Bhavya maths
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes470 views
maths ppt on number system . easy and simple to understand. ti hope that this ppt will help many people . thanks for watching .
1 of 12
Downloaded 14 times











Recommended
Evolution on number



Evolution on numberdhunda munda
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of different number systems including decimal, binary, Mayan, natural numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. It discusses key concepts like place value, bases, rationalization, and successive magnification on the number line. The document was written by a student as part of a school project on mathematical numbers and systems.Maths PPT on NUMBER SYSTEM



Maths PPT on NUMBER SYSTEMKANIKA59
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of a maths project on number systems. It discusses different types of numbers including real numbers, rational numbers, irrational numbers and integers. Rational numbers are divided into fractions and integers. Integers are divided into negatives and whole numbers, with whole numbers further divided into zero and natural numbers. Irrational numbers cannot be represented as fractions, while rational numbers can. The document also covers decimal expansions, representing real numbers on a number line, laws of exponents and the process of rationalization.Power point presentation 



Power point presentation saranyavipin222
Ã˝
This document defines irrational numbers as real numbers that cannot be expressed as a ratio of integers or as a decimal. It provides examples of common irrational numbers such as pi, the golden ratio, e, and the square root of 2. These numbers are irrational because their values continue infinitely without repeating patterns, and thus cannot be written as exact fractions. The document also notes how Pythagoras' theorem relates to rational and irrational numbers in right triangles.Number systems



Number systemsAnkit Goel
Ã˝
This document contains information about different types of numbers including rational numbers, irrational numbers, integers, natural numbers, and real numbers. It discusses how rational numbers can be expressed as fractions with integer numerators and non-zero denominators, and how irrational numbers cannot be expressed as fractions. It also contains examples of terminating and non-terminating decimals. Additionally, it discusses number lines and includes an example of marking distances on a number line.Number system



Number systemjahnvi tanwar
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of different types of real numbers:
- Rational numbers can be written as fractions p/q where p and q are integers. Their decimals are terminating or repeating.
- Irrational numbers cannot be written as fractions and have non-terminating, non-repeating decimals.
- Real numbers include all rational and irrational numbers and can be represented on the real number line. The document discusses properties and operations of real numbers.Number System



Number Systemsamarthagrawal
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of number systems used by different civilizations and an introduction to basic number concepts:
- It discusses ancient number systems including the Egyptian base-12 and Babylonian base-60 systems, as well as modern systems like binary and decimal.
- Basic number types are defined such as integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and real numbers. Fractions and decimal expansions are also introduced.
- Famous mathematicians who contributed to the study and development of number systems throughout history are acknowledged.The Evolution of the Number System 



The Evolution of the Number System immanueljohnisaac
Ã˝
The document discusses the history and evolution of different number systems used by humans over time, from ancient Babylonian and Egyptian numerals to modern Hindu-Arabic numerals. It explains key concepts like natural numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, real numbers, imaginary numbers, and complex numbers. The concept of zero, which represents nothing, was an important development that allowed for more advanced mathematics. Number systems provide a consistent way to represent quantities and solve problems.Numebr system



Numebr systemnidhiyagnik123
Ã˝
This document discusses different types of numbers. It begins with counting numbers which start from 1 and have no largest number. Natural numbers also start from 1 and are infinite. Whole numbers include 0 and are also infinite. Integers include both positive and negative numbers and have an equal and opposite number for every integer. Rational numbers are numbers that can be represented as fractions. Real numbers include both rational numbers like fractions as well as irrational numbers like pi which have non-terminating, non-repeating decimals. The real number set contains all other number sets.NUMBER SYSTEM



NUMBER SYSTEMRap Aishu
Ã˝
This document discusses different types of number systems. It begins by introducing natural numbers, which are counting numbers formed by repeated addition of 1. Whole numbers include all natural numbers and 0. Integers extend whole numbers infinitely in both the positive and negative directions. Rational numbers are numbers that can be written as fractions p/q where p and q are integers. Irrational numbers have non-repeating decimal expansions and cannot be written as fractions. Real numbers include all rational and irrational numbers and are represented on the number line. Methods for finding rational numbers between two given numbers and representing different types of numbers on the number line are also described.Number system



Number systemPrajjwal Kushwaha
Ã˝
The document discusses the history and development of numeral systems. It notes that the most commonly used system today, using the digits 0-9, was developed in India by mathematicians like Aryabhata and Brahmagupta. This Hindu-Arabic numeral system later spread to the Middle East via Arab traders and was modified before being adopted in Europe. Key aspects included the development of place-value notation and the introduction of the zero symbol. This system is now used globally due to its simplicity compared to earlier additive systems.Harsh math ppt number system



