings, these systems are not routinely employed due to high cost or limited accessibility. The aim of this presentation is to develop recommendations to guide monitoring and ICP-driven therapies in TBI using non-invasive ICP (nICP) systems.
Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISM



Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISMShri Shivayogeeshwar Rural Ayurvedic Medical college, INCHAL,
╠²
Hingula(Cinnabar)
Synonyms - Churna Parada, Darada, Mleccha, Rasagarbha,Rasodbhava,
Shukatunda, Hamsapada, Lohagna
Mineralogical Identification
Chemical Formula- HgS
Chemical name- mercury sulfide
Nature ŌĆō Crystalline
Colour- Bright Red
Crystal- Trigonal.
Clevage- -
Diaphaneity- Transparent to Translucent
Fracture- Uneven
Tenacity- Brittle
Lustre- Vitreous
Streak- Red
Sp. Gravity- 8 to 8.1
Hardness- 2 to 2.5
Sources
- It is found near volcanic region and near mercury mines(extracted).
- It is associated with other minerals like Stibnite, pyrite, realgar, calcite etc.
- Almaden (Spain), California, Texas.
Types
1) Charmara
2) Shukhatunda
3) Hamsapada ( Ap 2/69)
1) Khanija
2) Kritrima (RT 9/4)
Grahya ad Agrahyata
Óż£Óż¬ÓżŠ ÓżĢÓźüÓżĖÓźüÓż« ÓżĄÓż░ÓźŹÓżŻÓżŠÓżŁ: Óż¬ÓźćÓżĘÓżŻ ÓżĖÓźüÓż«Óż©ÓźŗÓż╣Óż░: |
Óż«Óż╣ÓźŗÓż£ÓźŹÓżĄÓżŠÓż▓Óźŗ ÓżŁÓżŠÓż░Óż¬ÓźéÓż░ÓźŹÓżŻÓźŗ Óż╣Óż┐ÓżéÓżŚÓźüÓż▓: ÓżČÓźŹÓż░ÓźćÓżĘÓźŹÓżĀ ÓżēÓżÜÓźŹÓż»ÓżżÓźć || RT 9/3
Doshas
Andya( Blindness)
Kshinata
Klama
Bhrama
Moha
Prameha ( AP 2/73)
Shodhana
1) Grahya Hingula ChurnaŌĆöArdraka rasa bhavana(7)--Shuddhahingula (RT 9/12)
Marana
Other Processing Techniques
Satwa Patana
-Shuddha HingulaŌĆöAdhaha patana/Urdhwa patana -Satva (Parada) (RRS ŌĆō 3/144)
Yogas
Hinguleshwar rasa
Anandabhairava Rasa,
Mrutunjaya Rasa,
Tribhuvana keerti Rasa, etc.
Research Updates
A CONCEPTUAL REVIEW ON HINGULA (CINNABAR- HgS)
https://ijapr.in/index.php/ijapr/article/view/1237
EXTRACTION OF PARAD FROM HINGULA, A TRADITIONAL AYURVEDIC METHOD
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323601866_EXTRACTION_OF_PARAD_FROM_HINGULA_A_TRADITIONAL_AYURVEDIC_METHOD
DrMahantesh.B.Rudrapuri,
M.D.(Ayu) FAGE , PGDYT
HOD Department of Rasa Shastra&BhaishajyaKalpana
Shri Shivayogeeshwar Rural Ayurvedic Medical College,
INCHAL ŌĆō 591 102, Dist: Belgaum
Mob: 9972710790
HUMAN SEXUALITY AND SEXUAL RESPONCE CYCLE



HUMAN SEXUALITY AND SEXUAL RESPONCE CYCLEdaminipatel37
╠²
It is all about topic of obg for new semester students MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
╠²
The course covers the steps undertaken from tissue collection, reception, fixation,
sectioning, tissue processing and staining. It covers all the general and special
techniques in histo/cytology laboratory. This course will provide the student with the
basic knowledge of the theory and practical aspect in the diagnosis of tumour cells
and non-malignant conditions in body tissues and for cytology focusing on
gynaecological and non-gynaecological samples.SAPIENT Medi-trivia Quiz (FINALS) | TRI-ORTA 2025