Harsh math ppt number systemMohit Kumar Singh
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of different number systems and concepts in mathematics related to numbers. It defines real numbers, rational numbers, integers, whole numbers, and natural numbers. It discusses that rational numbers can be divided into integers, whole numbers, and natural numbers. Irrational numbers are also introduced. Important mathematicians who contributed to the study and understanding of numbers are referenced, including Pythagoras, Archimedes, Aryabhatta, Dedekind, Cantor, Babylonians, and Euclid.number system ppt 



number system ppt Akash dixit
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of number systems throughout history. It discusses how ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Babylonians experimented with different bases like base-12 and base-60 systems. It then covers the decimal system and describes number types like rational, irrational, integer, natural numbers and their properties. The document also discusses concepts like fractions in ancient Egypt, binary numbers and the expansion of numbers into terminating, non-terminating recurring and non-recurring decimals.CBSE Class IX-Maths



CBSE Class IX-Maths0wlish0racle
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of different number systems including natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, and rational numbers. It begins with definitions of each number type and examples of how they are represented on a number line. An activity is described where students classify random numbers into the different categories. Rational numbers between two other rationals are discussed, as well as equivalent rational number representations. The document concludes with sample multiple choice questions to assess understanding.number system school ppt ninth class



number system school ppt ninth classManan Jain
Ã˝
To download -https://clk.ink/MS2T
this will lead to a google drive link./
its a ppt based on the topic no. system.
it covers all the basics of ninth class cbse.types of numbers



types of numbersArjuna Senanayake
Ã˝
This document defines and explains different types of numbers:
1. Natural numbers are the positive whole numbers {1, 2, 3...}. Whole numbers include 0. Integers include positive and negative whole numbers. Rational numbers can be written as fractions. Irrational numbers cannot be written as fractions.
2. Real numbers include rational and irrational numbers and can be written as decimals. Complex numbers are numbers in the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers. Complex numbers contain both real and imaginary parts.
3. The set of complex numbers contains all real and imaginary numbers. Operations on complex numbers follow specific rules: addition/subtraction combine real and imaginary parts separately, multiplication distributes andnumber system class 9



number system class 9sri chaithanya e tecno
Ã˝
This document introduces different number systems, including natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. It defines each type of number and provides examples. Rational numbers can be written as fractions using integers, while irrational numbers cannot be expressed as ratios of integers. Together, rational and irrational numbers make up the set of real numbers, which correspond one-to-one with points on the real number line. Famous mathematicians like Pythagoras, Cantor, and Dedekind contributed to the understanding and classification of these different number systems.Number Systems 



Number Systems Hardik Agarwal
Ã˝
Real numbers include rational numbers like integers and fractions as well as irrational numbers like square roots and pi. Real numbers can be represented on a continuous number line and include both countable and uncountable infinite numbers. Real numbers have the properties of a field where they can be added, multiplied, and ordered on the number line in a way compatible with these operations. Rational numbers are numbers that can be represented as fractions of integers, and they include integers, whole numbers, and natural numbers. Irrational numbers cannot be represented as fractions.NUMBER SYSTEM



NUMBER SYSTEMShikha Pandey
Ã˝
This document reviews representations of different types of numbers on the number line. It discusses natural numbers, integers, rational numbers like terminating and repeating decimals. Irrational numbers like ‚àö2 that are non-terminating and non-repeating are also reviewed. Key properties of real numbers are listed, including that every point on the number line corresponds to a unique real number, and real numbers satisfy closure, commutative, associative, identity and inverse properties.number system 



number system murugesh waran
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of the history and types of number systems. It discusses how ancient civilizations like the Egyptians, Babylonians, and Mayans developed different base number systems based on counting fingers and toes. It then explains the modern decimal number system and provides examples of different types of numbers like rational, irrational, integer, natural numbers. The document also briefly touches on concepts like terminating and recurring decimals as well as scientists who contributed to the study of number systems.Introduction to Rational numbers



Introduction to Rational numbersPratima Nayak ,Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan
Ã˝
This is meant for age group 11 to 14 years.
For Class VIII CBSE.
Some viewers have requested me to send the file through mail.
So I allowed everybody to download.My request is whenever you are using plz acknowledge me.
Pratima Nayak ,Teacher,Kendriya Vidyalaya,Fort William,Kolkata
pnpratima@gmail.com
Based on Text bookNumber types



Number typesTerry Gastauer
Ã˝
The document reviews different types of numbers including natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and real numbers. It also discusses converting between decimals and fractions. Key points covered include the different types of numbers, comparing types of numbers using a visualization of concentric circles, determining which number type a given number belongs to, and the steps for converting decimals to fractions and fractions to decimals. Students are encouraged to ask the teacher or contact the presenter if any areas are unclear or difficult to understand.Maths number system



Maths number systemSanjay Crúzé
Ã˝
The document discusses different number systems used in mathematics. It begins by explaining that a number system is defined by its base, or the number of unique symbols used to represent numbers. The most common system is decimal, which uses base-10. Other discussed systems include binary, octal, hexadecimal, and those used historically by cultures like the Babylonians. Rational and irrational numbers are also defined. Rational numbers can be written as fractions of integers, while irrational numbers cannot.Number system for class Nine(IX) by G R Ahmed TGT(Maths) at K V Khanapara



Number system for class Nine(IX) by G R Ahmed TGT(Maths) at K V KhanaparaMD. G R Ahmed
Ã˝
Here are the answers with explanations:
(i) True. Every natural number is a whole number. The set of natural numbers is a subset of the set of whole numbers.
(ii) True. Every integer is a whole number. The set of integers contains the set of whole numbers.
(iii) False. Not every rational number is a whole number. Rational numbers also include fractions and terminating/repeating decimals.
(iv) True. Every irrational number is a real number. The set of irrational numbers is a subset of the set of real numbers.
(v) False. Not every real number is irrational. The set of real numbers contains both rational and irrational numbers.
(vinatural numbers ppt for class 9 th



natural numbers ppt for class 9 thakhilprasadkerla
Ã˝
The document discusses different types of number systems including natural numbers, whole numbers, rational numbers, integers, and irrational numbers. It provides definitions and examples of each type of number system. Natural numbers are used for counting and include zero depending on the system. Whole numbers include all natural numbers and zero. Rational numbers include integers and fractions. Integers include both positive and negative whole numbers. Irrational numbers have decimal values that continue forever without repeating patterns, such as pi.Math ppt6



Math ppt6muktha nanda
Ã˝
The document discusses different types of real numbers. It states that real numbers have two basic properties: they form an ordered field that can be represented on a number line, and if a non-empty set of real numbers has an upper bound, it has a least upper bound. It then defines different types of real numbers including integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and provides examples of each.Maths project (number line)



Maths project (number line)agrawal342
Ã˝
maths project useful for 7th to 9th std. For NCERT school project on number line. More description on number line. Real numbers



Real numbers∑°ªÂ≥‹≥¶≤π≥¶æ±√≥≤‘
Ã˝
The document discusses rational and irrational numbers. It defines rational numbers as numbers that can be represented as fractions with integer numerators and non-zero denominators. Irrational numbers are numbers that cannot be expressed as fractions and have infinite, non-repeating decimal representations. The set of all rational and irrational numbers is called the set of real numbers. The document also discusses converting between decimals and fractions, as well as different types of intervals on the real number line including open, closed, and half-closed intervals.Algebra 101 real numbers and the real number line



Algebra 101 real numbers and the real number lineChloeDaniel2
Ã˝
The document defines and provides examples of different types of real numbers, including natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. It explains that the set of real numbers contains all rational and irrational numbers. The key properties of real numbers are described, such as closure, commutativity, and distributivity. The real number line is introduced as a way to visually represent and order real numbers on a line. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to classify numbers as rational or irrational, positive or negative, and plot them on the real number line in relation to zero.Secondary Lecture



Secondary LectureAmalia Indrawati Gunawan
Ã˝
This document discusses different types of number systems, including natural numbers, integers, rational numbers, real numbers, and complex numbers. It provides details on key concepts for each system. Natural numbers are the counting numbers starting from 1. Integers add negative whole numbers. Rational numbers are fractions with integer numerators and denominators. Real numbers include rational and irrational numbers, which can be represented by decimals. Complex numbers consist of real numbers combined with imaginary numbers using the imaginary unit i, where i^2 = -1. Each number system forms a proper subset of the next largest system.Y7 m280115workw ithnumb1



Y7 m280115workw ithnumb13SNEducation
Ã˝
The document discusses various topics related to working with numbers including:
1) Different types of numbers such as counting numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and real numbers.
2) Divisibility tests for numbers 2-11 including using sums of digits or units places.
3) Methods for finding the highest common factor (HCF) and lowest common multiple (LCM) of numbers through division or using common divisors.
4) Examples of using divisibility tests and calculating HCF and LCM to solve word problems.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
NUMBER SYSTEM



NUMBER SYSTEMRap Aishu
Ã˝
This document discusses different types of number systems. It begins by introducing natural numbers, which are counting numbers formed by repeated addition of 1. Whole numbers include all natural numbers and 0. Integers extend whole numbers infinitely in both the positive and negative directions. Rational numbers are numbers that can be written as fractions p/q where p and q are integers. Irrational numbers have non-repeating decimal expansions and cannot be written as fractions. Real numbers include all rational and irrational numbers and are represented on the number line. Methods for finding rational numbers between two given numbers and representing different types of numbers on the number line are also described.Number system



Number systemPrajjwal Kushwaha
Ã˝
The document discusses the history and development of numeral systems. It notes that the most commonly used system today, using the digits 0-9, was developed in India by mathematicians like Aryabhata and Brahmagupta. This Hindu-Arabic numeral system later spread to the Middle East via Arab traders and was modified before being adopted in Europe. Key aspects included the development of place-value notation and the introduction of the zero symbol. This system is now used globally due to its simplicity compared to earlier additive systems.Harsh math ppt number system