SAPIENT Medi-trivia Quiz (FINALS) | TRI-ORTA 2025Dr. Anindya
╠²
Final Round of SAPIENT Medi-trivia quiz
Part of TRI-ORTA 2025
Venue: GLT, Medical College Kolkata
Date: 25-02-2025physiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation ž│žżž¦┘ä.pptx



physiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation ž│žżž¦┘ä.pptxamralmohammady27
╠²
┘ä┘ł ž╣┘åž»┘ā ┘䞦ž© ž¬┘łž© žŻ┘ł ž¬ž¦ž©┘䞬 ┘üž¦┘ä
power point show
┘ć┘Ŗ┘å┘üž╣┘ā ž¼ž»ž¦ ┘ü┘Ŗ ┘ģž▒ž¦ž¼ž╣ž® ž│ž▒┘Ŗž╣ž® ┘ä┘Ŗ┘äž® ž¦┘䞦┘ģž¬žŁž¦┘å
┘łž¦┘ä┘ä┘Ŗ ┘Ŗ┘éž»ž▒ ┘Ŗž╣┘ģ┘ä žŁž¦ž¼ž® ┘Ŗž╣┘ģ┘ä┘枦
┘łž┤┘āž▒ž¦ ┘ä┘äž»┘āž¬┘łž▒ž® ┘å┘łž¦┘ä ž╣┘ä┘ē ž¬ž¼┘ģ┘Ŗž╣ž® žŻž│ž”┘äž® ž¦┘äž©┘Ŗ┘łLocal Anesthetic Use in the Vulnerable Patients



Local Anesthetic Use in the Vulnerable PatientsReza Aminnejad
╠²
Local anesthetics are a cornerstone of pain management, but their use requires special consideration in vulnerable groups such as pediatric, elderly, diabetic, or obese patients. In this presentation, weŌĆÖll explore how factors like age and physiology influence local anesthetics' selection, dosing, and safety. By understanding these differences, we can optimize patient care and minimize risks.
DIAGNOSIS OF PREGNANCY PPT IN ALL TRIMESTER



DIAGNOSIS OF PREGNANCY PPT IN ALL TRIMESTERdaminipatel37
╠²
Diagnosis of all three trimester of pregnancy Sudurpaschim logsewa aayog Medical Officer 8th Level Curriculum



Sudurpaschim logsewa aayog Medical Officer 8th Level CurriculumDr Ovels
╠²
Sudurpaschim province psc ( lok sewa aayog) medical officer 8th level syllabusRegulation of tubular reabsorption _AntiCopy.pdf



Regulation of tubular reabsorption _AntiCopy.pdfMedicoseAcademics
╠²
Title: Regulation of Tubular Reabsorption ŌĆō A Comprehensive Overview
Description:
This lecture provides a detailed and structured explanation of the mechanisms regulating tubular reabsorption in the kidneys. It explores how different physiological and hormonal factors influence glomerular filtration and reabsorption rates, ensuring fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.
¤öŹ Who Should Read This?
This presentation is designed for:
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Medical Students (MBBS, BDS, Nursing, Allied Health Sciences) preparing for physiology exams.
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Medical Educators & Professors looking for structured teaching material.
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Healthcare Professionals (doctors, nephrologists, and physiologists) seeking a refresher on renal physiology.
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Postgraduate Students & Researchers in the field of medical sciences and physiology.
¤ōī What YouŌĆÖll Learn:
Ō£ģ Local Regulation of Tubular Reabsorption
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Glomerulo-Tubular Balance ŌĆō its mechanism and clinical significance
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Net reabsorptive forces affecting peritubular capillaries
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Role of peritubular hydrostatic and colloid osmotic pressures
Ō£ģ Hormonal Regulation of Tubular Reabsorption
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Effects of Aldosterone, Angiotensin II, ADH, and Natriuretic Peptides
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Clinical conditions like AddisonŌĆÖs disease & Conn Syndrome
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Mechanisms of pressure natriuresis and diuresis
Ō£ģ Nervous System Regulation
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Sympathetic Nervous System activation and its effects on sodium reabsorption
¤®║ Clinical Correlations & Case Discussions
Ō£ö’ĖÅ How renal regulation is altered in hypertension, hypotension, and proteinuria
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Comparison of Glomerulo-Tubular Balance vs. Tubulo-Glomerular Feedback
This presentation provides detailed diagrams, flowcharts, and calculations to enhance understanding and retention. Whether you are studying, teaching, or practicing medicine, this lecture will serve as a valuable resource for mastering renal physiology.
¤ōó Keywords for Easy Search:
#Physiology #RenalPhysiology #TubularReabsorption #GlomeruloTubularBalance #HormonalRegulation #MedicalEducation #NephrologyMORPHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF PNEUMONIA.....



MORPHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF PNEUMONIA.....maheenmazhar021
╠²
This presentation provides a detailed exploration of the morphological and microscopic features of pneumonia, covering its histopathology, classification, and clinical significance. Designed for medical students, pathologists, and healthcare professionals, this lecture differentiates bacterial vs. viral pneumonia, explains lobar, bronchopneumonia, and interstitial pneumonia, and discusses diagnostic imaging patterns.
¤ÆĪ Key Topics Covered:
Ō£ģ Normal lung histology vs. pneumonia-affected lung
Ō£ģ Morphological changes in lobar, bronchopneumonia, and interstitial pneumonia
Ō£ģ Microscopic features: Fibroblastic plugs, alveolar septal thickening, inflammatory cell infiltration
Ō£ģ Stages of lobar pneumonia: Congestion, Red hepatization, Gray hepatization, Resolution
Ō£ģ Common causative pathogens (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Mycoplasma, etc.)
Ō£ģ Clinical case study with diagnostic approach and differentials
¤ö¼ Who Should Watch?
This is an essential resource for medical students, pathology trainees, and respiratory health professionals looking to enhance their understanding of pneumoniaŌĆÖs morphological aspects.Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"



Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"Rehab Aboshama
╠²
Multimodal Approaches to Clitoral Augmentation for FGM (PRP _ filler)"
Optimization in Pharmaceutical Formulations: Concepts, Methods & Applications



Optimization in Pharmaceutical Formulations: Concepts, Methods & ApplicationsKHUSHAL CHAVAN
╠²
This presentation provides a comprehensive overview of optimization in pharmaceutical formulations. It explains the concept of optimization, different types of optimization problems (constrained and unconstrained), and the mathematical principles behind formulation development. Key topics include:
Methods for optimization (Sequential Simplex Method, Classical Mathematical Methods)
Statistical analysis in optimization (Mean, Standard Deviation, Regression, Hypothesis Testing)
Factorial Design & Quality by Design (QbD) for process improvement
Applications of optimization in drug formulation
This resource is beneficial for pharmaceutical scientists, R&D professionals, regulatory experts, and students looking to understand pharmaceutical process optimization and quality by design approaches.Pharm test bank- 12th lehne pharmacology nursing class