Harsh math ppt number systemMohit Kumar Singh
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of different number systems and concepts in mathematics related to numbers. It defines real numbers, rational numbers, integers, whole numbers, and natural numbers. It discusses that rational numbers can be divided into integers, whole numbers, and natural numbers. Irrational numbers are also introduced. Important mathematicians who contributed to the study and understanding of numbers are referenced, including Pythagoras, Archimedes, Aryabhatta, Dedekind, Cantor, Babylonians, and Euclid.number system ppt 



number system ppt Akash dixit
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of number systems throughout history. It discusses how ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Babylonians experimented with different bases like base-12 and base-60 systems. It then covers the decimal system and describes number types like rational, irrational, integer, natural numbers and their properties. The document also discusses concepts like fractions in ancient Egypt, binary numbers and the expansion of numbers into terminating, non-terminating recurring and non-recurring decimals.CBSE Class IX-Maths



CBSE Class IX-Maths0wlish0racle
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of different number systems including natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, and rational numbers. It begins with definitions of each number type and examples of how they are represented on a number line. An activity is described where students classify random numbers into the different categories. Rational numbers between two other rationals are discussed, as well as equivalent rational number representations. The document concludes with sample multiple choice questions to assess understanding.number system school ppt ninth class



number system school ppt ninth classManan Jain
Ã˝
To download -https://clk.ink/MS2T
this will lead to a google drive link./
its a ppt based on the topic no. system.
it covers all the basics of ninth class cbse.types of numbers



types of numbersArjuna Senanayake
Ã˝
This document defines and explains different types of numbers:
1. Natural numbers are the positive whole numbers {1, 2, 3...}. Whole numbers include 0. Integers include positive and negative whole numbers. Rational numbers can be written as fractions. Irrational numbers cannot be written as fractions.
2. Real numbers include rational and irrational numbers and can be written as decimals. Complex numbers are numbers in the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers. Complex numbers contain both real and imaginary parts.
3. The set of complex numbers contains all real and imaginary numbers. Operations on complex numbers follow specific rules: addition/subtraction combine real and imaginary parts separately, multiplication distributes andnumber system class 9



number system class 9sri chaithanya e tecno
Ã˝
This document introduces different number systems, including natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. It defines each type of number and provides examples. Rational numbers can be written as fractions using integers, while irrational numbers cannot be expressed as ratios of integers. Together, rational and irrational numbers make up the set of real numbers, which correspond one-to-one with points on the real number line. Famous mathematicians like Pythagoras, Cantor, and Dedekind contributed to the understanding and classification of these different number systems.Number Systems 



Number Systems Hardik Agarwal
Ã˝
Real numbers include rational numbers like integers and fractions as well as irrational numbers like square roots and pi. Real numbers can be represented on a continuous number line and include both countable and uncountable infinite numbers. Real numbers have the properties of a field where they can be added, multiplied, and ordered on the number line in a way compatible with these operations. Rational numbers are numbers that can be represented as fractions of integers, and they include integers, whole numbers, and natural numbers. Irrational numbers cannot be represented as fractions.NUMBER SYSTEM



NUMBER SYSTEMShikha Pandey
Ã˝
This document reviews representations of different types of numbers on the number line. It discusses natural numbers, integers, rational numbers like terminating and repeating decimals. Irrational numbers like ‚àö2 that are non-terminating and non-repeating are also reviewed. Key properties of real numbers are listed, including that every point on the number line corresponds to a unique real number, and real numbers satisfy closure, commutative, associative, identity and inverse properties.number system 



number system murugesh waran
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of the history and types of number systems. It discusses how ancient civilizations like the Egyptians, Babylonians, and Mayans developed different base number systems based on counting fingers and toes. It then explains the modern decimal number system and provides examples of different types of numbers like rational, irrational, integer, natural numbers. The document also briefly touches on concepts like terminating and recurring decimals as well as scientists who contributed to the study of number systems.Introduction to Rational numbers



Introduction to Rational numbersPratima Nayak ,Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan
Ã˝
This is meant for age group 11 to 14 years.
For Class VIII CBSE.
Some viewers have requested me to send the file through mail.
So I allowed everybody to download.My request is whenever you are using plz acknowledge me.
Pratima Nayak ,Teacher,Kendriya Vidyalaya,Fort William,Kolkata
pnpratima@gmail.com
Based on Text bookNumber types



Number typesTerry Gastauer
Ã˝
The document reviews different types of numbers including natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and real numbers. It also discusses converting between decimals and fractions. Key points covered include the different types of numbers, comparing types of numbers using a visualization of concentric circles, determining which number type a given number belongs to, and the steps for converting decimals to fractions and fractions to decimals. Students are encouraged to ask the teacher or contact the presenter if any areas are unclear or difficult to understand.Maths number system



Maths number systemSanjay Crúzé
Ã˝
The document discusses different number systems used in mathematics. It begins by explaining that a number system is defined by its base, or the number of unique symbols used to represent numbers. The most common system is decimal, which uses base-10. Other discussed systems include binary, octal, hexadecimal, and those used historically by cultures like the Babylonians. Rational and irrational numbers are also defined. Rational numbers can be written as fractions of integers, while irrational numbers cannot.Number system for class Nine(IX) by G R Ahmed TGT(Maths) at K V Khanapara



Number system for class Nine(IX) by G R Ahmed TGT(Maths) at K V KhanaparaMD. G R Ahmed
Ã˝
Here are the answers with explanations:
(i) True. Every natural number is a whole number. The set of natural numbers is a subset of the set of whole numbers.
(ii) True. Every integer is a whole number. The set of integers contains the set of whole numbers.
(iii) False. Not every rational number is a whole number. Rational numbers also include fractions and terminating/repeating decimals.
(iv) True. Every irrational number is a real number. The set of irrational numbers is a subset of the set of real numbers.
(v) False. Not every real number is irrational. The set of real numbers contains both rational and irrational numbers.
(vinatural numbers ppt for class 9 th



natural numbers ppt for class 9 thakhilprasadkerla
Ã˝
The document discusses different types of number systems including natural numbers, whole numbers, rational numbers, integers, and irrational numbers. It provides definitions and examples of each type of number system. Natural numbers are used for counting and include zero depending on the system. Whole numbers include all natural numbers and zero. Rational numbers include integers and fractions. Integers include both positive and negative whole numbers. Irrational numbers have decimal values that continue forever without repeating patterns, such as pi.Math ppt6



Math ppt6muktha nanda
Ã˝
The document discusses different types of real numbers. It states that real numbers have two basic properties: they form an ordered field that can be represented on a number line, and if a non-empty set of real numbers has an upper bound, it has a least upper bound. It then defines different types of real numbers including integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and provides examples of each.Maths project (number line)



Maths project (number line)agrawal342
Ã˝
maths project useful for 7th to 9th std. For NCERT school project on number line. More description on number line. Real numbers



Real numbers∑°ªÂ≥‹≥¶≤π≥¶æ±√≥≤‘
Ã˝
The document discusses rational and irrational numbers. It defines rational numbers as numbers that can be represented as fractions with integer numerators and non-zero denominators. Irrational numbers are numbers that cannot be expressed as fractions and have infinite, non-repeating decimal representations. The set of all rational and irrational numbers is called the set of real numbers. The document also discusses converting between decimals and fractions, as well as different types of intervals on the real number line including open, closed, and half-closed intervals.Algebra 101 real numbers and the real number line



Algebra 101 real numbers and the real number lineChloeDaniel2
Ã˝
The document defines and provides examples of different types of real numbers, including natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. It explains that the set of real numbers contains all rational and irrational numbers. The key properties of real numbers are described, such as closure, commutativity, and distributivity. The real number line is introduced as a way to visually represent and order real numbers on a line. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to classify numbers as rational or irrational, positive or negative, and plot them on the real number line in relation to zero.Similar to Bhavya maths (20)
Secondary Lecture



Secondary LectureAmalia Indrawati Gunawan
Ã˝
This document discusses different types of number systems, including natural numbers, integers, rational numbers, real numbers, and complex numbers. It provides details on key concepts for each system. Natural numbers are the counting numbers starting from 1. Integers add negative whole numbers. Rational numbers are fractions with integer numerators and denominators. Real numbers include rational and irrational numbers, which can be represented by decimals. Complex numbers consist of real numbers combined with imaginary numbers using the imaginary unit i, where i^2 = -1. Each number system forms a proper subset of the next largest system.Y7 m280115workw ithnumb1



Y7 m280115workw ithnumb13SNEducation
Ã˝
The document discusses various topics related to working with numbers including:
1) Different types of numbers such as counting numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and real numbers.
2) Divisibility tests for numbers 2-11 including using sums of digits or units places.
3) Methods for finding the highest common factor (HCF) and lowest common multiple (LCM) of numbers through division or using common divisors.
4) Examples of using divisibility tests and calculating HCF and LCM to solve word problems.math 11.pptx



math 11.pptxCheyeneReliGlore
Ã˝
Real numbers include any number that can be found in the real world, such as natural numbers, integers, rational numbers like fractions, and irrational numbers like the square root of numbers. Real numbers are represented by the symbol R and are the union of rational numbers Q and irrational numbers Ǭ. Examples of real numbers include integers, fractions, the square root of 5, and irrational numbers like pi, while complex numbers like √-1 are non-real numbers.Numeral System