Pharm test bank- 12th lehne pharmacology nursing classkoxoyav221
╠²
A pediatric nursing course is designed to prepare nursing students to provide specialized care for infants, children, and adolescents. The course integrates developmental, physiological, and psychological aspects of pediatric health and illness, emphasizing family-centered care. Below is a detailed breakdown of what you can expect in a pediatric nursing course:
1. Course Overview
Focuses on growth and development, health promotion, and disease prevention.
Covers common pediatric illnesses and conditions.
Emphasizes family dynamics, cultural competence, and ethical considerations in pediatric care.
Integrates clinical skills, including medication administration, assessment, and communication with children and families.
2. Key Topics Covered
A. Growth and Development
Neonates (0-28 days): Reflexes, feeding patterns, thermoregulation.
Infants (1 month - 1 year): Milestones, immunization schedule, nutrition.
Toddlers (1-3 years): Language development, toilet training, injury prevention.
Preschoolers (3-5 years): Cognitive and social development, school readiness.
School-age children (6-12 years): Psychosocial development, peer relationships.
Adolescents (13-18 years): Puberty, identity formation, risk-taking behaviors.
B. Pediatric Assessment
Head-to-toe assessment in children (differences from adults).
Vital signs (normal ranges vary by age).
Pain assessment using age-appropriate scales (FLACC, Wong-Baker, Numeric).
C. Pediatric Disease Conditions
Respiratory disorders: Asthma, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, cystic fibrosis.
Cardiac conditions: Congenital heart defects, Kawasaki disease.
Neurological disorders: Seizures, meningitis, cerebral palsy.
Gastrointestinal disorders: GERD, pyloric stenosis, intussusception.
Endocrine conditions: Diabetes mellitus type 1, congenital hypothyroidism.
Hematologic disorders: Sickle cell anemia, hemophilia, leukemia.
Infectious diseases: Measles, mumps, rubella, chickenpox.
Mental health concerns: Autism spectrum disorder, ADHD, eating disorders.
D. Pediatric Pharmacology
Medication administration (oral, IV, IM, subcutaneous).
Weight-based dosing calculations (mg/kg).
Common pediatric medications (antibiotics, analgesics, vaccines).
Parenteral nutrition and fluid management.
E. Pediatric Emergency & Critical Care
Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) basics.
Recognizing signs of deterioration (early vs. late signs).
Shock, dehydration, respiratory distress management.
F. Family-Centered Care & Communication
Parental involvement in care decisions.
Therapeutic communication with children at different developmental stages.
Cultural considerations in pediatric care.
G. Ethical and Legal Issues in Pediatric Nursing
Informed consent for minors.
Mandatory reporting of abuse and neglect.
Palliative care and end-of-life considerations in pediatrics.
3. Clinical Component
Hands-on experience in pediatric hospital units, clinics, or community settings.
Performing assessments and interventions under supervision.
Case study discECZEMA 3rd year notes with images .pptx



ECZEMA 3rd year notes with images .pptxAyesha Fatima
╠²
If itŌĆÖs not Itch ItŌĆÖs not Eczema
Eczema is a group of medical conditions which causes inflammation and irritation to skin.
It is also called as Dermatitis
Eczema is an itchy consisting of ill defined erythremotous patches. The skin surface is usually scaly and As time progress, constant scratching leads to thickened lichenified skin.
Several classifications of eczemas are available based on Etiology, Pattern and chronicity.
According to aetiology Eczema are classified as:
Endogenous eczema: Where constitutional factors predispose the patient to developing an eczema.
Family history (maternal h/o eczema) is often present
Strong genetic predisposition (Filaggrin gene mutations are often present).
Filaggrin is responsible for maintaining moisture in skin (hence all AD patients have dry skin.
Immunilogical factor-Th-2 disease, Type I hypersensitivity (hence serum IgE high)
e.g., Seborrheic dermatitis, Statis dermatitis, Nummular dermatitis, Dyshidrotic Eczema
Exogenous eczema: Where external stimuli trigger development of eczema,
e.g., Irritant dermatitis, Allergic Dermatitis, Neurodermatitis,
Combined eczema: When a combination of constitutional factors and extrinsic triggers are responsible for the development of eczema
e.g., Atopic dermatitis
Extremes of Temperature
Irritants : Soaps, Detergents, Shower gels, Bubble baths and water
Stress
Infection either bacterial or viral,
Bacterial infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species.
Viral infections such as Herpes Simplex, Molluscum Contagiosum
Contact allergens
Inhaled allergens
Airborne allergens
Allergens include
Metals eg. Nickle, Cobalt
Neomycin, Topical ointment
Fragrance ingredients such as Balsam of Peru
Rubber compounds
Hair dyes for example p-Phenylediamine
Plants eg. Poison ivy .
Atopic Dermatitis : AD is a chronic, pruritic inflammatory skin disease characterized by itchy inflamed skin.
Allergic Dermatitis: A red itchy weepy reaction where the skin has come in contact with a substance That immune system recognizes as foreign substances.
Ex: Poison envy, Preservatives from creams and lotions.
Contact Irritant Dermatitis: A Localized reaction that include redness, itching and burning where the skin has come In contact with an allergen or with irritant such as acid, cleaning agent or chemical.
Dyshidrotic Eczema: Irritation of skin on the palms and soles by
clear deep blisters that itch and burn.
Clinical Features; Acute Eczema:- Acute eczema is characterized by an erythematous and edematous plaque, which is ill-defined and is surmounted by papules, vesicles, pustules and exudate that dries to form crusts. A subsiding eczematous plaque may be covered with scales.
Chronic Eczema:- Chronic eczema is characterized by lichenification, which is a triad of hyperpigmentation, thickening markings. The lesions are less exudative and more scaly. Flexural lesions may develop fissures.
Pruritus
Characteristic Rash
Chronic or repeatedly occurring symptoms.OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE- Problem Oriented Approach.pptx



OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE- Problem Oriented Approach.pptxSelvaraj Balasubramani
╠²
Here discussing various cases of Obstructive jaundice namely Choledocholithiassis, Biliary atresia, Carcinoma Pancreas, Periampullary Carcinoma and Cholangiocarcinoma.Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISM



Hingula.ppt- Rasadravya parichaya- NCISMShri Shivayogeeshwar Rural Ayurvedic Medical college, INCHAL,
╠²
MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdf



MLS 208 - UNIT 4 A - Tissue Processing - ETANDO AYUK - SANU 1 - Secured.pdfEswatini Medical Christian University - EMCU / Southern Nazarene University - SANU
╠²
bacterial growth charactrstics.pptx Mbbs
- 1. BACTERIAL GROWTH CHARACTERISTICS Dr. Muhammad Khurram, B. Pharm., Ph. D.
- 2. Growth and Genetic Exchange ’é© Primarily itŌĆÖs the Binary fission ’é© But bacteria has the ability to exchange and share the DNA that helps them to adapt rapidly to the changes in their environment ’é© Three major processes of genetic exchange are 1. Transformation 2. Transduction 3. Conjugation
- 3. Transformation ’é© It is the process of transferring free DNA released from a donor bacterium into the extracellular environment that results in assimilation and usually an expression of the newly acquired trait in a recipient bacterium. ’é© Its of Two types: 1) Natural transformation occurs when some bacterial genera spontaneously release DNA from the cells into the environment free to be taken up by the competent cells. 2) Artificial transformation, is the transfer of artificially altered DNA into recipient cells
- 4. Transduction ’é© Bacterial transduction is a process of transferring bacterial DNA from a donor to a recipient bacterium via a virus particle called a bacteriophage or phage ’é© Its also of two types 1. Generalized transduction occurs when phages mistakenly package bacterial DNA instead of their own DNA during phage assembly. This results in an infectious virus particle containing bacterial DNA 2. Specialized transduction, on the other hand, occurs when a temperate phage integrates its DNA into the bacterial chromosome and then excises itself along with some flanking bacterial DNA. The phage DNA is then packaged into a phage particle and transferred to a new host bacterium
- 5. Conjugation ’é© Bacterial conjugation is a process by which genetic material is transferred between bacterial cells through direct cell-to-cell contact or a bridge-like connection between two cells. ’é© This process is facilitated by a pilus, which is a long and robust extracellular appendage that serves as a physical channel for translocation of DNA that is most often a plasmid or transposon.
- 6. Growth Rate.. ’é© Parameters placed on X-axis ’é© Growth is kept on Y-axis ’é© Relationship is studied Optimum X-axis Y-axis 0
- 7. Nutrients for Growth! ’é© Nutrients are substances used in biosynthesis and energy release and therefore are required for microbial growth.
- 8. Macronutrients.. ’é© Over 95% of cell dry weight is made up of a few major elements: Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Sulfur, Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium, and Iron. These are called Macroelements or Macronutrients because they are required by microorganisms in relatively large amounts. The first six (C, O, H, N, S, and P) are components of carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and