Numeral SystemAbility Skills Knowledge Fraternity
Ã˝
A numeral is a sign, or figure that represents a number. It is a mathematical numbering system. In other words, A numeral system is a way of writing numbers; it's a way of mathematically notating a collection of numbers by utilizing a consistent set of digits or other symbols.
Purpose:
This webinar by ASK aims to spread awareness about the practical use of the decimal number system in daily life to minimize errors and make calculations easier.Nombor nyata kuliah 1 & 2



Nombor nyata kuliah 1 & 2nooriza kassim
Ã˝
The document discusses various types of real numbers including natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. It provides examples and definitions of each type of number. Visual representations are also given using Venn diagrams to illustrate the relationships between the different sets of numbers.Mathematics class 8 



Mathematics class 8 manishamittal23
Ã˝
Rational numbers include integers, fractions, and numbers that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers, like p/q. Rational numbers can be positive or negative depending on whether the numerator and denominator have the same or different signs. Any rational number can be expressed in its standard form by dividing the numerator and denominator by their greatest common factor.ix-number system-ppt(2).pptx



ix-number system-ppt(2).pptxRajkumarknms
Ã˝
This document provides learning objectives and content about rational and irrational numbers for a Class 9 mathematics lesson. It begins by defining different types of numbers - natural, whole, integers, rational, and irrational - and provides examples. It then explains rational numbers as those that can be written as fractions p/q, and irrational numbers as those that cannot be expressed as fractions. Various methods are provided for representing and finding rational numbers between two given rational numbers, as well as representing irrational numbers on the number line. Finally, the document discusses operations involving rational and irrational numbers.Weeks idol powerpoint



Weeks idol powerpointrweeks4353
Ã˝
This document describes different types of numbers in the real number system. It explains that real numbers include both rational and irrational numbers. Rational numbers can be written as fractions a/b, and include integers, terminating decimals, and repeating decimals. Irrational numbers cannot be written as fractions and their decimal representations do not terminate or repeat, such as pi and the square root of 2. The real number line provides a way to visualize real numbers as points along a line.Programed instructional material: Rational Numbers



Programed instructional material: Rational NumbersAtul Thakur
Ã˝
This is an initial attempt by my students of B.Ed. in creating Programmed Instructional material using the template I had provided them. Your observations and suggestions are welcome!PEA305 workbook.pdf



PEA305 workbook.pdfRohitkumarYadav80
Ã˝
This document provides an introduction and table of contents to a workbook on analytical skills. The preface explains that aptitude tests are commonly used in company recruitment processes to test candidates' quantitative aptitude, verbal ability, and logical reasoning. It notes that practice is important for these types of timed tests. The table of contents outlines 6 units that will be covered, including number systems, percentages, logical reasoning, and analytical reasoning. Key concepts like integers, rational/irrational numbers, and divisibility rules are defined. Methods for finding the lowest common multiple and highest common factor of numbers are also presented.Number System



Number System9562
Ã˝
This document defines and explains various number systems including:
- Natural numbers which are 1, 2, 3, etc.
- Whole numbers which are the natural numbers and 0.
- Integers which are whole numbers and their opposites.
- Rational numbers which are fractions with integer numerators and denominators.
- Irrational numbers which cannot be written as fractions.
- Real numbers which are all rational and irrational numbers on the number line.
- Complex numbers which are numbers expressed as a + bi, where a and b are real numbers and i is the imaginary unit.Year 8 numbers factorisation and morefactorisation and morefactorisation and ...



Year 8 numbers factorisation and morefactorisation and morefactorisation and ...TaremwaPeter1
Ã˝
factorisation and morefactorisation andfactorisation and morefactorisation and morefactorisation and morefactorisation and morefactorisation and more morefactorisation and morefactorisation and moreNumbers



NumbersSagarika Rout
Ã˝
The document defines various types of numbers including natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and real numbers. It then defines even numbers, odd numbers, prime numbers, and composite numbers. The document concludes by describing divisibility tests for numbers 2 through 12, including testing the sum of digits, last digits, or differences of digit sums.1Types Of Numbers- Lecture Note of Mathematics Conversion Program.pdf



1Types Of Numbers- Lecture Note of Mathematics Conversion Program.pdfTHARUSHADIVYANGA
Ã˝
Mathematics ∫›∫›fl£sArithmetic



ArithmeticHaider Shishmahal
Ã˝
This document discusses different types of numbers and arithmetic concepts. It covers:
- Types of numbers including natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and real numbers.
- Properties of even and odd numbers as well as positives and negatives under addition, subtraction, and multiplication.
- Divisibility rules for numbers being divisible by 1 through 10 as well as squares.
- Strategies for solving word problems involving remainders, including picking numbers, back-solving, and elimination.Understanding Rational Numbers in Mathematics



Understanding Rational Numbers in Mathematicsrutveejplaysofficial
Ã˝
Rational numbers are a fundamental concept in mathematics, representing any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction
ÔøΩ
ÔøΩ
q
p
, where
ÔøΩ
p and
ÔøΩ
q are integers, and
ÔøΩ
q is not zero. This means that rational numbers include both positive and negative fractions, as well as whole numbers and zero. Essentially, if a number can be written in the form of a fraction, it is considered rational. This encompasses a broad range of numbers such as
1
2
2
1
, -3, 0.75, and 5, highlighting the flexibility and wide applicability of rational numbers in various mathematical contexts. The term "rational" itself is derived from the word "ratio," reflecting the idea that these numbers represent ratios of integers. Rational numbers are a subset of real numbers, and they can be precisely located on the number line. An important characteristic of rational numbers is that when expressed in decimal form, they either terminate or repeat. For example, the decimal representation of
1
4
4
1
is 0.25, which terminates, while
1
3
3
1
is 0.333..., which repeats. This property differentiates rational numbers from irrational numbers, which cannot be expressed as exact fractions and have non-terminating, non-repeating decimal expansions. Rational numbers play a crucial role in various areas of mathematics and everyday life. In algebra, they are used to solve equations and inequalities, and in geometry, they help in measuring lengths, areas, and volumes. In everyday life, rational numbers are used in financial calculations, such as determining interest rates, discounts, and budgeting, as well as in measurements and recipes. Understanding rational numbers is essential for mathematical literacy and is a foundational concept for more advanced topics in mathematics, such as calculus and number theory. Moreover, rational numbers are integral to computer science, particularly in algorithms and programming, where precise calculations and representations of numbers are necessary. The ability to manipulate and understand rational numbers enhances problem-solving skills and logical reasoning. The study of rational numbers also involves exploring their properties, such as the ability to perform arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, which follow specific rules and patterns. This exploration extends to understanding how rational numbers relate to other types of numbers, such as integers and irrational numbers, and how they fit within the broader number system. Overall, rational numbers are a versatile and essential component of mathematics, with applications that extend far beyond the classroom, influencing various fields and everyday situations. Their study provides a strong foundation for mathematical understanding and practical problem-solving abilities.
Rational numbers are also significant in the study of number theory and real analysis, where they provide insight into the properties and behaviors of numbers‡∏»®∏≥‡π∂ƒ‡∏™‡∏ô‡∏≠‡∏à‡∏≥‡∏ô‡∏߇∏ô‡∏à‡∏£‡∏¥‡∏á‡π∂ƒ‡∏û‡∏¥‡πà‡∏°‡π∂ƒ‡∏ï‡∏¥‡∏°



‡∏»®∏≥‡π∂ƒ‡∏™‡∏ô‡∏≠‡∏à‡∏≥‡∏ô‡∏߇∏ô‡∏à‡∏£‡∏¥‡∏á‡π∂ƒ‡∏û‡∏¥‡πà‡∏°‡π∂ƒ‡∏ï‡∏¥‡∏°Nittaya Noinan
Ã˝
The document discusses various types of real numbers including rational and irrational numbers. It provides examples and classifications of numbers as natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. It also discusses properties of real numbers such as closure, commutativity, associativity, identity, and inverses for addition and multiplication. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to classify numbers and identify properties of real numbers.Number system.pdf



Number system.pdfDeepuGuna
Ã˝
A number system is a method for writing and representing numbers using digits or symbols in a consistent way. It allows unique representation of numbers and performing arithmetic operations. The main types of number systems are decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal, which use bases of 10, 2, 8, and 16 respectively. Number systems are used daily for tasks like making phone calls, budgeting, cooking, using elevators, shopping, and more. [/SUMMARY]BROWS - Time and Work.pptx



BROWS - Time and Work.pptxpavan7211
Ã˝
Welfare Society- Bharathi ranga organisation for childer health and wellness aswell as foundation for childrensRecently uploaded (20)
The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .



The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .saanidhyapatel09
Ã˝
This PowerPoint presentation provides an insightful overview of the Constitution, covering its key principles, features, and significance. It explains the fundamental rights, duties, structure of government, and the importance of constitutional law in governance. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the foundation of a nation’s legal framework.
How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
Ã˝
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18



How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18Celine George
Ã˝
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to modify existing web pages in Odoo 18. Web pages in Odoo 18 can also gather user data through user-friendly forms, encourage interaction through engaging features. Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Finals of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...



Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...sandynavergas1
Ã˝
Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and Technical TermsPrinciple and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby Basnet



Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby BasnetBoby Basnet
Ã˝
Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding Full Note
|| Assistant Professor Boby Basnet ||IAAS || AFU || PU || FUTLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...



TLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...RizaBedayo
Ã˝
Hand Tools, Power Tools, and Equipment in Industrial ArtsHow to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£s



How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£sCeline George
Ã˝
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18. In Odoo, Init Hooks are essential functions specified as strings in the __init__ file of a module.Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptx



Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ã˝
This ppt has been made for the students pursuing PG in social science and humanities like M.Ed., M.A. (Education), Ph.D. Scholars. It will be also beneficial for the teachers and other faculty members interested in research and teaching research concepts.Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Finals of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity Briefing



N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity BriefingMebane Rash
Ã˝
The number of languages spoken in NC public schools.Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Prelims of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ã˝
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxCBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptx



CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptxsuhail849886
Ã˝
cbse arabic grammar
grade 10 cbse arabic grammar
cbse class 10 arabic grammar
arabic marathon cbse arabic 10
nominal sentences
Computer Application in Business (commerce)



Computer Application in Business (commerce)Sudar Sudar
Ã˝
The main objectives
1. To introduce the concept of computer and its various parts. 2. To explain the concept of data base management system and Management information system.
3. To provide insight about networking and basics of internet
Recall various terms of computer and its part
Understand the meaning of software, operating system, programming language and its features
Comparing Data Vs Information and its management system Understanding about various concepts of management information system
Explain about networking and elements based on internet
1. Recall the various concepts relating to computer and its various parts
2 Understand the meaning of software’s, operating system etc
3 Understanding the meaning and utility of database management system
4 Evaluate the various aspects of management information system
5 Generating more ideas regarding the use of internet for business purpose Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Bhavya maths
- 2. The numbers {0, 1, 2, 3, ...} etc. There is no fractional or decimal part. And no negatives. Example: 5, 49 and 980 are all whole numbers.
- 3. A natural number is a number that occurs commonly and obviously in nature. As such, it is a whole, non-negative number. The set of natural numbers, denoted N, can be defined in either of two ways: N = {0, 1, 2, 3, ...} N = (1, 2, 3, 4, ...}
- 5. A number with no fractional part. Includes: • the counting numbers {1, 2, 3, ...}, • zero {0}, • and the negative of the counting numbers {-1, -2, -3, ...} We can write them all down like this: {..., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ...} Examples of integers: -16, -3, 0, 1, 198
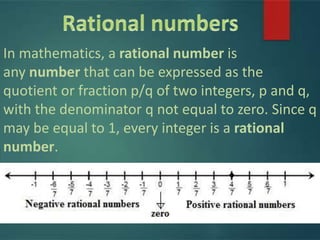
- 6. In mathematics, a rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction p/q of two integers, p and q, with the denominator q not equal to zero. Since q may be equal to 1, every integer is a rational number.
- 7. Question – 1- Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form of p/q, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0? Answer – We know that, rational number is a number which can be written in the form of p/q, where q is not equal to zero. Thus, (a) Yes, zero is a rational number, as it can be written in the form of p/q. (b) Since, 0 (zero) is an integer thus, zero can be written in the form of p/q Example : 0/1, 0/2, 0/3, etc. where 0 (zero) is an integer.
- 8. Question – 2 - Find six rational numbers between 3 and 4. Answer – First method to find rational number between two number: A rational number between two numbers can be found by calculating average of two given numbers. Thus, six rational numbers between given two numbers i.e. 3 and 4 can be calculated as follows: (1) First rational number between 3 and 4 can be calculated by finding average between them. (2) As 7/2 is a rational number between 3 and 4, consequently, rational number between 3 and 7/2 will be one of the rational number between 3 and 4, which can be found by calculating average between 3 and 7/2
- 9. (3) Again as 7/2 is a rational number between 3 and 4, consequently, rational number between 4 and 7/2 will be the rational number between 3 and 4, which can be found by average between 4 and 7/2 (4) Similarly, rational number between 3 and 13/4 will be the rational number between 3 and 4, since 13/4 is a rational number between 3 and 4. Thus next rational number between 3 and 4 can be found by calculating average between 3 and 13/4
- 10. (5) Similarly, rational number between 4 and 13/4 will be the rational number between 3 and 4, which can be found by calculating average between 4 and 13/4 (6) Similarly next rational number between 3 and 4 can be found by calculating average between 3 and 15/4, since 15/4 is a rational number between 3 and 4 which we calculated in the step (3). Thus, six rational numbers between 3 and 4 are 7/2, 13/4, 15/4, 25/8, 29/8 and 27/8. One can find as many rational number between given any two numbers by calculating average as above
- 11. Question – 3 - Find five rational numbers between 3/5 and 4/5. Answer: First method to find rational number between two number: Since we have to find 5 rational numbers between 3/5 and 4/5, so we will multiply the numerator and denominator of or the given numbers by 5+1, i.e. equal to 6. We get, Now, we have to find 5 rational numbers between 18/30 and 24/30, which will come as Thus, five rational numbers between 3/5 and 4/5 are You can find as many rational numbers between given numbers using method given above.