- 9. ’é© The remaining four macroelements exist in the cell as cations and play a variety of roles. For example, Potassium (K+) is required for activity by a number of enzymes, including some of those involved in protein synthesis. Calcium (Ca+2), among other functions, contributes to the heat resistance of bacterial endospores. Magnesium (Mg+2) serves as a cofactor for many enzymes, complexes with ATP, and stabilizes ribosomes and cell membranes. Iron (Fe+2 and Fe+3) is a part of cytochromes and a cofactor for enzymes and electron-carrying proteins.
- 10. MicronutrientsŌĆ” ’é© All microorganisms require several nutrients in small amounts. These are called micronutrients or trace elements. The micronutrientsŌĆö Manganese, Zinc, Cobalt, Molybdenum, Nickel, and CopperŌĆöare needed by most cells. ’é© Micronutrients are normally a part of enzymes and cofactors, and they aid in the catalysis of reactions and maintenance of protein structure. ’é© Naturally present in media, water, etc.
- 11. Growth factors.. ’é© Organic compounds that are essential cell components or precursors of such components but cannot be synthesized by the organism are called growth factors. ’é© There are three major classes of growth factors: (1) Amino acids, (2) Purines and Pyrimidines, (3) Vitamins. ’é© Amino acids are needed for protein synthesis; purines and pyrimidines for nucleic acid synthesis. ’é© Vitamins are small organic molecules that usually make up all or part of enzyme cofactors and are
- 12. Physicochemical factors impact ’é© The physicochemical factors that affect the growth and survival of bacteria ’éż Temperature ’éż pH ’éż Water activity / Solutes ’éż Availability of Oxygen ’éż Pressure ’éż Radiation
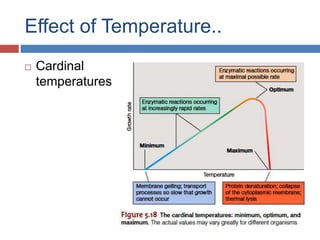
- 13. Effect of Temperature.. ’é© Cardinal temperatures
- 16. Effect of pH.. ’é© Optimum pH ’é© Metabolic activities
- 18. Water activity / SolutesŌĆ” ’é© Water activity (aw) ’é© Availability of water OR The ratio of vapor pressure of the air in equilibrium with a substance or solution to the vapor pressure of pure water. ’é© Osmosis: Water flow from its higher concentration to lower concentration ’é© Compatible solutes: The solute used inside the cell for adjustment of cytoplasmic water activity that are non-inhibitory to macromolecules within the cell. E.g. Sugars, Alcohols, Amino acid derivatives
- 20. Effect of O2.. 1) Aerobes 2) Anaerobes 3) Facultative aerobes 4) Microaerophiles 5) Aerotolerant ’é© Capnophiles..
- 24. Biofilms ’é© Microbes in aquatic environments were found attached to surfaces (sessile) rather than were free-floating (planktonic) ’é© These attached microbes are members of complex, slime-encased communities called biofilms ’é© Major concern is the formation of biofilms on medical devices such as hip and knee implants. ’é© These biofilms often cause serious illness and failure of the medical device.
- 26. ’é© Biofilm coated on artificial knee joint
- 27. Measuring the Growth ’é© Direct Microscopy
- 28. Viable Counts..
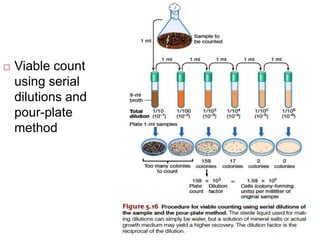
- 29. ’é© Viable count using serial dilutions and pour-plate method
- 30. Turbidimetric methods ’é© Optical Density at a particular ’ü¼
- 31. Thank you!









